-
紫苏为重要的药食两用中药,来源于唇形科植物紫苏Perilla frutescens(L.)Britt,干燥叶与成熟果实分别作为紫苏叶与紫苏子入药,历版《中国药典》均有收载,紫苏子能降气化痰,止咳平喘,润肠通便,用于痰壅气逆,咳嗽气喘,肠燥便秘[1]。紫苏叶有解表散寒,行气和胃的功效,用于风寒感冒,咳嗽呕恶,妊娠呕吐,鱼蟹中毒。
紫苏在我国栽培极广,紫苏叶除了供药用外,还可作蔬菜、香料以及代茶。紫苏叶和肉类煮熟可增加后者的香味。日本人多用于料理,作为生鱼片佐料。紫苏子榨出的油(苏子油)也可供食用。由于紫苏应用历史悠久,形态变异大,栽培品种多,通常将叶背腹面均绿色者称为白苏,叶背为紫色者称为紫苏。紫苏与白苏的分类处理至今仍存在较大争议。如《中国植物志》[2]与《中国药典》[1]均将紫苏与白苏合为一种。而《中药志》[3]《中药辞海》[4]《新编中药志》[5]以及《中药品种理论与应用》[6]等均认为紫苏为白苏的变种。
研究表明,紫苏与白苏的形态差别并非由于栽培条件差异导致,其化学成分方面也存在明显区别,紫苏的挥发油类成分主为紫苏醛型,而白苏为紫苏酮型[7],本文对药食两用中药紫苏的名称、形态和功效进行本草考证,以正本清源,为临床安全合理应用提供科学依据。
-
紫苏原名苏,始载于《名医别录》,列为中品。李时珍在《本草纲目》中也记载:“苏性舒畅,行气和血,故谓之苏”[8]。陶弘景所著的《本草集经注》记载,“苏,味辛,温。主下气,除寒中,子尤良。叶下紫色而气甚香,其无紫色不香似荏者,名野苏,不堪用”。
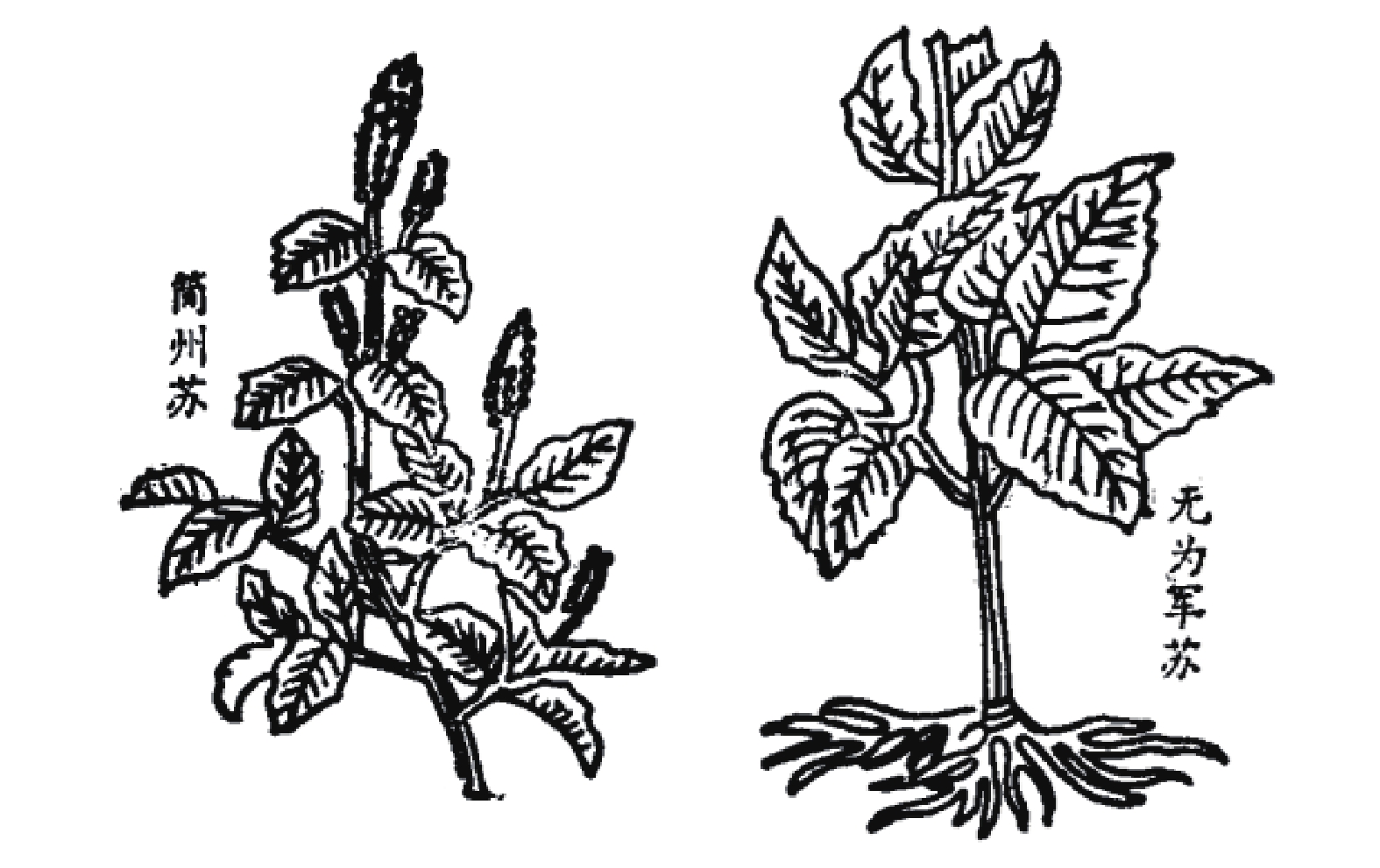
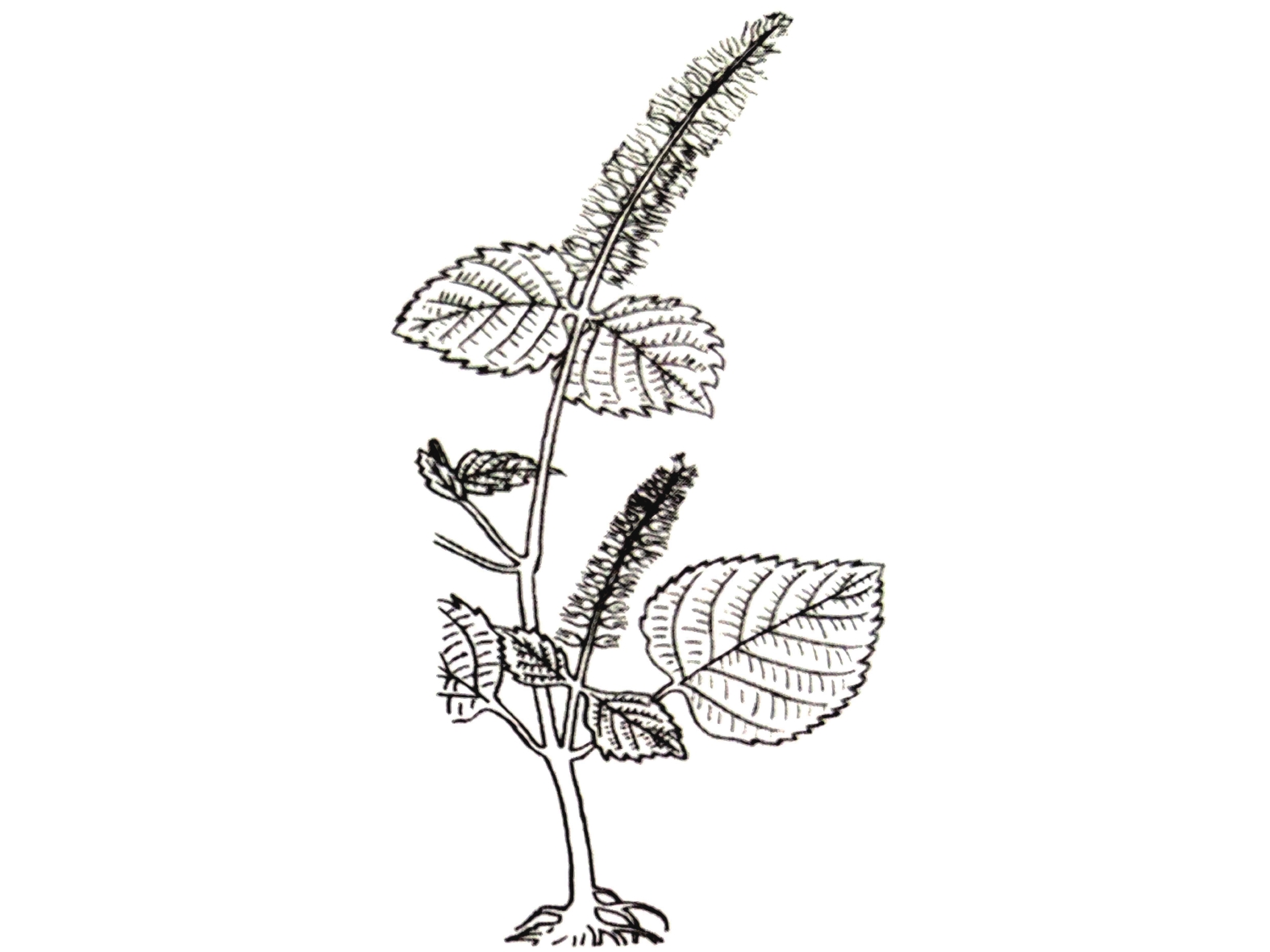
宋代苏颂所著的《图经本草》记载:“苏,紫苏也。谨按《尔雅》谓苏为桂荏。盖以其味辛,而形类荏,乃名之。然而苏有数种,有水苏、白苏、鱼苏、山鱼苏,皆是荏类”[9]。根据其形态描述及附图(图1),并为后来的本草文献支持,苏为现代唇形科植物紫苏Perilla frutescens (Linn.) Britt.。《救荒本草》记载:紫苏一名桂荏,又有数种,有勺苏、鱼苏、山苏,出简州及无为军,今处处有之[10]。这里提到的桂荏即紫苏,李时珍在《本草纲目》 解释到:“苏乃荏类,而味更辛如桂,故《尔雅 》谓之桂荏”。产地简州及无为军,《宋史》载:“无为军,同下州。太平兴国三年,以庐州巢县无为镇建为军,以巢、庐江二县来属。”《图经本草》有附图简州苏、无为军苏,与此也相符。
苏(舒)的名称来源于其功效。《尔雅义疏》也云:“苏之为言舒也”。紫苏则是指苏之茎叶之色为紫色。《本草求真》记载,紫苏专入肺,兼入心 、脾。背面俱紫,辛温香窜,凡风寒偶伤,气闭不利,心膨气胀,并暑湿泄泻,热闭血衄、崩淋,喉腥口臭,俱可用此调治。取其辛能入气,紫能入血,香能透外,温可暖中,使其一身舒畅,故命其名曰苏[11]。紫苏又称紫舒,相传还与东汉名医华佗有关。一次华佗在某地水边采药,无意中发现一只水獭因吃了螃蟹,难受在地上打滚,找到一种紫色的草吃了后竟安然无事。后来华佗用这种紫色的草熬汤救治了因多食螃蟹腹痛的患者。因该草紫色,患者喝后病痛解除,顿觉舒服,故称之为“紫舒”[12]。
古代本草中提到的“荏”即“白苏”,桂荏则指紫苏。李时珍《本草纲目》载:“曰紫苏者,以别白苏也。其面背皆白者即白苏,乃荏也”。《植物名实图考》中对荏也有解释,“荏,别录中品,白苏也”[13]。至于现代紫苏名称较多,紫苏又称野苏、红苏、香苏,青苏等名字。白苏又称白紫苏、青苏、臭苏等。
-
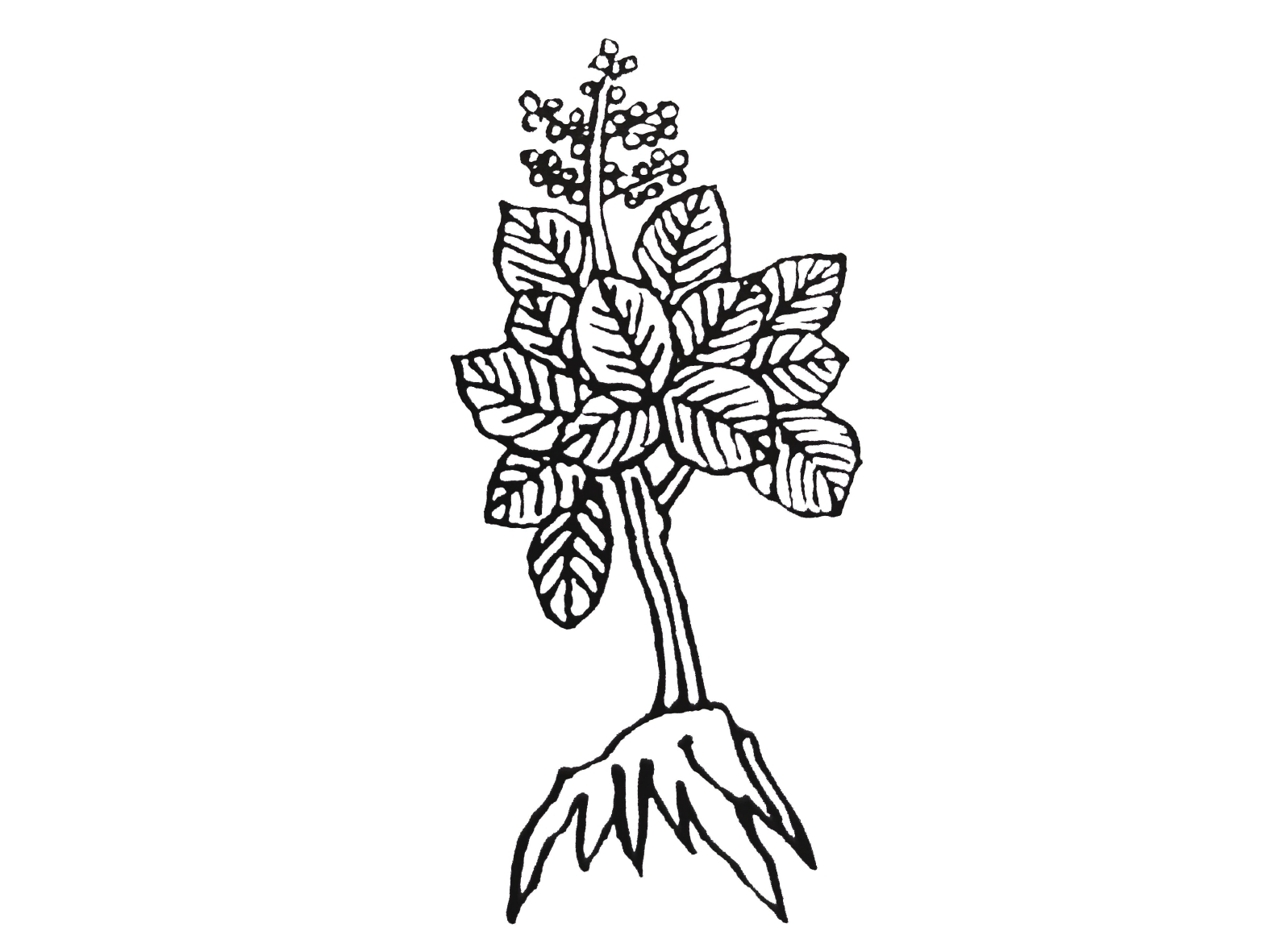
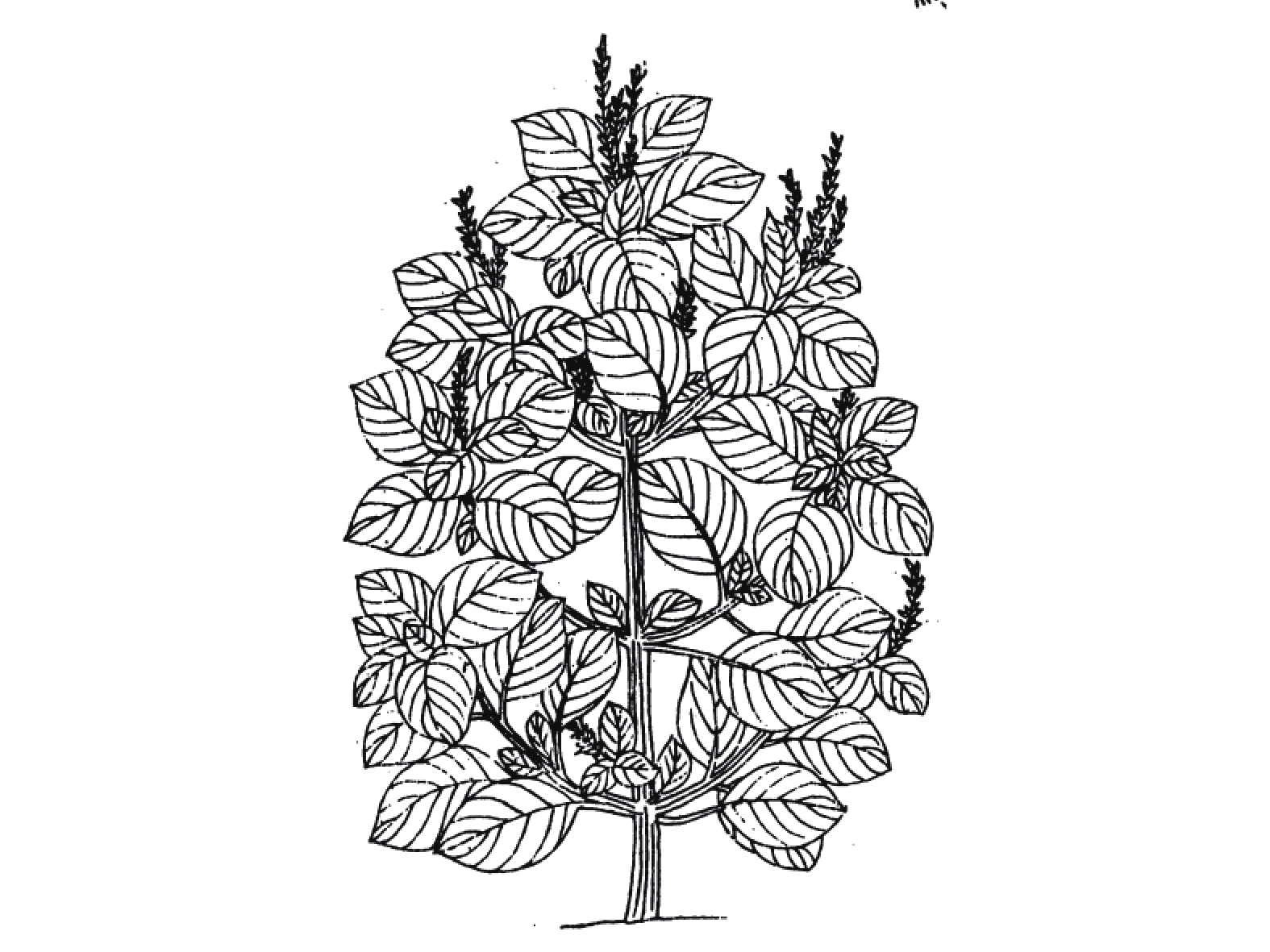
紫苏与白苏形态方面的差异目前争议颇多,分类上多被作为同一种处理,认为其形态的差异是由栽培条件不同导致。然而古代本草记载以及现代研究均表明紫苏、白苏在形态与成分方面存在明显差异。《图经本草》记载:“紫苏,叶下紫色,而气甚香,夏采茎叶,秋采实。《本草纲目》曰:“紫苏,其茎方,其叶圆而有尖,四围有锯齿;肥地者面背皆紫,瘠地者面青背紫”,并有附图(图2)。据此有人认为紫苏与白苏的形态差异由于生长环境导致。《本草崇原》也记载:紫苏,其叶面青背紫,气甚辛香,开花成穗,红紫色,穗中有细子,其色黄赤,入土易生,后人于壤土莳植,面背皆紫者名家紫苏。野生瘠土者,背紫面青。《别录》首次提到野生与栽培紫苏的区别。此外,还提到一种面背皆青,气辛臭香者,为荠。一种面背皆白者,名白苏,俱不堪入药。这里提到的“荠”应为现唇形科植物荠苧Mosla grosseserrata Maxim.,又称臭苏,青白苏。而《植物名实图考》记载紫苏并有附图(图3),形态特征十分清晰,与现代文献描述的紫苏形态特征相符。
白苏又称为荏,最大区别为叶不为紫色,历代本草对此均有记载,如《本草经集注》载:“荏,状如苏,高大白色,不甚香”;而《本草图经》载:“苏有数种,有水苏、白苏、鱼苏、山鱼苏,皆为荏类。白苏,方茎圆叶,不紫,亦甚香,实亦入药。事实上无论紫苏,白苏皆含挥发油,具有特殊香气,不过紫苏味更辛如桂。《本草纲目》 :“其面背皆白者即白苏,乃荏也”。《救荒本草》记载:“(荏)苗高一二尺,茎方。叶似薄荷叶,极肥大。开淡紫色花,结穗似紫苏穗,其子如黍,其枝茎对节生”(图4)。苏与荏形态上较为相似,主要为叶面颜色差异。
-
紫苏叶、紫苏梗、紫苏子均可入药,紫苏叶具有解表散寒,行气和胃的功效,紫苏梗具有理气宽中,止痛,安胎的功效。紫苏子具有降气化痰,止咳平喘,润肠通便的功效。在历代本草中均有详细记载,如《别录》:“主下气,除寒中。”《食疗本草》:“除寒热,治冷气”[14] 。《日华子本草》:“补中益气。治心腹胀满,止霍乱转筋,开胃下食,并一切冷气,止脚气,通大小肠。”《履巉岩本草》:“止金疮出血,疗痔疾,煎汤洗之”。紫苏叶入药始见于南北朝时期的《雷公炮炙论》[15]。《图经本草》记载,其茎并叶,通心经,益脾胃,煮饮尤甚,与橘皮相宜,气方中多用之。 实主上气咳逆,……,若欲宣通风毒,则单用茎,去节良。
《滇南本草》:“苏叶,发汗,解伤风头疼,定吼喘,下气,宽臌,消胀、消痰。苏子,止咳嗽,降痰,定吼喘,下气,消痰涎。” 明代《本草汇言》则记载:“紫苏,散寒气,清肺气,宽中气,下结气,化痰气,乃治气之神药也”,突出强调其治气功效。明代《本草纲目》也记载:“(紫苏)行气宽中,消痰利肺,和血,温中,止痛,定喘,安胎。其味辛,入气分,其色紫,入血分。” 清代《本经逢原》则认为紫苏可“散血脉之邪。”[16]。
关于紫苏梗的功效,明代《医学入门·本草》记载:“(紫苏)治风寒湿痹,及筋骨疼痛,脚气” [17]。明代《本草通玄》认为其“能行气安胎”。清代《本草崇原》:“主宽中行气,消饮食,化痰涎。治噎膈反胃,止心腹痛”。清代《得配本草》记载:“疏肝,利肺,理气,和血,解郁,安胎” [18]。 明代《本草蒙筌》[19]:“下诸气略缓,体虚者用宜”。
清代张志聪的《侣山堂类辩》曾有详细记载[20]:“庭前植百合、紫苏各数茎,见百合花昼开夜合,紫苏叶朝挺暮垂,因悟草木之性,感天地阴阳之气而为开阖者也,……,苏色紫赤,枝茎空通,其气朝出暮入,有如经脉之气,昼行于阳,夜行于阴,是以苏叶能发表汗者,血液之汗也(白走气分,亦走血分)。枝茎能通血脉,故易思兰先生常用苏茎通十二经之关窍,治咽膈饱闷,通大小便,止下利赤白。予亦常用香苏细茎,不切断,治反胃膈食,吐血下血,多奏奇功”。详细描述了紫苏不同部位的功效,紫苏长于解表理气之功效,紫苏叶与紫苏茎功效各有不同。
紫苏与白苏均有食用记载,《证类本草》将紫苏列为菜部中品,将荏列为菜部上品[21]。紫苏多以叶食用,《救荒本草》记载,“紫苏一名桂荏,今处处有之,苗高二尺许,茎方叶似苏子叶微小,茎叶背面皆紫色而气甚……,救饥采叶炒食,煮饮亦可,子研汁煮粥食之皆好。叶可生食与鱼作羹味佳”。白苏的食用主要为种子,“子可炒食;又研杂米作粥,甚肥美。亦可笮油用”[10]。《食物本草》也记载:“(紫苏)子,研汁煮粥长食,令人肥白身香”[22]。紫苏食用沿袭至今,许多地区仍有紫苏叶生食并与生鱼片同食习惯。
紫苏子作药用,秦、汉时期《别录》就有记载:“主下气,除寒中”。南北朝《本草经集注》记载:“苏子,主下气,与橘皮相宜同疗也”。唐代《药性论》则有不同的记载,认为苏子“主上气咳逆,治冷气及腰脚中湿风结气”。五代时期《日华子本草》则认为紫苏子“主调中,益五脏,下气,止霍乱、呕吐、反胃,补虚劳,肥健人,利大小便,破癥结,消五膈,止嗽,润心肺,消痰气”。北宋时期《本草衍义》记载紫苏子“治肺气喘急”[23]。《本草纲目》认为“苏子与叶同功,发散风气宜用叶,清利上下则宜用子也”。
紫苏以种子、叶、梗入药,白苏多以种子、叶和根入药。白苏又称南苏,叶功效与紫苏相似,而白苏根又有洗疮祛风的功效。《别录》记载:“主治欬逆,下气,温中”。《日华子本草》记载:“调气,润心肺,长肌肤,益颜色,消宿食,止上气咳嗽,去狐臭,敷蛇咬”。《滇南本草》则记载:“南苏,治伤寒发热,无汗头痛,其效如神。此草治一切风寒,痰涌结而霍乱转筋,咳嗽吐痰、小儿风症,定痛止喘。梗能补中益气。根能洗疮祛风。子能开胃健脾”。
-
紫苏的毒副作用记载较少,多数不良反应为药物或食物的配伍导致。如《本草纲目》记载:“不可同鲤鱼食,生毒疮”。明代的《神农本草经疏》[24]:“病属阴虚,因发寒热或恶寒及头痛者,慎毋投之,以病宜敛宜补故也。火升作呕者,亦不宜服,惟可用子”。《本草通玄》则记载:“久服泄人真气”。《药性切用》提到“气虚者禁用”。《医学入门·本草》也提到“脾胃气虚常泄者禁用”。《本经逢原》记载:“性主疏泄,气虚久嗽,阴虚喘逆,脾虚便溏者皆不可用”。因紫苏性温,主下气,故阴虚、气虚及温病患者慎用。
我们对紫苏与白苏的形态与化学成分研究结果表明,白苏的挥发油类成分主要为紫苏酮型,具有一定的毒性,存在安全隐患,因此作为食用以紫苏为好,不宜使用白苏。
-
通过对紫苏名称的文献考证结果表明,历代本草所言“紫苏”“苏”“白苏”均属“荏”类,为唇形科紫苏Perilla frutescens及其变种,“紫苏”源于“苏”,为其形态与功效的延伸。李时珍区分“紫苏”与“白苏”,白苏又称为荏,紫苏又称桂荏。通常将叶背腹面均绿色者称为白苏,叶背为紫色称为紫苏。白苏不甚香,不堪入药。紫苏茎、叶、子均入药,主下气,治风寒。
根据历代本草记载,紫苏和白苏为两种不同的植物,现代分类处理尚存在争议,认为紫苏是同种植物因环境不同产生的变异。然而其形态、功效及化学成分均存在明显差别。根据历代草本的紫苏附图、形态描述,紫苏与白苏应作为不同的分类单元。
紫苏茎、叶、子均入药,功效有所不同,对于不同病症注意合理的配伍,以免产生不良反应。此外,气虚、阴虚及温病患者慎用。紫苏作为药食两用的种类,应用较为广泛,为保证临床应用的安全有效,应与白苏加以区分。
Textual research on the name and reality of edible and medicinal Zisu
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202112055
- Received Date: 2021-12-19
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-04-21
- Available Online: 2023-07-14
- Publish Date: 2023-03-25
Abstract:
| Citation: | LI Chunyan, XU Chen, LU Pengfei, HUANG Baokang. Textual research on the name and reality of edible and medicinal Zisu[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2023, 41(3): 173-176. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202112055 |










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: