-
丽蕾金线兰Anoectochilus lylei Rolfe ex Downie是兰科金线兰属植物,主要分布于云南省,其植物形态与同属植物金线兰A. roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl非常相似,在民间被当作金线莲使用[1-2]。金线莲是闽台特色中药,基原是金线兰A. roxburghii(Wall.)Lindl[3],主要活性成分包含内酯苷和多糖等,具有降血糖、抗氧化、抗肝损伤、抗骨质疏松,还有减肥等生物活性[2,4-9]。前期研究发现,丽蕾金线兰和金线兰中的内酯苷类成分(金线莲苷和goodyeroside A)含量有较大的差异,12批金线兰金线莲苷含量为57.10 ~164.98 mg/g,仅1批检测到goodyeroside A,含量为1.69 mg/g;而丽蕾金线兰中goodyeroside A含量达到91.23 mg/g,金线莲苷含量仅为6.2 mg/g。金线莲苷和goodyeroside A是差向异构体,其药理作用具有明显的不同,金线莲苷具有抗高脂血症、降血糖和抗自身免疫性肝炎的作用,而goodyeroside A却无上述活性 [2]。因此,笔者对丽蕾金线兰植物形态特征、显微特征做了较全面的研究,以期为丽蕾金线兰的准确鉴定以及进一步的开发利用提供参考。
-
SZ2体视镜显微镜(日本OLYMPUS);200D单反相机(日本佳能);YS100生物显微镜(日本Nikon公司)。
-
试剂:水合氯醛、盐酸、F.A.A 固定液、间苯三酚等,丽蕾金线兰Anoectochilus lylei采自云南西双版纳景洪市,经福建中医药大学药学院吴岩斌副研究员鉴定为兰科金线兰属丽蕾金线兰 (Anoectochilus lylei Rolfe ex Downie)。
-
采集野生丽蕾金线兰,移栽至开花后用数码相机拍照,记录植株形态特征,并在体视显微镜下对花进行解剖、拍照。取丽蕾金线兰的根、茎、叶制成片,观察其横切面特征,取新鲜叶片,撕下上表皮和下表皮,进行制片,观察上、下表皮的主要特征。
-
植株高8~28 cm。茎淡绿色,半透明,肉质。叶卵心形,长2.0~6.5 cm,宽2.5~4.5 cm,上面深绿色或黑紫色,通常具红色网脉,有绢丝光泽,有 5 条弧形主脉,背面淡紫红色;叶柄的基部扩大成鞘,抱茎。总状花序具2~8朵花;花苞片淡红色,卵状披针形,先端渐尖;花倒置;中萼片长卵形,侧萼片呈偏斜的长圆状椭圆形;花瓣镰刀状披针形,与中萼片近等长;具Y字形白色的唇瓣,基部距呈圆锥状,前部裂片条状长圆形,中唇两侧各具1 ~ 3个极短的细齿,距中部呈绿色或黄色,末端白色,2 浅裂,与子房平行,内侧胼胝体2个,盾状;蕊柱黄色,长4 ~ 5 mm,蕊柱翅基部具急尖翅,见图1。上述特征与文献报道的丽蕾金线兰植物形态特征一致[1]。
-
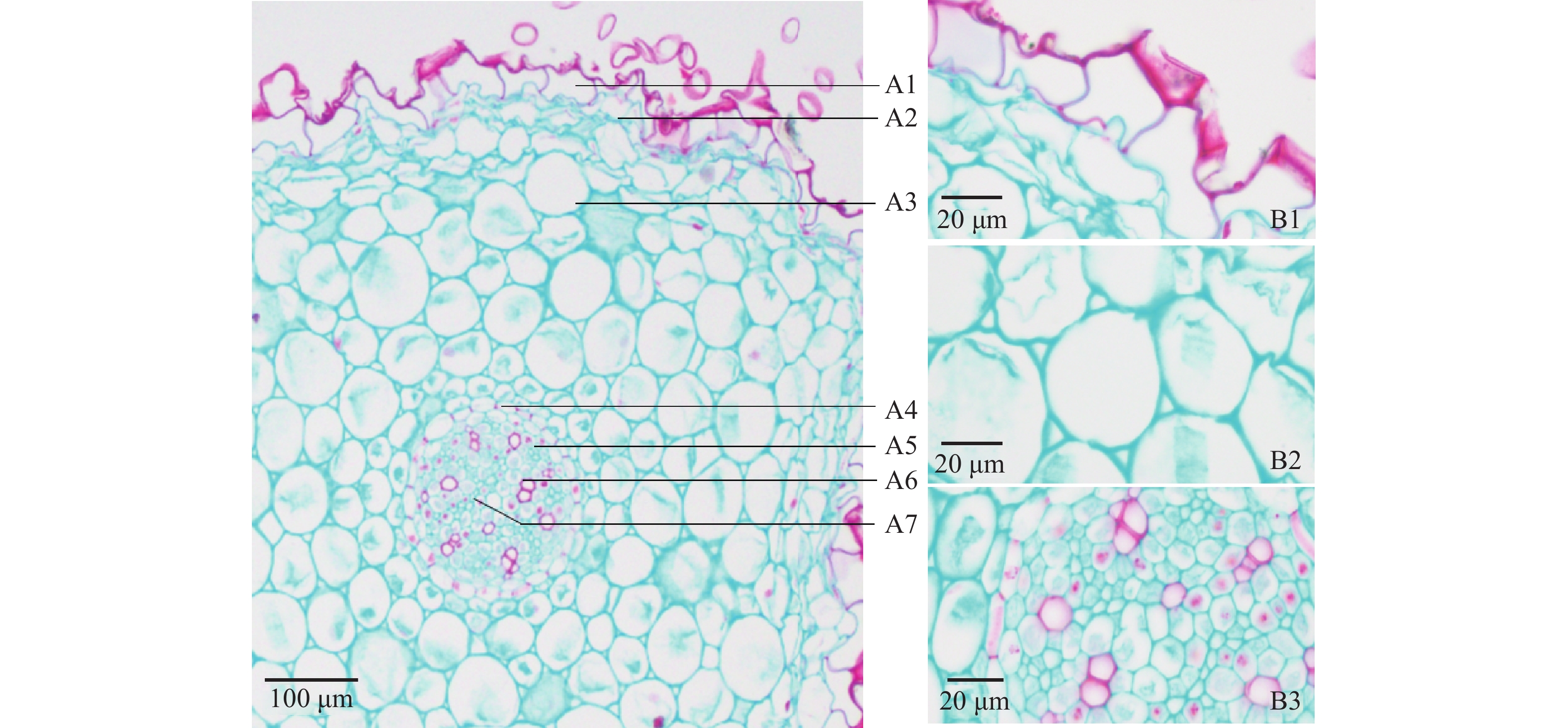
近圆形,最外层表皮为1层不规则的类方形细胞构成,外具栓质化根被,排列紧密;皮层占横切面的5/6左右。外皮层为 2~3排列较紧密的不规则细胞;中皮层细胞为大小不等的类圆形,有草酸钙针晶分布;内皮层细胞类圆形;中柱鞘明显,维管束为木质部与韧皮部相间排列的辐射状,木质部导管多角形或类圆形,1~5个成束;中央髓部常不明显,见图2。
-
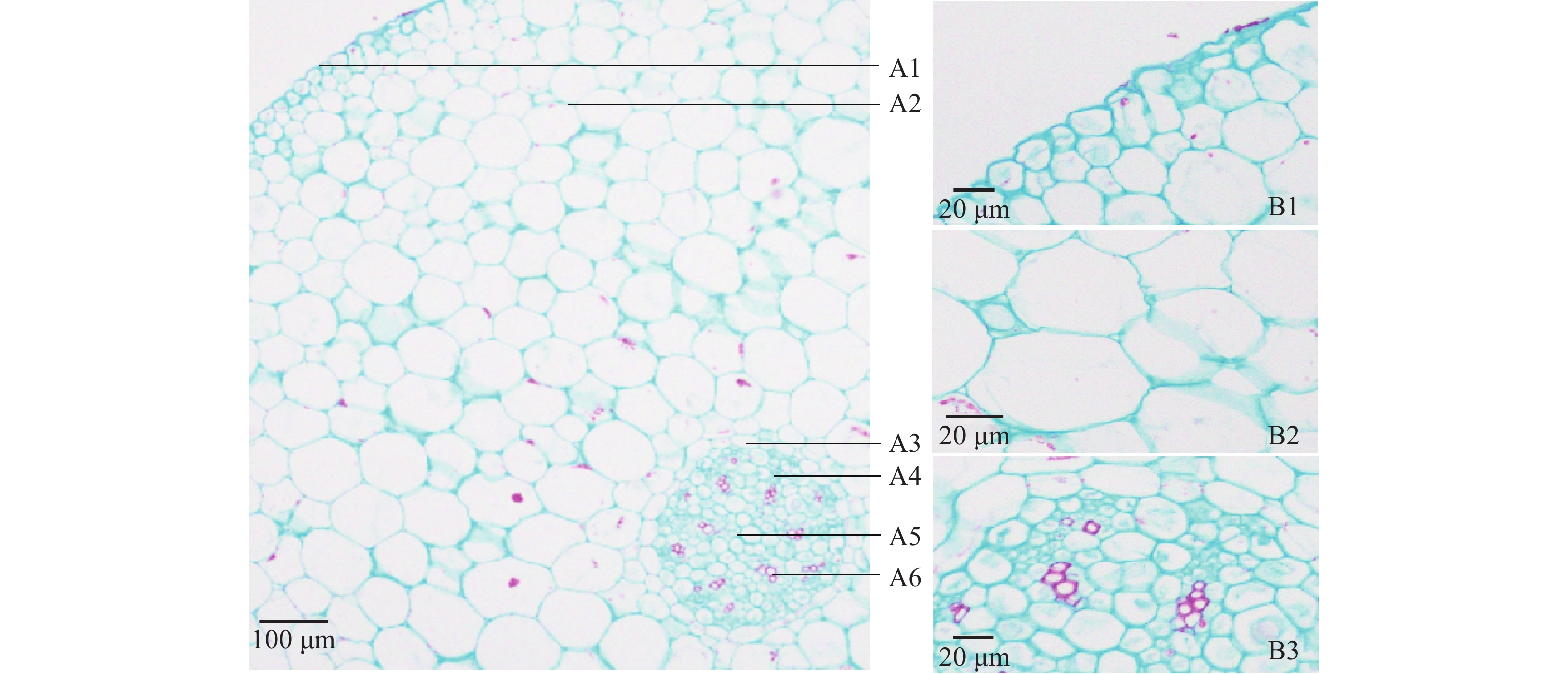
类圆形,表皮为1层排列紧密的类圆形细胞,具角质层;皮层占横切面的 4/5左右,由排列较疏松的类圆形薄壁细胞组成,常可见草酸钙针晶分布,内皮层明显,由1层排列紧密的长椭圆形细胞组成,凯氏点明显可见;维管柱内无序散在13~30个有限外韧型维管束;木质部导管多类圆形,1~7个成束,髓部不明显,见图3。
-
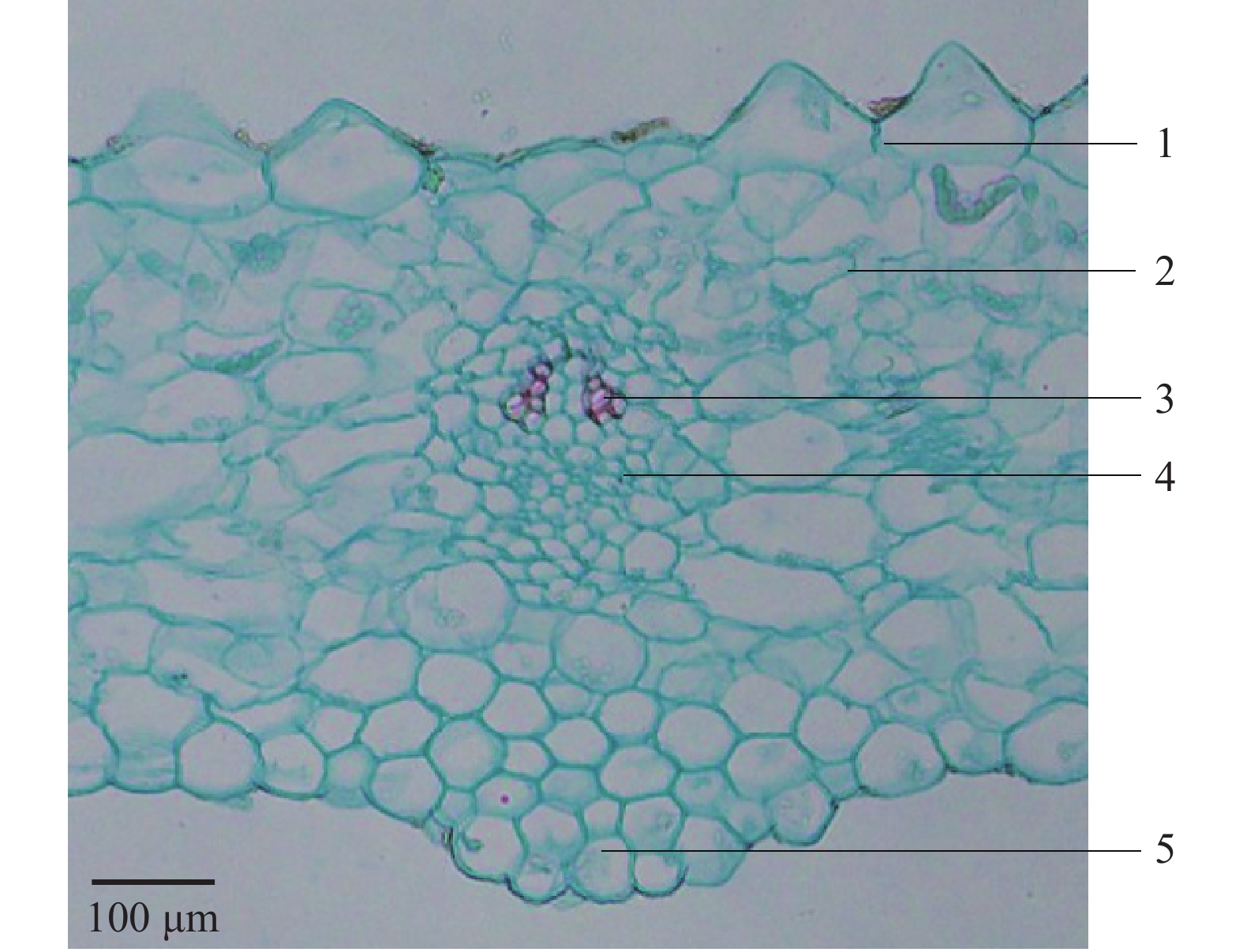
上表皮细胞1层,排列紧密,表面常具乳突状或类三角状的突起,具角质层,气孔未见;下表皮由一列类长方形细胞组成,叶肉细胞多列,含较多叶绿体,偶见草酸钙针晶;主脉上方平整,下方微凸,维管束 1 个,为有限外韧型,见图4。
-
叶片上表皮细胞类方形或类圆形,排列紧密,未见气孔分布;下表皮细胞类圆形或为不规则多角形,常见的气孔类型有不定式、直轴式和不等式气孔,见图5。
-
金线兰属植物形态相似,在民间均当作金线莲使用[2,11-12]。市场上销售的金线莲大多数是经过组织培养的瓶苗或者瓶苗经过种植后的栽培品,但是组培金线莲的外植体常常未经过准确鉴定,多种金线兰属植物均作为金线莲组培的外植体,导致市场上出现了多种形态各异的金线莲品系,如“小圆叶” “尖叶” “大圆叶” “红霞”[10,13]。丽蕾金线兰叶片较大,民间称为“大圆叶”金线莲,但是其主要化学成分与金线兰明显不同。因此,为避免丽蕾金线兰与金线兰混淆,有必要对其进行准确鉴定。
本实验对丽蕾金线兰的植物形态及组织构造、鉴别特点等进行了较为全面的研究,结果显示丽蕾金线兰与金线兰的植物形态、显微特征存在一定的差异[13-17]。差异之处在于丽蕾金线兰根茎和叶片较金线兰粗大,叶片长多数在5 cm以上,叶主脉上表面较平整,下表面微凸;花倒置,唇瓣位于下方,唇瓣前唇裂片条状圆形,中唇两侧各具1 ~ 3个极短的细齿,距中部呈绿色或黄色,末端白色,与子房平行,蕊柱黄色,蕊柱翅基部具急尖翅。金线兰根茎和叶片较小,叶主脉上表面微凹,下表面呈半圆形凸出,花不倒置,唇瓣位于上方,唇瓣前唇裂片近长圆形或近楔状长圆形,中唇两侧各具6~8条、4~6 mm流苏状细裂条,距白色,与子房近垂直,蕊柱白色,蕊柱翅基部不具急尖翅。上述形态特征可作为丽蕾金线兰与金线兰鉴别的主要依据。
Morphology and microscopic identification of Anoectochilus lylei
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202207092
- Received Date: 2022-07-26
- Rev Recd Date: 2023-02-14
- Publish Date: 2023-05-25
Abstract:
| Citation: | ZHANG Ruolan, PENG Mengchao, ZHENG Chengjian, WU Jianguo, WU Yanbin, WU Jinzhong. Morphology and microscopic identification of Anoectochilus lylei[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2023, 41(5): 321-324. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202207092 |










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: