-
随着我国经济的发展以及居民生活水平的提高,越来越多的人来到高原生活、工作和旅游,但由于高原地区氧分压较低,高原病的发病率呈现逐年上升的趋势[1]。高原脑水肿(HACE)是高原病发生发展过程中最为严重的阶段,其临床表现为头痛、协调丧失、虚弱、意识水平降低[2],并对机体造成不可逆的损伤。7-羟乙基白杨素(7-hydroxyethyl chrysin,7-HEC)是课题组前期筛选发现并合成的具有自主知识产权的抗高原缺氧化合物[3],研究发现[4-5],其对脑缺血再灌注大鼠和模拟高原低压性缺氧致脑组织损伤大鼠均具有明显的保护作用,并能够减轻低压低氧诱导的认知功能损伤[6],在抗高原缺氧方面表现出优异的活性与前景。因此,本文主要从7-HEC对高原脑水肿的可能作用机制出发,探究其与自噬、周期、凋亡等通路之间的关系,为防治高原脑水肿的可能作用机制奠定基础。
-
27只SPF级雄性Wistar大鼠(体重180~200 g),购自联勤保障部队第九四〇医院动物实验科,合格证号:SCXX(军)2012-0029,动物伦理委员会编号:2021KYLL173。
7-HEC由实验室景林临副教授自行合成;MDA、SOD试剂盒(南京建成生物工程研究所);CDK2、CDK6、CyclinD1、CyclinE2、PARP、Bax、Bcl-2、P62、LC3B抗体(英国Abcom公司);BCA蛋白试剂盒(Solarbio公司);脱脂奶粉(美国BD公司);Western Bright TM ECL(美国Advansta)。
IEC-Micromax高速离心机(美国ThermoElectron公司);Tissuelyser快速研磨仪(上海净信科技公司);BP210S电子天平(赛多利斯有限公司);HP-8453紫外分光光度计(美国惠普公司);SpectraMax i3全自动荧光酶标仪(美国Molecular Devices公司);FLYDWC20-ⅡA大型低压低氧动物实验舱(中航贵州风雷航空军械有限责任公司)。
-
将27只SPF级雄性Wistar大鼠适应性饲喂3 d后,随机分为3组,正常对照组、缺氧模型组、7-HEC给药组。给药组连续灌胃7-HEC(350 mg/kg)7 d,对照组和模型组给予等量灭菌注射用水。第四天,模型组和给药组放入大型低压低氧动物实验舱中,以10 m/s速度减压上升至相当于海拔6000 m处,缺氧处理3 d后处死,取脑组织。缺氧处理期间,氧舱温度:8:00~20:00,12 ℃,20:00~次日8:00,2 ℃;动物自由摄食及饮水;给药组继续灌胃给药。
-
每组分别取6只大鼠脑组织标本,准确称重后,按质量(g)∶体积(ml)=1∶9 加入生理盐水制成10 %组织匀浆,采用WST-1法检测SOD活性、采用硫代巴比妥酸法检测MDA含量,以上操作均按试剂盒说明书进行。
-
每组选取3只大鼠脑组织,称重后加入9倍量高效裂解液,使用组织研磨仪进行组织匀浆,于冰上裂解30 min,低温离心后吸取上清匀浆液10 μl,BCA法测蛋白含量,剩余上清与4×上样缓冲液按体积3∶1比例混匀,封口膜封口,95 ℃煮沸10 min进行蛋白变性,取等量蛋白样品上样,采用 SDS-PAGE 进行分离,电泳完成后将蛋白转至PVDF膜上,含5 %脱脂牛奶室温封闭2 h,一抗4 ℃孵育过夜。用TBST缓冲液漂洗4次,每次10 min。加入二抗,室温孵育2 h,TBST缓冲液洗涤PVDF膜4次,每次10 min。配制ECL发光液,按照A液和B液1∶1进行配制,涂抹发光液,放入ChemiDoc MP Imaging System全能型成像系统进行曝光。用Image J软件对蛋白条带进行灰度值分析。
-
实验结果以(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )表示,采用 SPSS 21.0 软件进行数据分析,选用单因素方差分析法进行组间变量分析,LSD-t 法比较组间差异。以P<0.05表示有显著性差异,以P<0.01表示有极显著性差异。 -
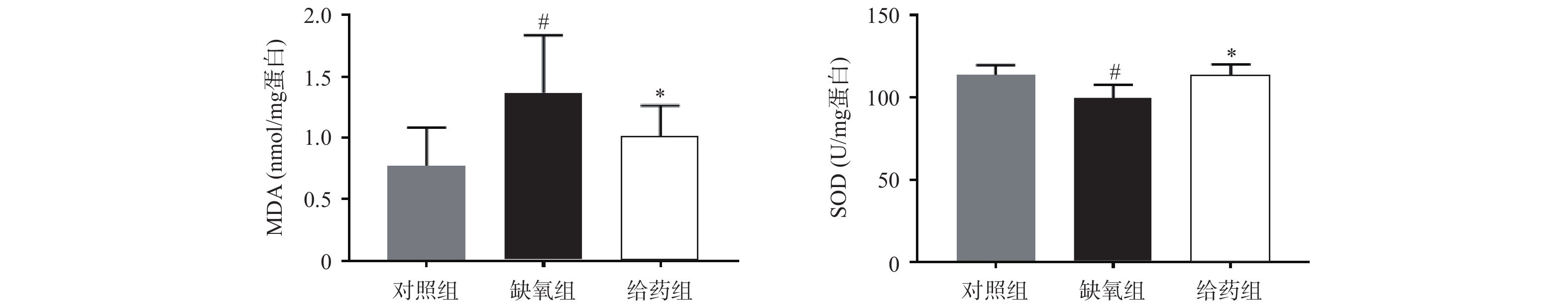
大鼠脑组织中氧化应激相关指标MDA与SOD的测定结果如图1所示,与对照组相比,缺氧组大鼠脑组织中MDA含量显著性升高,SOD活力显著性下调(P<0.05),当给予7-HEC时,缺氧组大鼠脑组织中MDA含量下调,SOD活力上调,且差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结果提示,7-HEC可能参与机体氧化应激的调节,起到防护高原脑水肿的效果。
-
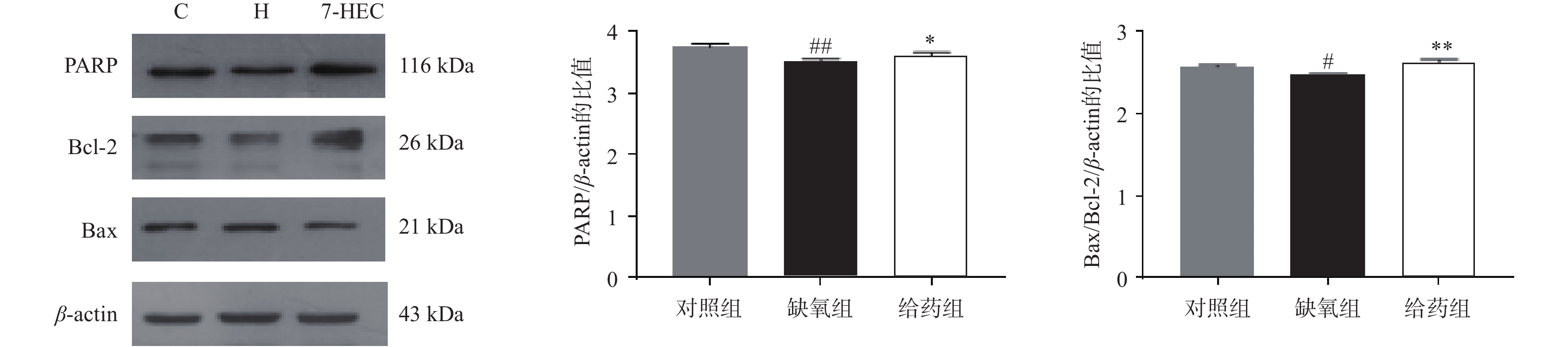
如图2所示,大鼠脑组织中PARP与Bcl-2的蛋白表达在缺氧组下调,给药后显著上调(P<0.01),大鼠脑组织中Bax的蛋白表达在缺氧组上调,给药组显著下调(P<0.01),为进一步探讨Bcl-2与Bax对凋亡的易感性,对Bax/Bcl-2的比例进行比较,结果显示,与对照组相比,缺氧组显著下降,与缺氧组相比,给药组极显著上调(P<0.01)。结果提示,7-HEC可能参与细胞凋亡从而防治高原脑水肿。
-
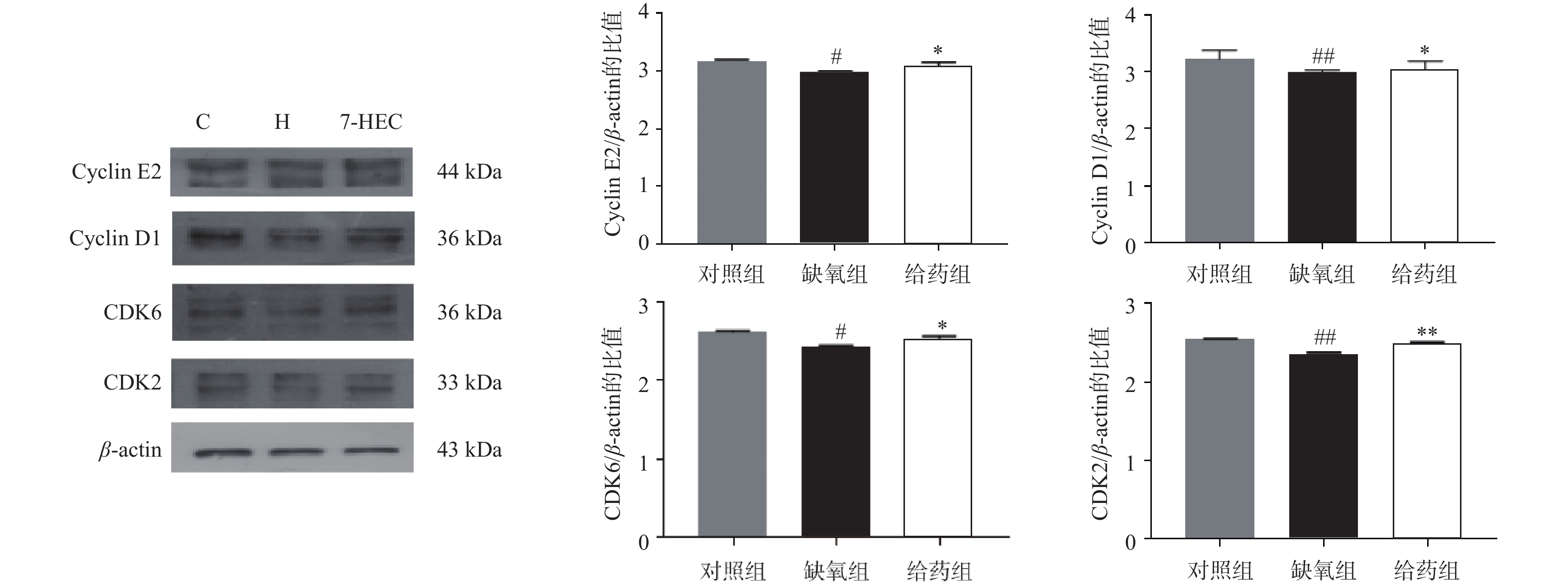
如图3所示,与对照组相比,大鼠脑组织中周期相关蛋白CyclinE2、CyclinD1、CDK6、CDK2的表达在缺氧组均下调(P<0.05);与缺氧组相比,在给药组中,CyclinE2、CyclinD1、CDK6、CDK2蛋白的表达显著上调(P<0.05)。结果提示,7-HEC可能参与细胞周期调控从而防治高原脑水肿。
-
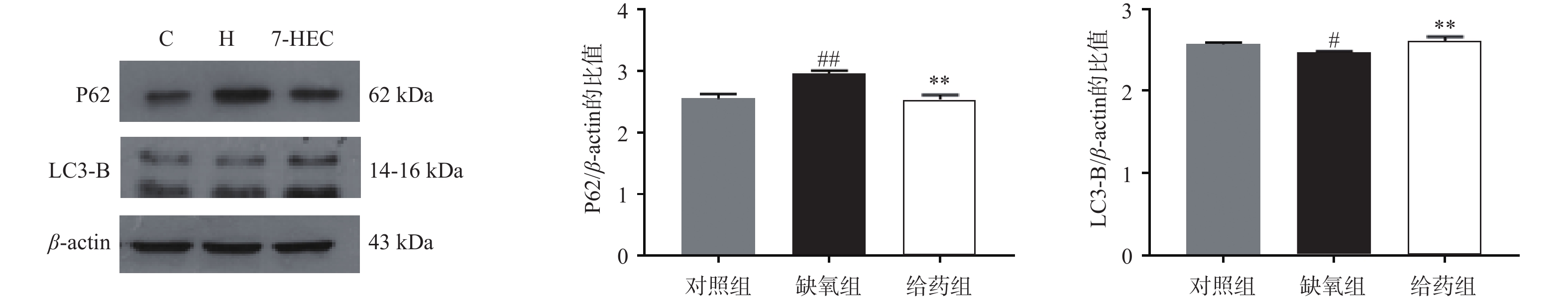
如图4所示,大鼠脑组织中P62的蛋白表达在缺氧组极显著上调,给药后显著下调(P<0.01);与对照组相比,大鼠脑组织中LC3-B的蛋白表达在缺氧组显著下降,与缺氧组相比,给药组极显著上调(P<0.01)。结果提示,7-HEC可能参与细胞自噬过程从而防治高原脑水肿。
-
氧化应激是一种有害事件,可导致活性氧大量产生或抗氧化防御功能不足,损害神经血管单元的完整性,造成神经元不可逆死亡,进而血脑屏障破坏形成脑水肿[8]。MDA是脂质过氧化的产物,其含量可以间接反映组织氧化应激的水平,SODs是一类具有催化超氧化物生成过氧化氢的抗氧化酶[9],可以直接或间接地反映氧化应激的水平。本研究发现,经给药干预后,大鼠脑组织MDA含量显著降低,SOD活力显著提高,表明7-HEC可改善脑水肿大鼠的氧化损伤,从而对脑水肿起到一定的预防作用。
研究表明,缺氧与细胞周期、凋亡、自噬密切相关,细胞周期蛋白表达异常会引发细胞凋亡[10]。细胞周期失调的细胞有机会通过DNA损伤反应的各种机制来阻止DNA修复、细胞周期调节和DDR基因转录。目前研究认为,自噬是另一种DDR机制,它通过促进或防止细胞死亡来应对DNA损伤,从而发挥作用[11]。细胞周期从G1期到S期的调节因子是CDK2蛋白,自噬主要影响细胞周期的G1期和S期,因此自噬与周期也存在密不可分的关系。
细胞凋亡是一种受基因调控的细胞程序性死亡方式,是一种正常的生理变化。缺氧是细胞凋亡的诱导因子之一,细胞凋亡加剧是低氧环境诱发机体机能损伤的重要途径[12]。其受Bax和Bcl-2控制。Bcl-2蛋白的过表达在动物模型中被证明可以减轻肝和肾的损伤,而Bax的过度表达则可诱导细胞凋亡[13]。本实验的结果表明,缺氧组大鼠脑组织中Bax/Bcl2比值降低,诱导细胞凋亡,加重脑水肿,7-HEC可上调Bax/Bcl2比值,进而抑制细胞凋亡,起到抗高原脑水肿的作用。
细胞周期在细胞增殖和分裂中起着关键作用,其由两类蛋白精确调控,CDKs、cyclin作为关键的周期蛋白。这两类蛋白决定了细胞维持在停滞状态或继续进行细胞周期。细胞周期抑制已被证明可以提供神经保护,减少星形胶质细胞瘢痕形成和微胶质激活,并改善创伤性脑损伤后的运动和认知恢复[14]。在本实验中,缺氧环境可下调周期蛋白的表达,而7-HEC可上调周期蛋白的表达,对高原脑水肿起到一定的预防作用。
缺氧与自噬密切相关。缺氧条件下,会诱导自噬的发生。自噬是一种高度调控的连续过程,它是一种重要的程序性细胞死亡[15]。LC3蛋白与P62蛋白相互作用,是自噬的标志物。P62蛋白通常存在于自噬体中,并在自溶酶体形成时被降解[16]。LC3蛋白是哺乳动物自噬蛋白和自噬小体标记物,LC3B是自噬体标记的四种不同亚型中使用最广泛的一种。自噬受体包括P62等一系列连接泛素化底物和LC3的适配器,自噬体一旦形成,就会经历成熟阶段,然后与溶酶体融合,发生自噬。此外,P62还可调节细胞凋亡,主要通过选择性减少胞质中促凋亡蛋白来减轻细胞死亡,保护机体免受伤害[17]。在本实验中7-HEC可下调P62、上调LC3B的表达,从而促进自噬,保护机体免遭高原脑水肿损害。
凋亡、自噬、周期三种生物过程相互联系,相互影响,作用于机体,保障机体的正常运行。凋亡、自噬、周期相关因子的变化又会影响氧化应激通路的发生发展。在本实验中,7-HEC降低大鼠脑组织中MDA含量,上调SOD含量,从而抑制HACE引发的氧化应激;其还可上调周期和自噬蛋白的表达,从而增强大鼠脑神经元细胞的增殖活性,加速损伤细胞的自噬,保护机体免受HACE的损害。综上,7-HEC可抑制细胞凋亡和周期,增强自噬,进而抑制机体氧化应激,从而达到防护高原脑水肿的作用。
A preliminary study on the mechanism of 7-HEC on high altitude cerebral edema
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202205090
- Received Date: 2022-05-23
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-08-25
- Available Online: 2022-09-29
- Publish Date: 2022-09-25
-
Key words:
- high altitude cerebral edema /
- oxidative stress /
- apoptosis /
- cycle /
- autophagy
Abstract:
| Citation: | SHI Zhiqun, GAO Yingchun, ZHANG Dongmei, CHEN Keming, JING Linlin, MA Huiping. A preliminary study on the mechanism of 7-HEC on high altitude cerebral edema[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2022, 40(5): 399-402, 415. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202205090 |









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: