-
2型糖尿病(T2DM)是一种以高血糖为特征的慢性代谢性疾病,主要是由于胰岛素分泌不足而导致的空腹血糖升高[1]。冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病(CHD,简称冠心病)是一种常见的心血管疾病,主要是由于冠状动脉的粥样性硬化引起的血管阻塞或管腔狭窄,从而导致心肌缺血或缺氧性坏死,进而影响心脏功能[2]。近年来,T2DM的患病人数不断增加。据相关不完全统计,预计到2045年,全球T2DM患病人数将增加至7.83亿,已成为全球关注的重要人类问题之一[3]。目前,我国60岁以上的老年人中T2DM患病率超过20%,其中心血管疾病是最常见的并发症,而CHD则是T2DM患者最常见的致残或致死原因[4, 5]。有研究表明,T2DM患者发生心血管疾病的概率是非T2DM人群的2~4倍,葡萄糖耐受量受损是影响CHD进展的重要因素[6]。由此可见,T2DM与CHD相互影响,相互促进。
中药复方制剂麝香保心丸源于宋代《太平惠民和剂局方》中治疗“寒闭证”的经典名方苏合香丸,由戴瑞鸿教授在1972年改良而来。麝香保心丸已在临床应用40余年,方中麝香通窍温阳、活血化瘀为君药;苏合香辟秽通窍、人参扶正益气为臣药;牛黄开窍醒神、肉桂助阳通脉、蟾酥开窍止痛为佐药;冰片开窍醒神为使药。全方寒温并用、通补兼施、益气强心,主要用于治疗气滞血瘀所致的胸痹,症见心前区疼痛固定不移,心肌缺血所致的心绞痛、心肌梗死等[7-9]。目前临床上将麝香保心丸与基础西药中的降糖药联合应用,表现出比单用降糖药更好的血糖调节效果[10],还可以降低患者血清胆固醇水平[11],显著降低心血管事件发生率[12]。但目前关于麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD共同作用机制的研究相对不足。本研究旨在通过运用网络药理学方法,探索麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的共同作用机制,为今后的研究和应用提供理论依据。
-
运用中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP)、中药成分数据库(TCMID)、中医药百科全书数据库(ETCM)和BATMAN-TCM数据库,以“人工麝香、人参提取物、人工牛黄、苏合香、蟾酥、肉桂、冰片”为关键词,检索麝香保心丸的化学成分。将口服生物利用度(OB)≥20%、类药性(DL)≥0.1,同时文献报道具有确切活性的化合物,以及本课题组前期研究鉴定的入血成分,均视为麝香保心丸的活性化合物。取BATMAN-TCM中score≥48、TCMID中score≥400、ETCM中score≥0.8的靶点,同时将仅有1个成分对应的靶点去除,筛选得到麝香保心丸的潜在作用靶点,然后通过Uniprot数据库规范靶点蛋白的基因名。
-
在DisGeNET数据库和GeneCards数据库中以“type 2 diabetes mellitus”和“coronary heart disease”为关键词筛选出T2DM和CHD的相关靶点,为获得与疾病相关度更高的靶点,将GeneCards数据库中score≤10的靶点去除。
-
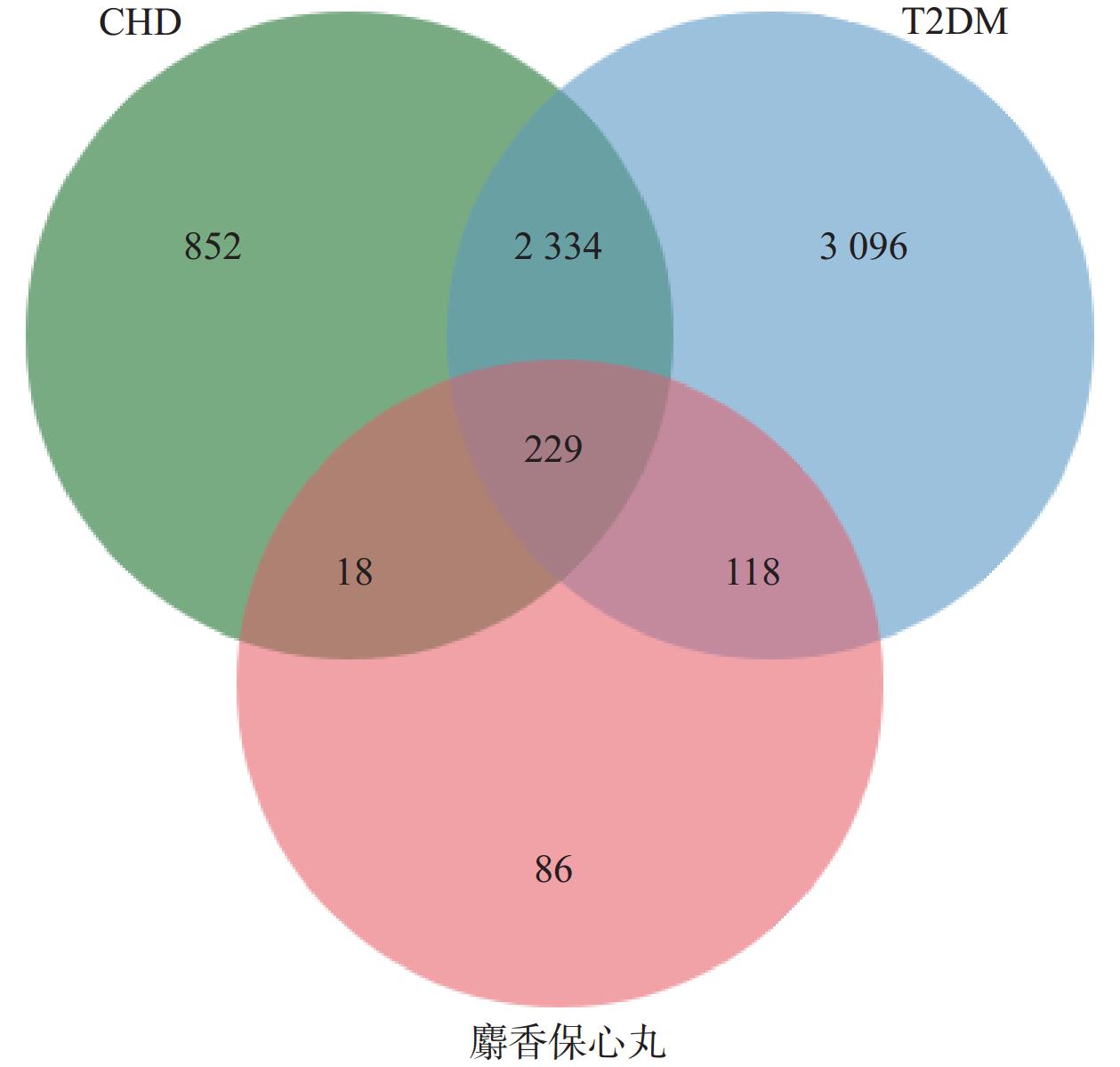
绘制麝香保心丸组方中筛选出的化合物靶点、T2DM相关靶点和CHD相关靶点的Venn图,取三者交集,得到麝香保心丸同时治疗T2DM和CHD的潜在作用靶点。
-
运用Cytoscape 3.8.2软件构建麝香保心丸发挥“异病同治”作用的“药物-成分-靶点”网络图,运用“Network Analyzer”功能进行分析,其中节点代表药物、成分、靶点,边代表药物与成分、成分与靶点之间的关系。
-
运用STRING数据库,导入“药物-疾病”交集靶点,物种限制为“人”,构建PPI网络图,然后将STRING数据库得到的数据导入Cytoscape 3.8.2软件进行网络分析,依据度值筛选出核心靶点。
-
运用DAVID在线数据库导入交集靶点进行GO功能富集分析和KEGG通路富集分析,研究麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD可能靶点的潜在关键生物学过程和相关通路。
-
通过TCMSP、TCMID、ETCM和BATMAN-TCM数据库共检索得到2 535个化学成分,以OB≥20%、DL≥0.1,文献报道具有确切活性的化合物,以及本课题组前期研究鉴定的入血成分,并以BATMAN-TCM中取score≥48;TCMID中取score≥400;ETCM中取score≥0.8,同时将仅有1个成分对应的潜在靶点去除为标准,共筛选出七味中药的108个活性成分,对应451个靶点。
-
在DisGeNET和GeneCards数据库中共检索筛选得到T2DM相关靶点5 777个,CHD相关靶点3 433个。利用Venn图将麝香保心丸预测筛选出的活性成分潜在靶点与疾病靶点作交集,得到麝香保心丸作用于T2DM和CHD的潜在共同靶点229个(图1)。
-
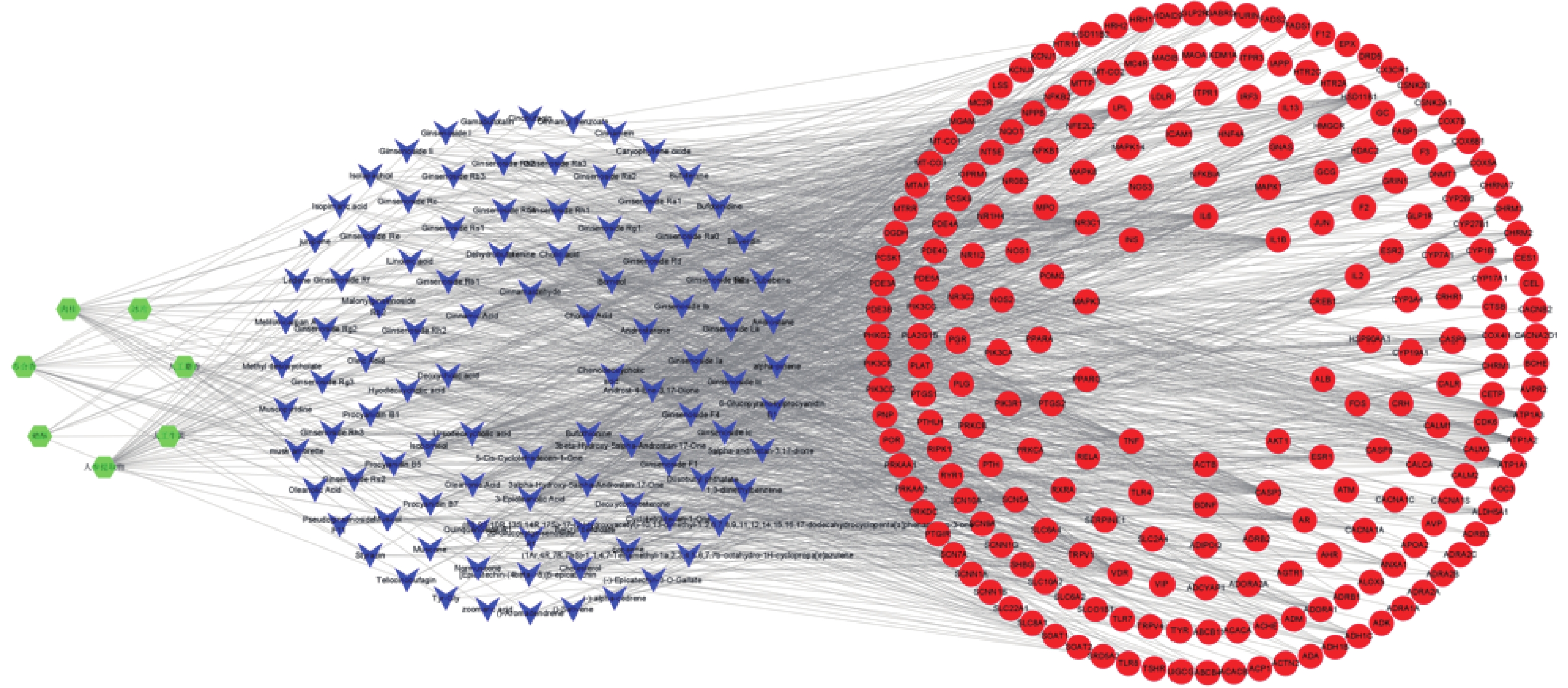
运用Cytoscape 3.8.2软件构建“药物-成分-靶点”网络图,网络中共有337个节点,其中药物7个、活性成分101个、靶点229个。其中绿色代表麝香保心丸组方中的7味中药,蓝色代表活性成分,红色代表作用于疾病的靶点。根据度值大小筛选贡献较大的活性成分,其中鹅去氧胆酸、熊去氧胆酸、肉桂醛、胆汁酸、人参皂苷Rh2、人参皂苷Rb1、肉桂酸等活性成分排名靠前,可能是麝香保心丸发挥治疗T2DM和CHD作用的主要贡献成分(图2)。
-
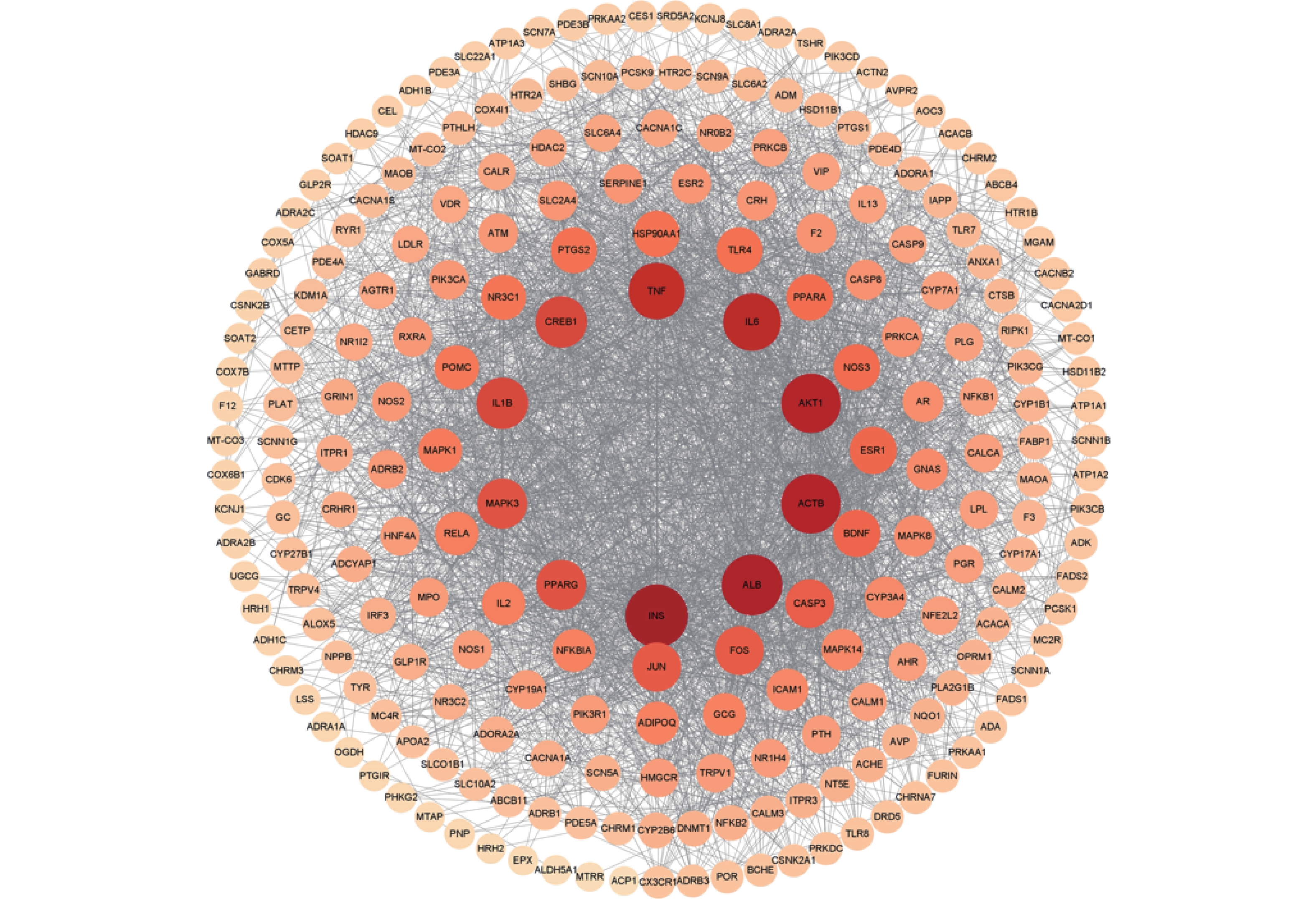
将麝香保心丸229个交集靶点导入STRING数据库中,并利用Cytoscape 3.8.2软件对PPI图进行可视化分析(图3)。根据度值由大到小对节点进行筛选,选取排名前10的潜在核心靶点,分别是胰岛素(INS)、白蛋白(ALB)、蛋白激酶B(Akt1)、白介素-6(IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)、环腺苷酸反应元件结合蛋白1(CREB1)、白细胞介素-1(IL-1β)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶3(MAPK3)、过氧化物酶体增生激活受体γ(PPARG),这些靶点可能是麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD的关键核心靶点。
-
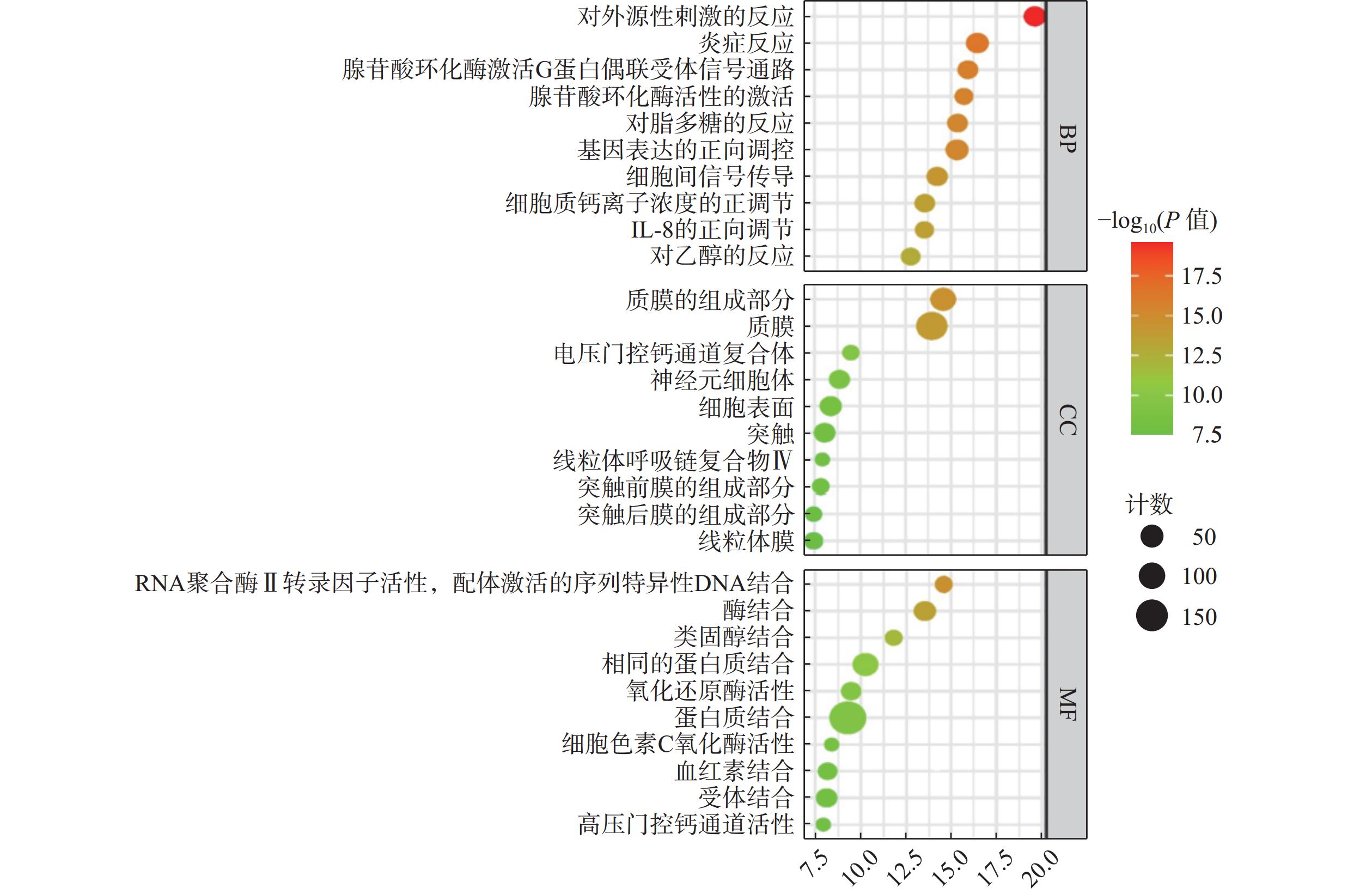
将麝香保心丸229个交集靶点导入DAVID在线数据库进行GO功能富集分析,以P≤0.05为筛选标准,共筛选出生物过程(BP)724条、细胞成分(CC)112条、分子功能(MF)208条,分别选取前10条绘制气泡图(图4)。BP主要涉及对外源性刺激的反应、炎症反应、基因表达的正调控等过程;CC主要涉及质膜、电压门控钙通道复合物、神经元细胞体等过程;MF主要涉及RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录因子活性、配体激活序列特异性DNA结合、类固醇结合、氧化还原酶活性等过程。
-
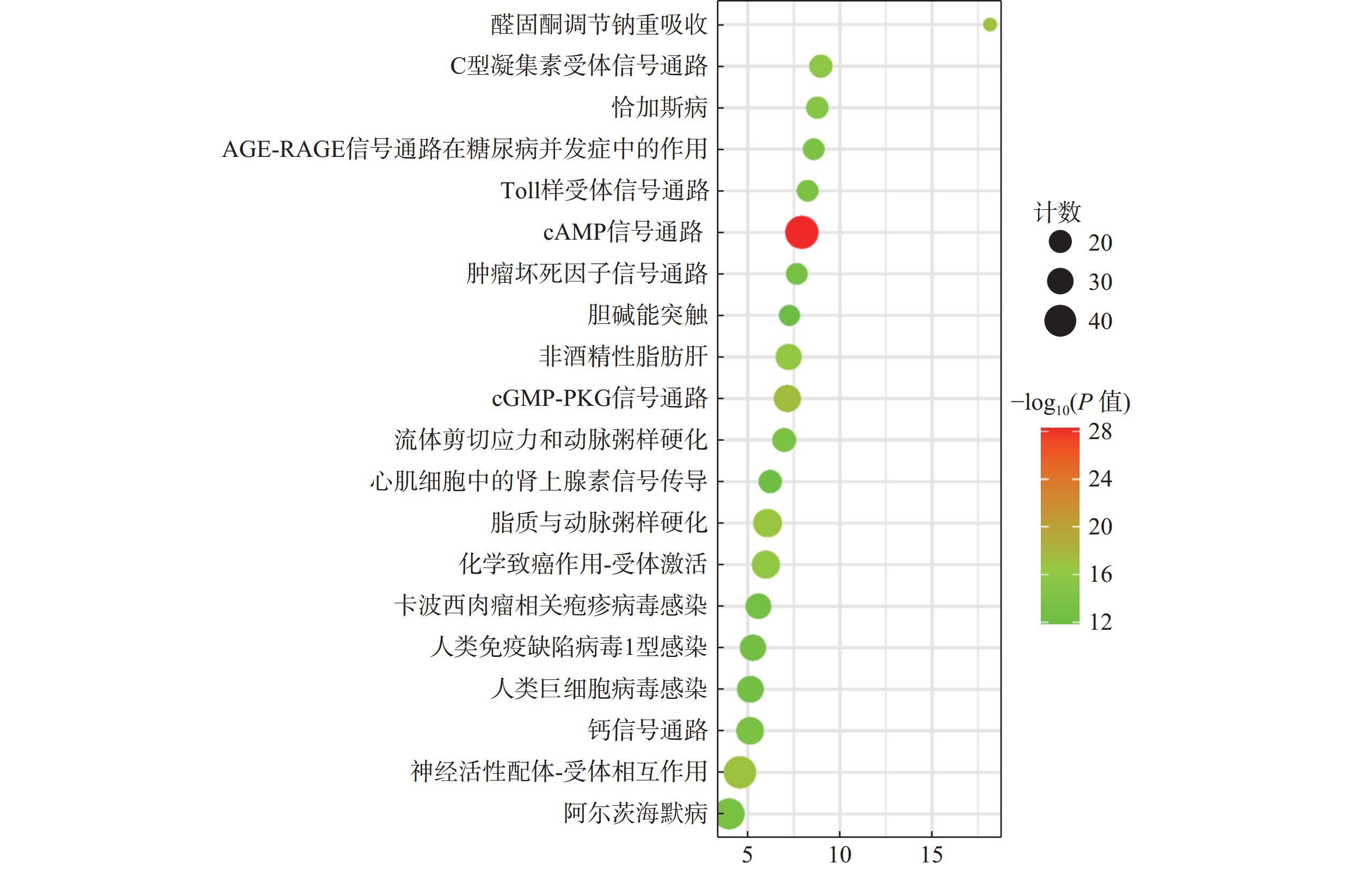
通过KEGG通路富集分析229个交集靶点,以P≤0.05为筛选标准,共得到麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD的188条信号通路,选取排名前20的绘制气泡图(图5)。cAMP信号通路、cGMP-PKG信号通路、糖尿病并发症中的AGE-RAGE信号通路、Toll样受体信号通路、TNF信号通路、钙信号传导通路等可能在麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD中发挥重要作用。
-
中医将以多饮、多食、多尿、身体消瘦为主要特征的T2DM归结为“消渴症”范畴,以气阴两虚和阴虚内热为主要病机[13]。CHD以气虚血瘀为主要病机,虚证多以阳虚、气虚、气阴两虚为主,实证多以气滞血瘀、痰凝寒浊为主[14]。中药复方制剂麝香保心丸作为中医经典名方“苏合香丸”的发展延续,是我国目前最常用的芳香温通类药物,为益气活血剂,临床上广泛应用于治疗心血管疾病[15]。由于T2DM与CHD均有“气阴两虚”表型,故现临床上将麝香保心丸用于治疗T2DM比单用西药进行基础治疗表现出更好的控制血糖、促进心功能恢复、改善糖尿病患者微循环障碍、降低血液粘度等作用[15, 16]。虽然麝香保心丸在治疗T2DM和CHD方面具有良好的临床疗效,但其“异病同治”的作用机制尚不明确。本研究主要运用网络药理学方法,探讨麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的潜在作用机制。
本研究运用网络药理学分析方法共筛选得到麝香保心丸的101个活性成分和“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的共同靶点229个。其中人参总皂苷提取物是麝香保心丸的臣药,文献报道其具有抑制IL-1β等炎性因子的表达[17],调节线粒体能量代谢和糖脂代谢,改善胰岛素抵抗、抑制心肌细胞凋亡[18]的作用,人参皂苷Rg1、Rb1可通过抑制IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α等炎症因子的表达,减轻肝脏损伤和胰岛素抵抗[19] ,缓解心肌损伤[20]。已有研究表明,肉桂提取物可以减少氧化应激,保护胰岛β细胞,增加胰岛素分泌[21],改善血脂异常[22],减轻糖尿病心肌并发症症状。肉桂中的有效成分肉桂醛[23]可通过自噬途径减轻缺氧复氧导致的H9C2心肌细胞的损伤,抑制自噬水平,增强心肌细胞活力。肉桂酸[24]则能通过激活PI3K/Akt/FoxO1信号通路,降低db/db小鼠空腹血糖水平、调节血脂、改善胰岛素抵抗。牛黄中的有效成分熊去氧胆酸可增加肝脏能量消耗、改善线粒体功能和胆汁酸代谢,减少甘油三酯(TG)和FFA,改善糖脂代谢[25]。由此可见,麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD可能是其多个活性成分共同发挥作用的结果。
绘制PPI网络图,根据度值分析得到排名前10的核心靶点,INS、ALB、Akt1、IL-6、TNF、CREB1、IL-1β、MAPK3、PPAGR、ACTB是麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的潜在核心靶点。研究表明,促炎细胞因子和炎症相关核转录因子与胰岛素分泌受损有关,可能会诱导T2DM的发生[26],例如,IL-6被认为可能与胰岛素抵抗和β细胞功能障碍有关[27]。此外,有研究表明,在血管生物学中,IL-6还可能与动脉粥样硬化形成相关的成纤维细胞和内皮细胞分泌有关[28]。因此,抑制IL-6炎症因子的激活能有效改善胰岛素抵抗,缓解动脉粥样硬化。有研究表明,PPARG(即PPARγ)是一种过氧化物酶体增殖受体,是配体激活受体,参与能量稳态调节,其在脂肪组织、脾脏和大肠中的表达最高,主要表现为调节脂肪生成、脂质和葡萄糖代谢以及炎症途径,因此,激活PPARG受体不仅可以改善胰岛素敏感性,还可以调节血管生成[29]。ACTB是一种β-肌动蛋白,是重要的细胞骨架蛋白,可以通过调节内皮NO合酶活性改变NO产生,从而导致内皮功能障碍,这被认为可能是导致CHD的潜在作用机制[30]。同时有研究表明,ACTB是与T2DM风险有关的一种可靠的基因蛋白[31]。由此可见,麝香保心丸通过作用于多个靶点发挥“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的治疗作用。
GO生物功能分析发现,麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的潜在调控生物过程,主要涉及炎症反应、基因表达的正调控、对脂多糖的反应、酶结合、蛋白质结合、受体结合、电压门控钙通道复合物等生物过程。KEGG通路富集分析发现,麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD的通路主要富集在脂质与动脉粥样硬化、糖尿病并发症中的AGE-RAGE信号通路、TNF信号通路、Toll样受体信号通路、cGMP-PKG信号通路等信号通路。晚期糖基化终产物(AGEs)是游离还原性糖和蛋白质、脂质、核酸之间非酶促糖化反应的结果,主要发生于持续高血糖状态的患者体内,属于有害分子,AGEs会与其晚期糖基化终产物受体(RAGE)发生非特异性作用[32],产生氧化应激,导致促炎细胞因子产生和炎症反应,从而干扰细胞内信号,导致胰岛素抵抗[33]。有研究表明,AGE水平升高与动脉壁硬度增加、冠状动脉疾病等心血管风险有关,与T2DM患者冠状动脉粥样硬化的严重程度和心血管事件的发生有关,这主要是因为AGE诱导的血管和心肌蛋白交联会降低血管弹性和心肌灵活性,导致血管壁柔韧性降低,血管和心肌僵硬以及影响细胞内皮功能,最终导致CHD[34]。Toll样受体(TLRs)属于炎症小体,主要有2个亚型:①在其外域中具有多个半胱氨酸簇的TLR(mccTLRs);②在其外域中具有单个半胱氨酸簇的TLR(sccTLRs)[35]。动脉粥样硬化主要是由慢性炎症引起的血管壁结构和功能异常,TLR信号通路的激活参与动脉粥样硬化的炎症过程,其中TLR2和TLR4在动脉硬化过程中上调使CHD进一步加剧[36]。胰岛素抵抗是T2DM的主要症状之一,起因之一是肥胖,脂肪组织分泌各种激素和细胞因子,在代谢应激的作用下,TLR4信号传导的激活会引起免疫细胞释放促炎因子,使脂肪组织中的巨噬细胞聚集极化为M1和M2亚型,导致慢性低度炎症,干扰代谢组织中的胰岛素信号传导,进而发展成T2DM[37]。cAMP是一种单磷酸腺苷,由腺嘌呤、核糖以及磷酸基团组成,是细胞内的第二信使分子。cAMP信号通路主要包括cAMP合成环化酶、降解磷酸二酯酶(PDE)和cAMP效应,主要来源是细胞质膜上的跨膜腺苷酸环化酶(tmACs)和细胞内的可溶性腺苷酸环化酶(sAC),负责激素诱导的肝糖原分解[38],可刺激胰岛素分泌,是胰岛素依赖性cAMP信号通路[39]。蛋白激酶A(PKA)是主要的cAMP效应靶标,cAMP水平升高和PKA激活可调节内皮屏障稳态,促进血管舒张[40]。上述分析结果表明,麝香保心丸发挥治疗T2DM和CHD的作用是方中的多种化学成分作用于多个信号通路的结果,主要涉及氧化应激和炎症反应。
-
“异病同治”治疗思想是中医对《黄帝内经》“同病异治”传统理论的继承与发展,目前临床应用广泛,但相关作用机制尚不明确[41]。本文运用网络药理学方法研究发现,麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的靶点和信号通路主要涉及炎症反应和氧化应激,与目前关于T2DM和CHD的相关作用机制研究相符,证实麝香保心丸通过多成分、多靶点、多通路发挥治疗T2DM和CHD的共同作用。研究结果为麝香保心丸的临床应用及进一步实验验证研究提供了理论依据。
Mechanisms of Shexiang Baoxin Pill in homo-therapy for heteropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease based on network pharmacology
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202305037
- Received Date: 2023-05-22
- Rev Recd Date: 2023-11-23
- Available Online: 2024-04-24
- Publish Date: 2024-04-25
-
Key words:
- Shexiang Baoxin Pill /
- type 2 diabetes mellitus /
- coronary heart disease /
- homo-therapy for heteropathy /
- network pharmacology
Abstract:
| Citation: | ZHU Zifan, WANG Zhicong, XIE Bin, LIU Runhui. Mechanisms of Shexiang Baoxin Pill in homo-therapy for heteropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease based on network pharmacology[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2024, 42(4): 173-180. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202305037 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: