-
河豚毒素(TTX)是一种强效生物毒素,是目前已知毒性最强的生物毒素之一,主要存在于河豚鱼和部分海洋生物中。据报道,河豚毒素能与电压门控钠离子通道1∶1结合,阻断钠离子内流,从而发挥抑制兴奋的作用[1]。基于其对钠离子通道不同亚型的阻断,河豚毒素在一定剂量范围可以起到镇痛、局麻等多种药用效果[2-6]。其中镇痛效用为当前主要研究领域,相较于临床常用的阿片类药物,河豚毒素发挥镇痛作用无成瘾性,副作用小,肝肾功能损害小,但其治疗剂量极低,且治疗窗口狭窄,低剂量往往带来频繁的给药次数,要想良好的发挥镇痛作用,就需要选取合适的剂型来更好的发挥其作用。微球作为长缓释制剂的优良载体,经常包载治疗窗狭窄、半衰期较短的药物以发挥长周期药效的作用,为测定微球中TTX含量等数据,需要一套适用的检测方法。
目前针对河豚毒素定量检测的方法多为生物样本检测,应用于动物体内河豚毒素检测和人河豚毒素中毒血液检测,针对河豚毒素的体外测定方法较少,药用制剂的检测方法更是稀少。本方法的建立适用于河豚毒素药用制剂中的含量检测,为河豚毒素药用开发的含量测定提供了新选择。主流的河豚毒素含量测定方法包括小鼠生物法[7-8]、免疫测定法[9-11]、高效液相色谱法(HPLC)[12-13]、液相色谱-质谱联用法[14-16]、气相色谱-质谱联用法[17]等。高效液相色谱法因其适用性广、稳定性好及灵敏度良好而备受欢迎。但由于河豚毒素不溶于任何有机溶剂,仅溶于弱酸水溶液,常见的方法难以较好地保留河豚毒素。本研究使用庚烷磺酸钠作为离子对试剂,通过河豚毒素与离子对试剂结合形成复合分子,提高其在色谱柱上的保留能力,从而更好地分离河豚毒素与其他物质 [18-19]。
根据河豚毒素的作用功效和缓释长效镇痛目标,本研究制备了河豚毒素缓释微球。为考察微球中河豚毒素的含量,需要建立相应的含量测定方法。因此,本研究采用HPLC方法建立针对河豚毒素缓释微球的含量分析方法,以期为河豚毒素微球中的含量测定提供依据。
-
LC-20AD高效液相色谱仪(日本岛津制作所);电子天平(METTLER TOLEDO,瑞士);数显pH计(sartorius,德国),紫外可见分光光度计[安捷伦科技(中国)有限公司];循环水式真空泵(上海豫康科教仪器设备有限公司);SECURA125-1CN型十万分之一电子天平(赛多利斯,德国);Arium@ mini超纯水机(赛多利斯,德国)。
-
河豚毒素标准品(98%,中洋生物科技股份有限公司);PBS缓冲液(武汉普诺赛生物科技有限公司);聚乳酸羟基乙酸共聚物(PLGA, RG 503H,sigma-Aldrich Company);甲酸(色谱纯,国药集团);三氟乙酸(色谱纯,sigma-Aldrich Company);氢氧化钠(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司);泊洛沙姆-188(sigma-Aldrich Company);叠氮钠(Sigma-Aldrich Company);纯净水(杭州娃哈哈集团有限公司);乙腈(色谱纯,sigma-Aldrich Company);二氯甲烷(色谱纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司);河豚毒素-PLGA微球、空白PLGA微球(海军军医大学药剂学教研室提供)。
-
色谱柱:Agilent ZORBAX SB C18柱(4.6 mm×150 mm,5 μm);流动相:8 mmol/L庚烷磺酸钠(0.005%TFA,1 mol/L NaOH调节pH4.0)水溶液∶乙腈=95∶5;检测波长:200 nm;流速:1.0 ml/min;柱温:30 ℃;分析时间:12 min;进样量:20 μl。
-
精密称取叠氮钠、泊洛沙姆-188适量,加入磷酸盐缓冲液配制成含0.02%NaN3、0.02%F-68的释放介质,取10 mg河豚毒素标准品,用6 ml 0.1%甲酸溶液溶解,以PBS介质(0.02%NaN3、0.02%F-68)定容得100 μg/ml的对照品溶液。
-
精密称取20.00 mg河豚毒素冻干微球,加入1 ml二氯甲烷(DCM)超声使完全溶解,加入经甲酸调节pH至4.0的释放介质,超声后充分振摇,取上层水相溶液过0.22 μm水系滤膜作为供试品溶液。
-
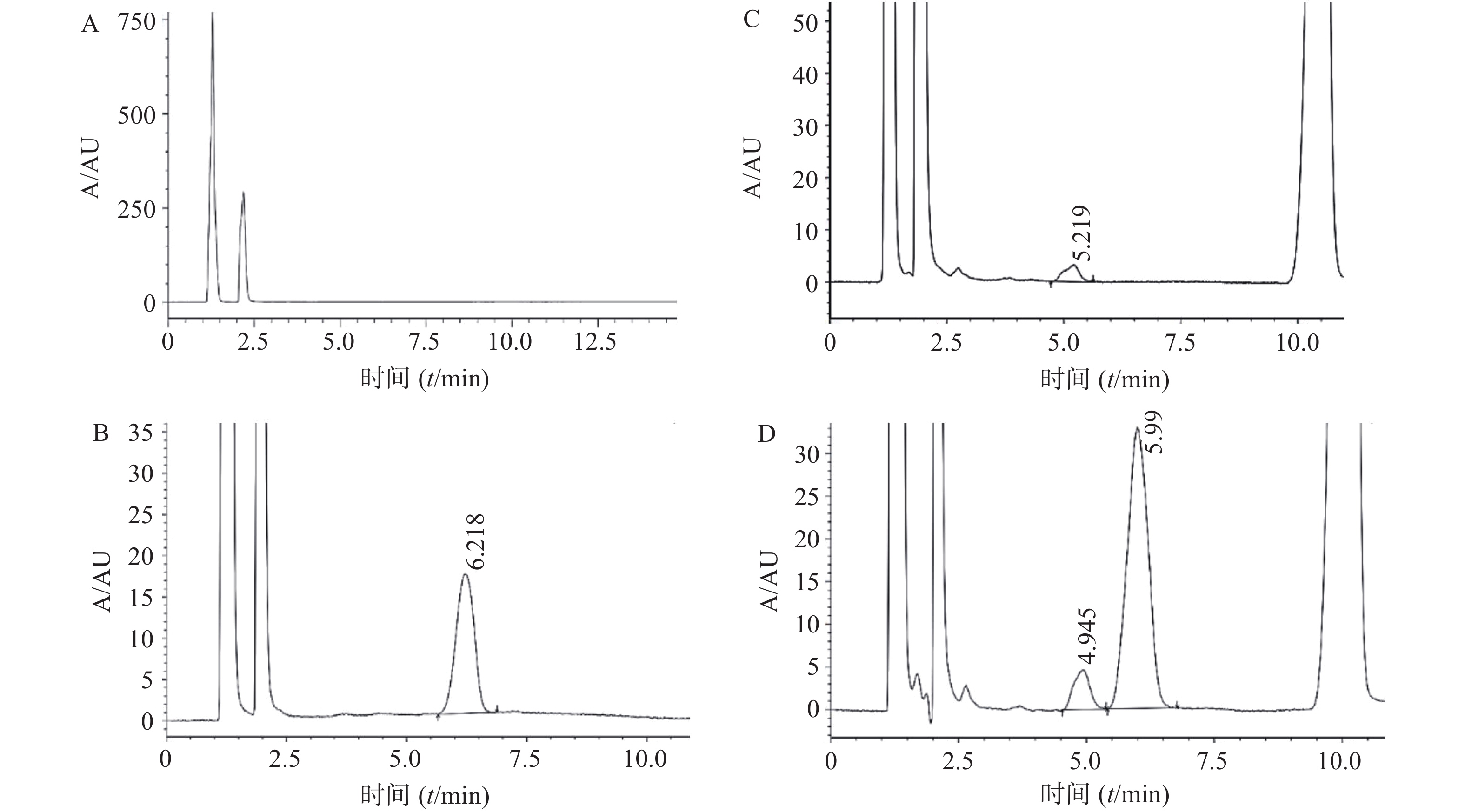
配制以下样品,考察方法专属性:① 1ml PBS释放介质加入50 μl 1%甲酸,为空白释放介质;② 甲酸调节pH的PBS介质稀释得的10 μg/ml TTX标准品溶液;③ 精密称取10 mg空白微球于5 ml EP管,加入1 ml二氯甲烷超声2 min使完全溶解,加入1 ml PBS介质及50 μl 1%甲酸,充分振摇后超声10 min,取上层水相过0.22 μm水系膜,为空白微球样品;④ 精密称取10 mg 空白微球于5 ml EP管,准确加入10 μg/ml TTX标准液1ml,加入1 ml二氯甲烷超声2 min使完全溶解,甲酸调节pH的PBS溶液提取,过膜处理后为河豚毒素微球样品。按照“2.1”项下方法进样检测,图谱如图1。实验结果表明,该方法专属性良好,河豚毒素得到了较好的分离。
-
精密量取对照品溶液于10 ml量瓶,加入PBS介质,分别稀释得20、15、12、10、5、2、1 μg/ml的系列浓度标准液。按照“2.1”项下方法进样检测,记录TTX峰面积。以峰面积(A)为纵坐标,河豚毒素的浓度(Xr μg/ml)为横坐标进行线性回归,得回归方程为Y=22 216X+591.8,r=0.999 9,证明本方法在1~20 μg/ml浓度范围内线性良好。
-
由对照品溶液配制低、中、高三个浓度的河豚毒素标准液,分别为2、10、20 μg/ml,进行日内精密度及日间精密度测定。日内精密度测定方法为样品测定5次,计算日内相对偏差;日间精密度测定法为3个浓度样品连续测定5 d,计算日间相对偏差。3个浓度由低到高的日内精密度RSD值分别为0.81%、0.43%、0.58%,日间精密度RSD值分别为1.32%、1.10%、0.68%,均小于2.0%,符合精密度要求。
-
按照“2.2.2”项下方法,平行制备5份河豚毒素供试品溶液,按照“2.1”项下色谱条件进行测定。结果显示,RSD值为1.49%,表明该方法重复性良好。
-
选取低、中、高3个浓度标准溶液,分别为2、10、20 μg/ml,称取10 mg空白微球于5 ml EP管,加入1 ml 二氯甲烷超声溶解和1 ml 标准溶液及50 μl 1%甲酸,充分振摇后超声10 min,超声后取上层水相过膜进样检测,计算回收率,结果见表1。
加入量(μg/ml) 测得量(μg/ml) 回收率(%) RSD(%) 2 1.96 1.98 1.99 98.88±0.82 0.83 10 10.04 9.96 10.00 100.00±0.43 0.43 20 20.04 20.18 20.08 100.49±0.37 0.37 试验结果表明,低、中、高3个浓度的回收率均在98.0%~102.0%之间,3组不同浓度的RSD均小于2%,符合方法学要求。
-
为了考察该方法能否测定微球中还未释放的河豚毒素含量,本实验进行微球中药物含量测定。精密称取河豚毒素-PLGA微球20 mg,加入0.5 ml DCM超声溶解,再加入1%甲酸调节pH至4的PBS溶液2.5 ml,充分振摇后超声10 min,取上清液过膜后进样检测。测定河豚毒素浓度为2.52 μg/ml,换算后计算微球包封率(EE)及载药量(DL),计算方法如下:
换算可得微球包封率为60.77%,载药量为0.024%。因此,通过此方法可以计算微球的载药量和包封率,为下一步微球释放情况考察时通过测定微球中未释放含量从而间接测定微球的释放量提供依据。
-
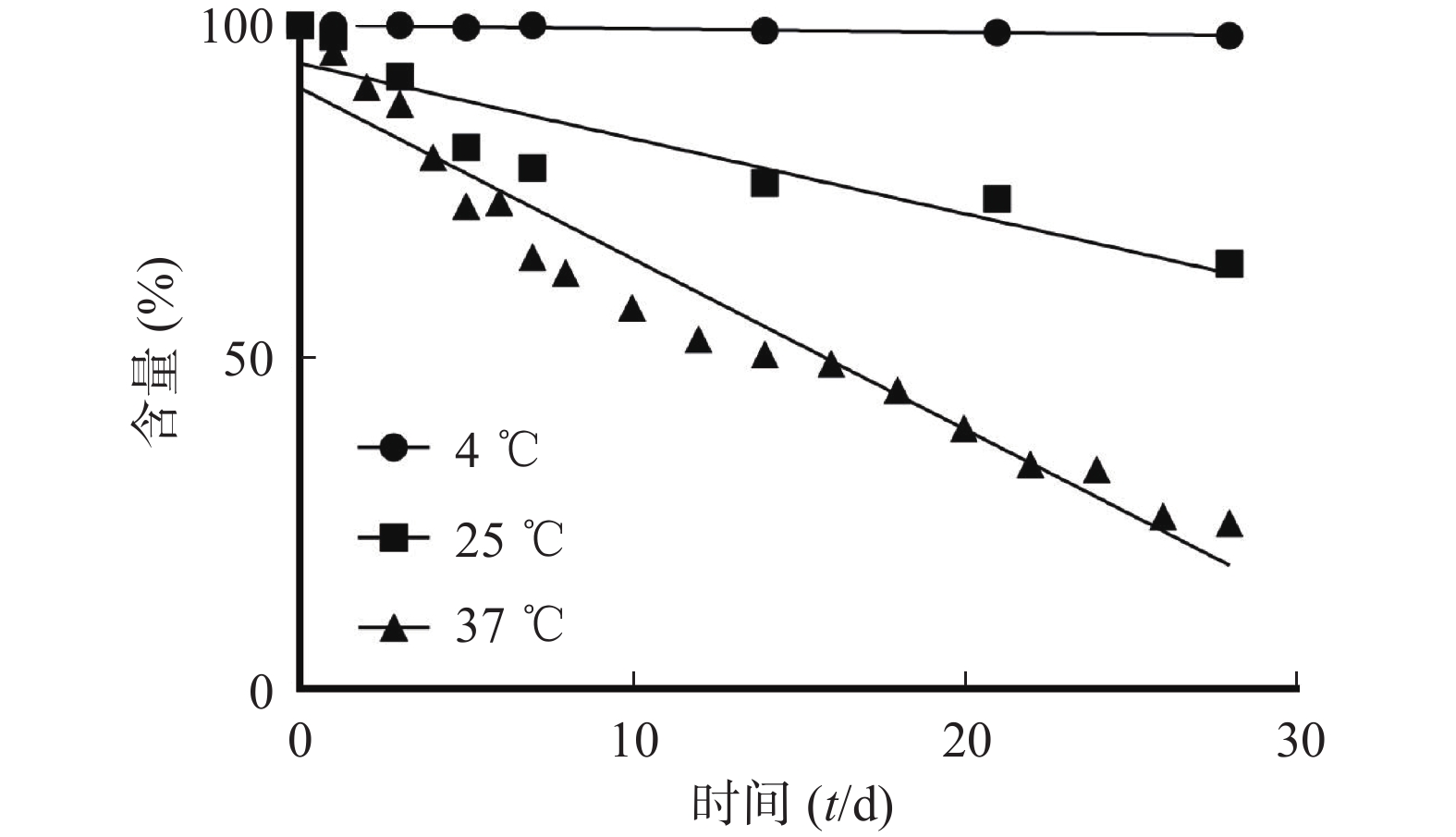
由于河豚毒素溶液受温度影响较大,温度越高,河豚毒素降解越快,在微球长期释放过程中,已释放的河豚毒素发生降解会影响体外释放的测定,故对河豚毒素标准品溶液进行4、25、37 ℃条件下释放介质中的稳定性考察,样品pH均为7.4。4 ℃和25 ℃样品分别在第1、3、5、7、 14、 21、28天取样检测;37 ℃样品在第1周每天取样,其后隔天取样。取12 μg/ml TTX标准品溶液分别置于4、25、37 ℃,100 r/min条件下考察,用于测定TTX在体外释放条件下稳定性,结果见图2。
结果表明,河豚毒素在水溶液中稳定性受温度影响比较大。28 d考察中,河豚毒素在4 ℃放置降解约1.53%,25 ℃放置降解约32.67%,37 ℃放置降解约74.96%。所以,在河豚毒素微球释放测定时不能直接测定释放介质中的河豚毒素含量,而应测定微球中还未释放的河豚毒素含量,从而间接测定微球的释放。
-
目前针对河豚毒素定量检测的方法多为生物样本检测,应用于动物体内河豚毒素检测和人河豚毒素中毒血液检测,针对河豚毒素的体外测定方法较少,药用制剂的检测方法更是稀少。本方法的建立适用于河豚毒素药用制剂中的含量检测,为河豚毒素药用开发的含量测定提供了借鉴。
针对河豚毒素微球的含量测定,我们尝试了许多方法,发现常规的反相色谱法对这类物质分离度不高,而反相离子对色谱法分离效果好。为了取得更佳的分离效果,分别考察了Agilent Zorbax SB-C8柱(4.6mm×150mm, 5μm)、shim-pack GIST C18-AQ(4.6mm×250mm, 5μm)、Agilent Zorbax SB C18柱(4.6mm×150mm, 5μm)等不同色谱柱对河豚毒素的分离效能及峰型的影响。结果显示,当色谱柱为Agilent Zorbax SB C18柱时,河豚毒素的分离效果及峰形最佳。
在离子对色谱法中,河豚毒素的分离及峰型等受到多种因素影响,在该方法建立过程中,我们考察了流动相pH、流动相比例等条件对河豚毒素分离效果的影响。流动相pH:我们考察了流动相中pH3.0、4.0、4.5和5.0,不同pH对其峰型有一定的影响,对比筛选后,我们确定了pH4.0时为最佳峰型。流动相比例:流动相比例对TTX出峰时间存在较大的影响,我们考察了90∶10、92∶8、94∶6、95∶5、98∶2等比例,保留时间在4~25 min不等,在保证出峰完整的情况下,调整进样时间至适宜,最终确定比例为95∶5。
微球中的河豚毒素提取我们尝试了不同的有机溶剂破乳,其中包括二氯甲烷、三氯甲烷、乙腈等有机溶剂,最终选用速度最快、溶解最完全的二氯甲烷溶剂破乳提取。
结果证明选用本方法测定缓释微球中的河豚毒素在一定浓度范围内线性良好,专属性强,精密度和回收率均符合方法学要求,可以作为TTX微球含量、释放量的测定方法。
Establishment of determination of tetrodotoxin sustained-release microspheres
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202208060
- Received Date: 2022-08-13
- Rev Recd Date: 2023-02-02
- Publish Date: 2023-03-25
-
Key words:
- Tetrodotoxin /
- HPLC /
- sustained-release microspheres /
- sodium heptane sulfonate
Abstract:
| Citation: | WANG Qi, LU Guangzhao, LI Yuan, FAN Li, ZHANG He, LU Ying. Establishment of determination of tetrodotoxin sustained-release microspheres[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2023, 41(3): 182-186. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202208060 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: