-
心力衰竭是由心脏结构重塑和功能受损引起的临床症状,全球约有4千万人患有心力衰竭[1]。肺循环淤血是心力衰竭的主要症状之一,故易引发肺部感染。同时,肺部感染又增加了心脏负担。研究指出,感染是影响心力衰竭患者预后的危险因素[2]。但是在临床工作中,鉴别老年心力衰竭患者合并肺部感染较为困难,常常延误治疗,导致预后不佳,因此其早期诊断就显得尤为重要。目前,我们受益于一系列对心力衰竭患者具有预后价值的生物标志物,其中研究最多的是B型利钠肽(BNP),实践指南不仅推荐其用于心力衰竭的阳性诊断,还被用于预后和治疗监测[3]。而中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值(NLR) 检测可反映肺部感染的严重程度,对感染的临床鉴别诊断具有重要的意义[4]。并且NLR也被应用于心脑血管病等发病、严重程度及预后的预测[5]。因此,本研究将BNP和NLR指标联合,探讨其在老年心衰合并肺部感染病人中的预测价值。
-
收集2018年6月至2020年5月我院就诊的老年心力衰竭病人178例,回顾性分析其资料。纳入标准:①心力衰竭的诊断根据《中国心力衰竭诊断和治疗指南》[6]的诊断标准;②年龄≥60岁;③患者血液学检测指标以及重要的相关临床资料完整,患者知情同意。排除标准:①存在恶性肿瘤、自身免疫系统疾病、肝肾功能异常者;②存在严重感染者;③存在外科重大手术者。心力衰竭患者分为合并肺部感染组92例,无肺部感染组(对照组)86例。肺部感染的诊断根据《中国成人医院获得性肺炎与呼吸机相关性肺炎诊断和治疗指南(2018年版)》[7]的诊断标准。
-
收集病人的相关资料,有年龄、性别、患病史、卧床时间、心功能分级情况、吸烟史等信息。参考美国纽约心脏病学会的标准进行本研究纳入病人的心功能分级,分为 Ⅱ-Ⅳ级。
-
于病人就诊时抽取2管外周静脉血,各3 ml,分别用于血常规(中性粒细胞计数、白细胞计数、淋巴细胞计数等)和BNP检测。血常规用全自动血细胞分析仪(希森美康XT4000i)进行检测,BNP用免疫发光法于全自动化学发光仪(美国贝克曼库尔特公司DXI800)进行检测。中性粒细胞淋巴细胞比值(NLR)= 中性粒细胞计数(×109/L)/淋巴细胞计数(×109/L)。
-
数据的收集和整理均采用SPSS 24.0软件进行,数据符合正态分布,计量资料采用均数±标准差(
$ \bar{x} \pm s $ )表示,组间比较采用t检验。计数资料用构成比表示,采用$ {\chi ^2} $ 检验。采用Pearson相关分析变量间的相关性,采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线判断各指标预测心力衰竭合并肺部感染的价值。Logistic回归分析用来探讨心力衰竭合并肺部感染的影响因素。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。 -
对照组与感染组在年龄、高血压史、吸烟史、心功能分级、卧床时间、慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)史、中性粒细胞计数、BNP和NLR的差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);两组在性别构成、BMI、糖尿病史和淋巴细胞计数的比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具体见表1。
项目 对照组(n=86) 感染组(n=92) t/χ2 P 年龄(岁) 63.48±7.12 65.77±6.70 2.215 0.028 男性(%) 54(62.8) 64(69.6) 0.913 0.339 BMI(kg/m2) 22.57±2.97 22.81±2.93 0.547 0.585 高血压史(%) 50(58.1) 71(77.2) 7.398 0.007 糖尿病史(%) 21(24.4) 31(33.7) 1.850 0.174 吸烟史(%) 31(36.0) 58(63.0) 12.959 <0.001 心功能分级(%) Ⅱ 22(25.6) 11(12.0) 6.984 0.030 Ⅲ 39(45.3) 41(44.6) Ⅳ 25(29.1) 40(43.5) 卧床时间(%) ≤7 d 47(54.7) 33(35.9) 6.337 0.012 >7 d 39(45.3) 59(64.1) 慢性阻塞性肺疾病史 13(15.1) 27(29.3) 5.167 0.023 BNP(ng/L) 654.67±529.64 1072.45±674.87 4.573 <0.001 中性粒细胞计数
(×109/L)3.07±1.09 4.76±1.03 10.635 <0.001 淋巴细胞计数
(×109/L)1.36±0.83 1.15±0.77 1.751 0.082 NLR 2.26±1.10 4.14±1.75 8.539 <0.001 -
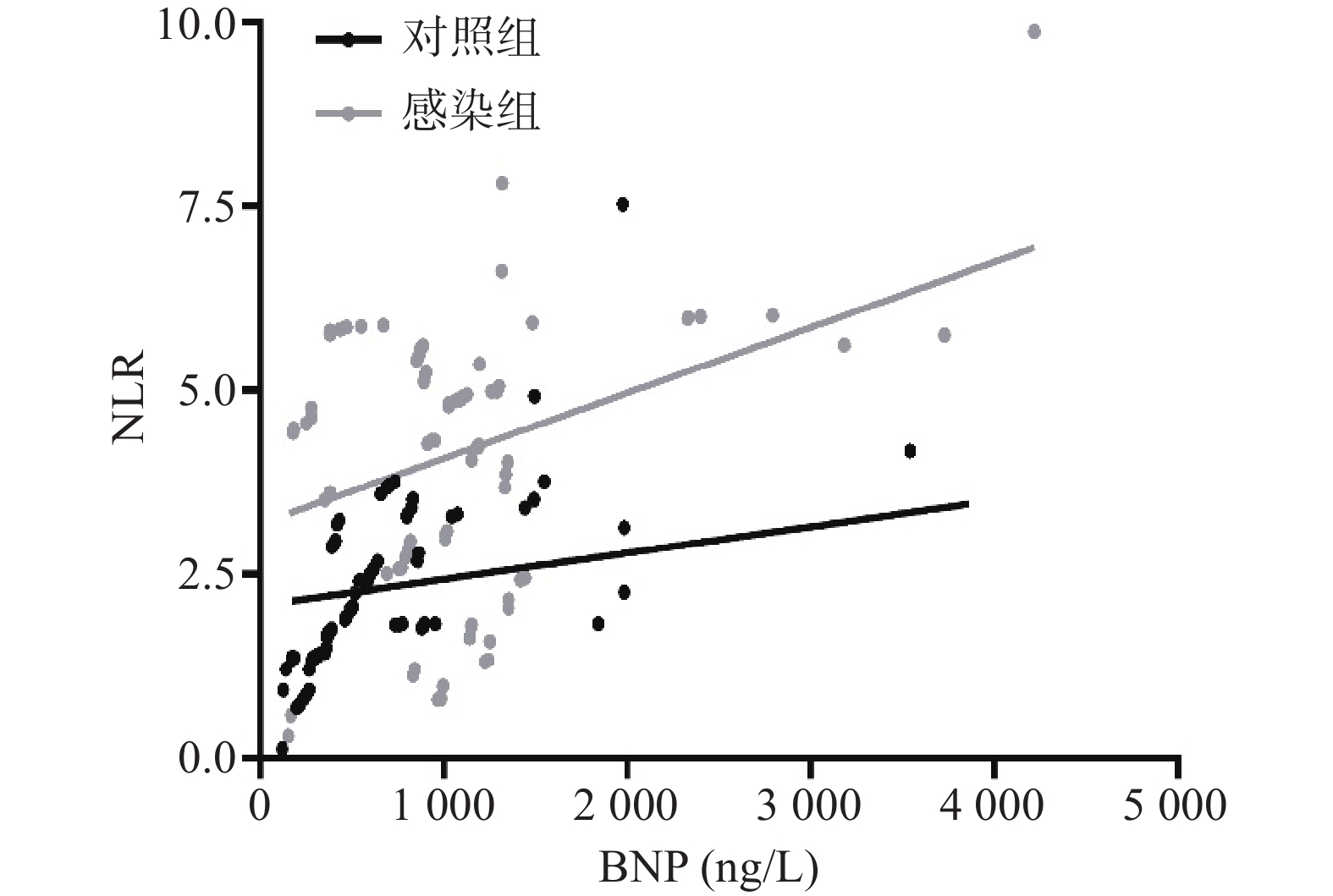
结果显示,心力衰竭合并肺部感染患者中BNP水平与NLR水平呈正相关(r=0.400, P<0.001)。具体见图1。
-
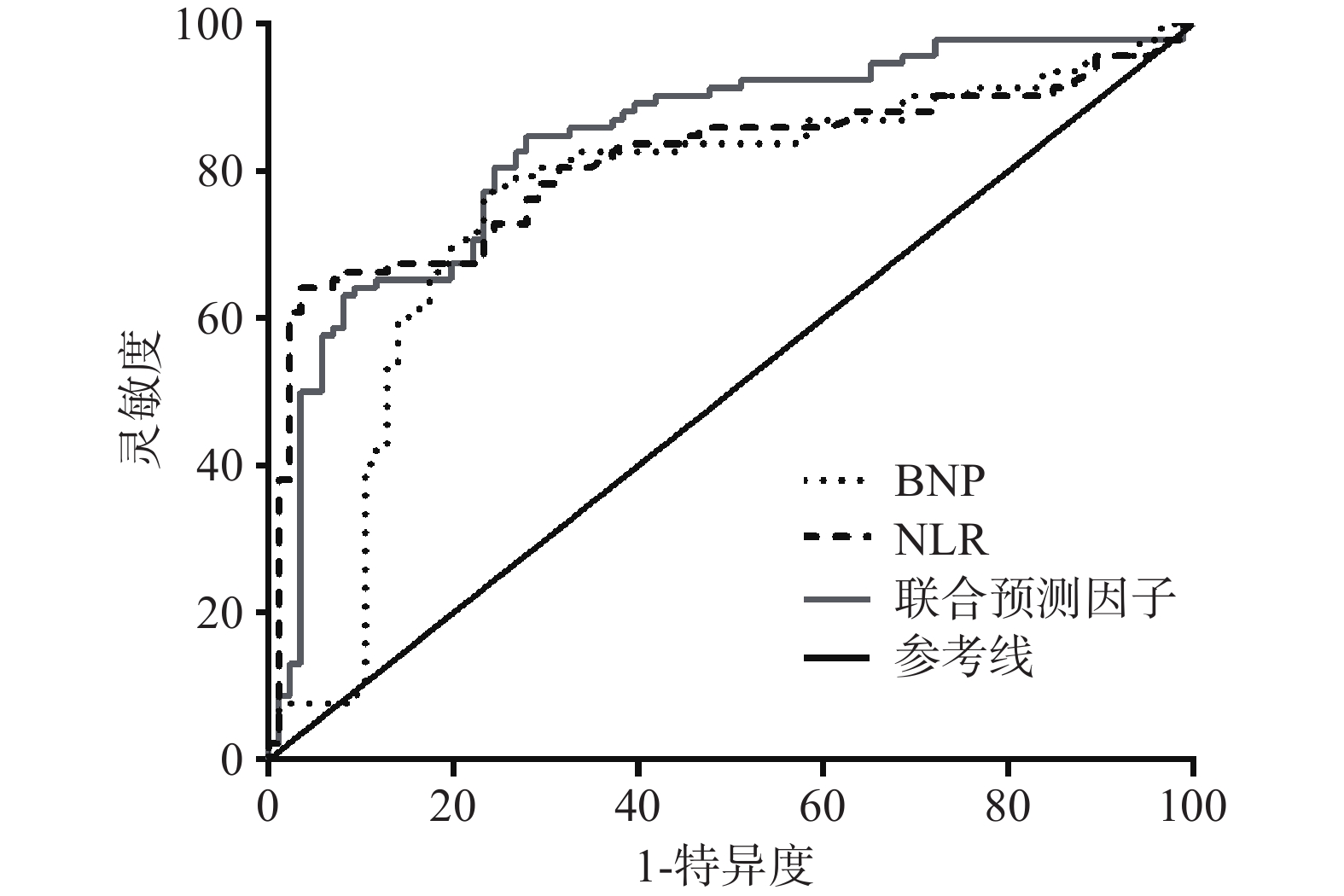
结果显示,NLR、BNP和二者联合对预测心力衰竭患者伴发肺部感染的 ROC的曲线下面积分别为0.810(95% CI 0.743~0.877)、0.756(95% CI 0.680~0.832)、0.838(95% CI 0.777~0.898),P<0.001;灵敏度分别为0.641、0.772和0.826,特异度分别为0.965、0.767、0.733,见图2。其中,NLR、BNP的最佳诊断界值分别为3.81和804.5 ng/L,见图1。
-
以是否伴发肺部感染为因变量(0=对照组,1=感染组),以单因素分析中P<0.1的变量纳入多因素分析中,纳入连续性变量:年龄和分类变量:高血压史、吸烟史、慢性阻塞性肺疾病史、卧床时间以及NLR(低组≤3.81,高组>3.81)、BNP(低组≤804.5 ng/L,高组>804.5 ng/L)、心功能分级为自变量,进行多因素Logistic回归分析。结果显示, 吸烟史、NLR和BNP高组、慢性阻塞性肺疾病史是心力衰竭患者伴发肺部感染的危险因素,具体见表2。
自变量 B值 SE waldχ2 P值 OR值 95%CI 年龄 0.149 0.094 2.513 0.113 1.161 0.965~1.395 高血压史 −0.230 0.550 0.121 0.727 0.793 0.218~2.895 吸烟史 1.005 0.565 3.167 0.075 2.733 0.903~8.272 心功能分级 0.531 0.322 2.719 0.099 1.701 0.905~3.196 卧床时间 0.056 0.549 0.010 0.918 1.058 0.360~3.105 COPD 1.108 0.636 3.030 0.082 3.027 0.870~10.537 NLR分组 2.029 0.454 19.952 <0.001 7.606 3.123~18.526 BNP分组 1.450 0.475 9.334 0.002 4.264 1.682~10.811 常量 −4.973 1.654 9.040 0.003 -
心力衰竭是一种典型的老年心血管综合征,由年龄相关的心血管疾病以及心血管结构和功能改变引起。心力衰竭和肺部感染是两个相互关联、不断演变共存的过程,二者之间相互促进[8]。肺部感染是诱发患者出现心力衰竭和加重常见因素之一;另一方面,心力衰竭患者容易出现肺部淤血,导致肺实质损伤,肺部抵抗力下降,容易滋生细菌,形成恶性循环。心力衰竭和心力衰竭合并感染患者均有气促、胸闷、呼吸困难、下肢水肿等临床表现,二者无特异性表现,且肺水肿状态下明确区分二者的难度较大,使得心力衰竭合并感染患者无法及时被发现,影响患者治疗效果。因此,采用一种简单快速的方法发现心力衰竭合并感染患者意义重大。
近年来,NLR 作为一个炎症生物标志物不仅在感染性疾病中水平升高,同时在心血管疾病中也被发现有不同水平的变化。NLR在临床中是比较容易得到的简单的检查数据,并能客观反映两者不同免疫活性的综合指标。有研究证实在心血管疾病中,NLR预测能力高于白细胞计数或者中性粒细胞计数的单独预测能力[9]。其不仅可作为一种危险分层指数,在预测心血管疾病患者死亡率方面,NLR升高是心力衰竭患者短期和长期死亡率不良预后的标志物[10, 11]。另一方面,NLR在心血管疾病合并肺部感染方面也具有一定的预测价值[12]。
BNP是近年用于心力衰竭患者预后的可靠生物标志物,实践指南不仅推荐其用于心力衰竭的阳性诊断,还被用于预后和治疗监测[3]。BNP是一种具有生物活性的由32个氨基酸组成的神经激素,属于结构相关的利钠肽(NPs)家族,达到排钠利尿以及扩血管的效果[13]。正常情况下,BNP主要源于心房组织,循环水平较低,而在心室容积改变、心肌缺血缺氧等病理条件下,由心室肌细胞分泌,其水平会明显升高[14]。王大强等[15]发现血浆BNP是心力衰竭合并肺部感染患者敏感性指标。
在本研究中,我们发现NLR和BNP在心力衰竭合并肺部感染患者体内的水平都显著高于单纯心力衰竭的患者,提示 NLR和BNP水平与心力衰竭患者是否合并肺部感染密切相关。研究显示,在心力衰竭患者中NLR和BNP关系密切,本研究相关性分析显示,二者水平呈现正相关,与之前的研究结果一致[16],提示NLR、BNP可能共同参与心力衰竭合并肺部感染。本研究采用ROC曲线计算各指标的诊断效能,结果发现NLR 联合BNP检测在心力衰竭合并肺部感染ROC曲线下面积高于NLR和BNP单独检测的结果,表明NLR 联合BNP可有效检测心力衰竭患者是否并发感染,对判断疾病有很好的临床应用价值。研究最后以ROC曲线截断值为端点,将NLR、BNP分为高NLR组、低NLR组、高BNP组、低BNP组,采用多因素分析发现,高NLR、高BNP均为心力衰竭合并肺部感染的危险因素。其原因可能是肺部感染往往由于呼吸道受到病原微生物侵染而发生感染,NLR由中性粒细胞计数和淋巴细胞计数两个检查指标得到,中性粒细胞计数一定程度上可反映非特异性炎症的激活程度,当机体受到致病因子侵犯时,中心粒细胞增多而增加蛋白水解酶的释放以帮助机体清除致病因子;而淋巴细胞则可反映机体免疫状况,当淋巴细胞计数下降时,表明机体免疫功能可能受损,产生应激[17]。同时也有研究显示,在重症肺部感染患者中血液中BNP浓度显著升高[18]。可能与感染发生导致的肺部通气异常,循环阻力增加,心脏负荷进一步升高,从而释放更多 BNP有关。因此,联合NLR和BNP预测心力衰竭合并肺部感染效果较好。
综上所述,NLR和BNP联合检测对老年病人的心力衰竭合并肺部感染有一定的预测价值,可用于临床中患者预后观察。
Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio combined with BNP in elderly patients with heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202112010
- Received Date: 2021-12-04
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-08-23
- Available Online: 2022-09-29
- Publish Date: 2022-09-25
-
Key words:
- heart failure /
- pulmonary infection /
- NLR /
- BNP
Abstract:
| Citation: | ZHANG Jie, CHAO Shengwu, YANG Jishun. Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio combined with BNP in elderly patients with heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2022, 40(5): 469-472. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202112010 |








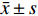
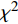
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: