-
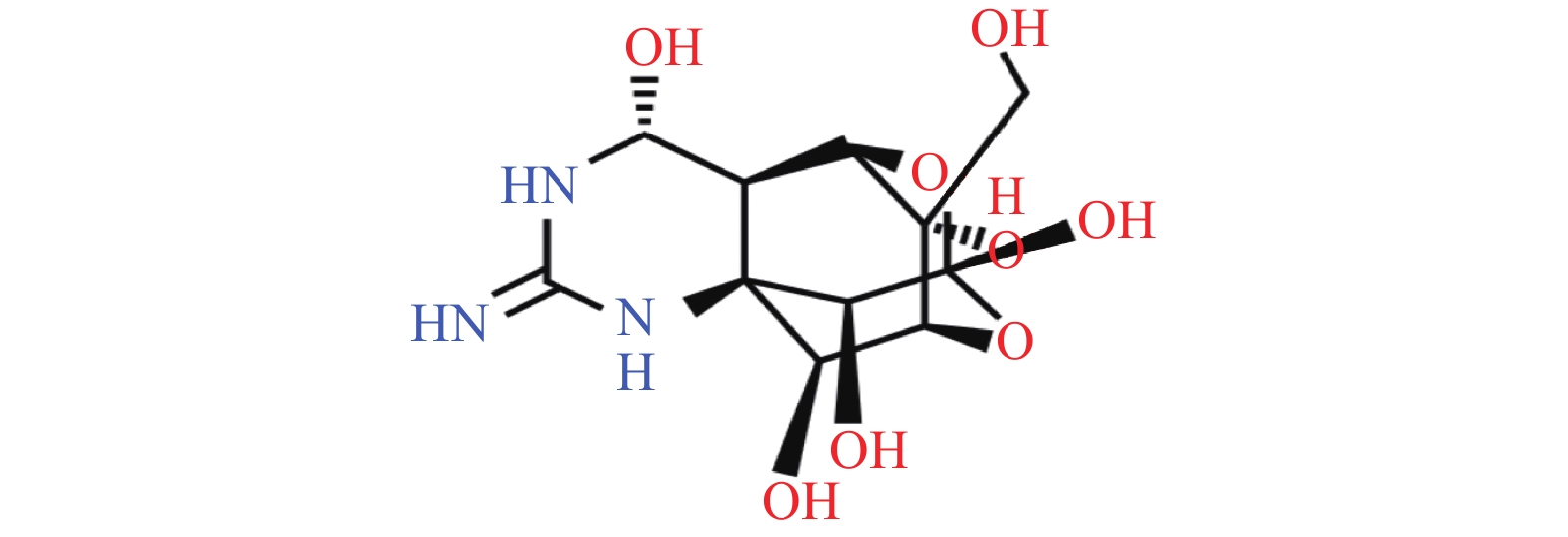
河豚毒素(TTX)属于氨基全氢化喹唑啉化合物,分子式为C11H17O8N3,分子量为319。其分子结构类似于生物碱[1],呈独特的笼形,如图1。河豚毒素粗品为黄褐色粉末,纯品为白色晶体,呈弱碱性,容易潮解,微溶于水溶液,易溶于无机酸水溶液,且在弱酸条件下稳定;对于热不敏感,但在高温下毒性会增强,强酸强碱条件下其结构可被破坏[2]。
河豚毒素是一种高效的神经类毒素,由于能够特异性的阻断Na+离子通道,进而产生麻痹作用,因此低浓度的河豚毒素被认为是一种优良的神经类候选药物,一直受到科研人员尤其是新药研发人员的关注[3]。目前已有将河豚毒素作为止痛药[4-5]和成瘾戒断药[6]的相关探索和研究。由于河豚毒素在药学领域有着广阔前景,关于其药学应用的研究报道逐年增多,但大多集中在分析方法[7]、药理机制[8]或药物载体研究[9],对其可成药性的相关研究报道较少。本文按照新药研发要求,建立高效液相反相离子对色谱法,对河豚毒素在不同溶剂中的溶解性和不同pH环境中的稳定性进行考察,为河豚毒素的处方前研究积累数据,为其进一步临床应用提供有力支撑。
-
LC-2030C高效液相色谱仪(日本岛津制作所);AL-104电子天平(METTLER TOLEDO,瑞士);数显pH计(sartorius,德国);紫外可见分光光度计(安捷伦科技(中国)有限公司);循环水式真空泵(上海豫康科教仪器设备有限公司);SECURA125-1CN型十万分之一电子天平(赛多利斯,德国);Arium@ mini 超纯水机(赛多利斯,德国)。
-
河豚毒素原料药(中洋生物科技江苏有限公司,批号:20220089,含量88%);河豚毒素对照品(泰州康特生物工程有限公司,批号:201206,含量≥99%);磷酸、98%甲酸、柠檬酸、磷酸二氢钠、磷酸氢二钠、磷酸二氢钾、磷酸氢二钾、氢氧化钠、庚烷磺酸钠、磷酸二氢铵、乙酸铵、盐酸、30% H2O2和冰醋酸均为分析纯试剂(国药集团化学试剂有限公司)。
-
色谱柱为Shim-pack GISI C18-AQ(4.6×250 mm,5 μm);流动相为5 mmol/L庚烷磺酸钠-25 mmol/L磷酸二氢铵,等度洗脱;进样量为10 μl;柱温:25 ℃;流速1 ml/min;检测波长为196 nm;检测时长为40 min。
-
取TTX对照品适量,精密称定,用0.1%磷酸溶液溶解并稀释制成浓度为1.0 mg/ml的TTX对照品储备液。
-
取TTX原料药适量,精密称定,用0.1%磷酸溶液溶解并稀释制成浓度为1.0 mg/ml的供试品储备液。
-
按照《中国药典》(2020版)四部通则8004缓冲液配制方法,配制pH值分别为3.5、4.5、5.0、6.5、7.0、7.4、8.0的缓冲液[10]。称取研成细粉的TTX原料药各2 mg,分别置于4 ml不同pH值的缓冲液(25±2 ℃)中,30 min内每隔5 min强力振摇30 s,观察溶解情况,如无目视可见颗粒,视为完全溶解。如完全溶解则继续加入研成细粉的TTX原料药,同法操作直至饱和,取适量经滤膜滤过,作为溶解度试验测试溶液。
-
取研成细粉的TTX原料药约1 mg,置于10 ml容量瓶中,分别用0.1 mol/L盐酸和0.1 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液溶解并定容,置于70 ℃下反应20 min。精密量取各反应溶液适量,冷却至室温,分别加入对应体积的0.1 mol/L氢氧化钠或0.1 mol/L盐酸进行中和并终止反应。取适量样品经滤膜过滤后作为强酸与强碱破坏试验测试溶液。
-
取研成细粉的TTX原料药约1 mg,置于10 ml容量瓶中,加入30% H2O2溶液溶解定容后,室温反应10 min。精密量取反应溶液适量,经滤膜过滤,作为氧化破坏试验测试溶液。
-
取研成细粉的TTX各适量,精密称定,分别用PBS缓冲液(pH值=7.4)、0.1%甲酸溶液、0.1%柠檬酸溶液溶解,并稀释制成浓度为0.1 mg/ml的TTX溶液,然后分别置于4 ℃、25 ℃、37 ℃中储存,在第1、2、3、5、7、14、21、28 d各取适量经滤膜过滤,作为温度适应性测试溶液。
-
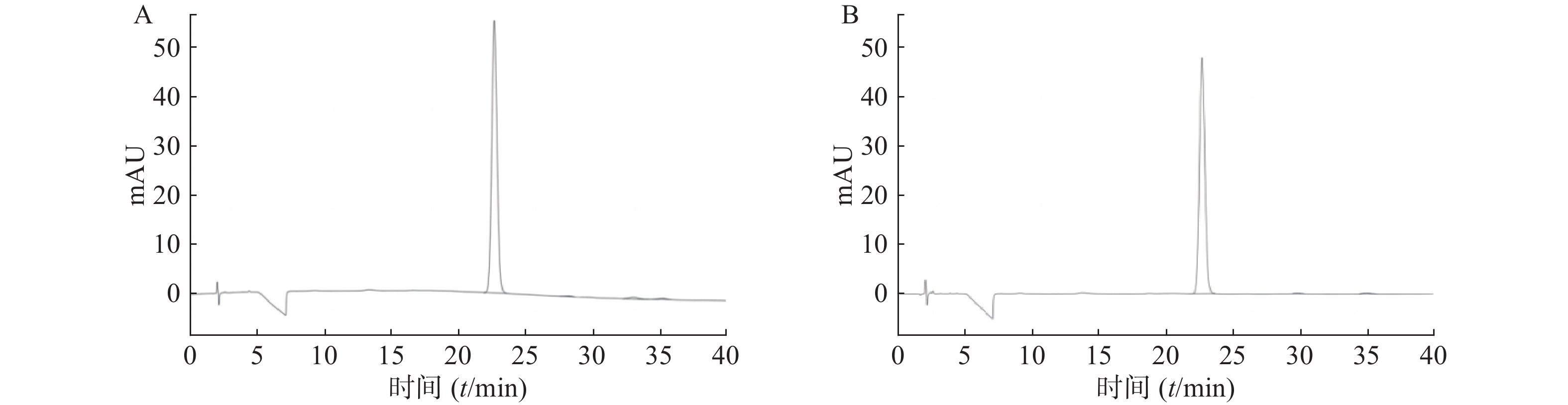
分别将对照品储备液及供试品储备液用0.1%磷酸溶液稀释至0.1 mg/ml,作为对照品溶液和供试品溶液,按“2.1”项进行测试。如图2所示,TTX的保留时间为22.665 min。理论板数为14 501,供试品溶液中主峰与邻峰的分离度为6.4。结果表明,此色谱条件可以满足TTX相关测试要求。
-
取对照品储备液,用0.1%磷酸溶液配制浓度为4、10、20、40、80 μg/ml的TTX对照品测试溶液,按“2.1”项进行测试。以浓度为横坐标(X),峰面积为纵坐标(Y),绘制标准曲线,得回归方程为Y=12 601.2X–2 263.69(r=0.999 9)。结果表明,TTX的浓度与峰面积在测试范围内呈良好线性关系。
-
取对照品储备液,用0.1%磷酸溶液分别稀释至10、20、40 μg/ml的溶液各3份,按“2.1”项进行测试,计算其含量的平均值为101.000%,RSD为0.60%,表明该方法准确度良好,满足测试要求。
-
取供试品溶液,按“2.1”项重复测试6次,计算得到的RSD为0.17%,表明该方法重复性良好。室温分别放置0、2、4、6、8、10、12、24、48 h后按“2.1”进行测试。计算得到的RSD为1.48%,表明供试品溶液在48 h内稳定性良好。
-
由表1结果可看出,TTX几乎不溶于碱性水溶液,但溶解度随着pH值降低而逐渐增大,易溶于pH值为3.5的酸性水溶液。
pH值 3.5 4.5 5.0 6.5 7.0 7.4 8.0 $ \bar{\rm{x}} $(mg/ml) 264.63 31.35 4.64 1.02 0.47 0.21 0.05 SD(mg/ml) 5.54 0.75 0.08 0.046 0.015 0.002 7 0.001 -
实验结果表明,强碱对TTX的破坏能力最强,在0.1mol/L氢氧化钠溶液中、70 ℃条件下反应20 min后,TTX被完全降解。强酸对TTX的破坏能力次之,TTX在70 ℃、0.1mol/L HCl溶液中反应20 min后的降解率为60.78%;氧化对TTX的破坏能力相对最弱,在30% H2O2溶液中反应20 min后的降解率为17.06%。
-
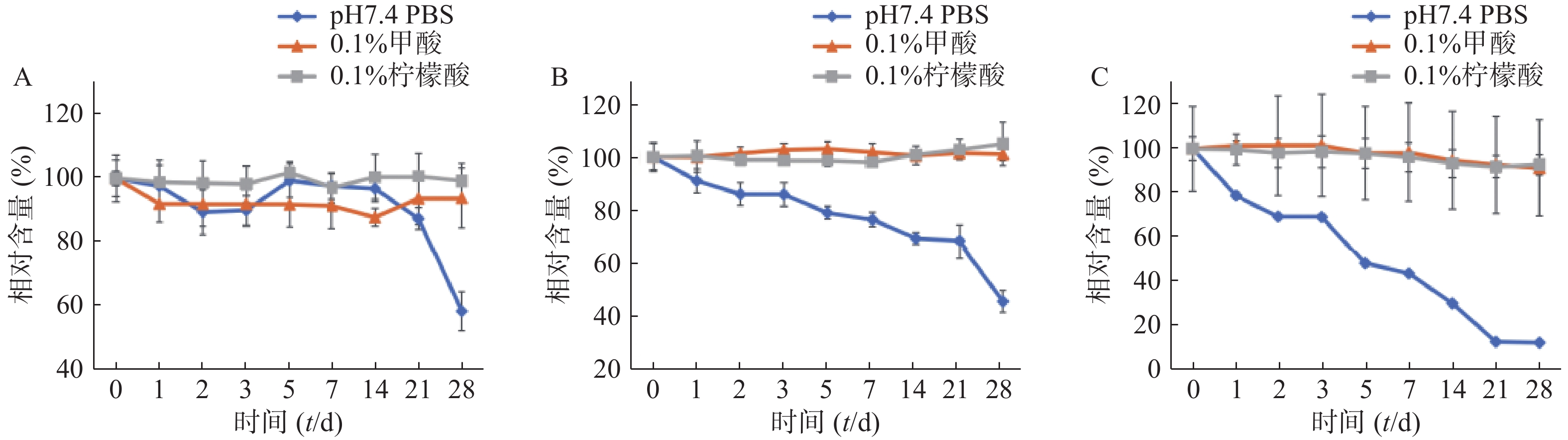
不同介质、不同温度条件下TTX稳定性试验结果见图3。当溶剂为pH值=7.4的PBS溶液时,不同温度下TTX均表现出降解趋势,在25 ℃与37 ℃条件下保存28 d的TTX溶液降解率均超过50%,在37 ℃时PBS溶液中的TTX降解率更高达88.07±0.27%,提示在后续剂型研究中,需注意TTX在体外释放液中的稳定性。以0.1%甲酸溶液或0.1%柠檬酸溶液为溶剂的TTX溶液则较为稳定,在25 ℃和37 ℃下保存28 d含量均未表现出显著性变化。
-
TTX作为一种具有广泛应用前景的潜在镇痛药物,其在药理和作用机制方面的相关研究已有较多报道[11-13],但对于其理化性质和成药性研究的报道极少。本研究建立了高效液相反相离子对色谱法,测定TTX在不同溶剂中的溶解性,并考察温度、溶剂pH值和氧化剂对其稳定性的影响。实验结果表明TTX在酸性条件下具有较高的溶解度,前期试验还表明TTX不溶于乙醇,二氯甲烷等有机溶剂。稳定性试验结果显示TTX在强碱溶液中较不稳定,实验条件下20 min即被强碱全部降解,而在酸性条件、氧化环境中较为稳定。不同温度稳定性试验结果同样显示,TTX在0.1%甲酸或柠檬酸溶液中4周内稳定性均良好;而在pH值=7.4 PBS中降解较为迅速,即使在4 ℃条件下,pH值=7.4 PBS中28 d的降解率仍然接近50%,37 ℃条件下28 d降解率接近90%。研究结果可为TTX处方设计及制备工艺提供实验依据,并提示研究者在开展TTX剂型研究和体外释放研究时应重点关注其稳定性和降解情况。
Preliminary pre-prescription study of Tetrodotoxin
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202304024
- Received Date: 2023-04-14
- Rev Recd Date: 2023-08-14
- Available Online: 2023-09-25
- Publish Date: 2023-09-25
-
Key words:
- Tetrodotoxin /
- HPLC /
- Stability /
- Solubility
Abstract:
| Citation: | XU Jiren, ZHENG Ziyun, LI Yuan, LU Ying, CHU Zhiyong. Preliminary pre-prescription study of Tetrodotoxin[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2023, 41(9): 544-546, 551. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202304024 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: