-
组织蛋白酶K(CTSK) 属于半胱氨酸蛋白酶,是细胞内重要的溶酶体酶,在很多组织中有表达,如肺、脑、皮肤、骨骼和甲状腺等。CTSK在体内主要发挥降解骨胶原蛋白、弹性纤维蛋白、甲状腺球蛋白及细胞外基质的作用,与人类多种疾病密切相关,如肿瘤[1]、骨疾病、心血管疾病和肺纤维化等[2]。CTSK最早发现在破骨细胞特异性高表达,主要发挥降解骨基质中含量达95%的Ⅰ型胶原[2]。基于生物化学和结构分析研究发现CTSK与黏多糖(GAGs)可形成一种复合物,如硫酸软骨素(chondroitin-4-sulfate, C4S或CSA),且只有这种复合物形成下才能更好发挥降解胶原作用[3]。
二至丸是治疗肾阴虚症的经典名方,由女贞子和墨旱莲组成,经考证出自明代吴曼辑所著的《扶寿精方》,收载于2020版《中国药典》,具补益肝肾,滋阴止血功效[4]。药理研究发现二至丸具有保肝降酶、增强免疫调节、改善血液系统功能、抗肿瘤、抗骨质疏松、抗衰老、抗氧化、抗变态反应性炎症和植物雌激素样等作用[5]。临床报道,二至丸常用于治疗骨质疏松[6-8],药理发现二至丸显著降低去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠血清中CTSK水平[5]。我们前期研究发现墨旱莲的正丁醇提取部位和活性成分墨旱莲皂苷IX能显著抑制CTSK的胶原降解活性[9]。因此,二至丸很有可能存在抑制组织蛋白酶K的活性成分,故有可能从中筛选组织蛋白酶K抑制剂。本研究采用荧光偏振法考察CTSK与硫酸软骨素A(CSA)复合物形成活性,荧光光度法考察CTSK与合成荧光底物benzyloxycarbonyl-Phe-Arg-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin (Z-FR-MCA)结合活性,十二烷基硫酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺(SDS-PAGE)凝胶电泳法考察CTSK降解生理底物胶原蛋白和明胶的活性,以期从二至丸不同提取部位和活性成分中筛查具有抑制CTSK活性的抑制剂,最终阐明二至丸抑制CTSK酶活性的物质基础。
-
墨旱莲、酒女贞子药材购自上海华宇药业有限公司, 经海军军医大学生药学教研室韩婷教授鉴定墨旱莲为菊科植物鳢肠 Ecliptaprostrata L. 的干燥地上部分,女贞子为木犀科植物女贞Ligustrum lucidum Ait.的干燥成熟果实。其活性成分异毛蕊花糖苷、橄榄苦苷、蟛蜞菊内酯、熊果酸、齐暾果酸、蒙花苷、槲皮苷、木樨草苷、异去甲基蟛蜞菊内酯、松果菊苷、特女贞苷、红景天苷、女贞苷、女贞苷G13等24种标准品均购自成都瑞芬思生物科技有限公司。
Z-FR-MCA购自日本WAKO公司;E-64 (L-3-carboxy-trans-2-3-epoxypropionyl-leucylamido-(4guanidino)-butane)和硫酸软骨素A (CSA)购自美国Sigma公司;荧光标记硫酸软骨素A(CSA*)购自日本株式会社Cosmo Bio公司;人I型胶原蛋白(Human collagen I)购自美国Affymetrix公司,牛不溶性I型胶原蛋白(Bovine type I insoluble collagen) 购自生工生物工程(上海)公司。
-
墨旱莲500 g,加入10倍量水(W/V),煎煮2次,每次1 h,合并提取液,煎煮浓缩,冷冻干燥,粉碎得墨旱莲水提取物。酒女贞子按照2020版药典二至丸制备方法,粉碎过80目筛。将酒女贞子粉末500 g与墨旱莲水提取物粉末混匀,用10倍量正丁醇(W/V)回流提取2次,每次1 h,过滤,合并滤液,旋转蒸发浓缩后,冷冻干燥得正丁醇部位提取物。滤渣挥干,按照正丁醇方法依次分别用石油醚、二氯甲烷和乙酸乙酯溶液对滤渣进行萃取,冷冻干燥得到二至丸的正丁醇、石油醚、二氯甲烷、乙酸乙酯提取物。
研究报道二至丸的活性成分,主要包括墨旱莲三萜皂苷类和女贞子环烯醚萜苷类成分,及一些黄酮类、苯乙醇苷类等成分[10-12]。本研究30个成分中墨旱莲皂苷 (Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅴ、Ⅶ、Ⅸ) 和刺囊酸是由墨旱莲正丁醇部位经凝胶柱层析分离得到[9],墨旱莲中蟛蜞菊内酯、异去甲基蟛蜞菊内酯、木樨草素、槲皮苷、木樨草苷和女贞子中异毛蕊花糖苷、橄榄苦苷、熊果酸、齐暾果酸、木樨草素、槲皮苷、木樨草苷、松果菊苷、特女贞苷、红景天苷、女贞苷、女贞苷G13、3-O-乙酰基齐墩果酸、19α-羟基熊果酸、大黄素甲醚、β-谷甾醇、3, 4-二羟基苯乙醇、对羟基苯乙醇等成分为购买标准品。
-
二至丸不同提取部位和化合物用DMSO溶解分别配置40 mg/ml和10 mmol/L的储备溶液,并在分析之前用100 mmol/L醋酸钠缓冲液(pH5.5,包含2.5 mmol/L DTT和2.5 mmol/L EDTA) 分别稀释至浓度为25 µg/ml和 25 µmol/ml (DMSO低于1%),加入黑色荧光96孔板,最终反应容量为0.2 ml。加入终浓度为5 nmol/L的CTSK孵育5 min,加入Z-FR-MCA底物(终浓度1 mmol/L),孵育30 s,实时检测5 min荧光生成斜率(slope)值(发散光波长460 nm,吸收光波长355 nm)。所有测量均使用荧光仪Tecan spark(美国)在96孔板中进行,单孔体积为200 µl。实验设阴性对照组(无抑制剂),阳性对照组(E-64,活性位点抑制剂)。计算公式:抑制率(%)= 100−(1−Vi /V0)。Vi和V0分别表示存在和不存在抑制剂情况下的荧光信号。
-
将100 µg/ml不同部位或25 µmol/ml有效成分与200 nmol/L的CTSK在含有2.5 mmol/L DTT和EDTA的100 mmol/L醋酸钠缓冲液(pH 5.5)中,混匀放置5 min,然后添加20 nmol/L CSA*,混匀放置15 min,室温下实时检测5 min荧光生成斜率(slope)值(发散光波长485 nm,吸收光波长520 nm),所有测量均使用荧光仪Tecan spark(美国)在黑色荧光96孔板中进行,总体积为100 µl。设置不使用抑制剂(阴性对照)和300 mmol/L NaCl(阳性对照)。CTSK和FP之间的关系使用抑制百分比进行分析,计算公式:抑制率(%)=100− [(100×(FPCTSK/抑制剂/CSA*−FP CSA*)/(FPCTSK/CSA*−FP CSA*)]其中,FPCTSK/抑制剂/CSA*和FPCTSK/CSA*分别是在存在和不存在抑制剂的情况下测定荧光信号。
-
人I型胶原0.6 mg/ml溶解于100 mmol/L醋酸钠缓冲液(pH5.5,包含2.5 mmol/L DTT和2.5 mmol/L EDTA)中,依次加入CTSK (最终浓度400 nmol/L)、CSA (最终浓度200 nmol/L) 和400 μg/ml二至丸不同提取部位或不同浓度潜在抑制剂(100、80、60、40、20、10 μmol/L),加入到含有I型胶原蛋白的缓冲液,单孔体积50 μl,混匀,28 ℃孵育4 h。取出后加入1μl的 100 μmol/L E64终止反应。采用10%的SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳分离,考马斯亮蓝染色20 min,用乙酸-甲醇(4∶1)脱色。I型胶原的α1条带的灰度用ImageJ 2软件进行定量分析。
-
称取1 mg不溶性牛I型胶原蛋白置于1.5 ml EP管中,加入1 μmol/L CTSK酶和25 μmol/L潜在抑制剂于40 μl缓冲液中(100 mmol/L醋酸盐缓冲液,pH值5.5,含有2.5 mmol/L DTT和2.5 mmol/L EDTA)。采用Z-FR-MCA底物结合活性方法在T0 min测定CTSK活性,在37 ℃下孵育30 min后,检测T30 min时的CTSK活性。从中取出40 μl上清液,添加2.0 μl NaCl(最终300 mmol/L),然后再次检查CTSK活性,记录为T30salt min。计算公式:结合率(%)=[1−(T0 min−T30salt min)/(T0 min−T30 min)]×100%。
-
用Discovery studio 2016软件中的libdock分子对接方法考察活性成分和组织蛋白酶K(1ATK) 蛋白进行刚性对接。利用LibDock得分作为表征化合物与活性位点结合的核心指标。LibDock得分分数越高,小分子与受体结合的活性越高。
-
每组实验重复3次。采用SPSS软件经ANOVA方差分析检验,若有显著性差异(α=0.05),再采用Student's t检验进行两组比较,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
-
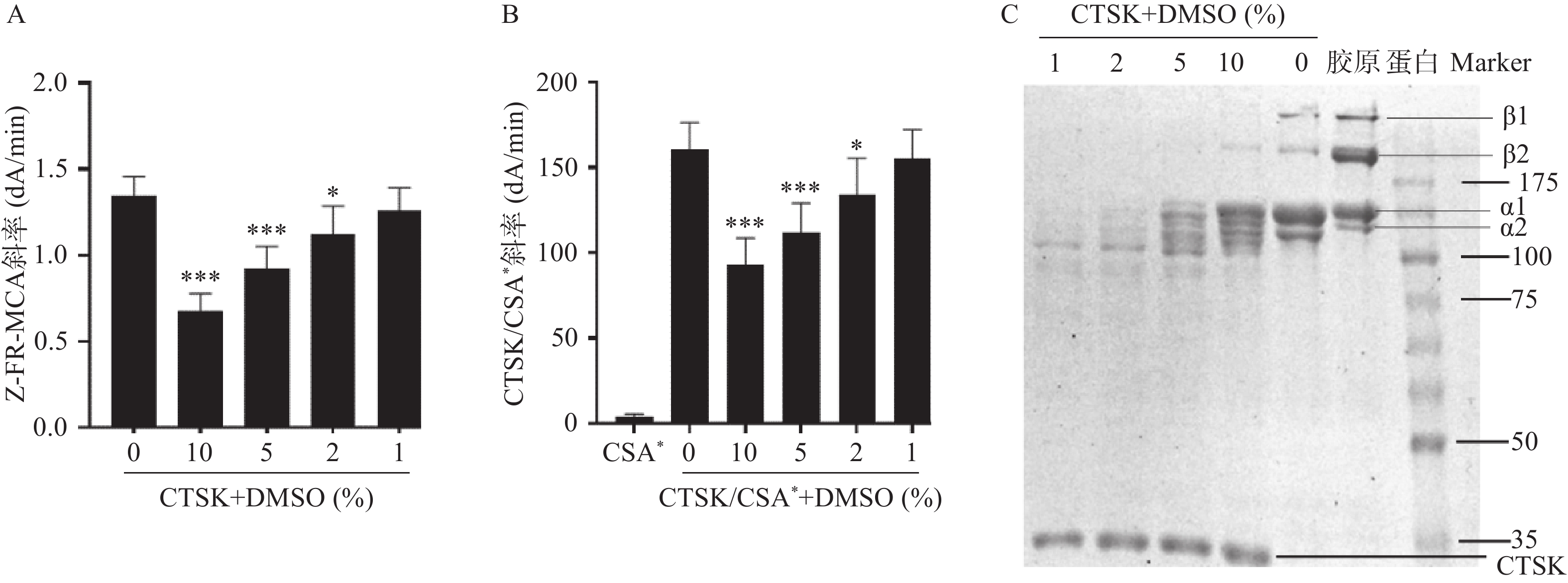
本研究考察了DMSO浓度(10%、5%、2%和1%)对CTSK的Z-FR-MCA活性和CTSK/CSA*复合物形成活性高通量筛查方法,及SDS-PAGE胶原降解活性筛选方法的影响。结果发现,10%、5%、2%的DMSO显著抑制CTSK的Z-FR-MCA底物结合(图1A)和CTSK/CSA*复合物形成活性(图1B)。10%的DMSO显著抑制CTSK的胶原降解,1%和2%的DMSO对胶原降解无明显抑制作用。因此,本研究筛查二至丸的抑制CTSK活性方法将DMSO浓度控制在1%以下。
-
对二至丸的不同提取部位(正丁醇、石油醚、乙酸乙酯和二氯甲烷) 进行了抑制CTSK活性筛选,其中Z-FR-MCA底物结合实验结果显示,二至丸的石油醚部位抑制作用明显,为96.3%,正丁醇、乙酸乙酯、二氯甲烷提取部位抑制率分别为26.1%、50.8%和43.5%(见图2A)。二至丸正丁醇、石油醚、乙酸乙酯和二氯甲烷提取部位提取物对CTSK/CSA*复合物形成的抑制率分别为99.6%、52.0%、94.8%和59.8%(见图2B),胶原降解活性结果显示二至丸的正丁醇部位抑制作用最明显,达到100%,石油醚提取部位抑制作用为58%,二氯甲烷和乙酸乙酯提取部位作用也不明显,分别为33.1%和6.7%(见图2C和2D)。
-
本研究对30种二至丸中的活性成分进行了体外筛选,结果发现25 μmol/L的墨旱莲皂苷Ⅸ、异毛蕊花糖苷、蟛蜞菊内酯、木樨草素、槲皮素、松果菊苷、女贞苷、特女贞苷、3,4-二羟基苯乙醇和对羟基苯乙醇抑制CTSK/CSA*复合物形成的抑制率超过50%,表儿茶素没食子酸酯为51.2%。而在25 μmol/L时,仅有齐墩果酸、3-0-乙酰基齐墩果酸、19α-羟基熊果酸、3,4-二羟基苯乙醇、对羟基苯乙醇对CTSK与Z-FR-MCA结合活性有超过50%的抑制率,熊果酸为47.1%抑制率。采用libdock技术发现仅有3,4-二羟基苯乙醇和对羟基苯乙醇与CTSK活性位点对接有得分。因此,这些超过50%抑制率的二至丸活性成分被认为具有潜在抑制胶原降解活性。 针对以上12种活性成分,进行胶原降解抑制实验,结果显示在100 μmol/L时,墨旱莲皂苷Ⅸ,对胶原降解抑制率达70.3%,女贞苷53.2%,蟛蜞菊内酯达50.1%和表儿茶素没食子酸酯为60.2%。异毛蕊花糖苷、木樨草素、槲皮素、松果菊苷、特女贞苷、熊果酸、齐墩果酸、3-O-乙酰基齐墩果酸、19α-羟基熊果酸、3,4-二羟基苯乙醇、对羟基苯乙醇均显示无抑制胶原降解活性(表1)。
化合物成分 英文名称 CTSK/CSA*
抑制率(%)ZFR-MCA
抑制率(%)Libdock
得分胶原降解
抑制率(%)来源 墨旱莲皂苷Ⅴ eclalbasaponin Ⅴ 0 0 / M 墨旱莲皂苷Ⅰ eclalbasaponin Ⅰ 0 0 / M 墨旱莲皂苷Ⅱ eclalbasaponin Ⅱ 0 0 / M 墨旱莲皂苷Ⅶ eclalbasaponin Ⅶ 11.3±1.3 0 / M 墨旱莲皂苷Ⅸ eclalbasaponinⅨ 88.6±9.2 0 / 70.3 M 红景天苷 Salidroside 27.8±3.1 0 / N 异毛蕊花糖苷 Isoacteoside 65.3±4.7 0 / / N 橄榄苦苷 Oleuroprin 35.9±2.4 0 / N 蟛蜞菊内酯 Wedelolactone 58.7±5.8 2.81 / 50.1 M 熊果酸 Ursolic Acid 0 59.7 / N 齐暾果酸 Oleanic acid 0 47.1 / N 刺囊酸 Echinocystic acid 0 0 / M 木樨草素 Luteolin 62.1±8.6 0 / M、N 蒙花苷 linarin 37.2±3.1 0 / M 槲皮素 quercitrin 68.5±5.9 0 / M、N 木樨草苷 galuteolin 33.2±3.7 0 / M、N 异去甲基蟛蜞菊内酯 Isowedelolactone 0 7.0 / M 松果菊苷 Echinacoside 55.9±6.5 9.7 / N 女贞苷 Nuezhenoside 51.2±4.7 0.10 / 53.2 N 特女贞苷 Specneuzhenide 58.6±6.4 17.9 / 49.7 N 女贞苷G13 Nuezhenoside G13 23.7±2.4 0.16 / N 3-O-乙酰基齐墩果酸 3-O-acetyl oleanolic acid 0 66.7 / N 19α-羟基熊果酸 19α-OH Ursolic Acid 0 53.2 / N 儿茶素 catechin 11.3 15.3 / M 表儿茶素 L-Epicatechin 12.7 18.7 / M 表儿茶素没食子酸酯 (-)-Epicatechin gallate 51.2±5.4 10.5 / 60.2 M 大黄素甲醚 Emodin monomethyl ether 19.8±1.7 0 / N β-谷甾醇 β- Sitosterol 0 0 / N 3’ 4-二羟基苯乙醇 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl 70.3±8.4 83.2 76.4848 N 对羟基苯乙醇 p-hydroxyphenethyl 62.4±6.7 79.5 73.9225 N 注:M:墨旱莲;N:女贞子。 -
不溶性胶原、抑制剂和CTSK共培养15 min,通过检测培养液中剩余CTSK的Z-FR-MCA活性,来验证潜在CTSK抑制剂在体外抑制与CTSK的结合实验,结果显示100 μmol/L的墨旱莲皂苷IX(ES-IX)、表儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG)、女贞苷(NZG)和蟛蜞菊内酯(WED)抑制率分别为54.8%、64.1%、36.4%和51.4% (图3)。
-
CTSK抑制剂的高通量筛选方法,多采用合成底物Z-FR-MCA结合活性来筛选,其原理是CTSK可裂解底物端FR-MCA基团, 释放游离的MCA 发色荧光基团, 通过抑制剂引起荧光信号变化差异来检测评价抑制剂活性。基于骨胶原降解需要CTSK与CSA结合发挥作用,采用荧光标记CSA*,形成CTSK/CSA*复合物,其原理为抑制剂与CTSK酶结合形成CTSK/抑制剂/CSA*复合物,导致荧光偏振信号差异,评价抑制剂与CTSK结合活性,可快速、灵敏和准确的判断化合物是否与CTSK存在相互作用。SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳法是常用蛋白质分类技术,将胶原蛋白及其降解产物按照分子量大小迁移,考马斯染色溶液染色,对α1胶原蛋白条带定量,计算胶原蛋白降解率。
二至丸的正丁醇提取部位抑制CTSK/CSA*复合物形成和胶原降解活性最强,超过95%,但对CTSK的Z-FR-MCA抑制率只有26%。Z-FR-MCA作为CTSK活性位点的合成底物,活性成分对Z-FR-MCA抑制率越高,证明对CTSK的活性位点抑制效率越高。基于Bromme教授提出的非活性位点抑制剂的概念[13],活性成分具有显著的抑制胶原降解活性,但对活性位点Z-FR-MCA底物无抑制活性,可称为非活性位点 (exosite) 抑制剂。结果发现,二至丸的正丁醇提取部位可显著抑制胶原降解,而对Z-FR-MCA无显著影响,证明正丁醇提取部位可能存在抑制 CTSK胶原降解活性的活性成分, 而不影响CTSK 活性位点的生理活性。二至丸的正丁醇提取部位的化学成分主要为墨旱莲皂苷类成分和女贞子三萜酸类成分,其中墨旱莲皂苷Ⅸ(ES-Ⅸ)、表儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG)、女贞苷(NZS)和蟛蜞菊内酯(WED)可能是潜在的CTSK非活性位点抑制剂。熊果酸和齐墩果酸具有较强的Z-FR-MCA活性,表明可作用CTSK活性位点,而女贞子乙醇提取物、熊果酸、齐墩果酸和墨旱莲的蟛蜞菊内脂均报道显著抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收活性和CTSK的mRNA表达[14-15],可能通过在细胞内直接作用CTSK酶,使其失去活性。
CTSK是抗骨质疏松药物研发的关键靶标,有报道,中草药尤其是补肾中药含有丰富的治疗骨质疏松的活性物质,但不清楚这些化合物是否能够抑制CTSK活性,或者特异性抑制胶原酶的活性。除了胶原降解活性,CTSK在甲状腺细胞中发挥降解甲状腺球蛋白,释放甲状腺激素[16],在成纤维细胞中发挥降解纤维蛋白的功能[17]。二至丸中有抑制CTSK活性的化合物,可进一步考察其对甲状腺球蛋白降解和纤维蛋白降解的作用活性,为中医药开发CTSK抑制剂提供新的思路。
Study on material basis of cathepsin K targeted inhibitor in Erzhi Wan
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202202008
- Received Date: 2022-02-09
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-11-05
- Available Online: 2023-07-14
- Publish Date: 2023-02-25
-
Key words:
- Erzhi Wan /
- osteoporosis /
- cathepsin K /
- active fraction /
- potential inhibitor
Abstract:
| Citation: | JIANG Yiping, JIN Yue, ZHANG Zhiwei, XIA Tianshuang, XU Jiale, XUE Liming. Study on material basis of cathepsin K targeted inhibitor in Erzhi Wan[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2023, 41(2): 91-96, 118. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202202008 |










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: