-
川芎Rhizoma Chuanxiong为伞形科植物川芎Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort.的干燥根茎[1],最早记载于《神农本草经》,有活血行气,祛风止痛的功效,是中医临床上最常用的药材之一,在活血化瘀类成方制剂中占有重要地位。
现代药理学表明,川芎含有多种药理活性成分,主要包括苯酞类化合物(如藁本内酯)、酚类和有机酸类(如阿魏酸)、生物碱类(如川芎嗪)、多糖类等,其中苯酞类化合物广泛的应用于治疗心脑血管系统和神经系统疾病,主要成分存在于川芎挥发油中,其含量占挥发油总质量的80%以上。川芎挥发油除含有苯酞类化合物,还含有烯萜醇、脂肪酸类化合物,近年来随制剂工艺的发展,川芎药材以挥发油入药已经比较常见,在制剂工艺方面,不同的提取工艺获得的川芎挥发油含量与成分不同,药效也会有差异[2-8]。川芎挥发油的常见提取方法主要有经典的水蒸气蒸馏法和近年来快速发展的超临界流体萃取技术(supercritical fluid extracation, SFE),本研究分别采用水蒸气蒸馏法和超临界CO2萃取法两种常用工艺对川芎药材中挥发油类成分进行提取,并对提取成分进行比较,旨在为不同药效中药制剂中川芎有效成分的提取工艺研究提供参考。
-
川芎药材(都江堰市伦洋中药材种植农民专业合作社,批号:Z02031-190201);乙酸乙酯(色谱纯,美国TEDIA试剂有限公司);无水硫酸钠(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司);CO2为医用级;水为重蒸馏水。
-
WF-20B高速万能粉碎机(江阴市海鑫药化机械制造有限公司);HA420-40-96型超临界萃取装置(南通市华安超临界萃取有限公司);挥发油测定器(天长市天沪分析仪器有限公司);智能数显加热套(上海豫康科教仪器设备有限公司);Thermo Fisher ITQ1100气相色谱-质谱联用仪(美国赛默飞世尔公司)。
-
取川芎药材粉碎品(过一号筛)200 g,置5 000 ml圆底烧瓶中,加入2 000 ml蒸馏水、少许碎瓷片,充分混匀后于室温浸泡2 h,按《中国药典》2015版四部通则2204挥发油测定法甲法进行。提取完成后分取油层,无水硫酸钠干燥离心,转移挥发油置棕色瓶中密封,4 ℃保存。
-
取川芎药材粉碎品(过一号筛)1 000 g,置萃取釜中,萃取条件为:萃取压力35 MPa,流体温度40 ℃,萃取1.5 h。萃取完成后从出料口放出挥发油,转移挥发油置棕色瓶中密封,4 ℃保存。
-
InertCap 5MS/NP熔融石英毛细管色谱柱(30 m×0.25 mm, 0.25 μm);载气氦气;程序升温,初始温度60 ℃,保持1 min,5 ℃/min升温至100 ℃,3 ℃/min升温至160 ℃,保持2 min,10 ℃/min升温至280 ℃,保持2 min;进样口温度280 ℃;分流比30:1;传输线温度280 ℃;进样量1.0 μl,体积流量1.0 ml/min;离子源温度220 ℃;溶剂延迟4 min;EI源电离方式;电子能量70 eV;质量扫描范围m/z 50-400;质谱检索数据库NIST 11。
-
精密移取挥发油提取物样品25 μl置于25 ml量瓶中,加入乙酸乙酯至刻度,摇匀,作为供试品溶液,吸取1.0 μl注入GC-MS联用仪进行分析。
-
按照水蒸气蒸馏和超临界CO2萃取法提取挥发油后,根据得油量和药材量计算两种提取方法的挥发油得率分别为0.35%和4.8%。
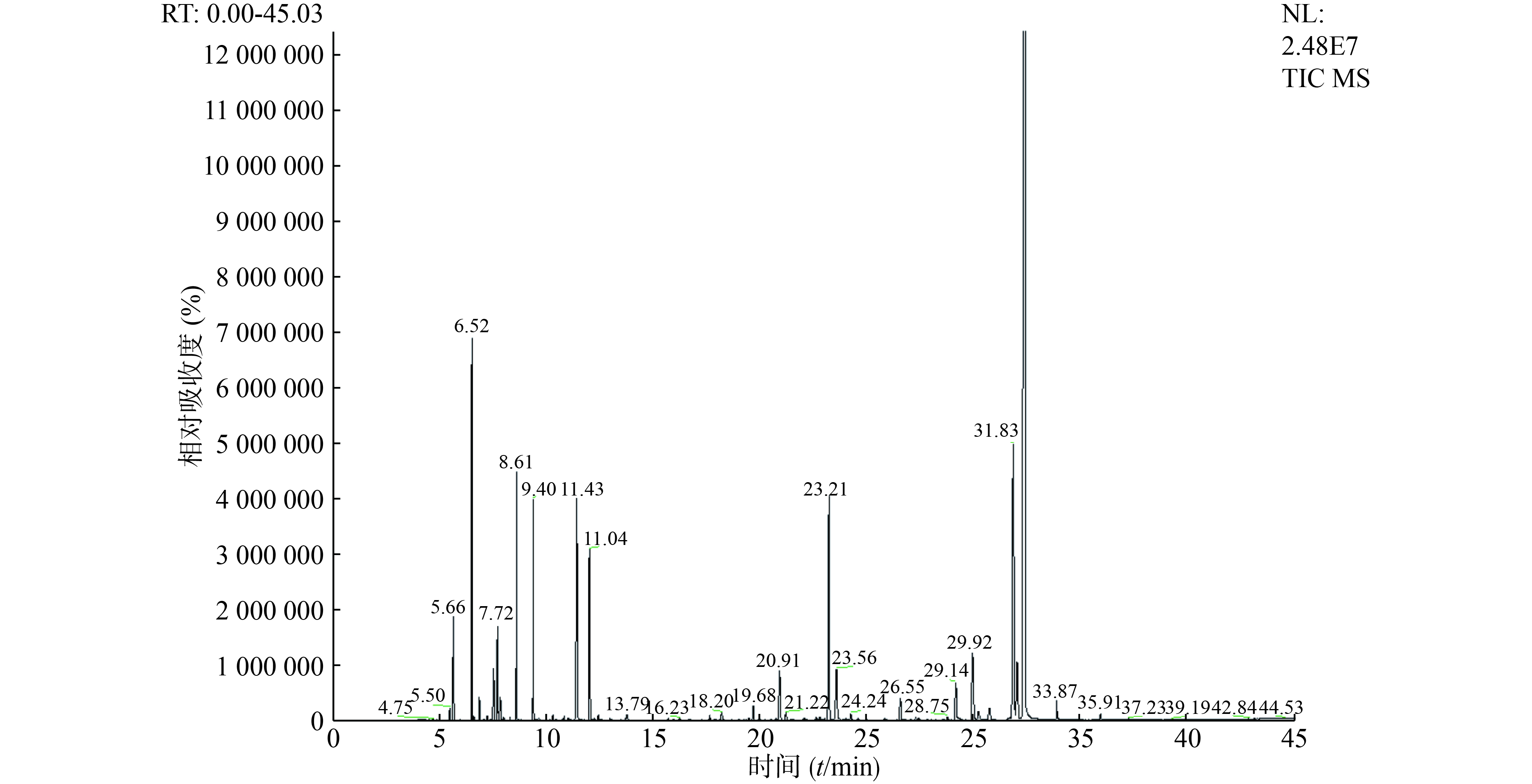
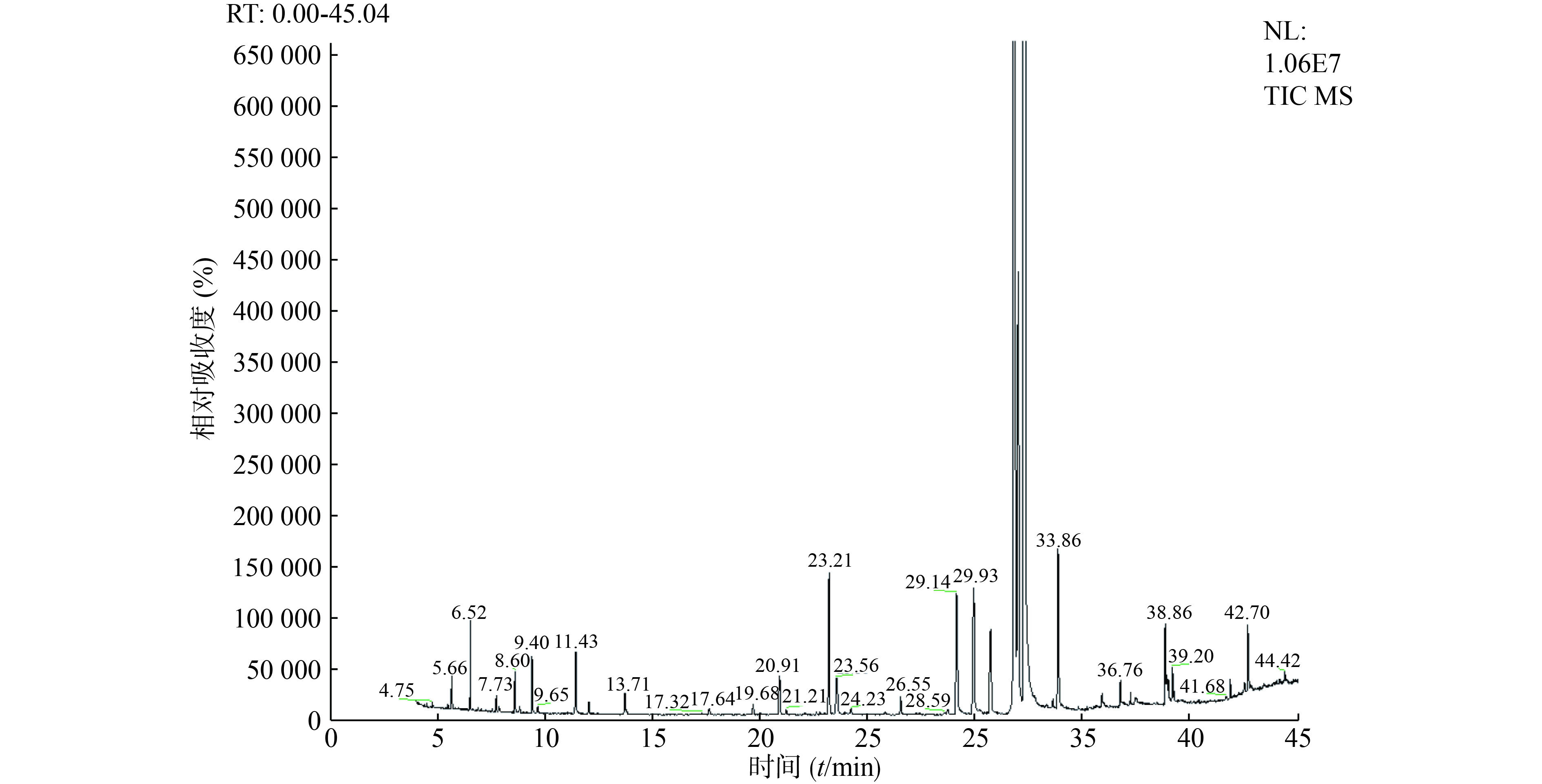
采用GC-MS联用技术对两种提取工艺所得的挥发油提取物进行分析,利用质谱检索数据库和相关文献资料[9-12],对挥发油中相对含量较大,与相邻峰分离度良好的主要色谱峰进行了分析,确定了18个主要成分,其峰面积总和占总峰面积的95%以上,结果见表1和图1、2。水蒸气蒸馏提取物中苯酞类成分约占61%,单萜类成分约占25%,倍半萜类成分约占10%;超临界CO2萃取物中苯酞类成分约占97%,单萜类成分约占1%,倍半萜类成分约占0.4%。两种提取工艺的挥发油中Z-藁本内酯含量最高,其次是洋川芎内酯A、丁烯基苯酞和丁基苯酞。
序号 TR/min 化合物 分子式 相对含量(%) 水蒸气蒸馏 超临界CO2萃取 1 5.66 α-蒎烯 C10H16 1.48 0.09 2 6.52 β-蒎烯 C10H16 5.70 0.30 3 7.71 邻伞花烃 C10H14 1.63 0.05 4 8.60 α-松油烯| C10H16 3.99 0.14 5 9.40 4-甲基-3-(1-甲基亚乙基)-1-环己烯 C10H16 3.66 0.21 6 11.43 1,3,5-十一碳三烯 C11H18 5.04 0.30 7 12.02 4-松油醇 C10H18O 3.56 0.05 8 20.91 4-异丙基-1,6-二甲基-1,2,3,4,4α,7-四氢化萘 C15H24 1.31 0.22 9 23.21 γ-古芸烯 C15H24 6.11 0.85 10 23.56 β-马榄烯 C15H24 2.14 0.34 11 26.56 桉油烯醇 C15H24O 0.66 0.11 12 29.15 丁基苯酞 C12H14O2 1.31 0.89 13 29.93 丁烯基苯酞 C12H12O2 2.32 0.97 14 30.73 6-丁基-1,4-环庚二烯 C11H18 0.45 0.60 15 31.83 洋川芎内酯A C12H16O2 9.53 25.60 16 32.02 - - 1.97 2.95 17 32.33 Z-藁本内酯 C12H14O2 45.40 65.59 18 33.86 E-藁本内酯 C12H14O2 0.49 0.75 注:-表示未鉴定 -
水蒸气蒸馏法是一种传统的挥发油提取工艺,对川芎药材中挥发性较强的成分如单萜和倍半萜类保留相对较强,适合低沸点、极性小的成分提取,且提取工艺对设备的要求不高,生产成本较低,在中药制剂工业上广泛应用,但是其挥发油提取率会相对较低。超临界CO2萃取法操作简单快速,基本2 h可完成提取过程,对川芎挥发油提取收率高,尤其对苯酞类有效成分的提取率相对较高,适合高沸点极性成分的提取,对环境及萃取产物无污染,便于提取工艺产业化。两种工艺的挥发油在成分上有一定的差异,因此在川芎挥发油入药的中药制剂工艺中,应根据制剂的功效充分考虑提取工艺对有效成分的影响,在适应证药效学研究的基础上分析不同工艺得到的挥发油的药效学和毒理学差异,而针对性的选择合适的提取工艺显得尤为重要。
Comparative study on volatile oil in Rhizoma chuanxiong by steam distillation and supercritical fluid extraction
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0111.201907022
- Received Date: 2019-07-08
- Rev Recd Date: 2019-11-13
- Available Online: 2020-04-23
- Publish Date: 2020-03-01
-
Key words:
- supercritical fluid extraction; steam distillation /
- Rhizoma Chuanxiong /
- volatile components
Abstract:
| Citation: | DENG Peng, WEI Feixue, WEN Yi, WANG Baoyi, CHEN Shan. Comparative study on volatile oil in Rhizoma chuanxiong by steam distillation and supercritical fluid extraction[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2020, 38(2): 152-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0111.201907022 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: