-
皮肤是人体最大的器官,日常生活中难免受到损伤形成伤口,如轻微的皮肤擦伤、割伤和烧伤等。对于日常的小伤口,一般可以任其自愈,但若稍不注意沾水或接触外界细菌,则容易造成感染,影响伤口愈合,甚至造成溃烂。我们常用的创面处理方法有:使用创可贴覆盖;双氧水或碘伏消毒处理;纱布包扎等。这些处理方法存在着防水透气性差、撕除时疼痛和使用不便等问题。20世纪60年代,Winter博士的研究证实了湿润的伤口环境有助于上皮组织更快的形成,并以此为依据提出了“湿性愈合”的概念[1]。这一研究提高了人们对伤口护理的认识,也为研发封闭敷料奠定了基础。由于传统的敷料不能在伤口处使用较长时间,也不能为伤口愈合提供一个湿润的环境,因此,各种高科技的湿性疗法的伤口护理产品层出不穷。在日本及美国等发达国家,出现以硝化纤维为主要材料的新型创伤敷料[2-4],可用于密封小型伤口甚至保护烧伤创面。此类创伤敷料在使用前为液体形态,涂抹在伤口后有机溶剂迅速挥发,短时间覆盖伤口形成保护膜,具有防水、杀菌、预防伤口感染等优点[5-7]。本研究拟以市售小林液体创可贴为基础,以硝化纤维为膜材,优化处方,制备一种性能更为优良的液体创伤敷料。
HTML
-
Agilent 1200高效液相色谱仪(美国Agilent公司);Shimadzu HS-20气相色谱仪(日本Shimadzu公司);拉力试验机(上海和晟仪器有限公司);AL204型电子天平(上海梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司);D2400型纯水/超纯水一体机(美国明澈公司);25型无极调速电动搅拌机(江苏江阴科技器械厂)。
-
小林液体创可贴(日本小林制药株式会社);硝化纤维(衡水东方化工有限公司);蓖麻油、樟脑、苯甲醇、乙酸丁酯、异丙醇、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺、甲醇(均为国药集团化学试剂有限公司);棕榈酸异丙酯(IPP,青岛优索化学科技有限公司);乙酸乙酯(上海联试试剂有限公司)。
1.1. 仪器
1.2. 试药
-
采用高效液相色谱法测定,色谱条件:采用Agilent 1200高效液相色谱仪;色谱柱:ODS-C18色谱柱;流动相:甲醇-水(50∶50 V/V);流速:1.0 ml/min;进样量:20 μl;柱温:40 ℃;检测波长:257 nm。
标准曲线的绘制:精密称定苯甲醇对照品151.3 mg置于100 ml容量瓶中,用甲醇稀释至刻度;精密量取上述溶液1、2、2.5、3、4 ml于25 ml容量瓶中,用甲醇稀释至刻度。市售产品(供试品)溶液的配制:精密称定244.3 mg市售产品于50 ml容量瓶中,用甲醇稀释至刻度。
实验结果:色谱图良好,苯甲醇对照品及市售产品均在5.87 min附近有峰且峰型良好。标准曲线回归方程为:Y = 13040X + 212.7 (r=0.999);经计算得市售产品苯甲醇的使用量为4.0%。
-
采用气相色谱法测定,色谱条件:采用 HS-20气相色谱仪;色谱柱:DB-624毛细管柱;载气:H2 50 ml/min;空气450 ml/min;进样量:1 μl;柱温:40 ℃/min持续3 min,10 ℃程序升温至200 ℃,持续1 min;检测器温度:250 ℃;气化室温度:220 ℃;FID检测器。
标准曲线的绘制:精密称定异丙醇1.0077 g,乙酸乙酯0.9933 g,乙酸丁酯1.0014 g于100 ml容量瓶中,加入适量N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)混合均匀,用DMF稀释至刻度。分别取上述溶液0.1、0.25、0.5、0.75、1.0 ml置于25 ml容量瓶中,用DMF稀释至刻度。
市售产品(供试品)溶液的配制:精密称定1.186 0 g市售产品于100 ml容量品中,加入适量的DMF超声溶解,用DMF稀释至刻度,精密量取1 ml上述液体于10 ml容量瓶中,用DMF稀释至刻度。
实验结果:色谱图良好,异丙醇对照品及市售产品均在6.84 min附近有峰且峰型良好,乙酸乙酯对照品及市售产品均在9.25 min附近有峰且峰型良好,乙酸丁酯对照品及市售产品均在14.07 min附近有峰且峰型良好;苯甲醇标准曲线、乙酸乙酯标准曲线和乙酸丁酯标准曲线的回归方程分别为:
Y = 20152X + 2.692, r=1.000
Y = 15311X + 33.45 ,r=0.999
Y = 24428X – 17.33, r=0.999
经计算得市售产品中异丙醇的使用量为35.1%,乙酸乙酯的使用量为21.4%,乙酸丁酯的使用量为5.3%。即三者使用比例为:6.6∶4∶1。
-
采用硝化纤维(4%~8%)作为成膜材料,蓖麻油(1%~9%)为增塑剂,苯甲醇(4%)为抑菌剂,棕榈酸异丙酯(IPP,2%)为皮肤柔润剂,樟脑(0.3%)为芳香剂,以异丙醇、乙酸乙酯、乙酸丁酯(三者比例为6.6∶4∶1)作为溶剂制备创伤敷料。制备方法如下:于50 ml烧杯中精密称定处方量蓖麻油、苯甲醇、IPP、樟脑,加入上述3种混合溶剂使混合均匀,加入处方量硝化纤维,密封静置过夜待硝化纤维充分溶解,过夜后搅拌使硝化纤维混合均匀,超声除气泡即得。
-
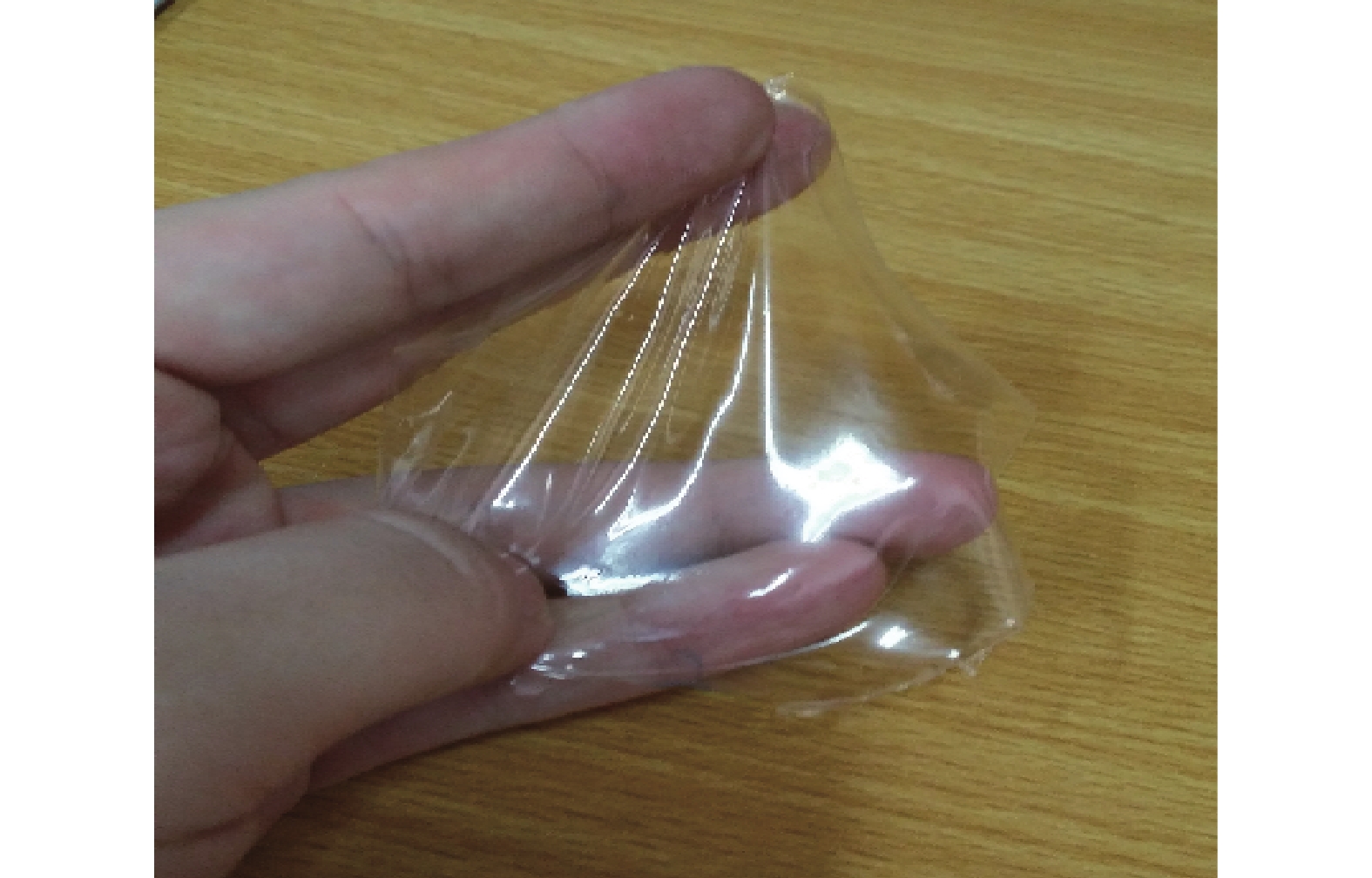
精密称定2 g按“2.2.1”项制备的液体创伤敷料,加入20 ml乙酸乙酯稀释使之混合均匀、黏度下降并充分溶解。将此液体置于90 mm培养皿中待溶剂挥干后可见均一透明无色薄膜。所制薄膜外观如图1所示。
-
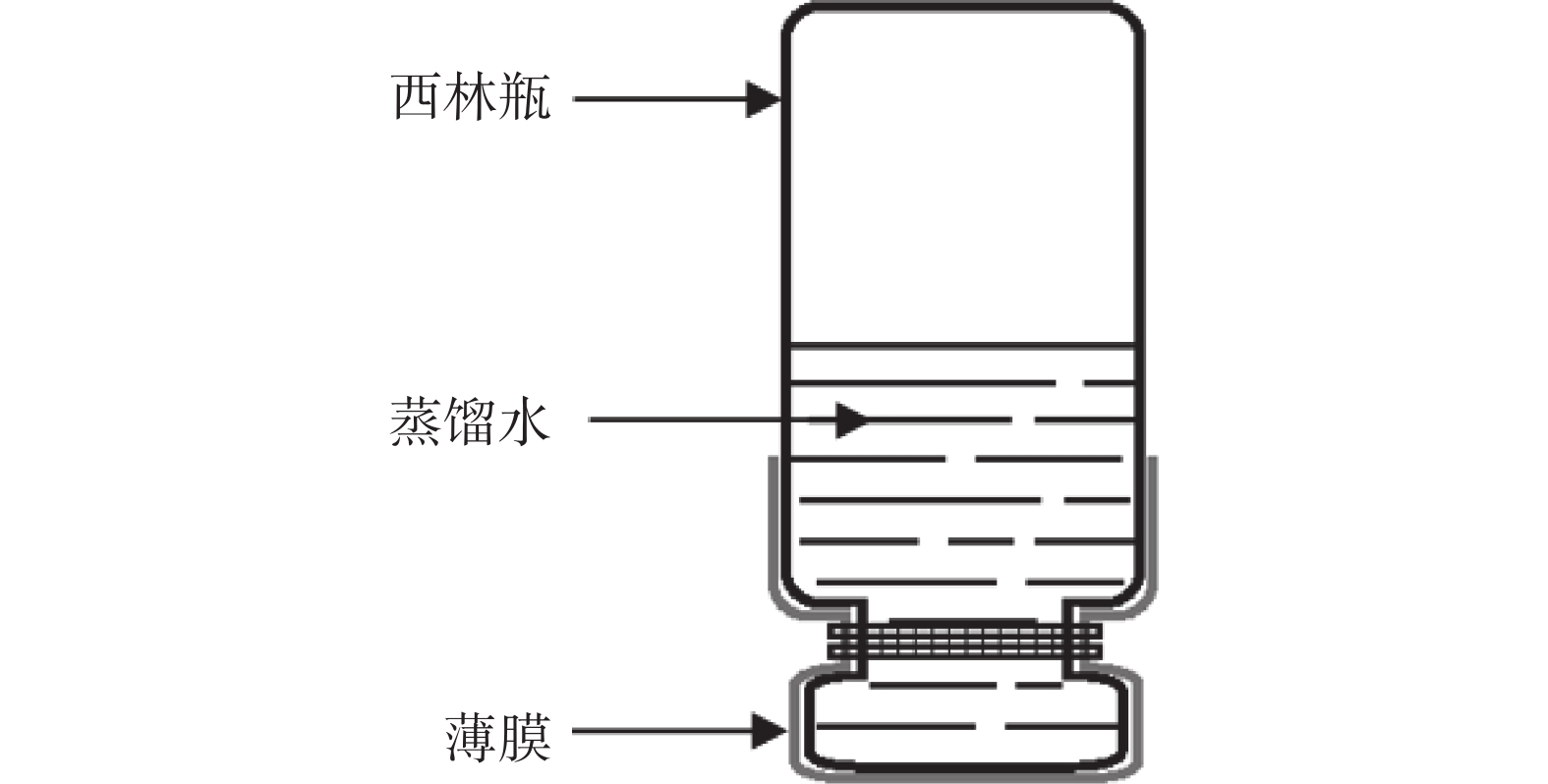
按照中华人民共和国医药行业标准YY/T 0471-2004对直接接触类创伤敷料,进行舒适性、防水性、透气性的考察。舒适性考察主要为考察敷料薄膜的抗张强度及断点伸长百分率[8-9];防水性考察薄膜的防水能力;透气性考察薄膜的水蒸气透过率(MVTR)[10]。抗张强度及断点伸长百分率的考察运用拉伸试验机,并采用公式1、公式2进行计算;防水性的考察采用倒杯法,记录24 h后的重量差异,如图2所示,以公式3进行计算;MVTR的考察方法:在西林瓶中加入蒸馏水,用薄膜覆盖密封,使水液面距薄膜(5±1)mm,置干燥器中,记录24 h后的重量差异,以公式4进行计算。
式中,F为拉伸力;S为薄膜面积;Lmax为拉伸最大距离;L0为初始膜长;M0为初始西林瓶重量;M24h为24 h后西林瓶重量;MW为西林瓶内水重量;s为瓶口面积;t为时间24 h。
-
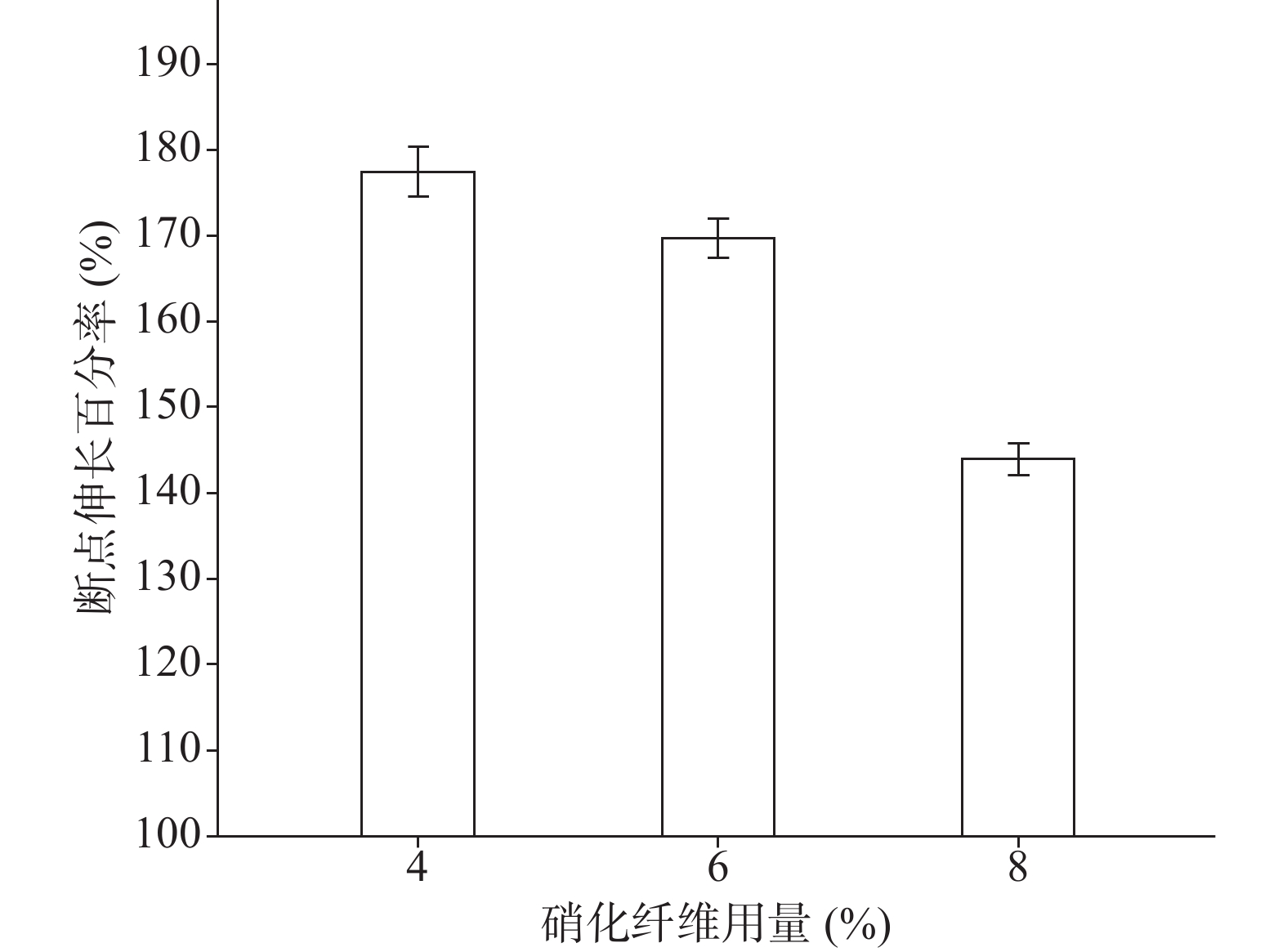
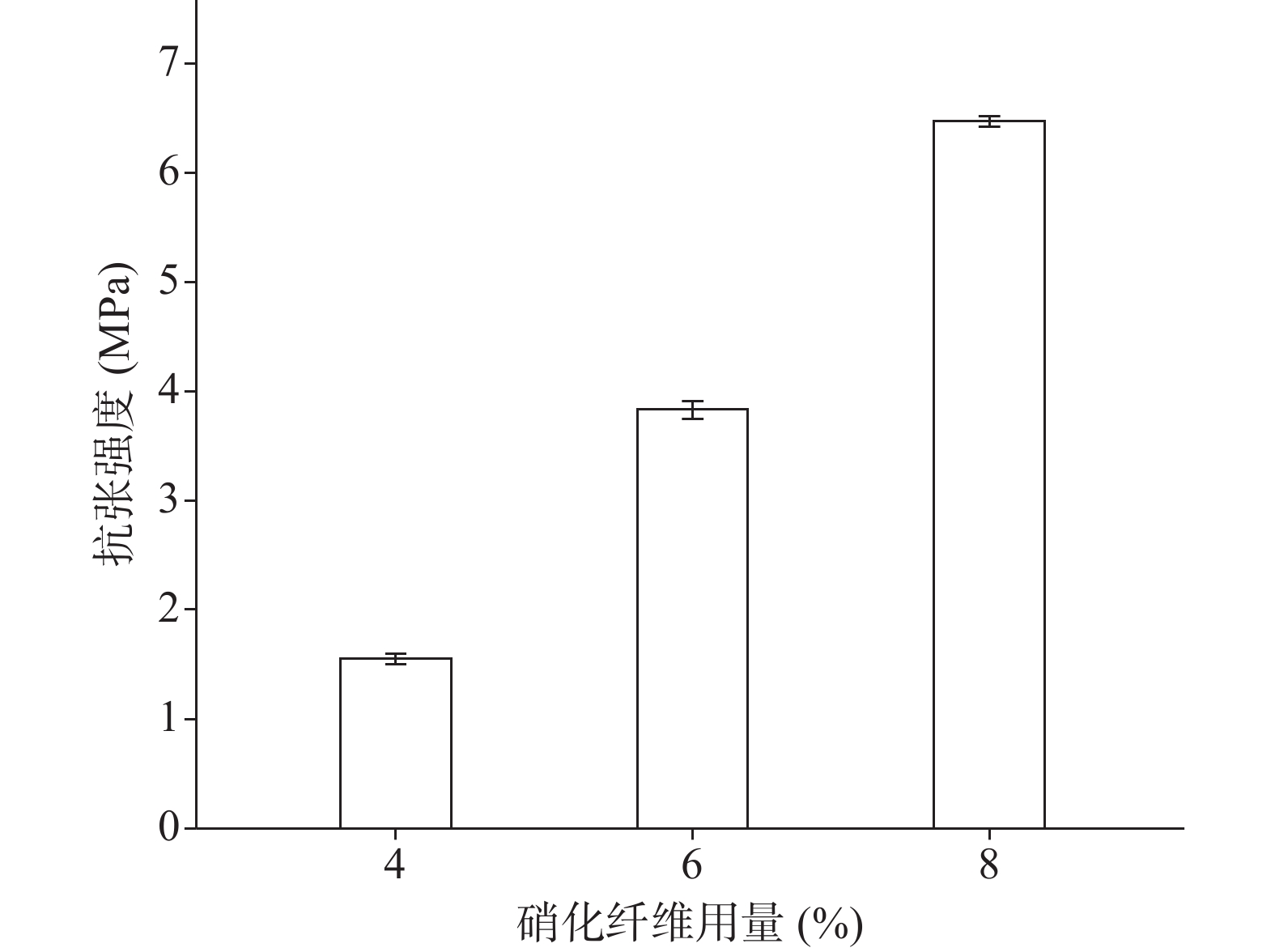
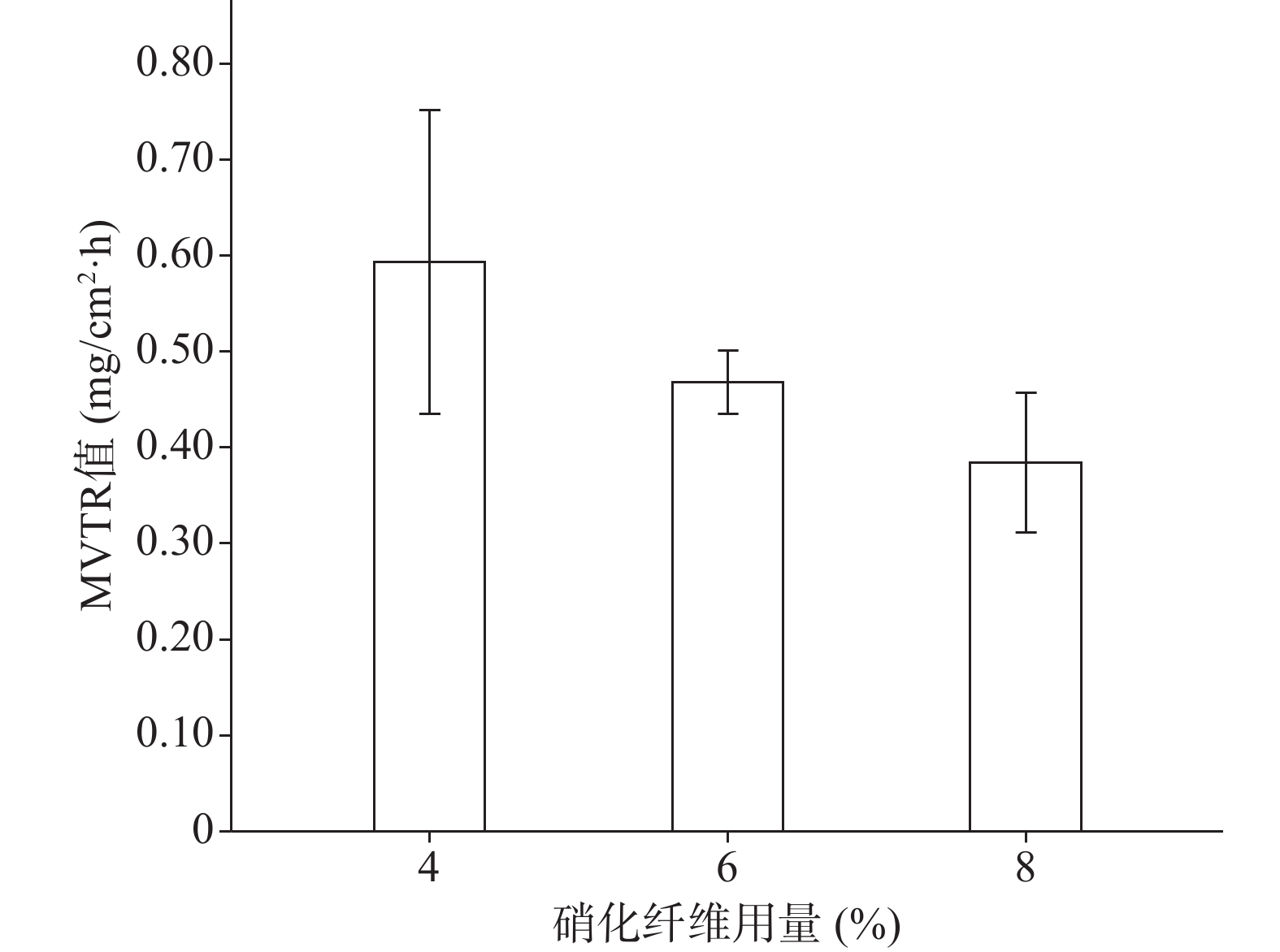
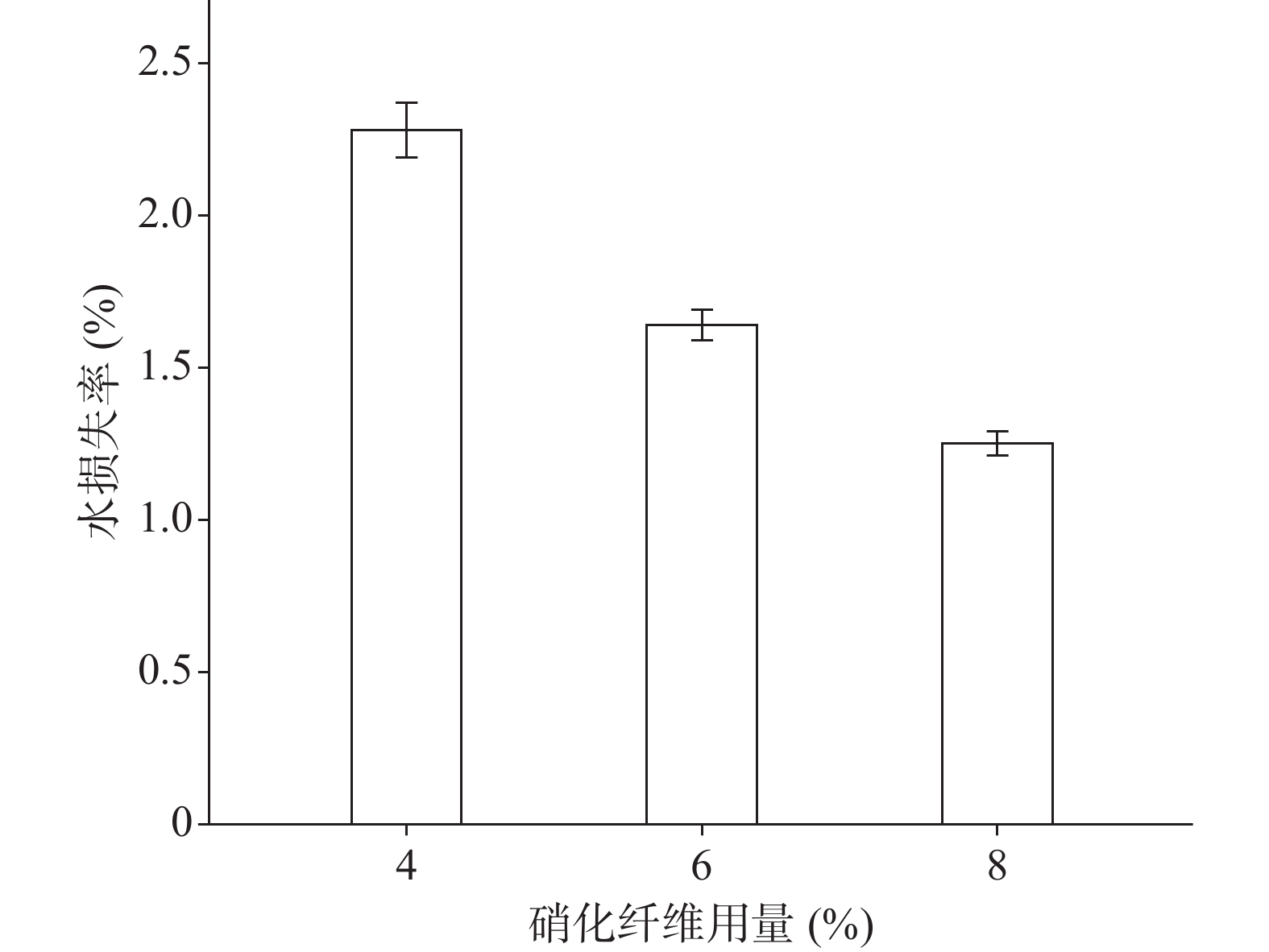
分别采用4%、6%、8%的硝化纤维制备液体创伤敷料,对所制的薄膜进行评价,其断点伸长百分率、防水性能考察的水透过率及MVTR值随着硝化纤维用量的增加呈下降趋势,抗张强度随着硝化纤维用量的增加呈上升趋势。其考察结果如图3~图6所示:
由图3、图4可知,硝化纤维的用量为4%、6%时,断点伸长百分率在170%以上,可认为薄膜韧性较好,在伤口表面有较好的舒适性,而硝化纤维用量为8%时,其断点伸长百分率较低,不足150%;在硝化纤维用量为4%时,所制薄膜过薄,导致其抗张强度较差,不及2.0 MPa。从图5可知,MVTR值在0.3~0.6 mg/(cm2·h)之间,随硝化纤维用量增加而减小,但均具有一定的透气性;由图6可知,三个不同梯度的硝化纤维在24 h内其水损失率均在2.5%以下,可认为防水性良好。综上考察结果,本次采用的硝化纤维用量为6%。
-
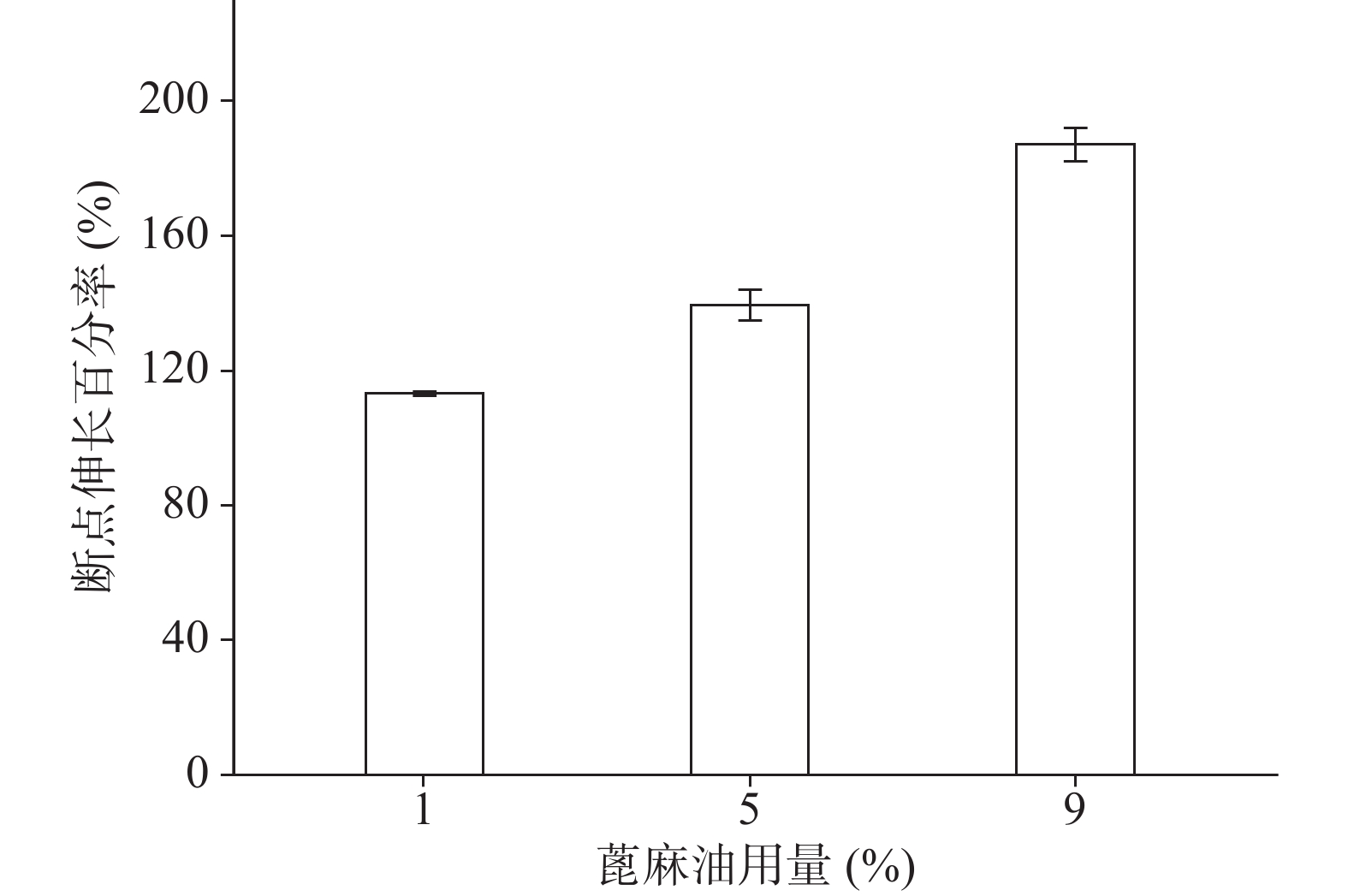
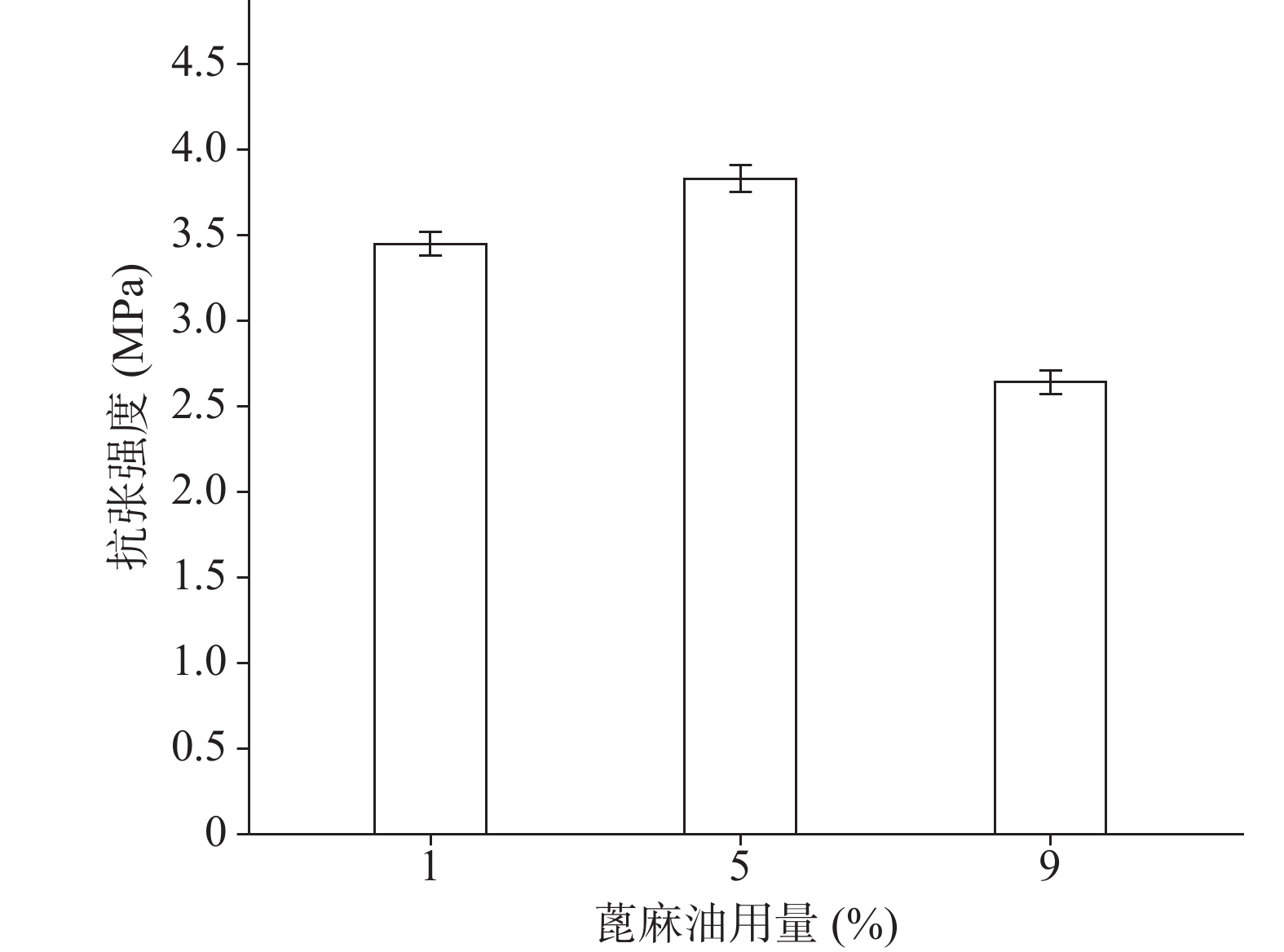
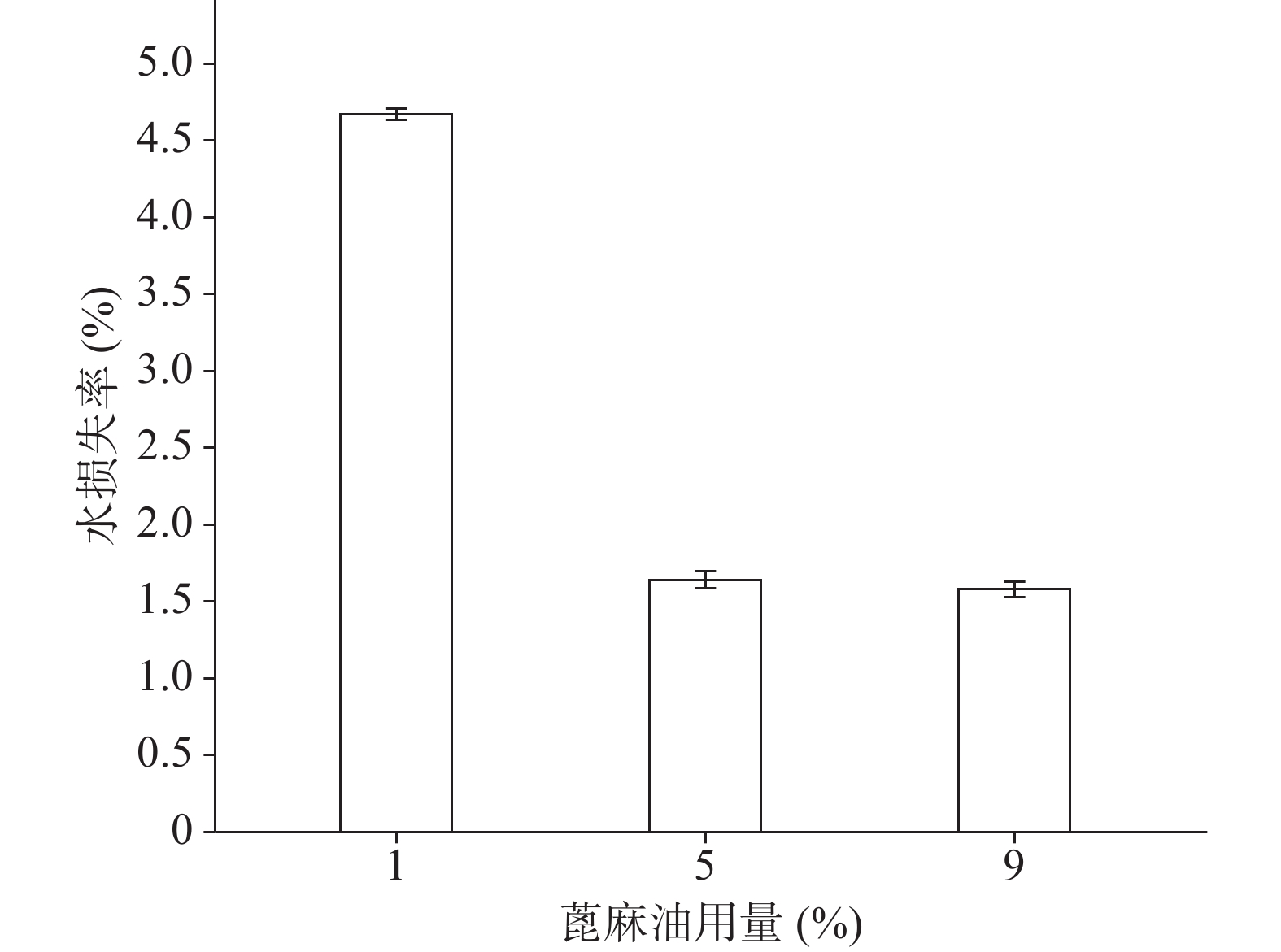
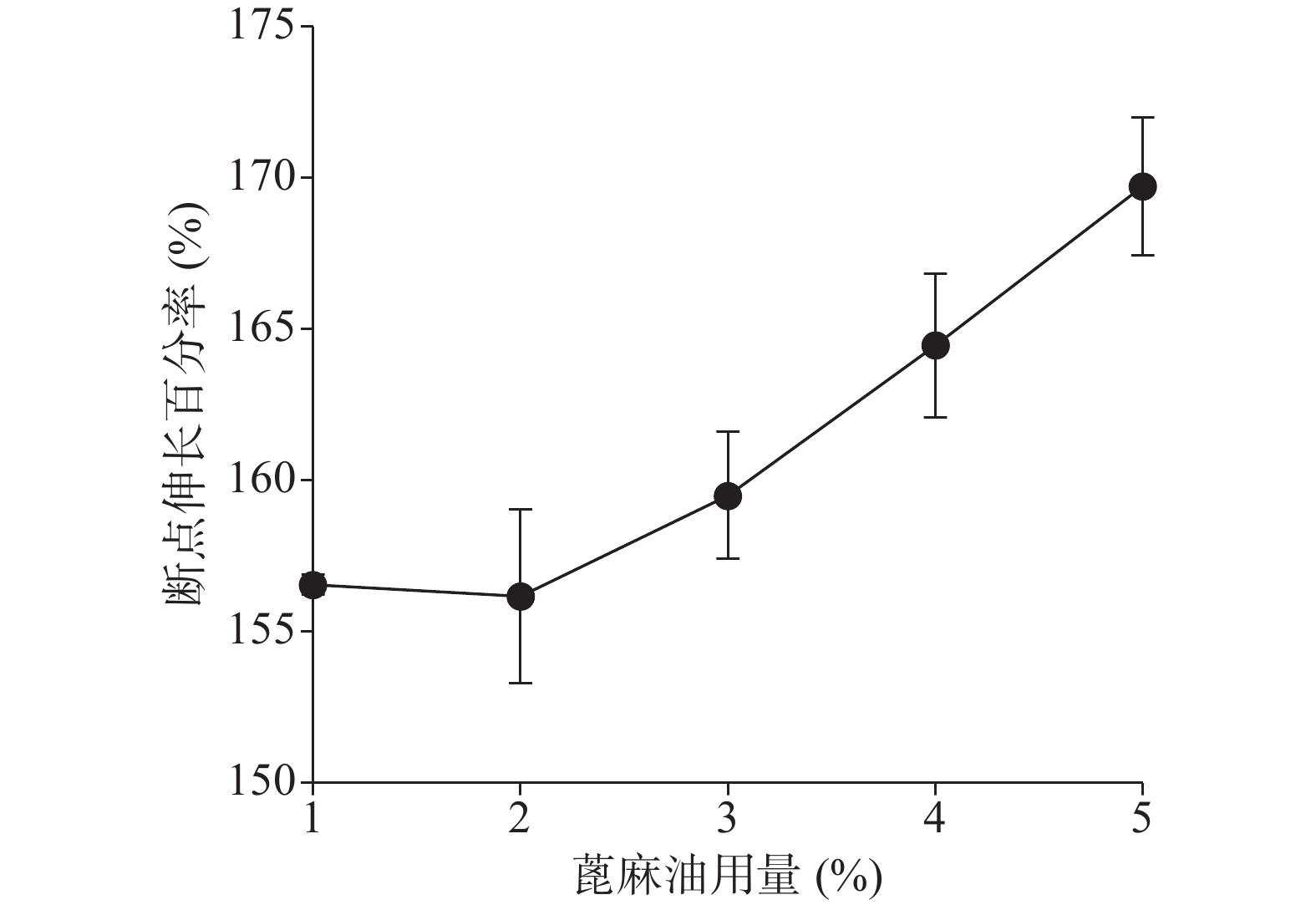
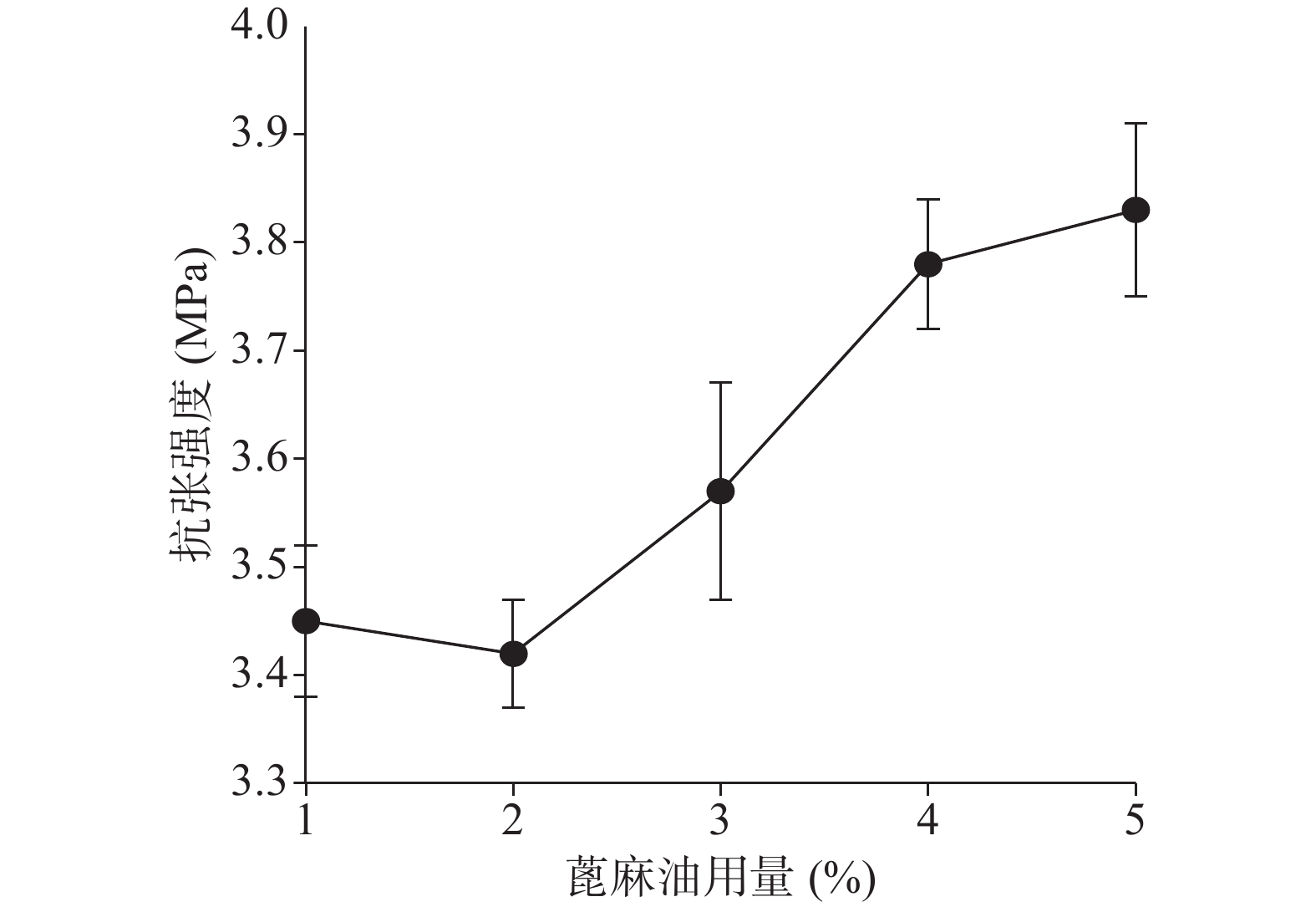
确定硝化纤维使用量为6%后,分别采用1%、5%、9%用量的蓖麻油制备液体创伤敷料,对所制的薄膜进行评价,由图7、图8可知,其断点伸长百分率随蓖麻油用量增加呈上升趋势,在蓖麻油使用量为1%时断点伸长百分率较差,不及150%,在5%~9%上升趋势明显且在蓖麻油用量为9%时达到190%,断点伸长百分率值数据较为理想;抗张强度随蓖麻油用量未呈明显下降趋势,反而是在蓖麻油使用量为5%时具有最大的抗张强度,而伸长率较好的9%用量蓖麻油处方抗张强度明显较小,在2.5 MPa左右,故蓖麻油用量选用浓度为5%。
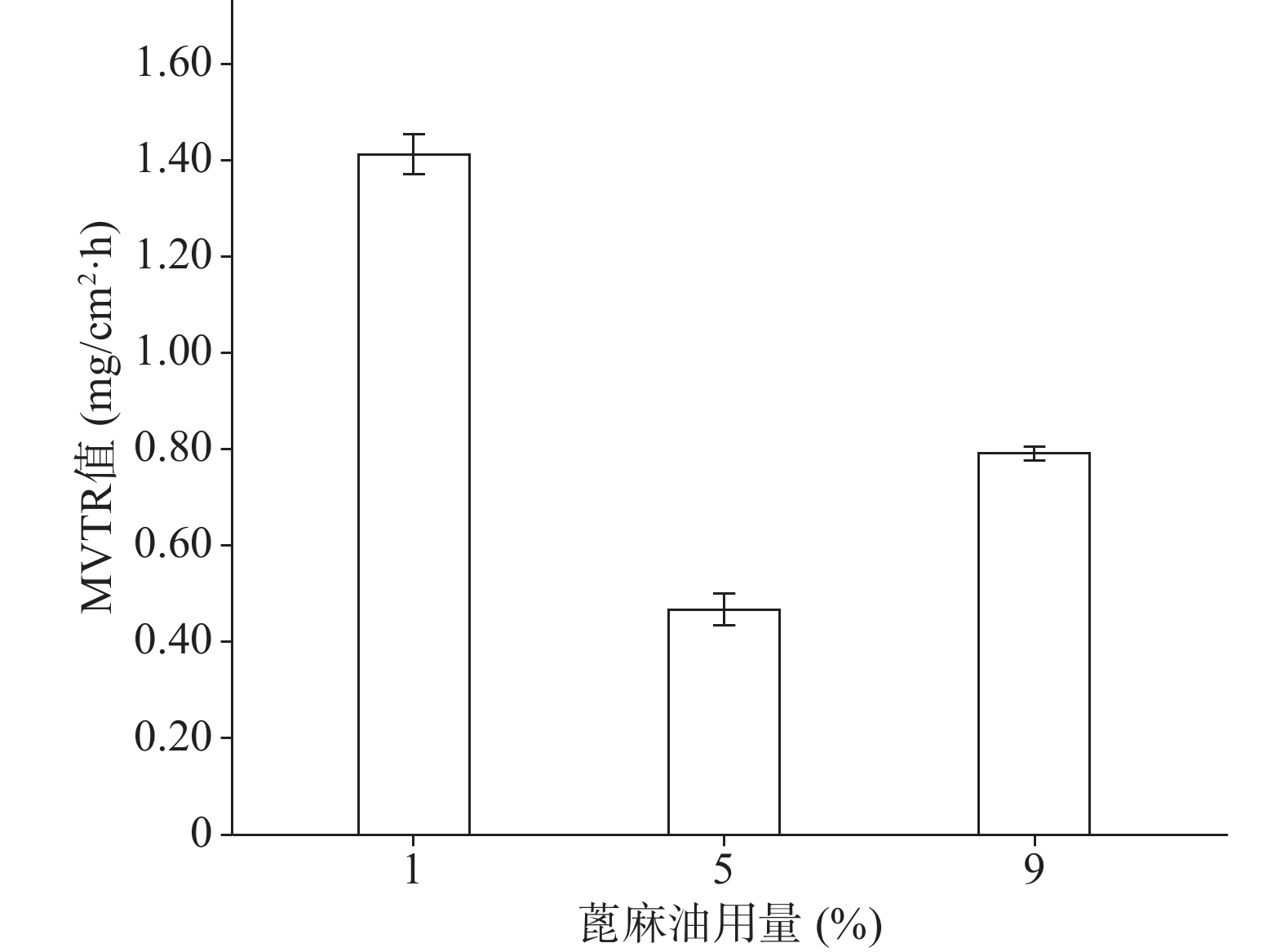
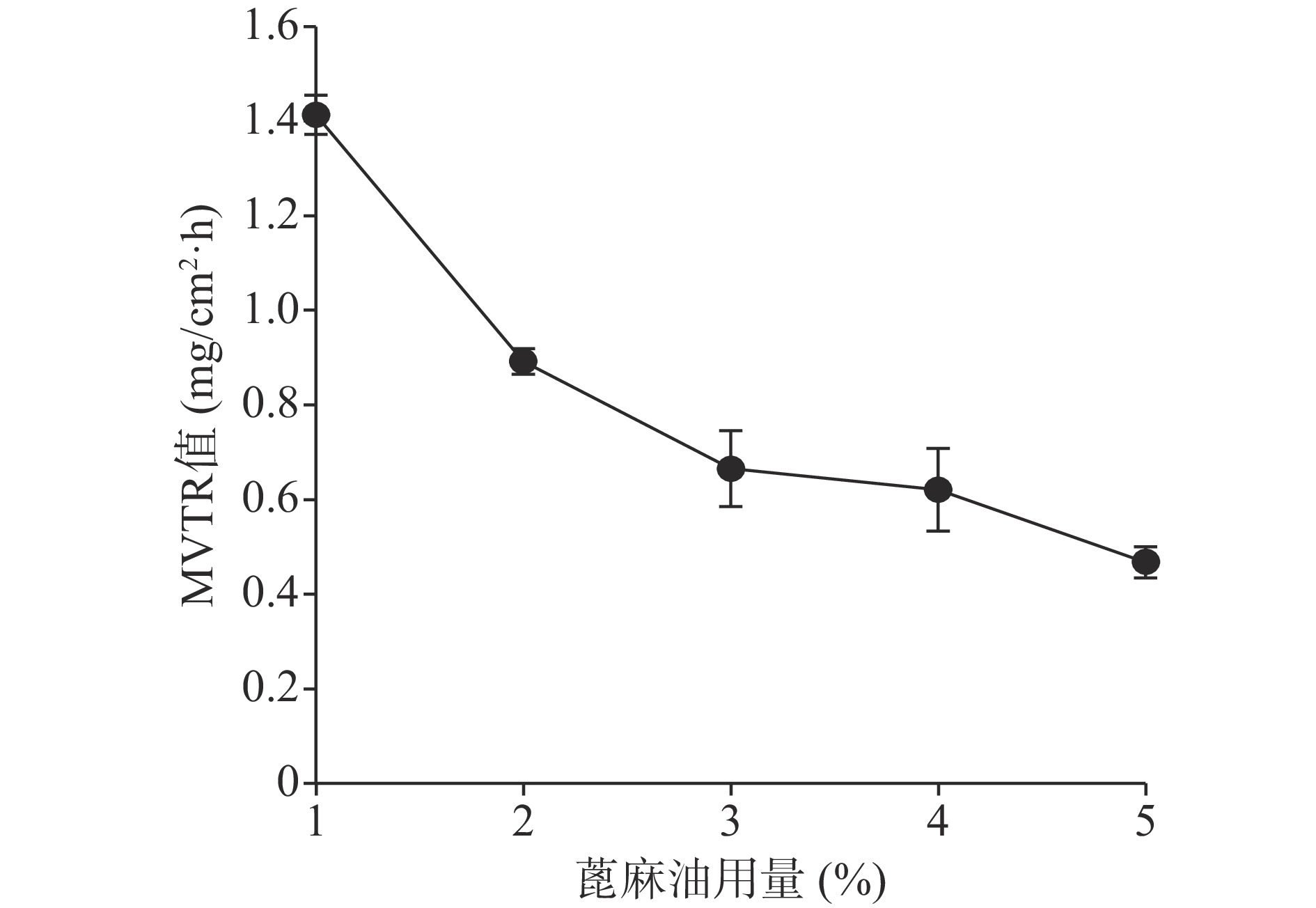
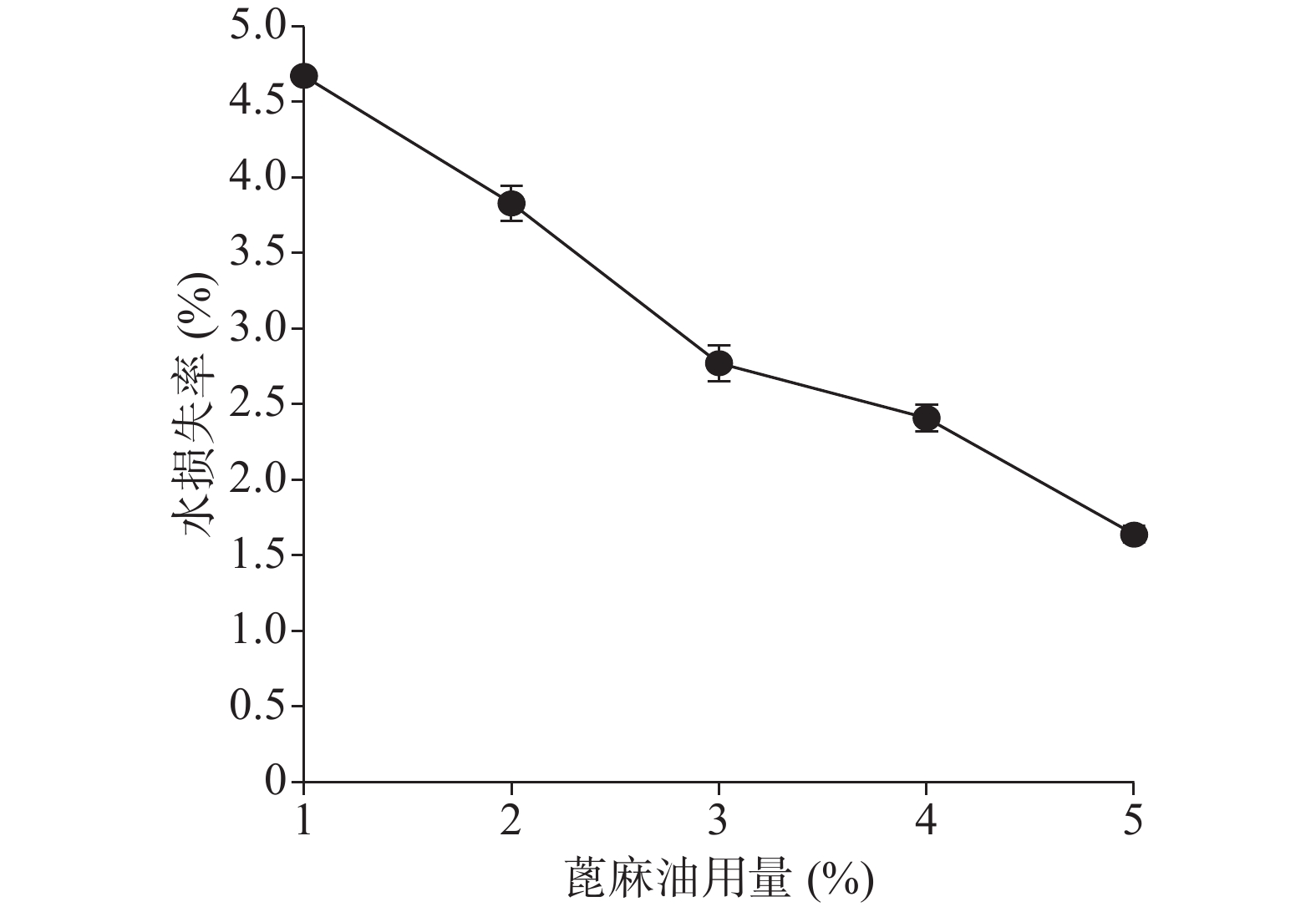
关于蓖麻油对防水性能和透气性能的影响如图9、图10所示,蓖麻油用量为1%时其MVTR值明显高于5%和9%时,且其水损失率也高于5%和9%时,由于5%与9%的防水性没有太大的差异。由此可以得出的结论是,随着蓖麻油的加入,创伤敷料的透气性变差,同时其防水性能却有所增强,1%用量蓖麻油透气性能极佳,但机械性能及防水性相对较差,又因其水损失率24 h也没有达到5%,也可以认为其防水性能良好。所以下一步的考察尽量满足透气性的需求。
综合断点伸长百分率、抗张强度、MVTR值、水损失率,在保证机械强度的同时尽量满足其透气性的要求。拟在1%~5%之间再另设梯度进行考察。拟定蓖麻油使用量为2%、3%、4%时对上述指标再行考察。
由图11、图12可知处方断点伸长百分率及抗张强度在1%~5%范围内随蓖麻油用量的增加总体上均有一定的上升趋势。断点伸长百分率在蓖麻油用量为1%、2%时相差不大,在2%~5%时有明显的上升趋势;抗张强度在蓖麻油用量1%、2%时和4%、5%时相差不大,在蓖麻油用量从2%~4%时有明显的上升趋势。
由图13、图14可知在蓖麻油用量为1%~5%范围内MVTR值及水损失率随处方中蓖麻油用量的增加而呈下降趋势。
综合以上几个因素对处方中的蓖麻油用量进行考察,从所制薄膜的机械性能来看,在蓖麻油用量为1%~3%时,断点伸长百分率不及160%,抗张强度较差,不及3.60 MPa,故此用量不予考虑,从所制薄膜的防水透气效果来看,4%、5%用量均有一定的透气效果,且防水性测试结果显示二者水损失率均不超过2.50%。综上考虑,确定蓖麻油的使用量为4%。
2.1. 市售产品小林液体创可贴中苯甲醇含量及溶剂组成的测定
2.1.1. 苯甲醇的含量测定
2.1.2. 溶剂组成的测定
2.2. 液体创伤敷料及敷料薄膜的制备
2.2.1. 液体创伤敷料的制备方法
2.2.2. 敷料薄膜的制备方法
2.3. 评价指标的确立
2.4. 硝化纤维用量的考察
2.5. 蓖麻油用量的考察
-
本文对市售产品的抑菌剂含量及溶剂组成进行了分析,以此作为基础对自制的液体创伤敷料进行单因素考察,确定了硝化纤维的最终用量为6%,蓖麻油的使用量为4%,所成薄膜具有良好的机械性能,具有透气性的同时又有着良好的防水效果。硝化纤维为主要的成膜材料,其用量对几个评价指标均有影响,其主要原因是其使用量的不同可造成所成薄膜的厚度不同,即创伤敷料薄膜厚度与硝化纤维用量成正比,其膜的厚度必然影响各项指标性能。蓖麻油作为增塑剂,对处方的影响主要在于:蓖麻油的加入能改变硝化纤维聚合物链之间的结构,使链与链之间的作用力产生变化从而在一定程度上影响薄膜的塑性。其次,蓖麻油的加入,可能堵塞了硝化纤维薄膜的纳米孔道,故呈现出其用量增加透气性能下降的趋势。
皮肤创伤,在临床和日常生活中都较为常见,伤口愈合的速度一定程度上取决于创伤表面环境,创伤表面环境需保持一定的潮湿性,即湿润表面可以加速伤口愈合,因此良好的创伤敷料,应具有一定的透气性,对于日常伤口来说,由于伤口表面的复杂,使用在创伤表面的敷料也应具有一定的机械性能。本实验主要探讨了硝化纤维和蓖麻油的用量对创伤敷料性能的影响,为下一步制备性能更加优良的创伤敷料提供研究基础。









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: