-
癫痫在神经科的发病率较高,仅次于脑血管疾病,患者首次发病后,经常会反复发作,彻底治愈难度大,一般需要长期服药以控制病情。在长期的抗癫痫治疗过程中,患者受到药物﹑气候及周围环境的影响,免疫功能下降,在治疗期间易获得院内细菌性感染[1]。癫痫合并耐药阳性菌感染的住院患者(尤其是ICU患者)常联合使用丙戊酸钠和万古霉素,以达到治疗效果。但丙戊酸钠治疗指数低、体内过程和疗效存在较大个体差异,其有效血药浓度范围为50~100 μg/ml,而且该药需要长期服用,易产生耐受,血药浓度相对不稳定,特别是与其他药物联用时,常发生相互作用而影响疗效[2-3]。另外,万古霉素疗效与其血药浓度密切相关[4],2011年美国感染病学会(IDSA)刊文指出,万古霉素的血药浓度应达到10 μg/ml以上,对于复杂、严重的感染应达到15~20 μg/ml方能起到更好的治疗效果,同时万古霉素的治疗窗相对狭窄,血药浓度过高可能导致肾功能损害及耳毒性发生。所以临床用药时需要对两者进行血药浓度监测。
目前对丙戊酸钠和万古霉素进行血药浓度监测主要有高效液相色谱法和免疫分析法。采用高效液相色谱串联质谱法(HPLC-MS/MS)对两者进行浓度检测的文献亦有报道,但均为对其单独检测,未见对两者同时进行浓度检测的报道。本研究拟建立同时测定血清中丙戊酸钠和万古霉素浓度的HPLC-MS/MS法,并应用于两者联合用药时的血药浓度监测,该研究结果会对两者在临床的安全合理使用、节省医疗资源和减少患者医疗费用等方面起到积极作用。
-
Agilent 1260 高效液相色谱仪(美国 Agilent),包括G1322A自动脱气机,G1318B自动调配四元泵,G1367E自动进样器,G1316A可调柱温箱;Agilent 6420 triple quad LC/MS,图谱分析软件MassHunter Workstation Software(版本号B. 06.00);XW-80A型旋涡混合器(原上海医科大学仪器厂);BP110S 型电子分析天平(德国 Sartorius);MIKRO12-24 型高速离心机(德国 Hettich)。
-
丙戊酸钠对照品、丙戊酸钠-d6对照品、万古霉素对照品、卡那霉素B对照品(European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare),甲醇、乙腈、甲酸(质谱纯,默克公司),水为重蒸去离子水。
-
色谱柱为美国Agilent ZORBAX Eclipse Plus C18(4.6 mm×100 mm, 3.5 μm),流速0.5 ml/min,柱温25 ℃,进样量4 µl,流动相为0.1%甲酸水溶液(A)-乙腈(B),梯度洗脱见表1。
时间(t/min) A(%) B(%) 0~1.5 85 15 1.5~4.5 30 70 4.5~5.5 10 90 5.5~12 85 15 -
离子源为电喷雾离子化源(ESI),用多反应监测模式(MRM)进行定量分析,用正负离子检测模式。毛细管电压4 000 V,喷雾气压力45 psi,干燥气体流速10 L/min,干燥气体温度350 ℃。丙戊酸钠和内标丙戊酸钠-d6,选择负离子模式检测,离子反应对[M-H]−分别为m/z 143→143和m/z 149→149,碰撞能量均为0 V,裂解电压均为110 V。万古霉素和内标卡那霉素B,选择正离子模式检测,离子反应对[M+H]+分别为m/z 725→100和m/z 484→324,碰撞能量分别为46 V和14 V,裂解电压分别为142 V和130 V。4种药物的四级杆捕捉时间均为0.2 s,电子倍增器300 V。
-
分别精密称取丙戊酸钠对照品和万古霉素对照品20 mg和10 mg,置于10 ml棕色容量瓶中,用乙腈-水(50∶50)溶液定容至刻度,得到浓度分别为2 000 μg/ml和1 000 μg/ml的丙戊酸钠和万古霉素混合对照品储备液,贮存于4 ℃冰箱备用。配制浓度均为100 μg/ml丙戊酸钠-d6和卡那霉素B内标溶液,置于4 ℃冰箱保存备用。
-
取血清样品200 µl,置于1.5 ml的EP管中,分别加入内标丙戊酸钠-d6和卡那霉素B溶液各20 µl,涡旋混匀30 s,加入乙腈200 µl,涡旋混匀60 s,于室温下以14 000 r/min离心5 min,吸取上清液300 µl,加入乙腈-水(50∶50)溶液500 µl,涡旋混匀30 s,进样分析,分析时间12 min。
-
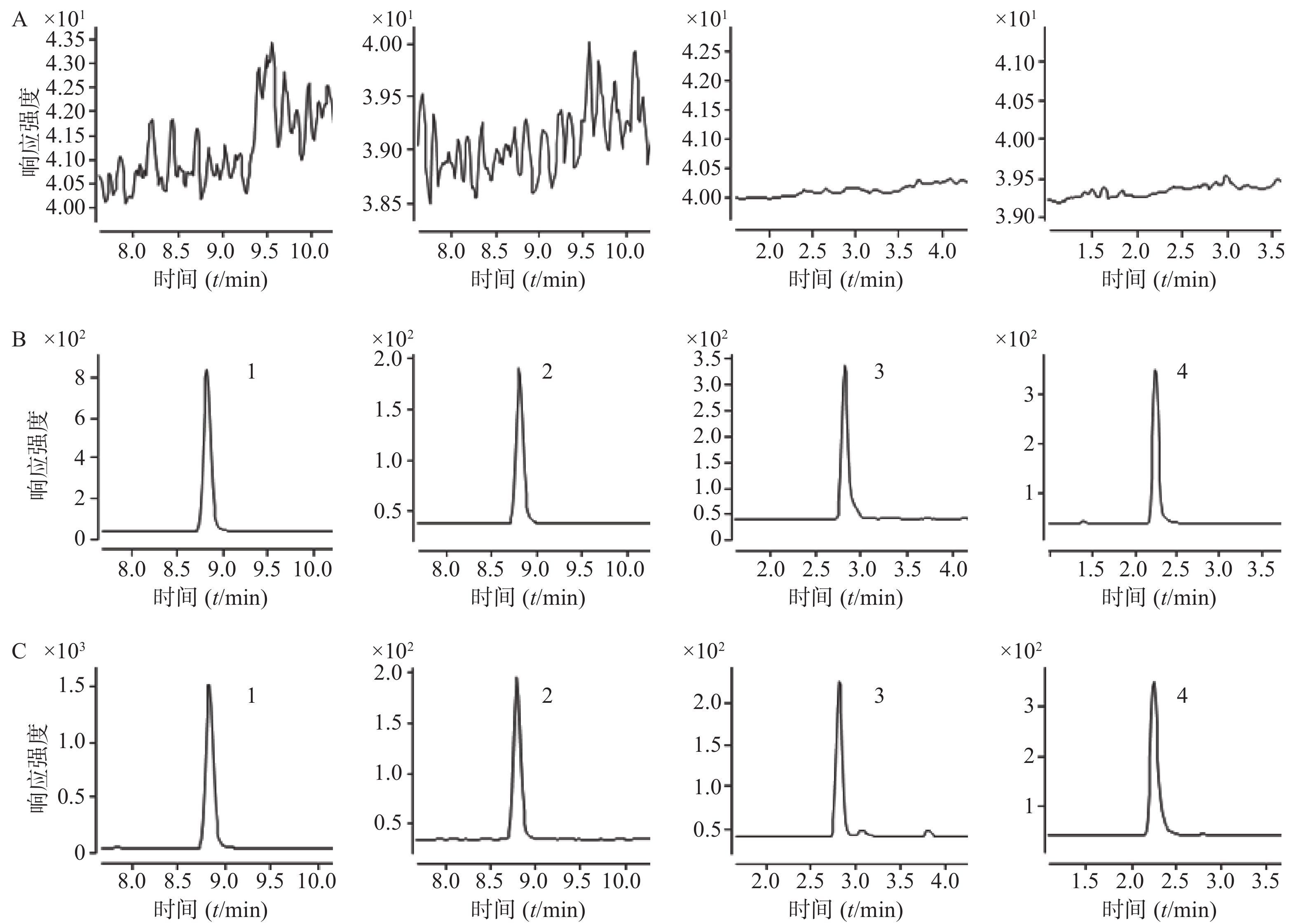
取空白血清200 µl置1.5 ml的EP管中,不加入内标溶液,按“2.4”项下操作进样分析,获得空白血清样品的色谱图;将一定浓度的标准溶液及内标加入空白血清中,依同法操作获得相应的色谱图;另取临床血清样品,依同法操作得色谱图。在该色谱质谱条件下得到的丙戊酸钠、万古霉素和内标物的色谱峰良好,无明显的杂质峰干扰,丙戊酸钠与丙戊酸钠-d6的保留时间均为8.81 min,万古霉素和卡那霉素B的保留时间分别为2.82、2.24 min。结果表明,空白血清中内源性物质不干扰丙戊酸钠和万古霉素的测定。色谱图见图1。
-
取空白血清180 µl,加入用乙腈-水(50:50)溶液将丙戊酸钠和万古霉素混合对照品储备液逐级稀释成相应的混合对照品系列溶液,按“2.4”项下操作法配制成血清中丙戊酸钠浓度分别为1、2、4、10、20、100和200 μg/ml,万古霉素质量浓度分别为 0.5、1、2、5、10、50和100 μg/ml的血清样品,进样分析。以待测物与内标质量浓度的比值为横坐标轴(X),以待测物与内标峰面积的比值为纵坐标轴(Y),绘制标准曲线。用权重系数为1/χ2计算线性回归方程。丙戊酸钠和万古霉素分别在1~200 μg/ml和0.5~100 μg/ml内具有良好的线性关系,标准曲线方程分别为Y=2.71X+0.003和Y=2.83X+0.19(r均>0.999)。丙戊酸钠定量下限为1.00 μg/ml,方法回收率为113.81%,RSD为1.64%;万古霉素定量下限为0.50 μg/ml,方法回收率为107.34%,RSD为4.20%。
-
按“3.2”项方法分别配制低、中、高3个浓度的丙戊酸钠(2、10和100 μg/ml)和万古霉素(1、5和50 μg/ml)的质控血清样品各15份,分为3批,每批5份,并与每批的标准曲线同时进行,按“2.4”项同法操作进样,求得本法的精密度和准确度。结果表明,低、中、高浓度的丙戊酸钠和万古霉素的批内、批间精密度RSD均小于15%,结果见表2。
分析物 浓度值(μg/ml) 准确度
(%)精密度RSD(%) 标示浓度 实测浓度 批内(n=5) 批间(n=15) 丙戊酸钠 2 2.06±0.09 102.78 0.87 5.05 10 9.27±0.32 92.67 0.21 3.71 100 99.55±1.99 99.54 0.23 2.15 万古霉素 1 1.07±0.09 106.87 7.54 9.93 5 5.03±0.13 100.69 1.07 2.86 50 50.64±2.49 101.28 3.54 5.32 -
按“3.2”项方法分别配制低、中、高3个浓度的丙戊酸钠(2、10和100 μg/ml)和万古霉素(1、5和50 μg/ml)的质控血清样品,按“2.4”项同法操作进样得峰面积A1。另取3份空白血清200 µl,先用200 µl乙腈沉淀蛋白,经14 000 r/min,5 min离心沉淀后,取180 µl该上清液,加入相应浓度的丙戊酸钠与万古霉素混合标准液和内标溶液各20 µl,得3个浓度的标准样品,进样得峰面积A2。再取3份180 µl重蒸去离子水,分别向其中加相应浓度的丙戊酸钠与万古霉素混合标准液和内标溶液各20 µl,得到3个浓度的标准样品,进样得峰面积A3。提取回收率即A1/A2×100%,基质效应即A2/A3×100%。结果表明,丙戊酸钠和万古霉素的基质影响均在85%~115%之间,RSD均小于15%,提取回收率平均值均达到70%以上,结果见表3。
分析物 标示浓度
(μg/ml)基质效应
(%)RSD
(%)提取回收率 RSD
(%)丙戊酸钠 2 106.60±2.95 2.77 78.23±5.39 6.89 10 92.63±2.69 2.91 73.76±3.58 4.85 100 92.82±1.59 1.72 75.83±3.53 4.66 万古霉素 1 96.90±1.88 1.94 71.62±7.99 11.16 5 99.07±1.79 1.80 73.08±4.99 6.82 50 99.19±0.84 0.85 71.23±4.87 6.84 -
按“3.2”项方法分别配制低、中、高 3个浓度的丙戊酸钠和万古霉素的质控血清样品,考察样品经室温放置24 h、4 ℃冷藏24 h、反复冻融3次以及-80 ℃冻存30 d的稳定性。结果表明,以上条件下3个浓度样品检测结果的RSD值均小于15%。结果见表4。
分析物 标示浓度
(μg/ml)25 ℃放置24 h 4 ℃放置24 h 反复冻融3次 -80 ℃冻存30 d 实测浓度(μg/ml) RSD(%) 实测浓度(μg/ml) RSD(%) 实测浓度(μg/ml) RSD(%) 实测浓度(μg/ml) RSD(%) 丙戊酸钠 2 2.16±0.14 6.55 1.86±4.73 7.38 1.77±0.18 10.23 1.83±0.12 6.34 10 10.71±0.38 3.56 10.18±0.37 4.32 8.97±0.69 7.72 9.49±0.64 6.79 100 104.30±1.50 1.44 107.40±2.70 2.48 91.63±10.81 11.79 88.58±4.91 5.55 万古霉素 1 1.20±0.07 5.62 1.04±0.05 9.11 0.96±0.13 13.37 0.84±0.08 9.39 5 5.43±0.31 5.63 5.03±0.25 6.51 4.78±0.43 9.06 4.59±0.34 7.51 50 52.72±2.70 5.12 46.26±0.78 7.85 44.69±3.69 8.26 44.57±3.22 7.23 -
近年来,有报道[5-8]使用HPLC-MS/MS法测定丙戊酸钠和万古霉素的血药浓度,但都是分别单独检测,对它们同时检测的HPLC-MS/MS法尚未见报道。目前HPLC-MS/MS法同时测定多种药物血药浓度的技术主要被用于测定同类药物。同类药物的理化性质相似,方法的建立更简单快速。但本实验测定的丙戊酸钠脂溶性强,而万古霉素则为水溶性药物,理化性质存在差异,方法建立难度较大。在血清样品的处理方法上,本实验考虑了包括液-液萃取法、固相萃取法及蛋白沉淀法多种处理方法,液-液萃取法及固相萃取法操作复杂,时间较长,本实验最终选择使用蛋白沉淀法。通过对比甲醇、乙腈、10%三氯乙酸、10%三氯乙酸-甲醇(50∶50)等沉淀剂的蛋白沉淀效果,确定乙腈作为有机蛋白沉淀剂效果最好,此方法稳定性好,同时也避免了引入新的杂质对实验结果产生影响。另外,样本单纯经乙腈沉淀蛋白后直接进样分析,会导致万古霉素提取回收率较低,因此我们在乙腈沉淀蛋白后尝试了按不同比例加入纯化水稀释,虽然万古霉素提取回收率得到了改善,但稳定性下降且峰形较差,杂峰较多。最后尝试比较了不同比例的甲醇-水溶液和乙腈-水溶液稀释法,确定了以乙腈-水(50∶50)溶液稀释乙腈沉淀蛋白后的提取液,不仅提取回收率得到了提高,且稳定性良好,可以满足临床样本检测的需要。在流动相的选择上,本实验选择了0.1%甲酸水溶液-乙腈作为流动相,与文献报道[5-8]使用的乙腈-20 mmol/L乙酸铵水溶液、0.1%甲酸水溶液-0.1%甲酸甲醇溶液等相比,该流动相配制简单,更适合用于丙戊酸钠和万古霉素2种药物的同时检测,峰形较好,无拖尾现象。
在临床上,丙戊酸钠和万古霉素均为监测其血药谷浓度,采血时间相同。采用本方法对丙戊酸钠和万古霉素同时进行血药浓度监测,不仅可以避免两次抽血给患者带来的不适,提高患者依从性,同时降低了检测成本,有利于节约医疗成本,减少患者医疗支出。
Determination of sodium valproate and vancomycin in human serum by HPLC-MS/MS
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202108087
- Received Date: 2021-08-18
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-04-18
- Available Online: 2022-07-27
- Publish Date: 2022-07-25
-
Key words:
- sodium valproate /
- vancomycin /
- blood concentration monitoring /
- HPLC-MS/MS
Abstract:
| Citation: | DUAN Jingjing, JI Guowen, GUO Zhijun, XU Feng. Determination of sodium valproate and vancomycin in human serum by HPLC-MS/MS[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2022, 40(4): 350-353, 378. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202108087 |









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: