-
乳腺癌是最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,近年来已经成为致女性死亡的第二大原因[1]。虽然临床研究人员和基础科学家对乳腺癌进行了广泛研究,同时手术切除、放射性同位素治疗、化学药物治疗、自体免疫细胞治疗、靶向治疗等技术也已经成功应用于乳腺癌患者的治疗[2]。然而,这些传统的治疗方法大多存在副作用,因此有必要寻找新方法来改善患者预后和生活质量。由于中药中含有复杂的化合物,且在多种人体疾病中发挥作用,因此,中药在癌症患者的康复及术后放/化疗的辅助治疗等方面越来越引起人们的关注。
月腺大戟(Euphorbia ebracteolata Hayata)为金虎尾目大戟科大戟属的多年生草本植物,多分布在土坡、草地或者林下。在我国的安徽、河南、江苏、山东、湖北省常见。月腺大戟作为传统中药最早记载于《神农本草经》,到目前为止已经有2 000多年历史,它以根入药,具有逐水祛痰、散结杀虫的功效,可治疗水肿、哮喘、消化不良、皮癣等疾病。近来发现研究中药月腺大戟中的提取物具有抗肿瘤活性。月腺大戟中含有多种化学成分,包括萜类、脂类、酚类、苯乙酮类、黄酮类以及鞣质类。本课题组前期实验中,从月腺大戟中提取了一种乙酰间苯三酚类化合物月腺大戟素A(EA),并证实它能抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力[3-4]。蛋白激酶D1(PKD1)是一种新型的丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,在多种癌症组织中异常表达,可以通过作用于MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT信号通路,调控乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力[5]。但是EA如何影响乳腺癌细胞增殖能力的具体机制,以及是否通过影响PKD1从而影响乳腺癌的增殖能力均不明确。
本研究根据前期实验对EA影响乳腺癌的具体机制的研究,结果表明EA具有通过干扰PKD1介导MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT信号通路以抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力。
HTML
-
人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞(美国模式菌种收集中心,ATCC);DMEM培养基、胎牛血清、青霉素/链霉素双抗溶液(Gibco公司);转染试剂脂质体2000和TRIzol(Invitrogen公司);RNA抽提、反转录、qRT-PCR试剂盒以及BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(北京康为世纪公司);CCK-8试剂(MedChemExpress公司);RIPA裂解液(碧云天公司);PKD1抗体(Santa Cruz Biotechnology公司),P-ERK1/2,ERK1/2,P-AKTAKT,GAPDH抗体(Cell Signaling公司);Western Blot增强化学发光试剂盒(Millipore公司)。PKD1过表达质粒pcDNA3.1-PKD1由Genescript公司构建,载体为pcDNA3.1。中药月腺大戟饮片购自安徽(产地:山东),其中,月腺大戟素A的制备采用课题组前期实验中的方法[4]。
-
人乳腺癌细胞系MCF-7细胞培养在含10%胎牛血清、100 U/ml青霉素和100 μg/ml链霉素溶液的DMEM培养液中,置于37 ℃、5% CO2的饱和湿度培养箱中进行贴壁培养。细胞转染时将处于对数生长期的细胞接种至6孔板中,提前混匀好转染试剂脂质体2000和质粒pcDNA3.1-PKD1或者对照质粒pcDNA3.1,添加至细胞培养板中,混匀后放置培养箱中培养6 h,换正常培养基继续培养。EA药物处理时,首先将处于对数生长期的MCF-7细胞按照1×105个/孔的数目接种到6孔板中,待细胞贴壁后加入不同浓度的EA药物(1、5、10、15、20 μmol/L)处理细胞,待进行后续试验。
-
通过CCK-8实验检测乳腺癌细胞增殖能力的变化。首先,将转染或加药处理的细胞按照每孔接种104/100 μl的浓度接种至96孔板中,每隔24 h检测一次,连续检测3 d,同时每个处理组在每个时间点均设置3个复孔,便于统计分析。每次检测前向96孔板中添加10 μl CCK-8试剂,在培养箱中孵育1 h后,放置酶标仪中震荡1 min,检测其在450 nm处的吸光值(OD)。统计3 d的OD值评估细胞增殖能力的变化。
-
通过qRT-PCR实验检测乳腺癌细胞中mRNA的表达。在转染或加药处理的孔板中添加TRIzol试剂,放置4 ℃摇床震荡5 min保证细胞充分裂解。利用抽提试剂盒提取细胞中的总RNA,并将其反转录为cDNA,根据qRT-PCR试剂盒说明书在ABI 7300实时PCR系统上进行qRT-PCR检测。反应过程中以GAPDH作为内参,计算PKD1的相对表达量。反应中的引物序列为:PKD1,reverse, 5’-CCCACGTGATGGACTCAAAGA-3’ forward, 5’-AAGGGTACGGGCCTCTCAAA-3’;GAPDH,reverse, 5’-AGGGGTCTACATGGCAACTG-3’和forward: 5’-GGCCTCCAAGGAGTAAGACC-3’。
-
通过Western Blot检测细胞加药或转染后相关蛋白的表达。将加药或者转染处理好的细胞加入RIPA裂解液裂解提取总蛋白。收集细胞裂解液,按照BCA蛋白定量试剂盒的说明书检测蛋白浓度。垂直电泳槽上样的每孔中加25 μg蛋白进行凝胶电泳分离,电压设置为80 V;待分离完成后将蛋白从凝胶中转至PVDF膜,电压设置为110 V,时间为120 min。转膜结束后将PVDF膜放置5%脱脂牛奶中进行封闭2 h;在4 ℃摇床中孵育一抗过夜(GAPDH以1:5 000稀释,PKD1以1:500稀释,其他抗体均按照1:1 000稀释),用TBST洗膜3次,每次10 min;室温摇床中用带有HRP标记的二抗(羊抗兔IgG或者羊抗鼠IgG均按照1:10 000稀释)孵育1 h,用TBST洗膜3次,每次10 min;用ECL显影液进行显影。
-
数据统计和分析均采用SPSS 20.0和GraphPad Prism 7.0软件进行,数据以(
${{\overline x} \pm s} $ )表示。采用Student’s t test和单因素方差分析进行组间差异的比较。检验水准(α)为0.05。
1.1. 细胞系与试剂
1.2. 细胞培养、转染与药物处理
1.3. 细胞增殖能力检测
1.4. RNA提取及荧光定量PCR检测(qRT-PCR)
1.5. 蛋白免疫印迹(Western Blot)检测蛋白表达
1.6. 统计学分析
-
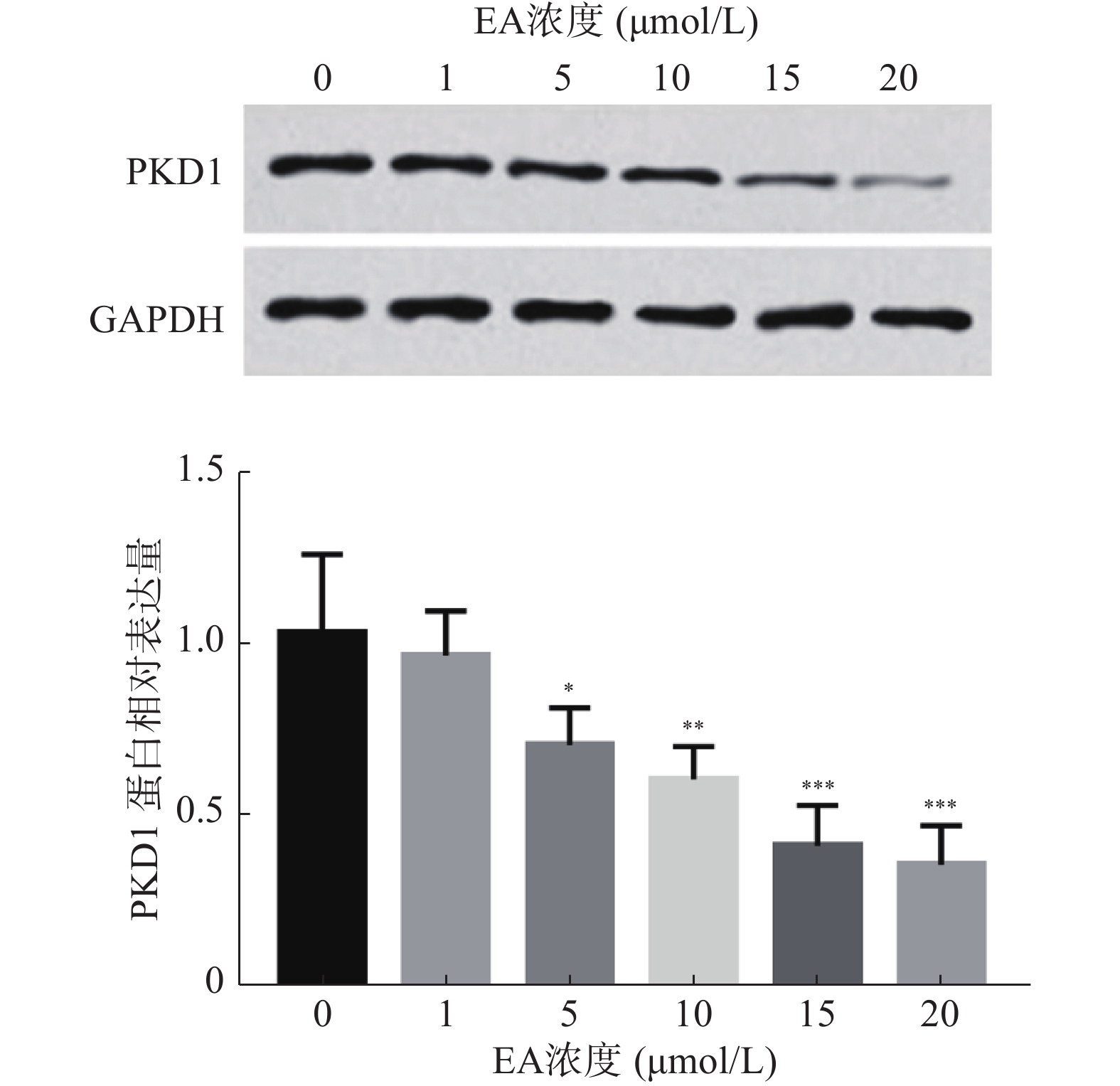
根据前期实验以及报道,推测EA通过调控PKD1的表达影响乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力,因此,在本研究中首先分析经不同浓度EA处理的乳腺癌细胞中PKD1蛋白水平的变化。结果如图1所示,EA显著抑制乳腺癌细胞中PKD1蛋白的表达水平(P< 0.05),且这种抑制呈剂量依赖性。同时,根据此实验结果EA在15 μmol/L时能显著降低PKD1的表达,故采用此浓度进行后续研究。
-
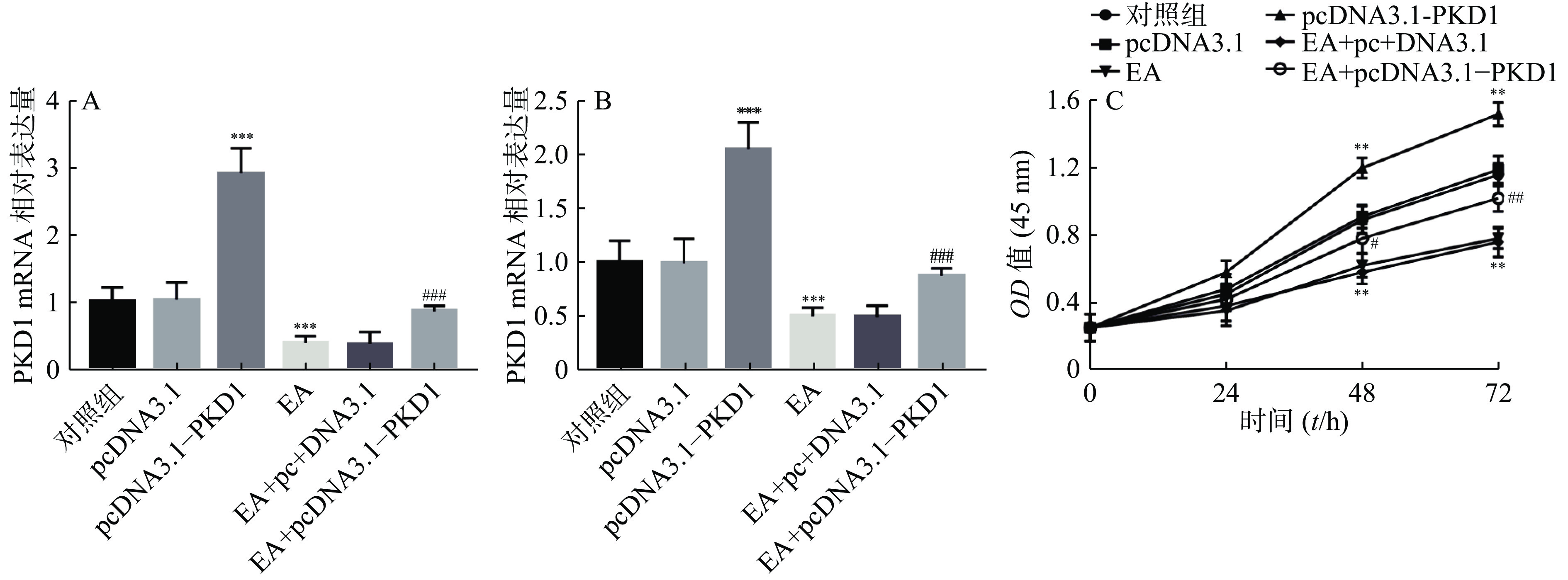
为了进一步研究EA是否通过PKD1调控乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力,课题组首先检测了EA的加药效果及过表达PKD1质粒是否转染成功。结果如图2A、图2B所示:乳腺癌细胞转染过表达质粒后PKD1的mRNA和蛋白水平显著升高(P<0.001)。结果证实过表达PKD1的转染效率较高。研究还发现EA干预处理后PKD1在mRNA和蛋白水平上均受到抑制(P<0.001),但是此抑制作用在转染过表达PKD1后被显著逆转(P< 0.001)。即PKD1能逆转EA对乳腺癌细胞中PKD1表达的抑制作用。通过CCK-8实验进一步验证EA是否通过PKD1影响乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力。结果如图2C所示,过表达PKD1后细胞的增殖能力显著升高。而EA药物干预后乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力显著被抑制(P< 0.01),当转染过表达质粒PKD1后,EA对乳腺癌细胞的增殖抑制作用被显著逆转(P<0.01)。
-
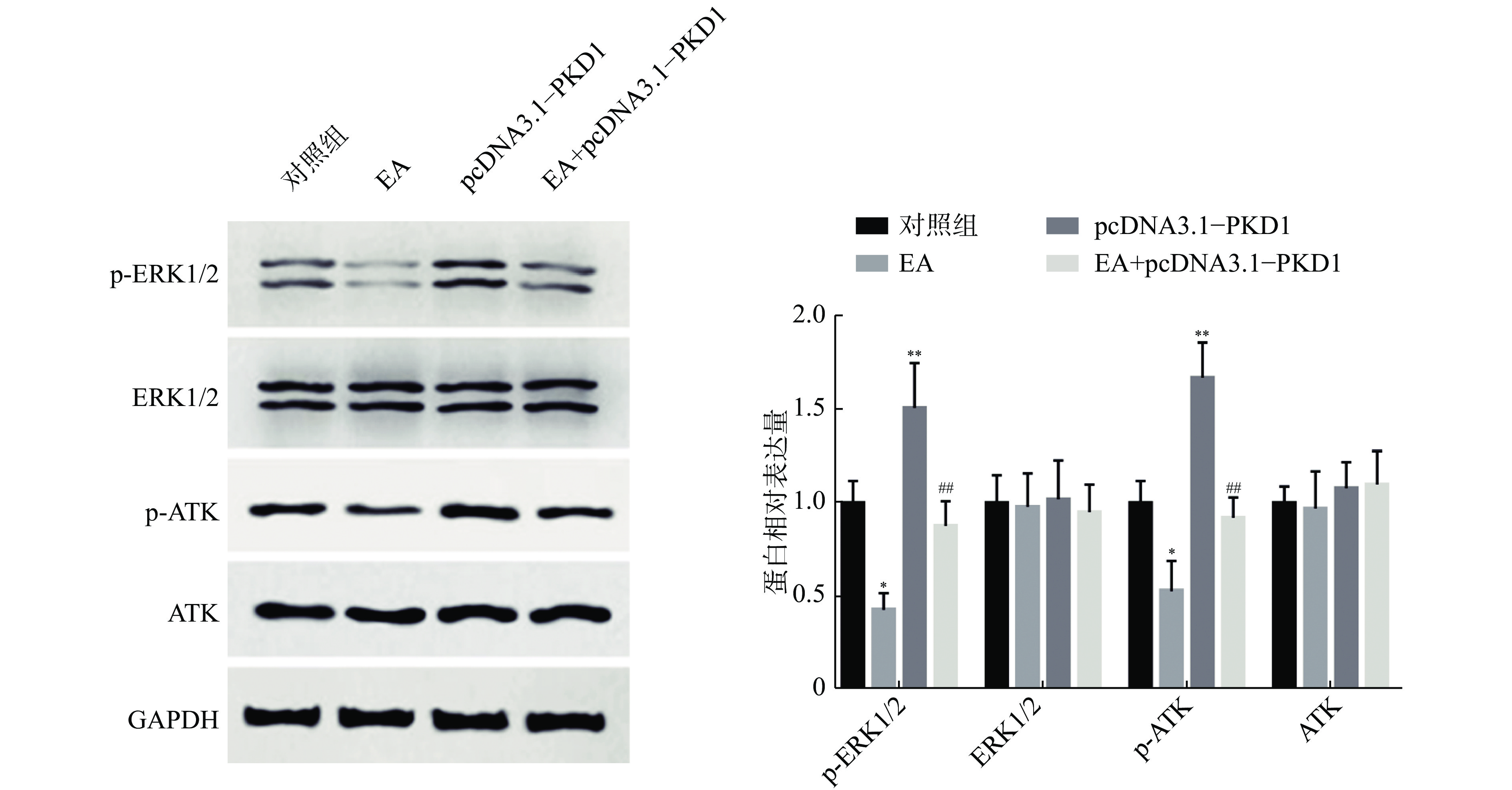
为了进一步阐明EA如何通过干扰PKD1影响乳腺癌细胞的体外增殖能力,课题组研究了PKD1调控的MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT信号通路的变化。如图3所示:乳腺癌细胞过表达PKD1后,p-ERK1/2、p-AKT表达水平显著升高(P<0.01);当EA药物处理后p-ERK1/2、p-AKT表达水平显著降低(P< 0.05)。然而对PKD1过表达的细胞给予EA药物处理后,PKD1能显著恢复EA药物处理对MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT信号通路中关键蛋白表达水平的影响。实验结果证实了EA可能通过调控PKD1介导的MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT信号通路来影响乳腺细胞的增殖能力。
2.1. EA抑制乳腺癌细胞中PKD1的表达
2.2. PKD1恢复EA对乳腺癌细胞增殖能力的抑制作用
2.3. EA通过干扰PKD1调控乳腺癌细胞增殖能力的机制研究
-
虽然近年来在乳腺癌的早期发现和治疗中取得了重大进展,但是乳腺癌患者的5年生存率仍然较低。基于中药的中医治疗在过去几十年中已得到越来越多的应用,并因其在增强化疗过程中的功效和降低毒性方面的重要作用而被关注,并且在多种癌症的预防和治疗方面具有一定作用[6-7]。据估计,美国国家癌症研究所(NCI)每年在中医相关研究项目上花费约1.2亿美元[8]。乳腺癌患者的治疗除了手术、放射疗法、化学疗法以外,还经常将中药治疗视为一种治疗方法[9]。
EA是从中药月腺大戟中提取的乙酰间苯三酚类化合物。在前期研究结果中证实EA可以抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力。蛋白激酶D(PKD)是一个进化保守的蛋白激酶家族,具有不同PKC家族成员的结构酶学和调控特性。PKD1是其中研究最多的家族成员。研究发现PKD1可以通过作用于MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT信号通路调控乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力[5]。因此,在本研究中首先验证了EA是否会影响PKD1的表达。结果显示EA呈剂量依赖的方式抑制乳腺癌细胞中PKD1蛋白表达。为了进一步证实EA是否通过影响PKD1的表达来调控乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力,课题组体外构建了PKD1过表达质粒转染乳腺癌细胞。在证实转染效率较高后,发现PKD1过表达能够逆转EA在mRNA和蛋白水平上对PKD1的抑制作用。同时,EA能显著抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力,这与前期研究结果一致。然而,原本受EA干预而降低的细胞增殖能力在PKD1过表达的情况下被显著逆转,证实PKD1能逆转EA对乳腺癌细胞的增殖抑制作用。
最后,课题组对EA如何通过干扰PKD1影响乳腺癌细胞增殖能力的机制进一步研究。既往的研究已经证明PKD1可以通过作用于MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT信号通路调控乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力[10]。因此,我们分析了MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT信号通路中关键蛋白的变化。实验结果证实EA药物作用于乳腺癌细胞时p-ERK1/2、p-AKT表达水平显著降低,说明EA能抑制MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT信号通路活性。但是,当EA药物和PKD1过表达同时处理时,PKD1过表达能显著恢复EA对p-ERK1/2、p-AKT的抑制作用。实验结果证实EA可能通过干扰PKD1介导MAPK和PI3K/AKT信号通路活性,从而抑制了乳腺癌细胞增殖。
此外,肿瘤的发生和发展是一个复杂的过程,本研究证实PKD1能显著促进乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力,这与已有的文献报道中PKD1会促进乳腺癌细胞增殖能力的结果是吻合的。但是在其他文献中报道过表达PKD1会显著抑制乳腺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭过程[11]。也就是说在肿瘤发生转移和侵袭前,肿瘤细胞大量增殖的阶段可以通过药物抑制PKD1的表达和活性,从而抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖。因此,在乳腺癌发生转移和侵袭前,使用EA抑制PKD1的表达和活性,可能具有抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖的功能。但是,如果肿瘤发生转移和侵袭后,药物抑制PKD1的表达,可能会产生促进肿瘤转移和侵袭的结果,使得肿瘤疾病向更加恶化的方向发展。因此,EA在乳腺癌中的应用应该严格注意肿瘤病理状态,在未发生转移和侵袭的患者中EA可通过抑制PKD1发挥抗肿瘤作用,而在已发生肿瘤转移和侵袭的患者中则应该谨慎使用调控PKD1的药物。
综上所述,经过一系列研究证实EA以剂量依赖的方式抑制乳腺癌细胞中PKD1的表达,而PKD1过表达能恢复EA对乳腺癌细胞增殖能力的抑制作用。同时,EA可能通过干扰PKD1介导的MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT信号通路的活性抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖能力。总之,本研究首次揭示了EA药物通过抑制PKD1的表达及其介导的MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT信号通路发挥抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖作用。









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: