-
高尿酸血症是一种威胁人类健康的常见代谢性疾病。血液中尿酸水平偏高,会导致关节及肾脏沉积尿酸盐晶体,是痛风性关节炎、急性尿酸肾病、心血管及肾脏疾病,特别是高血压的重要危险因子[1]。虽然抗高尿酸血症药物在治疗高尿酸血症和痛风方面已有进展,但作为常用的黄嘌呤氧化酶(XOD)抑制剂,别嘌醇可致严重的过敏(如轻度出疹)和粒细胞缺乏症,并会损害嘧啶代谢,从而加剧肾脏毒性。目前,中医药在抗高尿酸疾病中,有很好的临床疗效,受到研究者的青睐[2]。
萆薢降酸方是我院使用多年的协定处方,临床效果良好,深受患者认可,其治疗高尿酸血症、痛风和刺激性关节炎的疗效而被广泛应用。由萆薢、土茯苓、金钱草、泽泻、苍术等五味中药组成,具有利湿健脾,泄浊除痹的功效,临床上用于“腰痛” “石淋” “痹证”等病证,能消除代谢紊乱所致尿酸产生过多或排泄减少。方中萆薢具有利湿去浊、祛风除痹的功效,为“君药”;土茯苓具有清热解毒、健脾祛湿的功效,金钱草具有利湿退黄、利尿通淋、解毒消肿的功效,辅助“君药”排除尿酸,为“臣药”;泽泻具有利水渗湿、泄热、化浊降脂的功效,苍术具有燥湿健脾、祛风散寒的功效,辅佐“君臣”利湿去浊。
萆薢降酸方在降尿酸过程中的作用机制尚不清楚。本研究旨在探讨萆薢降酸方对实验性高尿酸血症小鼠血氧活性和尿酸排泄的影响。
-
实验用雄性ICR健康小鼠,体重约18~22 g,购自武汉大学动物实验中心,由武汉大学动物护理及使用委员会批准(编号:20121012)。
-
尿酸(UA,美国Sigma公司);肌酐(Cr)、尿素氮(BUN)测定试剂盒(美国BioAssay Systems);黄嘌呤氧化酶(XOD)测定试剂盒(南京建成生物工程研究所);RNA提取试剂盒(成都福际生物);逆转录试剂盒(日本Takara);Mill-iQ型纯水系统(美国Millipore);3K30高速低温离心机(德国Sigma);InfiniteM200型酶标仪(瑞士TECAN);7500型实时荧光定量PCR仪(美国Applied Biosystems)
-
萆薢、土茯苓、金钱草、泽泻、苍术(均购自安徽亳州中药材有限公司);别嘌醇片(江苏方强制药厂,国药准字H20033683);氧嗪酸钾(美国Sigma-aldrich,规格:25g/瓶)。
-
将ICR小鼠随机分为6组,每组10只。①阴性对照组:给予正常饲料喂养;②模型组:给予氧嗪酸钾(250 mg/kg,溶于5%CMC-Na溶液);③阳性对照组:给予氧嗪酸钾(同模型组)+别嘌醇(5 mg/kg);④高剂量组:给予氧嗪酸钾(同模型组)+药物(880 mg/kg);⑤中剂量组:给予氧嗪酸钾(同模型组)+药物(440 mg/kg);⑥低剂量组:给予氧嗪酸钾(同模型组)+药物(220mg/kg)。除阴性对照组外,其余各组按上述剂量灌胃给药,灌胃体积0.5ml/100g,每天1次,连续10 d。
-
经过连续10 d给药后,眼眶取血(取血前12 h禁食禁水),以3500r/min转速,离心20 min,分离血清;代谢笼收集24 h尿液,记录尿液体积,采用市售试剂盒以比色法测定血清及尿液中的黄嘌呤氧化酶(XOD)、尿酸(UA)、肌酐(Cr)及尿素氮(BUN)水平。
-
将肾组织匀浆,使用样品缓冲液裂解细胞,离心后收集上清液。样品用10%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳分离,转移到硝化纤维素膜上。使用尿酸转运蛋白1(URAT1)、有机阴离子转运蛋白1(OAT1)抗体孵育后,使用增强型化学发光检测试剂盒检测。使用Lab works 软件(GelPro 4.0)对条带光密度进行量化。
应用SPSS 16.0统计软件包对所有数据进行统计分析,计量资料以(
$\bar x $ ±s)表示,两组间均数比较采用t检验,多组间均数比较采用单因素方差分析,以 P<0. 05为差异有统计学意义。 -
如表1所示,模型组大鼠经灌胃氧嗪酸钾后,UA水平明显高于阴性组(P<0.05),表明高尿酸血症大鼠模型造模成功。连续给药治疗10 d后,与模型组比较,萆薢降酸方高、中、低剂量组血清尿酸水平显著降低(P<0.05)。虽然萆薢降酸方药物组小鼠血清尿酸水平均高于阳性组小鼠,但其尿酸排泄量呈剂量依赖性增加;与模型组比较,血清肌酐和尿素氮水平均有明显的降低(P<0.05),萆薢降酸方药物组对血清肌酐水平的改善作用约为模型组的2~3倍。如表2所示,与模型组比较,高剂量组萆薢降酸方对高尿酸血症模型小鼠中血清和肝脏氧化酶活性也有显著影响(P< 0.05)。
组别 剂量(mg/kg) 血清UA(mg/L) 尿液UA(mg/L) 血清Cr(µmol/L) 尿液Cr(mmol/L) 血清BUN (mmol/L) 阴性组 − 1.42±0.18 35.25±5.73 0.29±0.11 41.56±3.42 7.58±0.85 模型组 − 6.13±0.76* 12.68±4.79* 0.95±0.38* 17.33±4.68* 16.43±1.13* 阳性组 5 1.85±0.37 19.26±5.28 0.34±0.22 24.26±3.32 9.37±1.14 低剂量组 220 3.73±1.1# 19.79±6.21# 0.56±0.21# 18.13±2.79 13.38±0.68# 中剂量组 440 2.85±0.91# 28.65±7.55# 0.45±0.21# 26.72±3.02# 11.37±0.74# 高剂量组 880 2.04±0.64# 38.34±8.23# 0.35±0.18# 34.38±1.98# 8.83±0.71# 注:*P < 0.05,与阴性组比较;#P< 0.05,与模型组比较 组别 剂量 (mg/kg) 血清XOD
(u/L)肝脏XOD
(u/g prot)阴性组 − 16.27±1.15 65.34±3.68 模型组 − 26.58±1.46 84.53±4.56 阳性组 5 18.43±1.24 37.38±4.59 低剂量组 220 23.83±1.36 79.63±5.27 中剂量组 440 22.65±1.42 76.14±5.34 高剂量组 880 18.12±1.33* 70.15±5.20* 注:*P<0.05,与模型组比较 -
萆薢降酸方剂量依赖性地降低了URAT1的表达,增加了OAT1的表达。与模型组相比,萆薢降酸方组小鼠URAT1蛋白表达显著降低,而OAT1蛋白表达水平显著升高(P<0.05),见图1。
-
高尿酸血症是临床上痛风和慢性肾炎的主要危险因素。近年来,降低血清尿酸的治疗药物因其不良反应而受到限制。一些研究表明,中药可以下调高尿酸血症小鼠的肝氧化,并促进肾尿酸排泄[3]。为了扭转高尿酸血症早期复杂的病理状态,采用萆薢降酸方促进肾尿酸排泄。与模型组比较,不同剂量组血清尿酸水平显著降低,尿液尿酸水平显著升高(P<0.05)。高剂量萆薢降酸方对高尿酸血症患者血清和肝脏氧化酶活性也有显著影响(P<0.05)。越来越多的临床报道表明,高尿酸血症不仅与痛风有关,还与慢性肾炎和肾功能不全有关[4]。尿素氮和血肌酐水平是肾功能的有用指标,肾脏损害伴随着尿素氮和血肌酐的增加,表明尿素和肾功能下降[5]。与模型组相比,不同剂量的萆薢降酸方能显著抑制BUN和血清Cr水平(P<0.05),相反,萆薢降酸方诱导的尿液Cr水平是模型组的3倍左右。尿酸排泄是萆薢降酸方的主要调节因子,URAT1和OAT1在尿酸处理中起着重要作用[6]。URAT1是尿酸盐重吸收的重要因素,调解尿酸的一个药物靶点。OAT1介导主动摄取有机阴离子,并通过ATP动力转运器和双向交换器控制尿液的最终排出[7]。为了探讨萆薢降酸方增加尿酸清除率的作用机制,本文研究了萆薢降酸方对尿酸(URAT1)和氧化物(OAT1)活性的影响。萆薢降酸方对高尿酸血症小鼠肾组织中URAT1蛋白表达有剂量依赖性的抑制作用,并增强 OAT1蛋白的表达(P<0.05)。这些结果与萆薢降酸方促进尿酸排泄的作用是一致的,也提示萆薢降酸方抑制了由尿酸和OAT1信号转导靶点介导的尿酸的积累和尿量的减少。
Effect of Bixie deacidification fang on hyperuricemia mouse model and its effect on the expression of renal urate transporter
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202101017
- Received Date: 2021-01-03
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-03-03
- Available Online: 2022-03-29
- Publish Date: 2022-03-25
-
Key words:
- Bixie deacidification fang /
- hyperuricemia /
- renal urate transporters /
- uric acid /
- creatinine
Abstract:
| Citation: | WANG Qiong, ZHOU Bing, YANG Quanwei. Effect of Bixie deacidification fang on hyperuricemia mouse model and its effect on the expression of renal urate transporter[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2022, 40(2): 143-145. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202101017 |







 本站查看
本站查看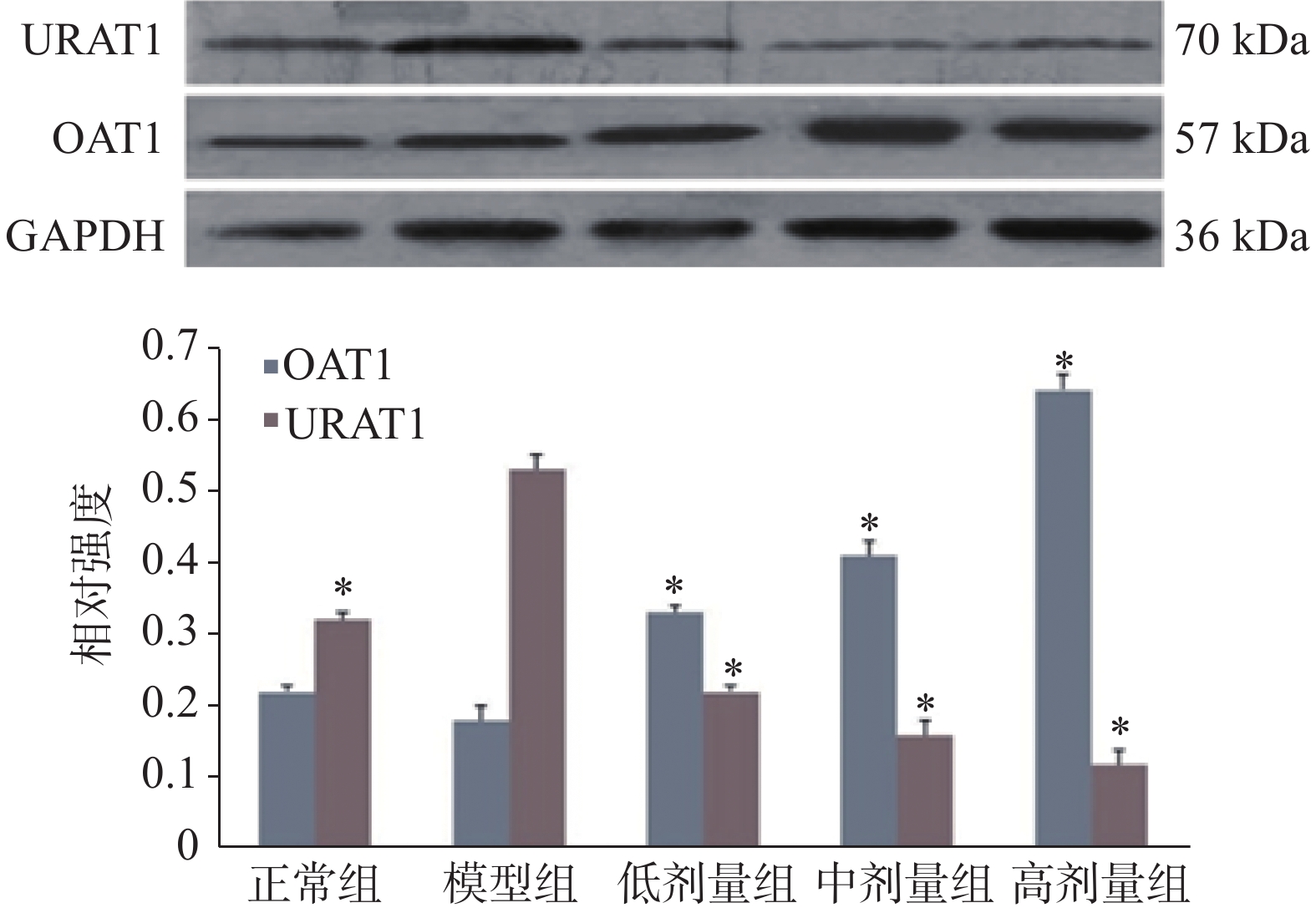



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: