-
晕动病又称晕动症、运动病,主要包括晕车、晕船、晕机(又称空晕病)[1-2]。晕动症在海军部队较为常见,主要发生于对航海环境尚未习服的官兵,遇到海况较差和乘坐较小船只时,晕动症的发生率会显著升高[3-4]。目前临床上用于治疗晕动病的药物非常有限,常用药物主要包括抗胆碱能药物(如东莨菪碱)和抗组胺药物(如苯海拉明、茶苯海明)。但是两者都有明显的中枢神经抑制作用,会造成服药者出现困倦、嗜睡等副作用[1, 5]。咖啡因是有效的中枢兴奋药,课题组将盐酸苯海拉明与咖啡因组成复方,在发挥盐酸苯海拉明抗晕动病作用的同时,利用咖啡因降低其中枢抑制导致的不良反应。前期课题组开展了盐酸苯海拉明咖啡因防治晕动病的药效学研究,沿用了盐酸苯海拉明用于晕动病防治的常用剂量,即25 mg/人次(70 kg),探索咖啡因的合用剂量,发现盐酸苯海拉明与咖啡因以1:2.4的比例组成复方效果最佳,既可以保持抗晕动病的效果,又可以克服盐酸苯海拉明单用导致的嗜睡不良反应。
既往的报道多用HPLC法、毛细管电泳法测定制剂中盐酸苯海拉明的含量;对生物样品中盐酸苯海拉明、咖啡因的测定方法也有研究报道,样品处理过程大都采用液-液萃取或固相萃取的方法,操作较为烦琐。本研究建立了UPLC-MS/MS方法测定大鼠血浆中盐酸苯海拉明与咖啡因的浓度,进一步考察了盐酸苯海拉明咖啡因复方在大鼠体内的药动学特点,为该复方制剂的临床应用提供参考依据。
-
Agilent 1290 UPLC 超高效液相色谱(安捷伦,美国);Agilent 6470 Triple Quad 三重四极杆质谱(安捷伦,美国),配备AJS-ESI 喷射流电喷雾离子源、MassHunter 分析工作站;Fresco 21 低温离心机(赛默飞,美国);SECURA125-1CN 型十万分之一电子天平(赛多利斯,德国);Arium® mini 超纯水机(赛多利斯,德国)。
-
对照品盐酸苯海拉明(中国食品药品检定研究院,批号100066-200807,纯度99.9%);内标盐酸苯海拉明-D6(加拿大TRC,批号8-CNN-25-2,纯度98%);对照品咖啡因(中国食品药品检定研究院,批号171215-200608,纯度>98%);内标咖啡因-D9(美国MTAR,批号90342,纯度97%);甲酸为色谱纯(麦克林,中国);甲醇、乙腈为质谱纯(霍尼韦尔,美国);水为超纯水。
-
SPF级SD 大鼠,6~8周龄[上海市计划生育科学研究所实验动物经营部,实验动物生产许可证号:SCXK(沪)2018-0006。合格证编号:20180006019969]。
-
色谱柱为ACE 3 C18-PFP(3.0 mm×150 mm,3 μm);流动相系统采用0.1%甲酸水溶液-乙腈(62∶38,V/V),等度洗脱,流速0.4 ml/min;柱温35 ℃;进样量5 μl,分析时间5 min。
-
采用AJS-ESI离子源,正离子模式,离子源参数设置:干燥气温度350℃;干燥气流速11 L/min;雾化器压力40 psi;鞘气温度350 ℃;鞘气流速11 L/min;毛细管电压4 000 V。多重反应监测(MRM)的参数设置:盐酸苯海拉明256.2→167.0(m/z),碎片电压75 V,碰撞能量10 eV;盐酸苯海拉明-D6(IS)262.0→167.0(m/z),碎片电压75 V,碰撞能量10 eV。盐酸苯海拉明和氘代内标的保留时间均为3.73 min。咖啡因 195.0→138.0(m/z),碎片电压80 V,碰撞能量20 eV;内标咖啡因-D9(IS)204.0→116.2(m/z),碎片电压80 V,碰撞能量40 eV。咖啡因和氘代内标的保留时间均为2.35 min。
-
(1)盐酸苯海拉明标准溶液
取盐酸苯海拉明对照品适量,精密称定,置10 ml量瓶中,加入甲醇溶解并稀释至刻度,配成浓度为1.0 mg/ml的对照品储备液;取上述对照品储备液适量,用甲醇按比例逐级稀释,配成浓度分别为20~20 000 ng/ml的系列对照品溶液,置4 ℃冰箱保存,备用。
(2)盐酸苯海拉明-D6内标标准溶液
取盐酸苯海拉明-D6对照品适量,精密称定,置10 ml量瓶中,加入甲醇溶解并稀释至刻度,配成浓度为1.0 mg/ml的对照品储备液;取上述储备液用甲醇稀释为50 ng/ml的内标溶液,置于4 ℃冰箱保存,备用。
(3)咖啡因标准溶液
取咖啡因对照品适量,精密称定,置10 ml量瓶中,加入甲醇溶解并稀释至刻度,配成浓度为1.0 mg/ml的对照品储备液;取上述对照品储备液适量,用甲醇按比例逐级稀释,配成浓度范围分别为300~3×106 ng/ml的系列对照品溶液,置于4 ℃冰箱保存,备用。
(4)咖啡因D-9内标标准溶液
取咖啡因-D9对照品适量,精密称定,置10 ml量瓶中,加入甲醇溶解并稀释至刻度,配成浓度为1.0 mg/ml的对照品储备液;取上述储备液用甲醇稀释为2×103 ng/ml的内标溶液,置于4 ℃冰箱保存,备用。
-
取50 µl血浆样品,依次加入50 µl的盐酸苯海拉明-D6内标溶液(50 ng/ml)、200 µl的100%乙腈,涡旋1 min,于5 ℃下以12 000 r/min高速离心5 min,取上清液100 μl进样,用于测定盐酸苯海拉明的含量。
取50 µl血浆样品,依次加入100 µl的咖啡因-D9内标溶液(2 000 ng/ml)、700 µl的100%乙腈,涡旋1 min,于5 ℃下以12 000 r/min高速离心5 min,取上清液100 μl进样,用于测定咖啡因的含量。
-
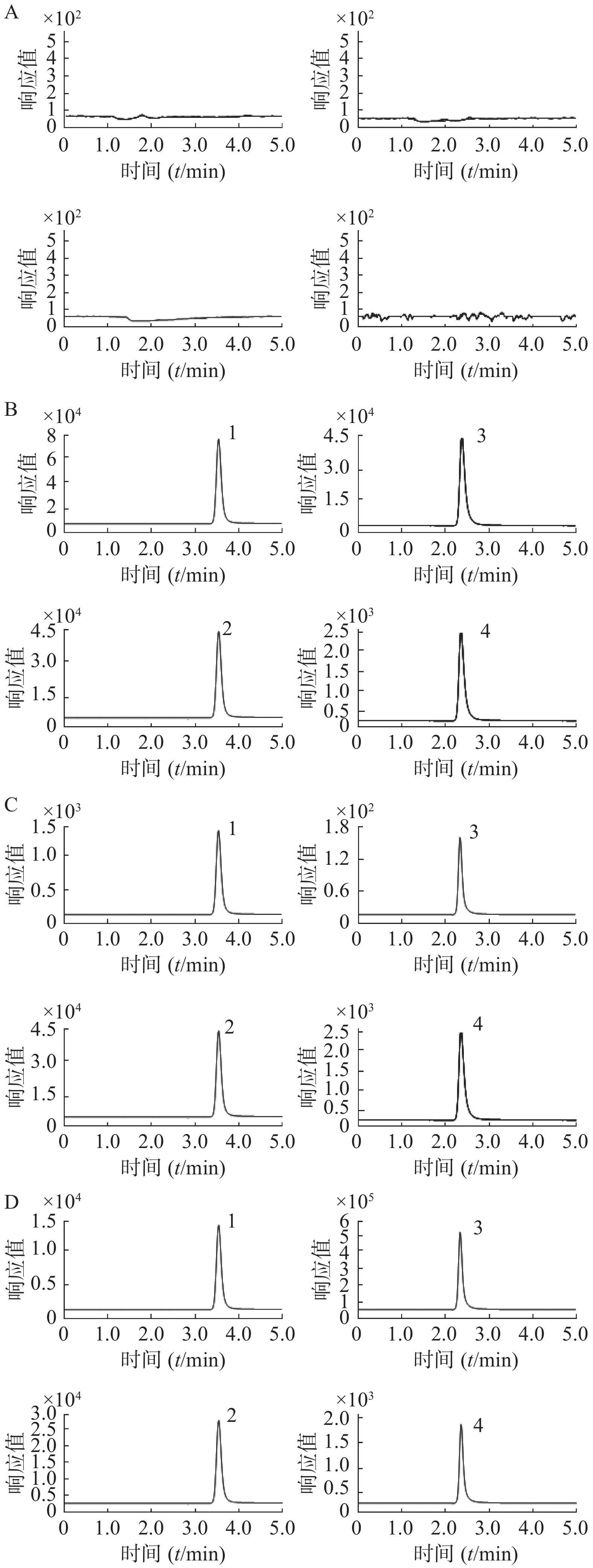
取空白大鼠血浆样品、空白大鼠血浆加盐酸苯海拉明与咖啡因的模拟血浆样品(盐酸苯海拉明浓度为100 ng/ml,咖啡因浓度为5×103 ng/ml)、定量下限模拟血浆样品(盐酸苯海拉明浓度为1 ng/ml,咖啡因浓度为15 ng/ml),以及大鼠给药后血浆样品,分别按“2.1.4”项下血浆样品前处理方法操作,进样,获得样品的色谱图。结果空白血浆中的内源性成分不干扰待测物和内标出峰,选择性良好,见图1。
-
取空白大鼠血浆,精密加入不同浓度的对照品溶液,制得浓度为1、5、10、50、100、200、500、1×103 ng/ml的盐酸苯海拉明标准曲线模拟样品和浓度为15、50、200、1×103、5×103、2×104、1×105、1.5×105 ng/ml的咖啡因标准曲线模拟样品。以血浆中待测物浓度 (X)为横坐标,待测物与内标的峰面积比值 (Y)为纵坐标,用1/X权重进行回归计算,求得盐酸苯海拉明回归方程:Y=0.022662X−0.006273,r=0.999 6,线性范围为1~1×103 ng/ml;咖啡因回归方程:Y=0.004275X−0.017169,r=0.999 9,线性范围为15~1.5×105 ng/ml。盐酸苯海拉明与咖啡因标准曲线的线性关系良好,权重因子在整个方法验证中保持一致。
-
分别制备低、中、高3个浓度水平的质控样品,其中盐酸苯海拉明浓度为2.5、250、800 ng/ml,咖啡因浓度为30、5×104、1.2×105 ng/ml,每个浓度平行操作5份,连续分析3 d,计算批内、批间的精密度(RSD)及准确度(RE),结果见表1。
待测物 浓度(ng/ml) 批内(n=6) 批间(n=18) 基质效应(%) 提取回收率(%) RSD(%) RE(%) RSD(%) RE(%) 盐酸苯海拉明 2.5 5.23 2.42 6.13 −0.60 114.89±2.09 93.22±7.10 250 4.12 −2.09 2.07 −0.06 110.75±0.44 92.82±5.69 800 1.40 7.00 2.81 4.38 118.45±0.51 92.38±2.60 咖啡因 30 3.94 −4.29 1.56 −5.38 114.28±13.38 56.59±5.79 5×104 8.20 −1.65 4.61 3.09 106.33±1.36 53.86±2.00 1.2×105 2.20 6.38 1.93 4.19 123.71±1.25 58.34±3.27 -
以6个不同来源的空白大鼠血浆作为基质,分别制备低、中、高3个浓度水平的质控样品,其中盐酸苯海拉明浓度为2.5、250、800 ng/ml,咖啡因浓度为30、5×104、1.2×105 ng/ml,按“2.1.4”项下进行处理并进样分析,记录盐酸苯海拉明和咖啡因峰面积A和A1;将6个不同来源的空白大鼠血浆提取后,加入待测物和内标溶液,使其最终浓度分别与低、中、高浓度质控样品的进样浓度一致,进样分析,记录峰面积B和B1;同时配制待测物和内标的纯溶液,浓度分别与低、中、高浓度质控样品的进样浓度一致,进样分析,记录峰面积C和C1。以A/B 的值计算提取回收率,B/C 的值计算基质效应,结果见表1。
-
首先通过新鲜配制盐酸苯海拉明、咖啡因和内标的储备液1.0 mg/ml,考察对照品储备液于4 ℃下放置30 d的稳定性;再以空白大鼠血浆作为基质,分别制备低、中、高3个浓度的质控样品,其中盐酸苯海拉明浓度为2.5、250、800 ng/ml,咖啡因浓度为30、5×104、1.2×105 ng/ml,考察血浆样品室温放置稳定性(3 h)、自动进样器稳定性(4 ℃放置24 h),冻融稳定性(反复冻融3次)、长期稳定性(−80 ℃放置30 d),结果见表2。
待测物 浓度(ng/ml) 室温(n=6) 冻融(n=18) 进样器(n=6) 长期(n=6) 储备液 RSD(%) RE(%) RSD(%) RE(%) RSD(%) RE(%) RSD(%) RE(%) RE(%) 盐酸苯海拉明 2.5 6.25 7.29 −0.67 6.32 −0.91 5.97 −5.28 6.5 −1.49 250 4.81 5.53 −5.16 5.61 −7.26 5.72 −2.43 8.61 800 2.15 4.96 0.01 5.08 −0.07 2.33 −0.46 5.2 咖啡因 30 −13.21 4.62 −6.89 4.84 −4.89 9.11 −6.84 5.67 3.44 5×104 2.16 5.92 −1.13 3.58 −5.84 1.79 0.77 7.69 1.2×105 2.09 4.31 0.31 2.96 −5.19 2.36 8.86 2.84 -
SD大鼠24只,随机分成4组,每组6只,雌雄各半。实验前禁食12 h不禁水,给药前称重并记录。灌胃组给予盐酸苯海拉明10 mg/kg、咖啡因24 mg/kg(低剂量组);盐酸苯海拉明20 mg/kg、咖啡因48 mg/kg(中剂量组);盐酸苯海拉明30 mg/kg、咖啡因72 mg/kg(高剂量组),收集给药前及给药后0.08、0.17、0.25、0.5、0.75、1、1.5、2、4、6、8和12 h的血样各0.15 ml;静脉注射组给予盐酸苯海拉明2 mg/kg、咖啡因4.8 mg/kg,收集给药前及给药后0.05、0.13、0.25、0.5、0.75、1、2、3、4、8和12 h的血样各0.15 ml。所有血样均放置30 min后,于3 000 r/min 离心5 min,分离得血浆,于−80 ℃保存待测。
-
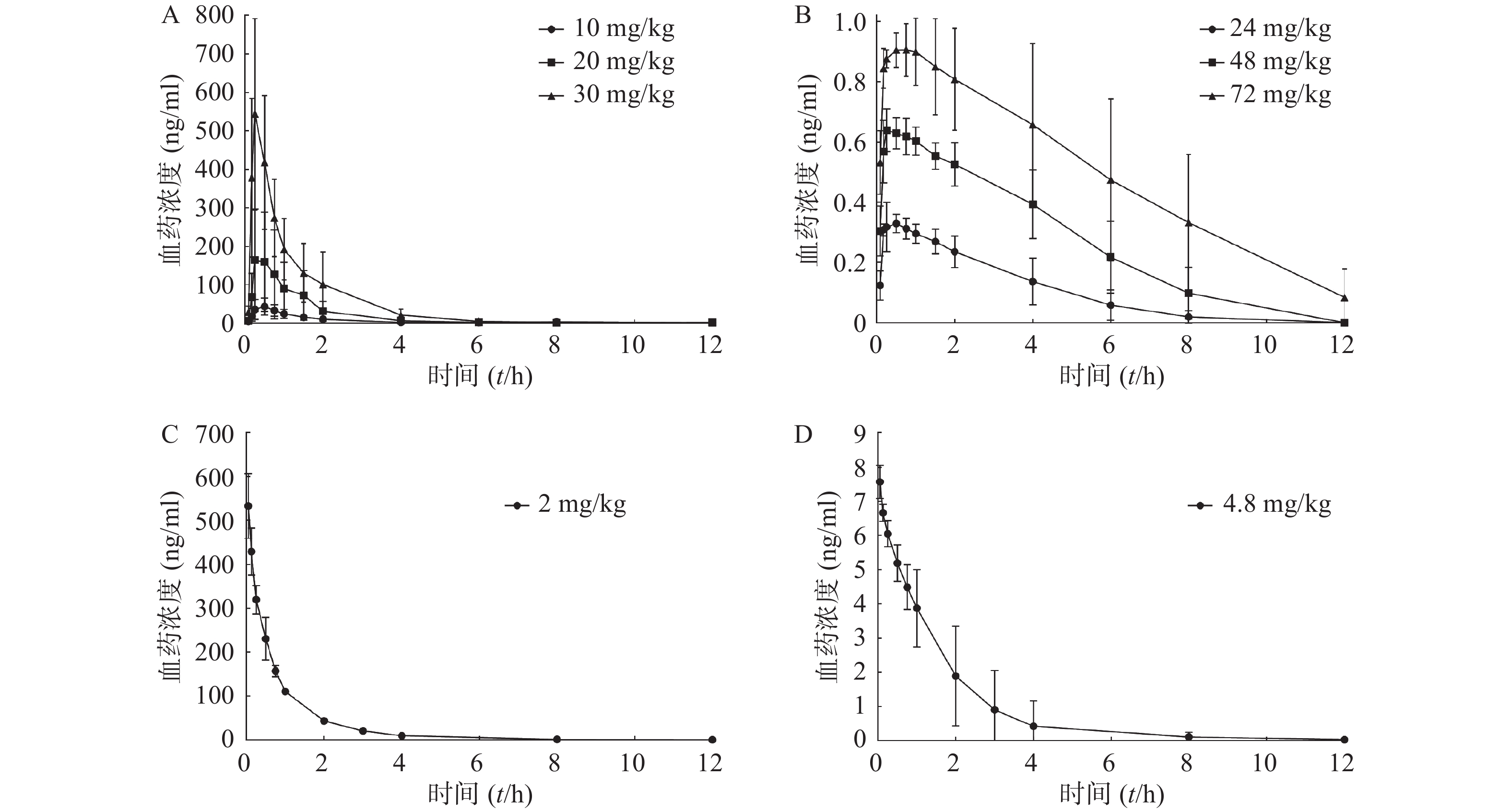
对动物实验中采集的大鼠血浆样本,按“2.1.4”项下进行处理并进样分析,将测得的血浆样品中盐酸苯海拉明和咖啡因的浓度与相应的采血点时间绘制药时曲线,见图2。
-
将对应采血时间测得的药物浓度采用非房室模型,计算主要药动学参数,见表3。结果显示,盐酸苯海拉明在10~30 mg/kg和咖啡因24~72 mg/kg 3种不同剂量大鼠灌胃给药后体内呈线性药动学特征,盐酸苯海拉明及咖啡因给药剂量相关系数分别为0.974 3及0.995 3。
参数 盐酸苯海拉明(mg/kg) 咖啡因(mg/kg) 灌胃组 静脉注射组 灌胃组 静脉注射组 10 20 30 2 24 48 72 4.8 t1/2(t/h) 1.90±
1.341.26±
0.331.24±
0.141.15±
0.150.85±
0.320.64±
0.091.52±
1.250.75±
0.43tmax(t/h) 0.46±
0.100.46±
0.290.25±
0.000.05±
0.000.28±
0.110.42±
0.200.74±
0.520.05±
0.00cmax(ng/ml) 43.78±
22.19174.76±
127.42543.63±
248.82533.01±
74.0734 375.44±
2 405.9664 746.08±
6 738.1393 972.11±
6 797.227 565.88±
485.30AUC0-12[ng/(ml·h)] 72.97±
22.21237.34±
182.66621.04±
327.27404.27±
46.51123 237.08±
42 277.09316 905.23±
86 946.7589 071.02±
224 376.2811 231.01±
5 769.43AUC0-∞[ng/(ml·h)] 78.73±
22.99241.29±
184.05623.82±
327.8407.5±
45.11124 138.53±
42 773.2317 012.42±
86 889.4618 141.98±
257 230.5411 282.98±
5 787.79AUC0-12/AUC0-∞ 0.93±
0.050.98±
0.010.99±
0.000.99±
0.010.99±
0.011.00±
0.000.97±
0.051.00±
0.00AUMC0-∞[ng/(ml·h2)] 238.18±
188.85384.96±
267.4884.65±
513.25420.08±
68.37331 730.74±
189 248.541 032 819.34±
461 031.262 870 085.86±
1 895 195.9816 391.02±
17 909.93MRT0-∞(t/h) 2.99±
2.241.64±
0.331.39±
0.131.03±
0.082.46±
0.753.12±
0.624.11±
1.541.2±
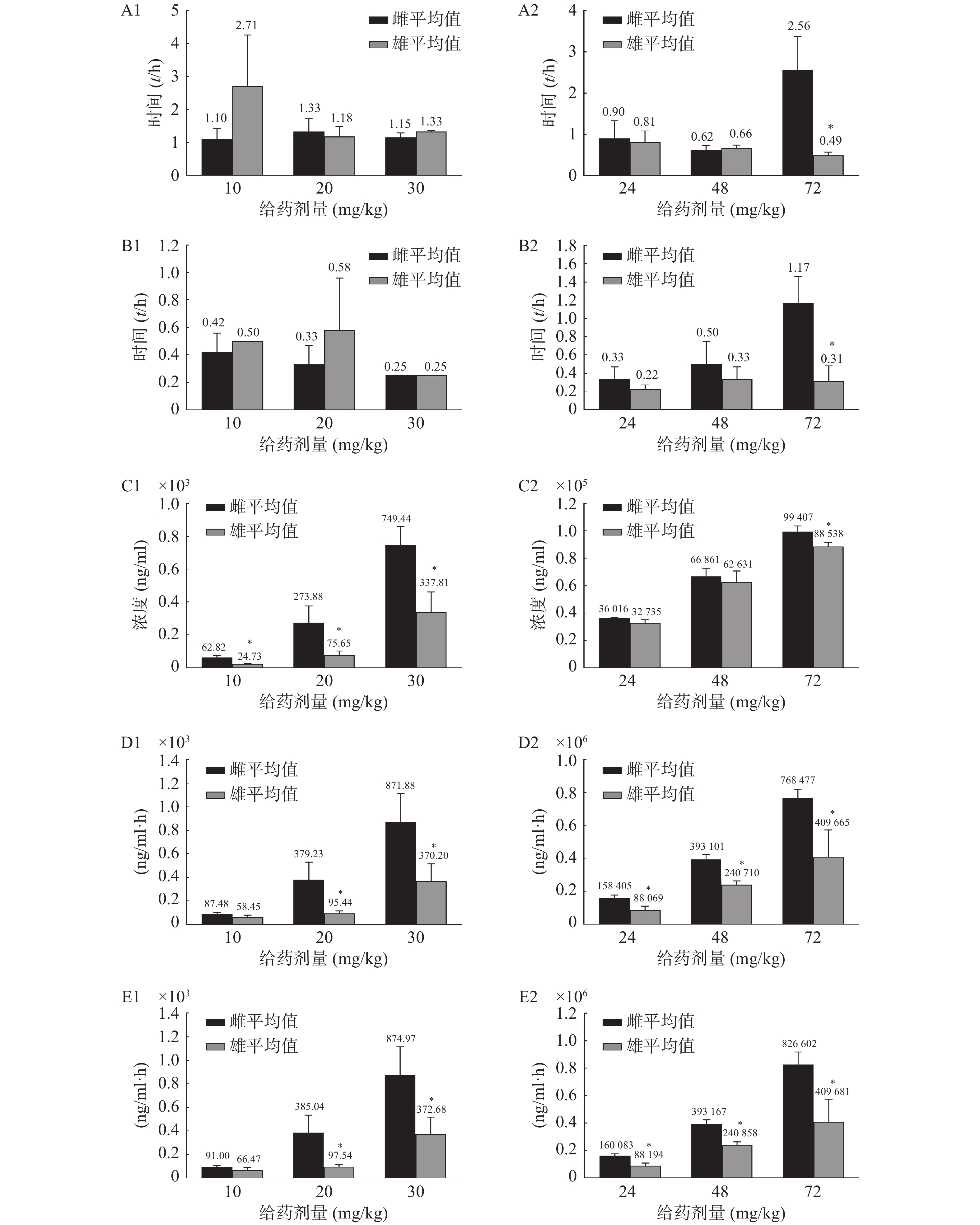
0.61同时观察到雌性和雄性大鼠在药动学参数上差异较大,通过t检验计算两组数据的P值,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义,见图3。高剂量给药时,咖啡因在雄性大鼠体内的半衰期(t1/2)及达峰时间(tmax)明显小于雌性;3个剂量给药组中雌性大鼠体内盐酸苯海拉明及咖啡因的达峰浓度(cmax)及药时曲线下面积(AUC)均大于雄性。
-
盐酸苯海拉明是经典的抗晕动病药物,咖啡因是常用的中枢兴奋药,然而对其开展的药动学研究较少,文献报道多为HPLC法、毛细管电泳法测定制剂中的含量[6-8];亦有生物样品中盐酸苯海拉明、咖啡因的测定方法报道,但样品处理过程大都需要采用液-液萃取或固相萃取的方法[9-14],较为烦琐。本文采用UPLC-MS/MS法定量血浆样品中的盐酸苯海拉明、咖啡因,采用乙腈作为蛋白沉淀剂,方法简便易操作。复方中盐酸苯海拉明咖啡因的处方组成为盐酸苯海拉明25 mg和咖啡因60 mg,两药在大鼠体内的血药浓度相差较大,盐酸苯海拉明的血药浓度很低,咖啡因的血药浓度相对很高,两药同时检测的难度很大。经过比较样品前处理的方法,最终确定将二者分开处理,按不同比例进行蛋白沉淀,最终使盐酸苯海拉明达到1 ng/ml较低的检测下限,而咖啡因达到15~1.5×105 ng/ml较大的线性范围,该方法能准确定量大鼠血浆样本中盐酸苯海拉明和咖啡因的浓度,是一次成功的方法学探索。
药动学研究显示,盐酸苯海拉明和咖啡因的达峰时间均在0.5 h左右、半衰期均在1 h左右,快速起效,盐酸苯海拉明的抗晕动作用和咖啡因的中枢兴奋作用可能同时发挥,可满足抗晕动病的同时克服嗜睡不良反应的需求。两药的药动学参数在雌雄大鼠间具有明显差异,可能与激素对代谢的影响有关。人们在日常生活中也会遇到服用盐酸苯海拉明的同时饮用茶或者咖啡的情况,茶或者咖啡因这样的中枢兴奋饮料中含有咖啡因,本研究考察了咖啡因与盐酸苯海拉明同服的药动学特点,对日常生活中药物的合理应用也有借鉴意义。
The pharmacokinetic study on compound diphenhydramine hydrochloride and caffeine in rats
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202106091
- Received Date: 2021-06-16
- Rev Recd Date: 2021-08-31
- Available Online: 2021-09-28
- Publish Date: 2021-09-25
-
Key words:
- diphenhydramine hydrochloride /
- caffeine /
- UPLC-MS/MS /
- content determination /
- pharmacokinetic
Abstract:
| Citation: | GAO Yu, LING Lin, XING Xinhao, ZHAO Liang, WANG Xinrong, WANG Yan. The pharmacokinetic study on compound diphenhydramine hydrochloride and caffeine in rats[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2021, 39(5): 415-421. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202106091 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: