-
抑郁症是一种使人衰弱的精神障碍,其特征是持续情绪低落,对几乎所有活动都失去兴趣或愉悦感,并与疲劳、睡眠障碍、焦虑和神经认知障碍症状有关[1],是全球残疾的第三大原因。抑郁症患者工作低下、具有较高的自杀倾向,严重影响患者的生活,造成沉重的社会经济负担[2]。由于疫情的影响,社会心理健康问题正在急剧增加[3,4]。目前,临床上使用的大多数抗抑郁药都具有耐药性,并伴有各种不良反应。因此,寻找安全性更高、不良反应更少的抑郁症治疗方法具有重要意义。既往研究表明,炎症反应在抑郁症中起着至关重要的作用[5]。抑郁症患者血液及额叶皮层中的促炎细胞因子增加[6,7]。抗炎治疗可以产生抗抑郁作用,而抗抑郁药可以减弱抑郁症中促炎细胞因子的表达[8,9]。因此,抑制神经炎症是治疗抑郁症的重要方向。
百合知母汤是中国东汉张仲景医典《金匮要略》中记载的一种经典中药方剂,用于治疗“百合病”[10]。中医“百合病”被认为与现代抑郁症的表现具有较高的相似性[11]。目前,百合知母汤在中医临床上被广泛用于治疗抑郁症[12]。药理学研究表明,百合知母汤在动物模型中具有显著的抗抑郁作用[13]。然而,百合知母汤治疗抑郁症的作用机制并未完全明了。前期研究发现百合知母汤能够通过抑制CUMS抑郁模型小鼠的神经炎症,降低海马IL-1β、 IL-6和TNF-α等促炎细胞因子的表达,来发挥抗抑郁作用[14]。鉴于NLRP1炎症小体在炎症反应过程中的重要的作用[15],且最近研究发现NLRP1炎症小体在抑郁症的发展过程中扮演重用角色[16]。该研究基于NLRP1炎症小体的活化,对百合知母汤的抗抑郁作用进行进一步的探索。
-
取百合药材400 g、知母药材200 g,浸泡0.5 h后,加10倍量水,煎煮两次,每次2 h,煎液过滤后,将两次滤液混合并浓缩至600 ml。
-
Muramyl dipeptide(MDP)购自Sigma-Aldrich公司;IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α、5-HT、NE、DA试剂盒和ELISA试剂盒均购自美国R&D公司;BSA购自美国Sigma-Aldric公司;去离子水采用Milli-Q纯水机制备(Millipore公司);NLRP1、ASC、caspase-1、BDNF、TrkB、ERK、AKT、mTOR、β-actin等抗体均购自 Cell Signaling公司; BCA蛋白测定试剂盒与RIPA裂解液购自碧云天公司。
-
雄性C57BL/6J小鼠8周龄,体质量22 g~25 g,购自浙江维通利华实验动物技术有限公司,生产许可证: SCXK(浙)[2019-0001]。所有小鼠均在标准条件下饲养(12 h光/暗循环,温度:22 ℃~24 ℃,湿度:55%±10%),在整个实验过程小鼠自由摄取食物和水。实验前对所有小鼠进行适应性喂养1周。该研究经上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院伦理委员会审批通过,实验操作严格按照动物福利和伦理原则进行。
-
CUMS造模过程参考前期研究,通过给予小鼠不同刺激构建抑郁症模型小鼠,主要过程如下:①禁食24 h;②禁水 24 h;③空瓶刺激 1 h;④昼夜照明 24 h;⑤笼子倾斜45◦ ,24 h;⑥潮湿垫料24 h;⑦摇笼30 min;⑧夹尾1 min;⑨冰水游泳5 min。小鼠每天接受不同的应激,持续5周。
-
根据前期研究[14],百合知母汤给药采用6 g生药量/kg(相当于百合4 g,知母2 g)和12 g生药量/kg(相当于百合8 g,知母4 g)两个剂量。将30只雄性C57BL/6J小鼠随机分为5组(n=6):对照组、模型组、百合知母汤低剂量组(百合知母汤,6 g/kg,i.g.)、百合知母汤高剂量组(百合知母汤,12 g/kg,i.g.)、百合知母汤+MDP组(百合知母汤,12 g/kg,i.g.;MDP,脑立体定位注射)。除对照组外,各组小鼠接受CUMS刺激,持续5周,对照组被放置在不受干扰的笼子里。从第6周开始,给药组按剂量通过灌胃给予百合知母汤浓缩液,1次/d,持续4周。模型组小鼠给予等量的蒸馏水。为考察NLRP1在百合知母汤抗抑郁过程中的重要作用,设立百合知母汤+MDP组,给药前接受脑立体定位注射NLRP1激活剂MDP,过程如下:经异氟烷麻醉的小鼠俯卧位固定于脑立体定位仪上,将眼中线靠后 2~3 cm 处用 75% 乙醇消毒、剪皮露出头骨,用注射器针头将头骨表层骨膜轻挑剥离,前后囟在同一水平,暴露前囟(冠状缝)。选择小鼠双侧海马CA1 区为注射位置,进针 1.6 mm 至海马区,注射MDP,剂量5 mg/kg,结束后使用可吸收缝合线进行无菌缝合。
-
每只小鼠置于单独的笼子里孤养,放置2瓶含有1%蔗糖溶液,进行24 h的适应。然后其中一瓶蔗糖溶液用蒸馏水代替,进行另一次24 h的适应。随后禁水、禁食 24 h。最后,放置2个预先称重的含有1%蔗糖溶液或蒸馏水的瓶子。3 h后,记录蔗糖溶液消耗量和水消耗量,计算蔗糖偏好指数。
-
用胶带固定每只小鼠的尾部,头部向下,离台面50 cm。在实验过程中,将小鼠隔开以避免互相干扰。记录6 min内小鼠的累计不动时间。
-
在室温下,将每只小鼠分别放入直径12 cm的塑料桶中,桶中装满25 cm深的水。在正式实验前24 h,进行15 min的预游泳适应训练。记录5 min内小鼠的累计漂浮不动时间。
-
将小鼠单独放置在敞箱装置中,给予6 min的自由探索时间,使其适应,然后记录其4 min内穿越的格子数。
-
各组小鼠用10%(w/v)水合氯醛深度麻醉。迅速取脑,置于冰上。分离海马,液氮预冷冻,于−80 ℃下储存,分析用。检测时,取海马,加入磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS:137 nmol/L NaCl、2.7 nmol/L KCl、10 nmol/L Na2HPO4、1.8 nmol/L KH2PO4),于冰上匀浆,4 ℃下以
12000 r/min,离心10 min,收集上清液。使用ELISA试剂盒检测小鼠海马中的炎症因子水平。IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α、5-HT、NE 和DA的水平,操作均按照说明书进行。 -
迅速取小鼠大脑放置冰上,分离海马,用液氮预冷冻,并在−80 ℃下储存。使用冷冻切片机将海马组织切成5 μm的切片。切片用PBS缓冲液洗涤2次。然后用含0.5% Triton X-100的PBS 缓冲液透化,并用0.5% BSA固定,加入一抗,4℃,孵育过夜。加入荧光素标记的二抗孵育(室温,1 h)。通过荧光显微镜对切片成像。
-
取小鼠海马组织,加入含1%蛋白酶抑制剂的RIPA裂解液,于冰上研磨,在4℃下,
12000 r/min,离心10 min。收集上清液,用BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒测定蛋白浓度后,用10%十二烷基硫酸钠/聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)分离总蛋白,分离后转移到聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)膜上,用5%牛血清白蛋白(BSA)在室温下封闭2 h,随后孵上一抗,4 ℃,孵育过夜。过夜后用TBST洗涤3次,每次洗涤10 min。然后与辣根过氧化物酶标记的二抗孵育1 h,TBST洗涤3次,每次10 min。最后使用ECL显影液进行显影。 -
使用GraphPad Prism 8.0(GraphPad Software,USA)进行统计分析。数据以平均值±标准差(SD)表示。使用单向方差分析和Tukey HSD检验评估各组之间的差异。P<0.05的显著性水平被认为是统计学显著性的指示。
-
为了评估百合知母汤的药理作用,首先进行糖水消耗实验、悬尾实验、强迫游泳实验和旷场实验,观察百合知母汤对CUMS小鼠行为学的影响。如图1所示,与对照组相比,CUMS模型组在糖水消耗实验中的蔗糖消耗百分比和旷场实验中的格子穿越数显著减少(P<0.01,P<0.05),而悬尾实验和强迫游泳实验的不动时间显著增加(P<0.01)。而百合知母汤能显著提高这些参数(P<0.05,P<0.01),并呈明显的剂量依赖性。表明百合知母汤能改善抑郁小鼠的行为学特征。值得注意的是,NLRP1炎症小体激活剂MDP能够显著的逆转百合知母汤对抑郁症小鼠行为学的作用(P<0.05,P<0.01),提示百合知母汤通过抑制NLRP1炎症小体活化来发挥抗抑郁作用。
-
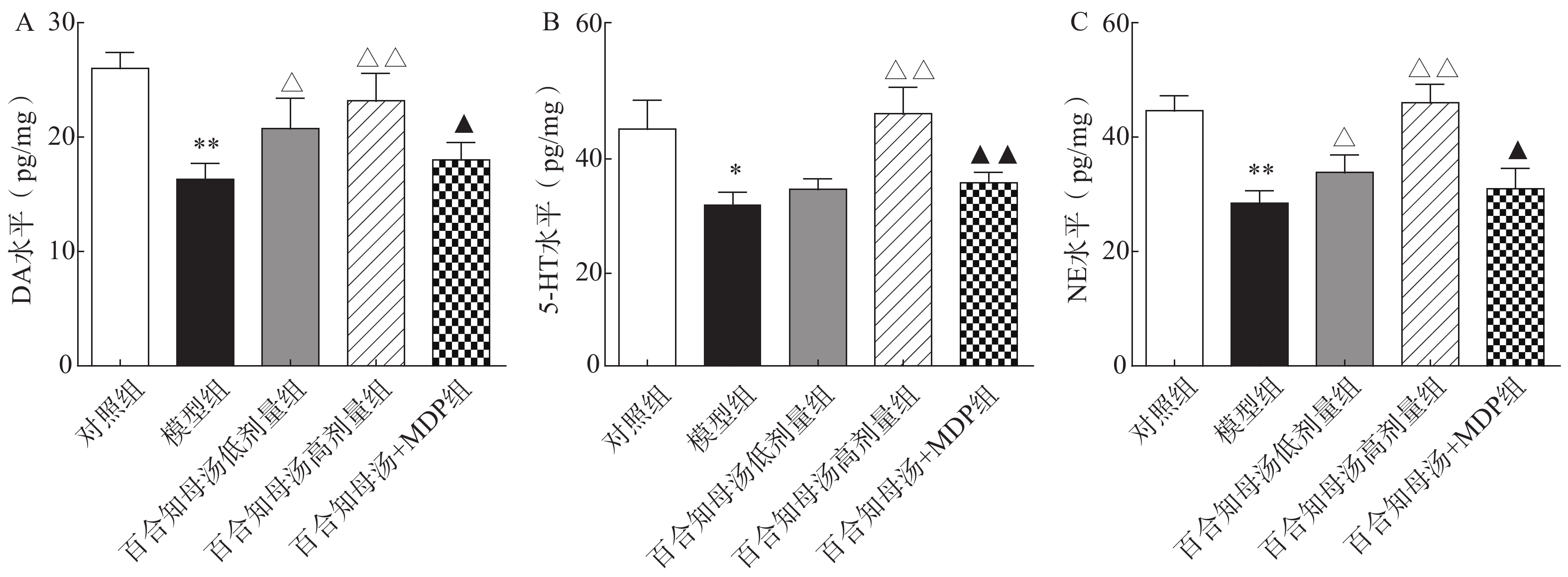
中枢神经系统单胺类神经递质水平降低与抑郁症的产生具有密切关系。图2结果表明,CUMS模型组的DA、5-HT、NE水平与对照组相比显著降低(P<0.05,P<0.01),而CUMS+BZD6组和CUMS+BZD12组上述神经递质的含量明显高于模型组(P<0.05,P<0.01)。NLRP1激活能够显著的逆转百合知母汤对上述神经递质的影响(P<0.05,P<0.01)。
-
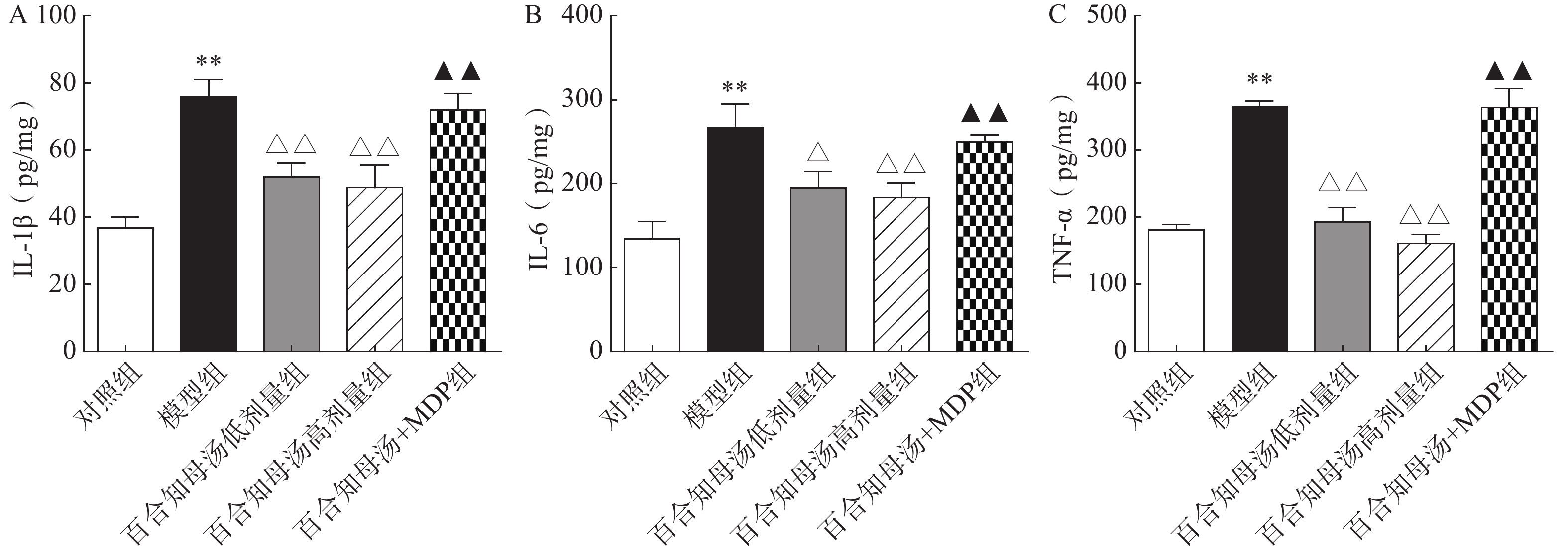
越来越多的研究表明炎症在抑郁症的病因中起着关键作用。因此,用ELISA法测定了几种关键的促炎细胞因子。如图3所示,与对照组相比,CUMS模型组小鼠海马中的IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平显著升高(P<0.01),而百合知母汤显著抑制了由CUMS引起的这些炎症因子的升高(P<0.05,P<0.01),NLRP1激活剂MDP能够显著的逆转百合知母汤对上述神经递质的影响(P<0.01)。
-
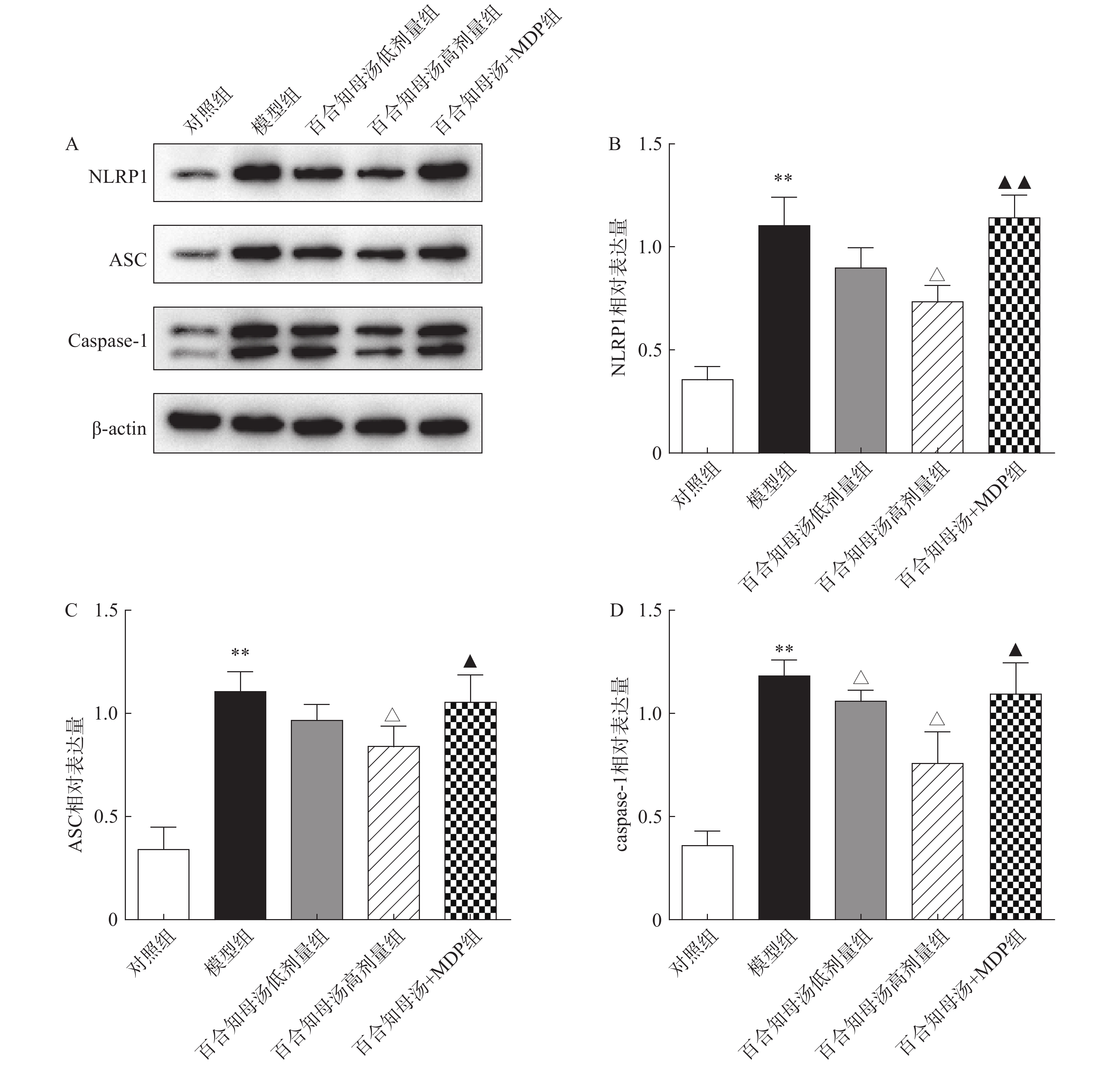
NLRP1炎症小体在神经炎症相关疾病中扮演重用角色,NLRP1炎症小体的活化能促进各种炎症因子的产生[17]。因此,采用Western blot检测NLRP1炎症小体的活化。图4结果显示,CUSM刺激显著增加了NLRP1、ASC和caspase-1的蛋白表达(P<0.01),表明NLRP1炎症小体在CUSM抑郁模型中被激活。而百合知母汤显著抑制了由CUMS引起NLRP1、ASC和caspase-1表达升高(P<0.05)。表明百合知母汤能抑制NLRP1炎症小体的激活。值得注意的是,NLRP1激活剂MDP能够显著逆转百合知母汤对上述蛋白表达的抑制作用(P<0.05,P<0.01),进一步表明百合知母汤通过抑制NLRP1炎症小体活化来发挥抗神经炎症的作用。
-
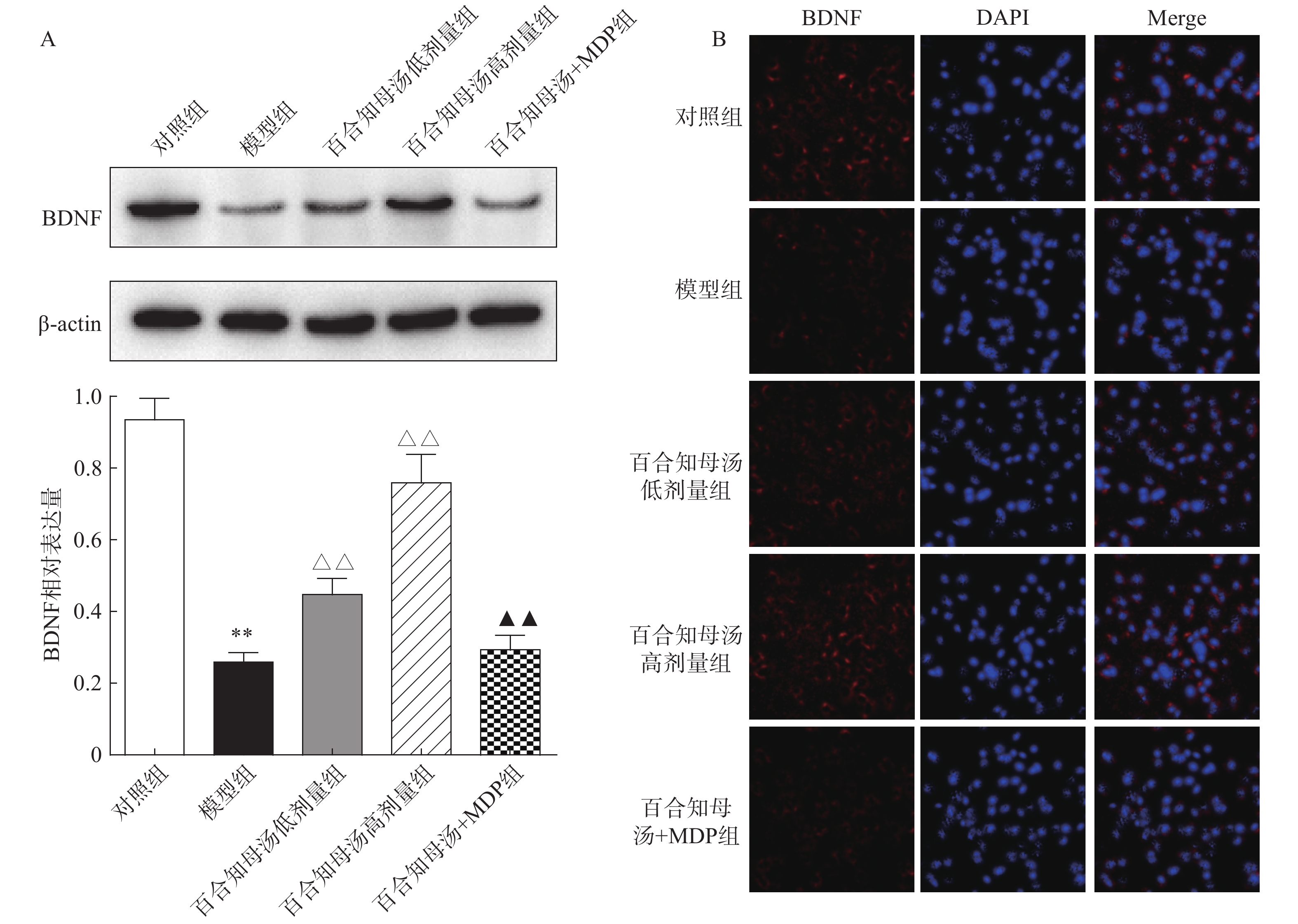
由于BDNF与抑郁症的发生发展密切相关[18],通过Western blot检测BDNF在不同组小鼠海马中的表达(图5A)。与对照组相比,CUMS模型组小鼠海马表达BDNF水平显著降低(P<0.01),而百合知母汤以量效依赖方式显著上调BDNF表达水平(P<0.01)。MDP能够显著阻断百合知母汤对BDNF表达水平的作用(P<0.01)。
随后,用免疫荧光对小鼠海马的BDNF表达进行检测(图5B)。结果发现,与对照组相比,CUMS模型组小鼠海马表达BDNF水平显著降低,而百合知母汤治疗组BDNF表达水平显著上调。NLRP1激活剂MDP能够显著的逆转百合知母汤对BDNF表达水平表达的上调作用。
-
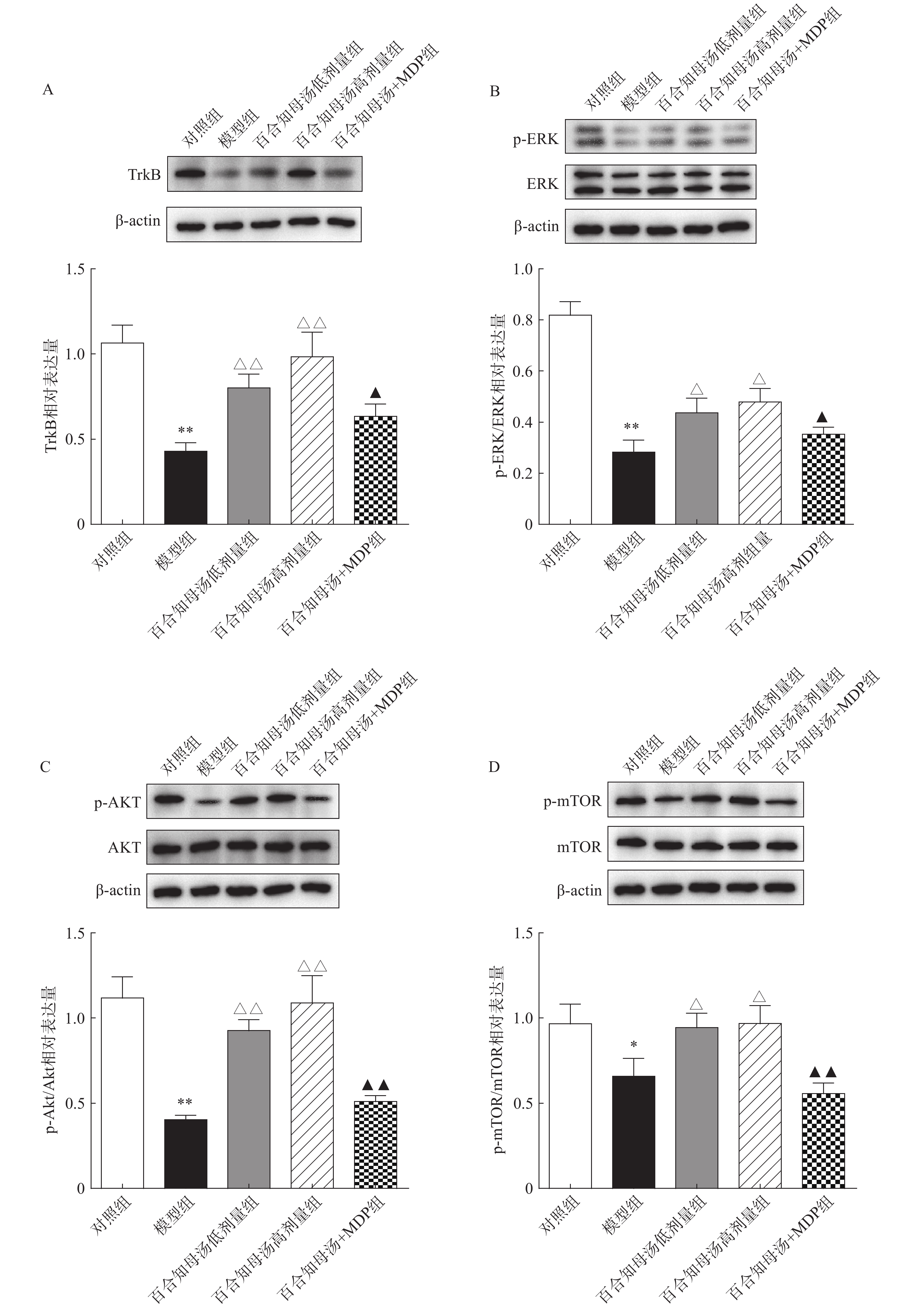
BDNF能够与TrkB结合,从而激活AKT/mTOR级联反应,最终通过调节突触蛋白合成和细胞骨架发育来增强树突的复杂性[19]。因此,继续探讨百合知母汤对TrkB及下游ERK/AKT/mTOR通路关键蛋白表达的影响。百合知母汤对小鼠海马TrkB表达的影响如图6A所示。与对照组相比CUMS模型组小鼠海马TrkB的表达显著降低(P<0.01),百合知母汤给药组小鼠海马TrkB的表达水平显著升高(P<0.01)。而MDP能够逆转百合知母汤对TrkB表达水平的上调作用(P<0.05)。
如图6B-D所示,与对照组相比,CUMS组小鼠海马ERK、AKT和mTOR的磷酸化水平显著降低,而百合知母汤给药可显著促进抑郁小鼠ERK、AKT和mTOR的磷酸化水平(P<0.05,P<0.01)。NLRP1激活剂MDP能够显著的逆转百合知母汤对上述蛋白磷酸化水平的促进作用(P<0.05,P<0.01)。
-
神经炎症是一种对组织损伤的先天免疫反应,在许多中枢神经系统疾病中发挥着重要作用,被认为与抑郁症的发生发展息息相关[20, 21]。大量证据表明,海马体的神经炎症对抑郁和焦虑障碍的发展至关重要。神经性疼痛诱导的抑郁样行为的发作与海马TNF及其受体TNFR1水平的增加相关[22]。敲减海马中IL-1β可以减轻LPS诱导的小鼠焦虑和抑郁样行为[23]。而给予IL-1受体拮抗剂可以改善神经性疼痛对抑郁样行为的影响[24]。以上研究结果表明,海马神经炎症在抑郁症的病理过程中起着重要作用。
炎症小体是先天免疫反应的关键成分,据报道与炎症相关神经系统疾病的机制有关[25]。NLRP1炎症小体由受体蛋白NLRP1、衔接蛋白ASC和效应蛋白caspase-1组成,在神经炎症相关疾病中起重要作用。NLRP1可被多种刺激激活,包括炭疽杆菌致死毒素、弓形虫、胞壁酰二肽、宿主细胞内ATP耗竭等[21]。NLRP1炎症小体的激活导致Caspase-1的直接成熟,随后诱导促炎细胞因子(如IL-1β和IL-18)的产生,从而触发神经炎症反应[26]。据报道,NLRP1炎症小体驱动的炎症途径与许多神经系统疾病有关,如脑损伤、神经退行性疾病、伤害感受和癫痫[27]。
百合知母汤抗抑郁作用及其机制既往已有研究[13,14],然而基于NLRP1炎症小体的活化对其抗抑郁机制的研究未见报道。该研究旨在通过探讨百合知母汤对NLRP1炎症小体的活化作用来阐释百合知母汤抗抑郁的作用机制。结果显示,百合知母汤抑制了CUMS抑郁症小鼠海马NLRP1、ASC和Caspase-1的表达升高。表明百合知母汤能够抑制NLRP1炎症小体的活化。为了证实百合知母汤通过NLRP1/Caspase-1通路发挥抗抑郁作用,采用NLRP1激活剂MDP注射抑郁症小鼠。结果发现,MDP逆转了百合知母汤对CUMS小鼠的抑郁样行为和神经炎症的改善作用。因此,百合知母汤可能通过抑制NLRP1炎症小体的活化,以调节抑郁症小鼠的神经炎症反应,来发挥抗抑郁作用。
BDNF属于神经营养因子家族,在神经的生成、发展和功能维持中起着至关重要的作用[28]。大量研究表明,BDNF与抑郁症的病理生理学和抗抑郁疗效有关[29]。研究发现,抑郁症动物和患者以及抑郁症受试者的尸检样本中,大脑BDNF水平降低[28, 30]。此外,给予LPS或促炎细胞因子可显著降低海马和大脑皮层的BDNF水平[31]。这表明炎症会影响BDNF的表达。抗抑郁药物治疗可以有效改善抑郁症引起的BDNF含量的降低,进一步促进神经发生,增强神经可塑性,并起到抗抑郁的作用[32]。研究发现,BDNF的释放以及与TrkB的结合能够触发多种下游信号级联,包括RAS/MAPK通路和PI3K/AKT通路,这些信号通路与抑郁症的发生发展密切相关[33]。慢性应激可抑制ERK信号的传递,抗抑郁治疗则可逆转这种抑制[34],表明ERK信号阻断会导致抑郁和焦虑行为。这与抑郁症患者的尸检报告一致[35]。此外,慢性应激还会导致内侧前额叶皮层锥体神经元的树突形态发生变化,具体表现为树突回缩和树突棘丢失[36]。而抗抑郁治疗可以通过AKT/mTOR途径逆转这一现象,并有效改善小鼠的抑郁样症状[37]。上述研究表明,BDNF与TrkB结合,进而通过ERK和AKT/mTOR信号通路引发的信号级联反应可能是抗抑郁药物发挥治疗作用的关键分子机制。本研究结果显示,百合知母汤能显著促进抑郁症小鼠海马BDNF和TrkB的表达水平,表明百合知母汤能上调BDNF/TrkB信号通路。同时,百合知母汤能显著促进RK、AKT和mTOR的磷酸化水平。表明百合知母汤能同时激活下游的ERK/AKT/mTOR信号通路。而采用NLRP1激活剂MDP活化NLRP1炎症小体后,百合知母汤对BDNF/TrkB信号通路和ERK/AKT/mTOR信号通路上调作用被显著逆转,表明百合知母汤通过抑制NLRP1炎症小体活化,激活BDNF/TrkB信号通路和ERK/AKT/mTOR信号通路。
综上所述,百合知母汤通过抑制NLRP1炎症小体活化,抑制CUMS抑郁症小鼠海马的神经炎症反应,进而激活BDNF/TrkB信号通路和ERK/AKT/mTOR信号通路来改善CUMS小鼠的抑郁样行为。
Exploration of the antidepressant mechanism of Baihe Zhimu decoction based on NLRP1 inflammasome
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202401033
- Received Date: 2024-01-15
- Rev Recd Date: 2024-03-26
- Available Online: 2024-08-22
- Publish Date: 2024-08-25
-
Key words:
- Baihe Zhimu decoction /
- Depression /
- Inflammatory response /
- NLRP1 inflammasome /
- BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway
Abstract:
| Citation: | YUE Chunhua, BEN Yongguang, WANG Haiqiao. Exploration of the antidepressant mechanism of Baihe Zhimu decoction based on NLRP1 inflammasome[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2024, 42(8): 325-333. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202401033 |







 本站查看
本站查看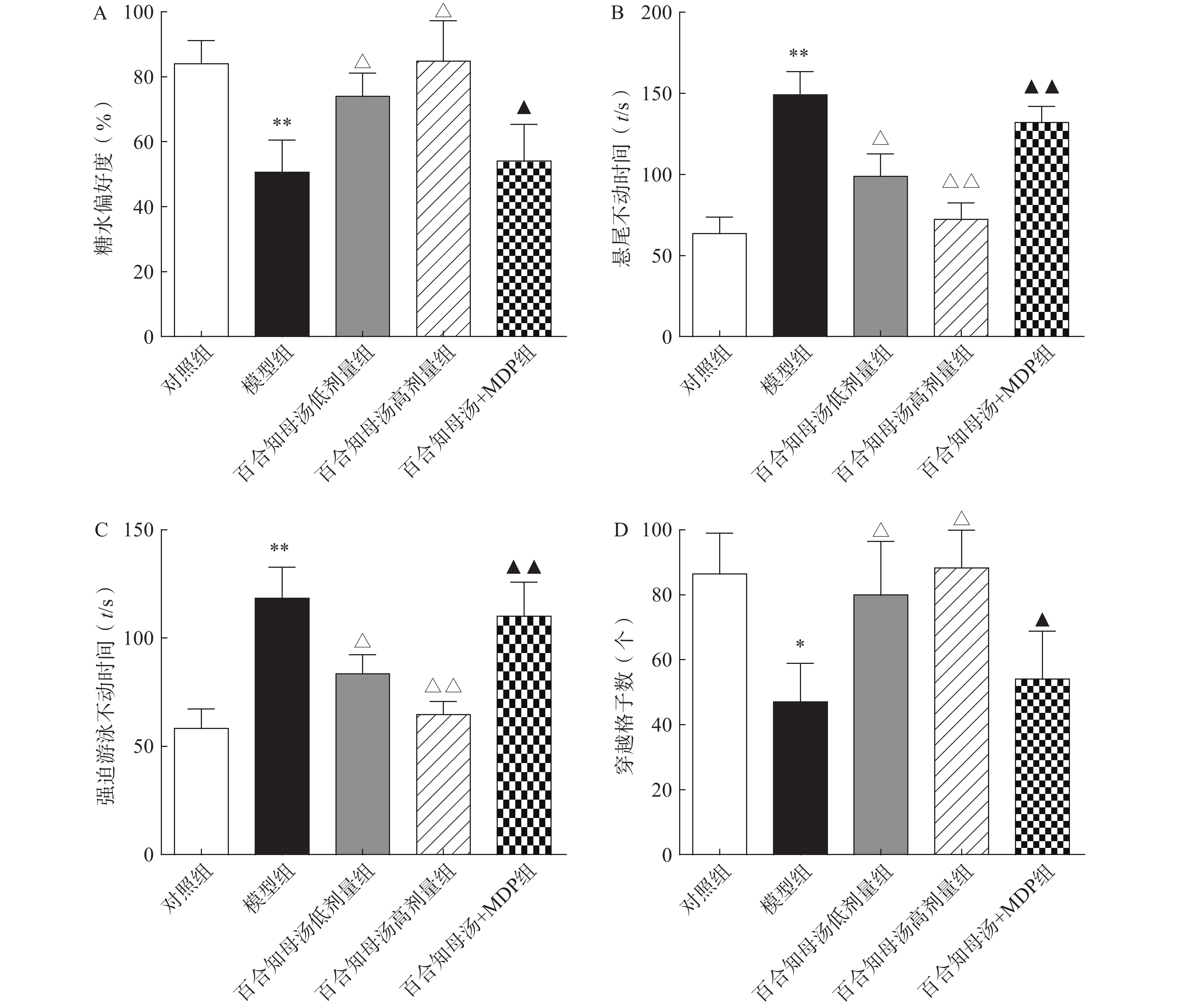


 DownLoad:
DownLoad: