-
癌症是导致人类死亡的重要原因,手术、放疗和化疗等传统的癌症治疗手段已经不能满足现代癌症治疗的需求。近年来,免疫检查点抑制剂(ICIs)的发现,掀起了肿瘤免疫治疗的热潮。目前,多种免疫检查点抑制剂已经投入临床使用,如细胞毒T淋巴细胞相关抗原4 (CTLA-4 )抗体药物伊匹单抗(ipilimumab)、PD-1抑制剂帕母单抗(pembrolizumab, keytruda)和纳武单抗(nivolumab, opdivo)以及PD-L1抑制剂阿替利珠单抗(atezolizumab)、阿利库单抗(avelumab)和德瓦鲁单抗(durvalumab)。ICIs生物制剂在疗效和特异性方面的优势已经得到充分的证明,并且已经应用于多种肿瘤的治疗,如转移性黑色素瘤、非小细胞肺癌、头颈部鳞状细胞癌和霍奇金淋巴瘤[1]。但是ICIs在临床使用中仍然存在局限性,如很多接受免疫治疗的患者都经历了胃肠道毒性、内分泌毒性以及皮肤毒性等免疫相关不良事件(immune-irAEs)。除此之外,根据免疫疗法的类型以及治疗周期,患者需要支付高额的治疗费用[2]。
人们研究发现传统中药具有“扶正驱邪”的双重抗肿瘤作用。许多中药活性成分一方面能够通过破坏癌细胞的氧化还原平衡,抑制癌细胞的增殖,诱导癌细胞周期阻滞和凋亡来“驱邪”,另一方面可以通过增强机体免疫功能来“扶正”起到治疗肿瘤的作用。近年来,研究发现许多中药活性小分子可以抑制PD1/PD-L1的表达,改善肿瘤微环境(TME)的免疫抑制[3]。本文主要就抑制肿瘤免疫微环境中PD-1/PD-L1表达的中药活性小分子进行综述,希望为免疫检查点小分子抑制剂的研究提供线索。
-
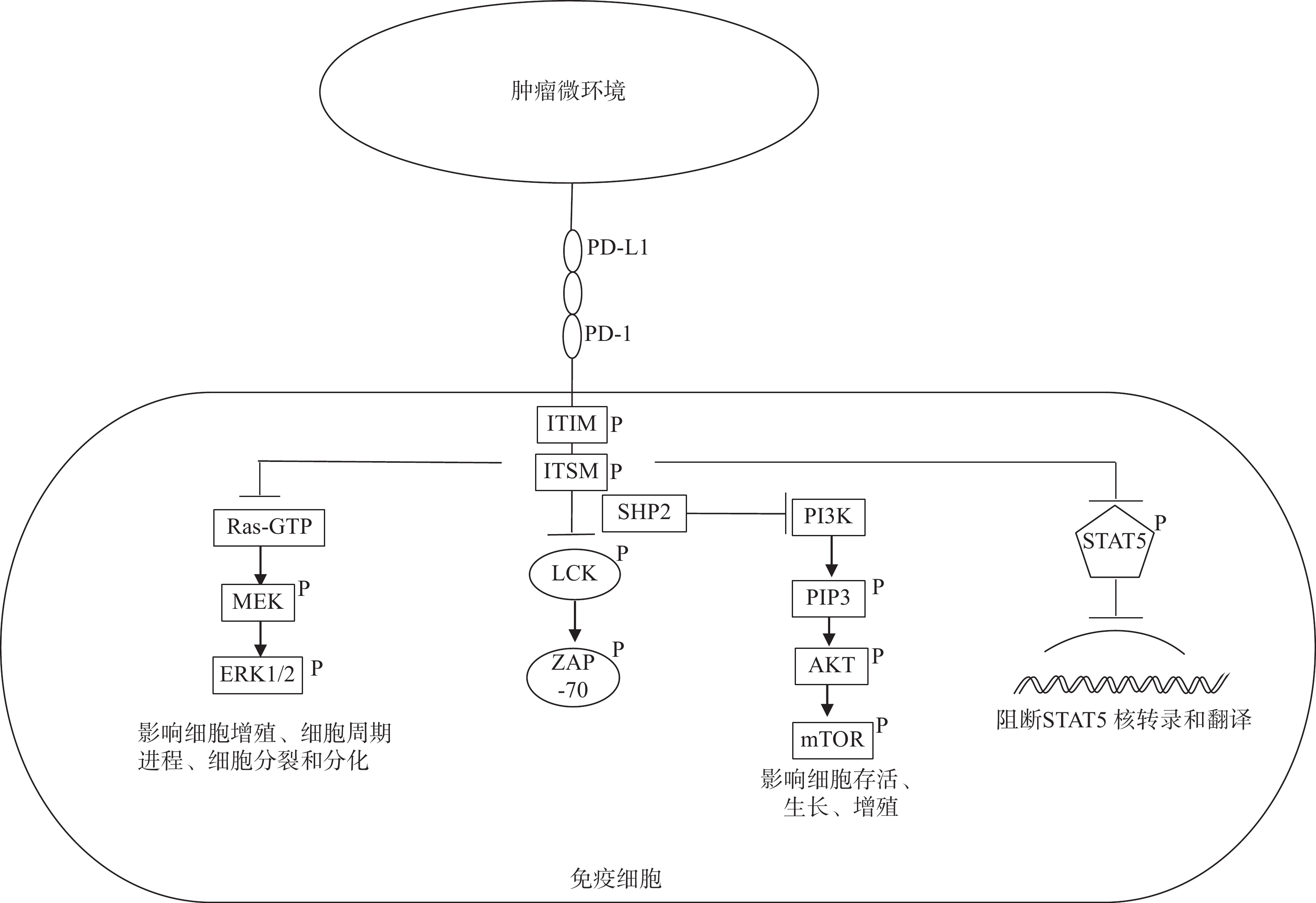
PD-1/PD-L1是T细胞活化过程中的免疫检查点。PD-1是一种细胞表面受体,主要表达于活化的T细胞,在B细胞、巨噬细胞等也有表达。人体内的PD-1蛋白由程序性死亡蛋白1(PDCD1)基因编码。PD-L1是PD-1的配体,是B7家族的成员,表达于T细胞、自然杀伤细胞、巨噬细胞、树突状细胞、B细胞、上皮细胞以及血管内皮细胞表面。在正常生理条件下,PD-1是一种重要的免疫调节分子,防止T细胞过度活化。然而在病理条件下,肿瘤细胞利用这一特点,大量表达PD-L1并且促进TME中抗原提呈细胞表达PD-L1。当这些PD-L1与免疫细胞表面的PD-1结合后,PD-1上的免疫受体酪氨酸抑制基序(ITIM ) 和免疫受体酪氨酸开关基序( ITSM)被激活,并招募蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶2 (SHP2)靠近T细胞受体,抑制T细胞LCK和ZAP-70的磷酸化,导致下游一系列通路受到抑制。PD-1抑制的第一个关键信号是PI3K -AKT信号通路, PD-1通过招募SHP2来阻断PI3K的激活[4]。PD-1抑制的第二个重要信号是有丝分裂原活化蛋白激酶Ras–MEK–ERK信号通路,PD-1通过抑制Ras的活化抑制 Ras–MEK–ERK信号通路的激活。这两条信号通路的抑制最终导致T细胞生长和增殖受阻,影响细胞周期进展,抑制细胞分裂和分化[5]。2型先天淋巴样细胞(ILC-2s)在机体免疫防御中起重要作用,有研究表明信号转导和转录激活因子5( STAT5)的激活对ILC-2s的增殖起到重要作用,然而PD-1的激活可抑制ILC-2s中STAT5的核转录和翻译[6](图1)。
研究表明PD-1和PD-L1的表达受到多种细胞因子和转录因子的调控。在急性感染T细胞激活阶段,活化T细胞核因子(NFATC1)可以促进PD-1的转录[7]。Notch信号通路可以直接激活CD8+T细胞中PD-1的转录[8]。除此之外, IL-6和IL-12可分别激活信号转导和转录激活因子3(STAT3)与STAT4,激活的STAT3与STAT4可以结合到PD-1增强子所在的STAT结合位点,从而促进PD-1的转录[9]。IFN-α能够促进T细胞形成由STAT1、STAT2和干扰素调节因子9(IRF9)组成的干扰素刺激因子3(ISGF3)复合物,该复合物可以增强T细胞活化期间PD-1的转录。在慢性感染T细胞激活阶段,FoxO1对维持 CD8+T细胞中PD-1的高水平转录具有重要作用[10]。在巨噬细胞中,核因子κB(NF-κB)能够在巨噬细胞激活期间激活PD-1的转录。在B细胞中,NFATC1和NF-κB均可以促进PD-1的转录[11]。相反,在急性感染期间,转录因子Blimp1抑制CD8+T细胞中PD-1的转录,而在慢性感染期间,Blimp1失去抑制PD-1转录的功能,转录因子T-bet代替它行使抑制PD-1转录的职能[12]。
研究表明,在小鼠卵巢癌模型中, IFN-γ能够增加肿瘤PD-L1的表达并且促进肿瘤的生长。当干扰素-γ受体1(IFNGR1 )缺失时,肿瘤细胞中PD-L1的表达水平也得到抑制。后续研究发现,IFN-γ通过IFN-γ-JAK1/JAK2-STAT1/STAT2/STAT3-IRF1轴来调控PD-L1的表达。JAK1、JAK2、STAT1和干扰素调节因子(IRF1)沉默,均可以显著抑制PD-L1的表达[13]。在TME中多种致癌转录因子如MYC,、STAT3、 缺氧诱导因子1α(HIF1α)、缺氧诱导因子2α(HIF2α)、c-JUN、NF-κB以及NF-κB p65蛋白(RelA)可以直接影响PD-L1的表达。因此,如何抑制肿瘤微环境中PD-1/PD-L1的表达成为肿瘤免疫治疗一个重要的突破点。
-
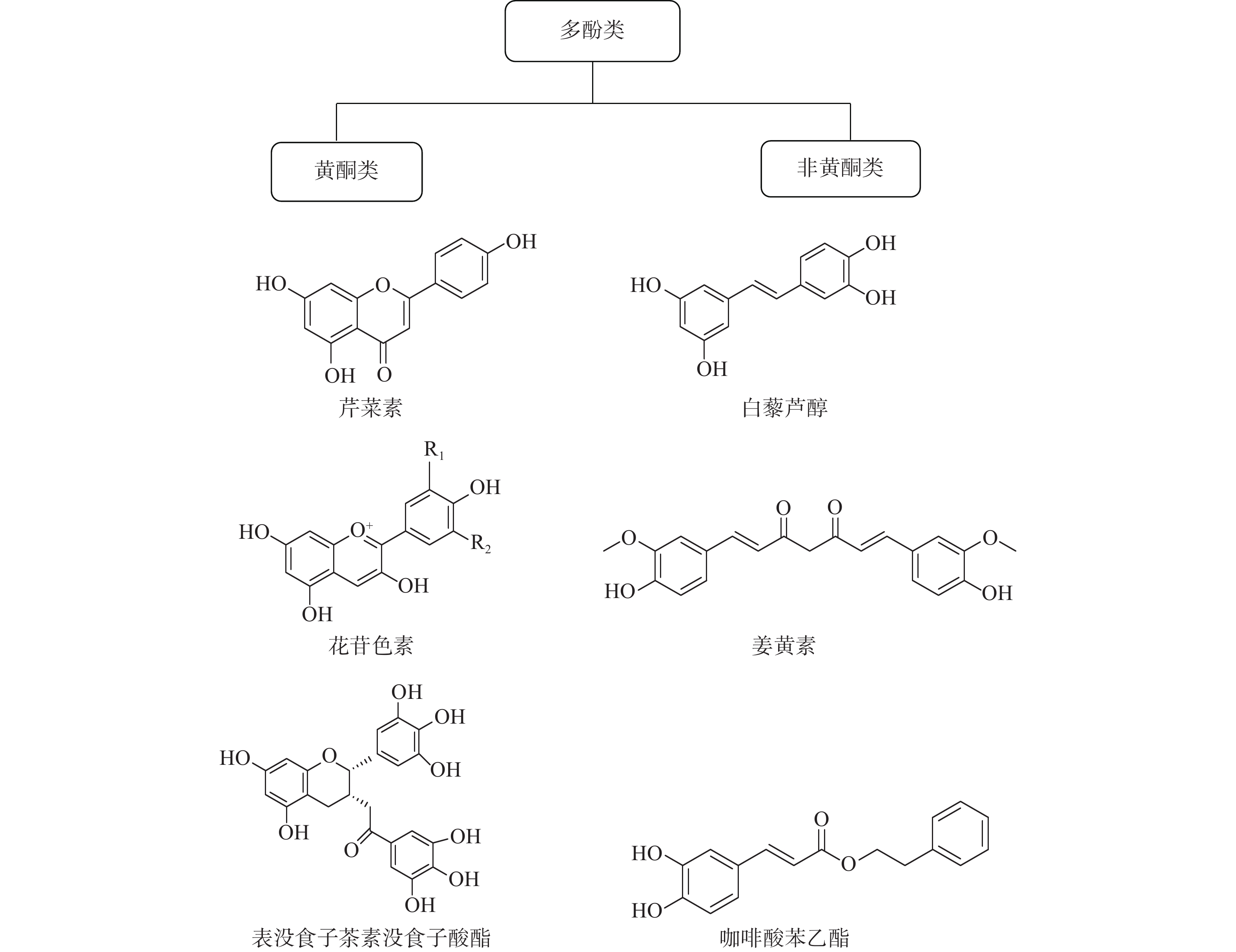
多酚是一类包含40多种化学结构的化合物,广泛存在于自然界和人们的日常生活中。我们日常食用的茶叶、葡萄酒、蔬菜、水果等物质中就富含多酚类化合物。据报道,多酚类物质具有抗炎、抗氧化、增强机体免疫力、抑制细菌以及癌细胞生长等广泛的生物学活性。研究表明,酚类化合物对人们的心血管疾病、神经退行性疾病、癌症、肥胖和糖尿病都有预防作用。多酚的化学结构中至少含有一个芳香环,并且根据不同的芳香环数目可分为黄酮类和非黄酮类化合物[14]。黄酮类化合物具有C6-C3-C6 的主链结构,可分为黄酮类、黄酮醇、双氢黄酮类、花青素等。非黄酮类化合物含有一个或多个酚环的化合物,包括酚酸、木酚素、二苯乙烯、姜黄素等(如图2)。许多的黄酮类和非黄酮类化合物可以通过调节免疫细胞、细胞因子的产生以及肿瘤细胞内在机制起到调控肿瘤免疫微环境的作用[15]。
-
芹菜素(apigenin)大量存在于蔬菜、水果、豆类和茶叶中,具有清除自由基、抗病毒、抗炎、抑制癌细胞生长等多种生物学功能。研究表明,芹菜素通过下调IFN-γ诱导人乳腺癌细胞中的STAT1激活,从而抑制PD-L1的表达和增强T细胞增殖[16]。芹菜素也可以抑制黑色素瘤细胞中STAT1的激活,显著下调IFN-γ诱导的PD-L1表达。体内实验表明,芹菜素能够显著抑制A357黑色素瘤异种移植瘤的生长,增强T细胞向肿瘤组织浸润,抑制人外周血成熟树突状细胞中PD-L1的表达[17]。由此可见,芹菜素可以通过下调PD-L1的表达起到抑制肿瘤生长,增强和恢复肿瘤浸润的免疫细胞的功能。
-
花色素苷(anthocyanin)是苯并吡喃的衍生物,广泛存在于绝大多数陆生植物的液泡中,是水溶性黄酮类色素中最重要的一种。其已经被证明具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗衰老、抗肥胖以及抗癌功能。有研究表明,花色素苷及其代谢产物可以显著抑制PD-1、PD-L1的表达,激活肿瘤微环境中的免疫应答并抑制结直肠癌的进展 [18]。肠道微生物可以提高免疫检查点抑制剂的治疗效果,目前有研究报道在小鼠MC38结肠癌模型中,使用壳聚糖和低分子柑橘果胶的越桔花色素苷组合,可以起到调节肠道微生物群和阻断PD-L1的作用。结果还显示,越桔花色素苷组合可以增加小鼠粪便中丁酸盐的浓度和比例,增强肿瘤组织中CD8+T细胞的浸润[19]。还有类似的研究发现,在结肠癌小鼠模型中,口服越桔花色素苷提取物可以显著增强抗PD-L1抗体的作用。这主要是由于花青素处理组的细菌多样性显著增加,小鼠粪便中具有免疫调节能力的梭状芽胞杆菌和约氏乳杆菌的数量也得到显著增加。这些研究都表明花色素苷可以通过改变肠道菌群协助ICIs发挥抗肿瘤的作用[20]。
-
表没食子茶素没食子酸酯 (EGCG),是茶多酚中最有效的活性成分,属于儿茶素类化合物。EGCG具有抗菌、抗炎、抗病毒、抗肿瘤等作用[21]。有研究报道,在非小细胞肺癌中,EGCG能够抑制IFN-γ和表皮生长因子(EGF)诱导的 PD-L1的表达。EGCG和绿茶提取物能够抑制A549人肺癌细胞中JAK2/STAT1信号通路,从而减少由IFN-γ诱导的PD-L1 mRNA以及蛋白质的表达水平;同时通过抑制EGF受体/AKT信号通路,使EGF诱导的PD-L1的表达降低。在腹腔注射4-甲基亚硝胺基-1-(3-吡啶基)-1-丁酮(NNK)诱导的小鼠肺癌模型中,小鼠的饮用水中加入0.3%的绿茶提取物,可以降低每只小鼠的平均肿瘤数目和70% PD-L1的阳性细胞率。在F10-OVA黑色瘤细胞和肿瘤特异性CD3+T细胞共培养模型中,EGCG能够使F10-OVA细胞的PD-L1 mRNA的表达降低,并且可以恢复肿瘤特异性CD3+T细胞IL-2 mRNA的表达[22]。这些结果表明,EGCG是PD-L1的有效抑制剂,具有抑制EGFR/Akt和IFNR/JAK2/STAT1通路的潜力。
-
姜黄素(curcumin)是一种从姜科植物姜黄的根茎中提取到的黄色色素。具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗凝、降脂、抗动脉粥样硬化、抗衰老及抑制肿瘤生长等生物活性[23]。近年来的研究表明,姜黄素对多种疾病都有疗效,其中抗肿瘤的作用最为广泛。最近有研究发现,姜黄素通过抑制舌鳞状细胞癌中STAT3通路介导的PD-L1表达,减少调节性T细胞(Tregs)和骨髓源性抑制细胞(MDSCs)的招募,部分逆转了免疫抑制[24],很有可能是潜在的肿瘤免疫治疗药物。还有文献报道,姜黄素通过下调小鼠结肠癌中NF-κB和STAT3信号通路促进肿瘤抗原特异性CD8+T细胞的产生,并增强树突状细胞(DCs)对T细胞激活[25]。尽管越来越多的证据证明姜黄素可能具有免疫调节作用,但目前仍然缺乏全面的机制研究和临床试验,因此在应用于临床之前还需要进行更深入的探讨。
-
白藜芦醇(RSV)又称 (E)-3,5,4-三羟基二苯乙烯,1993年在白藜芦的根茎中被首次发现。白藜芦醇是天然的抗氧化剂,具有清除自由基、抑制血小板非正常凝集、抗动脉粥样硬化、抗菌、抗炎、抗癌等生物活性。此外,RSV对免疫系统也有调节作用[26]。有大量的研究表明,RSV在各种类型的癌症中以直接或间接的方式调控肿瘤细胞和免疫细胞之间的联系,从而影响肿瘤微环境中的免疫应答。PD-L1是I型跨膜糖蛋白,糖基化的状态对PD-L1蛋白的稳定性和功能起着重要作用。此前有文献报道,RSV在卵巢癌细胞中通过激活糖原合成酶激酶-3β(GSK3β)抑制己糖胺生物的合成,阻断蛋白的糖基化[27]。最近,有研究发现RSV可以作为α-葡萄糖苷酶或α-甘露糖苷酶的直接抑制剂,破坏乳腺癌细胞中PD-L1的糖链修饰,促进PD-L1异常糖基化,最终阻碍PD-L1镶嵌到癌细胞膜。综上所述,RSV对PD-L1糖基化和二聚化的调节,可增强T细胞对癌细胞的杀伤活性[28]。还有研究报道,使用RSV治疗可以逆转口腔癌中甲状腺素的作用,减少PD-L1的表达和核积累[29]。不仅如此,RSV还可以诱导人和小鼠卵巢癌细胞免疫原性死亡。小鼠腹腔注射卵巢癌细胞,细胞经 RSV预处理后,可以显著抑制随后接种的异种移植瘤的生长。直接使用RSV治疗也可以抑制肿瘤的发展,并且经过RSV治疗后的移植瘤中成熟树突状细胞以及细胞毒性T细胞数量增加,转化生长因子β(TGF-β)的分泌减少,白介素12p7(IL12p7)和IFN-γ的分泌增加。与PD-L1抗体联合使用可提升其抗肿瘤作用[30]。关于RSV在肿瘤免疫中的更多机制还有待研究和发现。
-
咖啡酸苯乙酯(CAPE)是蜂胶中的主要成分之一,是一种含有儿茶酚结构的强氧化剂。免疫学研究表明,CAPE可以显著抑制丝裂原诱导的T细胞增殖、淋巴因子的产生以及NF-κB的活化。有文献发现,EB病毒(EBV)感染鼻咽癌细胞后,分别通过潜伏膜蛋白1(LMP1)和IFN-γ途径诱导PD-L1的表达。使用NF-κB抑制剂CAPE治疗后,EBV阳性鼻咽癌细胞株和过表达LMP1的正常鼻咽癌细胞株中PD-L1的表达显著降低[31]。结果表明,CAPE通过抑制NF-κB通路下调LMP1诱导的PD-L1的表达,说明CAPE是有潜力的免疫检查点抑制剂。
-
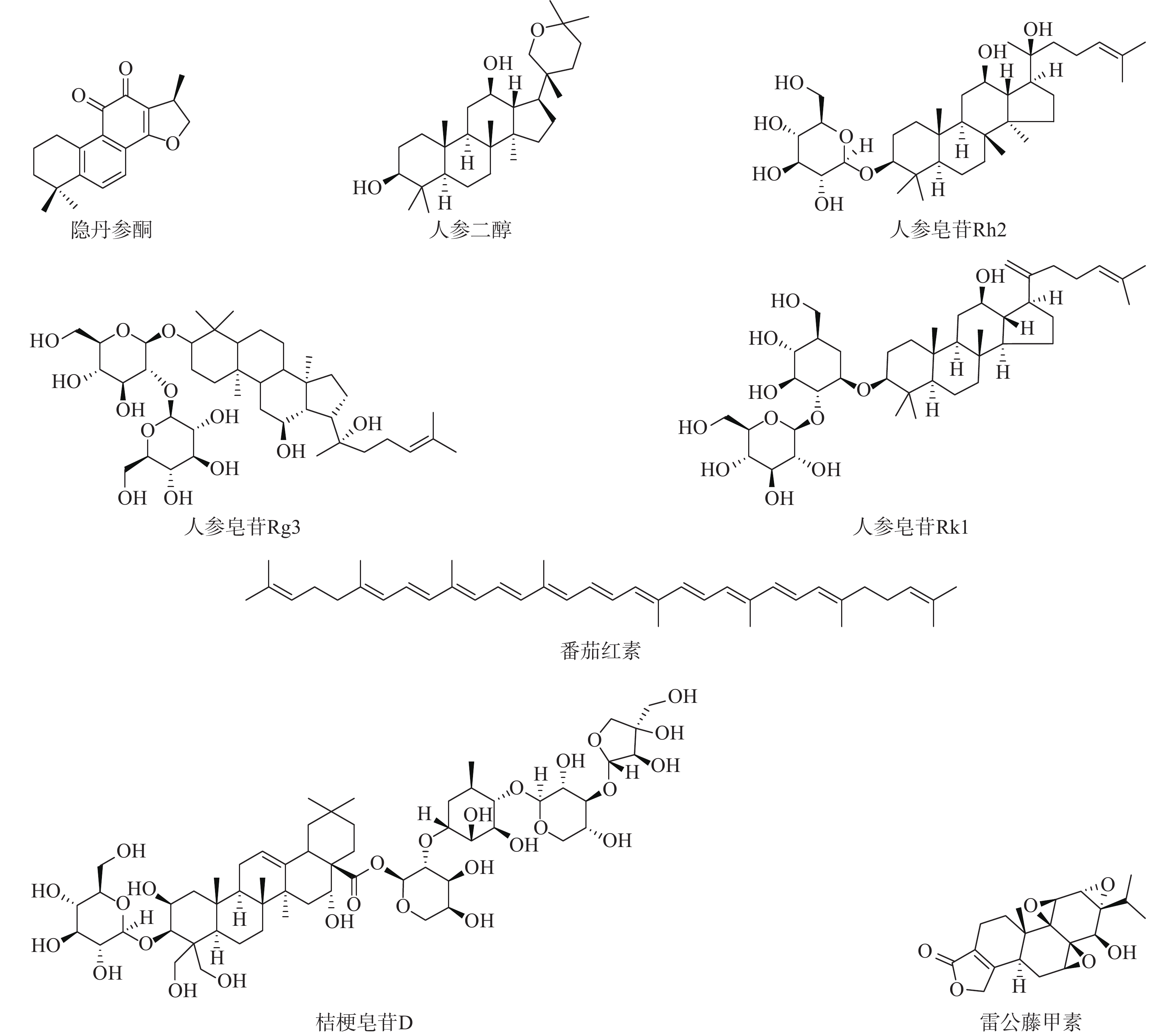
萜烯是一系列萜类化合物的总称,分子式为异戊二烯的整数倍的烯烃类化合物。根据异戊二烯的数目,萜烯可以分为单帖、倍半萜、二萜、二倍半萜、三萜、四萜、多聚萜等组成(如图3)。萜烯普遍存在于植物体和海洋生物体中,具有广泛的生物活性,包括降血糖、降血压、抗炎、抗病毒和抗肿瘤等[32]。
-
番茄红素(lycopene)是一种亮红色的类葫芦卜素(四萜),天然存在于红色和粉色的水果和蔬菜中,如西红柿。研究表明,番茄红素不仅具有抗癌抑癌的功能,而且在预防心血管疾病、动脉粥样硬化、增强机体免疫力以及延缓衰老等方面都有显著作用[33]。近期有研究表明,在Lewis肺癌小鼠模型中,番茄红素联合PD-1抗体使用可以显著降低肿瘤的体积和重量。此外,番茄红素还可以协助PD-1抗体提高荷瘤小鼠IL-1和IFN-γ的表达水平,降低IL-4和IL-10的表达水平;并且番茄红素可以通过激活JAK2/STAT3信号通路和抑制AKT磷酸化,降低IFN-γ诱导的肺癌细胞PD-L1的表达[34]。研究结果提示,番茄红素在高表达PD-L1和IFN-γ的肿瘤患者中可能发挥重要作用,其机制是通过激活JAK2信号通路来抑制IFN-γ诱导的PD-L1的表达,这与往常的作用机制不同,需要进一步的研究来确定番茄红素的作用方式。
-
隐丹参酮(cryptotanshinone)又称隐丹参醌,是一种从丹参根中提取的醌类二萜化合物,具有抗炎、抗菌、抗氧化、抗肿瘤等广泛的生物活性。有研究发现隐丹参酮不仅能抑制肺癌细胞增殖,还能促进抗肿瘤免疫。在小鼠Heap1-6肝癌模型中,隐丹参酮可以显著抑制小鼠肿瘤的生长,并且其与PD-L1抗体联合使用可以诱导长期抗Heap1-6的特异性免疫,达到完全治愈荷瘤小鼠的作用。隐丹参酮治疗的Heap1-6小鼠的免疫图谱显示,隐丹参酮可以激活肿瘤浸润的巨噬细胞和树突状细胞,诱导抗肿瘤T细胞应答,促进肿瘤组织中效应CD8 T细胞、记忆CD8 T细胞的浸润[35]。因此,隐丹参酮与PD-L1的联合使用可以促进CD8 T细胞毒作用并且诱导肿瘤特异性免疫,为人类肝细胞癌提供了一种有效的免疫治疗方案。
-
雷公藤甲素(triptolide)又称雷公藤内酯,是从中药雷公藤的根、叶、花和果实中提取的一种环氧二萜内酯化合物,是雷公藤提取物的主要活性成分之一。体内外研究表明,雷公藤甲素对乳腺癌、胰腺癌、肺癌等多种癌症都具有良好的抗肿瘤活性[36]。已有大量的研究报道,在多种癌细胞中,雷公藤甲素可以有效调节IFN-γ诱导的PD-L1的表达。比如,Liang等发现雷公藤甲素可以抑制乳腺癌细胞株中IFN-γ诱导的PD-L1的表达[37];Zhang等证实雷公藤甲素不仅可以抑制IFN-γ诱导的胶质瘤细胞PD-L1的表达,还能逆转胶质瘤细胞诱导的CD4+T细胞的抑制作用[38];Kuo等报道雷公藤甲素能够减少口腔癌细胞中IFN-γ的分泌,抑制IFN-γ相关的JAK2-STAT1信号通路,降低PD-L1的表达和抑制肿瘤的生长[39]。综上所述,在多种癌症中,雷公藤甲素与IFN-γ诱导的PD-L1的表达存在相关性,提示雷公藤甲素在肿瘤免疫治疗中具有不可估量的潜力。
-
皂苷(saponins)是苷元为三萜或螺旋甾烷类化合物的一类糖苷,主要存在于陆地高等植物中,包括人参、远志、桔梗、柴胡等。它们的主要特征是溶血活性和起泡性[40]。人参皂苷是从中药人参中提取的一种三萜皂苷。最近有研究发现12种人参皂苷中有8种人参皂苷在最大浓度(1μmol/L)时对PD-1/PD-L1相互作用的抑制率达到35%,其中Rg3和化合物K的抑制作用最强[41]。此外,还有研究报道人参皂苷Rg3通过抑制PD-L1、AKT和NF-κB p65,诱导对顺铂耐药的人肺癌细胞株(A549)的凋亡[42]。人参皂苷Rk1通过抑制肺癌细胞(A549)中NF-κB和B淋巴细胞瘤-2 (Bcl-2)诱导细胞凋亡并且抑制PD-L1表达[43]。人参二醇是人参根中提取的三萜皂苷元单体化合物。研究发现人参二醇通过抑制结肠癌细胞中低氧诱导因子(HIF)-1α的合成以及STAT3的激活,抑制PD-L1的表达和肿瘤细胞的增殖[44]。综上所述,皂苷在肿瘤免疫中的作用是不容忽视的。
-
近年来,肿瘤免疫治疗在实验室研究和临床应用中蓬勃发展,已逐渐替代传统癌症治疗方法。其中PD-1/PD-L1作为最具潜力的免疫检查点一直备受关注,如何更加有效的抑制PD-1/PD-L1已成为肿瘤免疫治疗热点。然而,目前市面上的PD-1/PD-L1抑制剂均为大分子单抗类生物制剂,此类制剂存在对组织和肿瘤的渗透性差、免疫原性强、价格昂贵等缺点。新型的小分子药物以吸收快、副作用小、免疫原性低等优势,已成为PD-1/PD-L1免疫检查点抑制剂的新的研究方向。中药作为中国传统中医文化的宝藏,是我国劳动人民通过长期的生活实践和医疗实践取得的成果。近年来研究发现,许多中药活性小分子具有抗肿瘤作用,但其具体的作用机制还需要进行深入探讨。
本文介绍了免疫共抑制分子PD-1/PD-L1的分子作用机制和常见的中药活性小分子及其在肿瘤免疫中的作用。由于PD-1/PD-L1主要通过抑制PI3K -AKT和Ras–MEK–ERK信号通路的激活,从而抑制T细胞生长和增殖,使得肿瘤细胞逃逸于细胞免疫;PD-1/PD-L1还可通过抑制ILC-2s中STAT5的核转录和翻译影响ILC-2s的增殖,减弱机体对肿瘤细胞的免疫防御能力。然而,研究发现很多中药活性小分子与PD-1/PD-L1的表达及功能密切相关,它们不仅可调控STAT以及NF-κB等信号通路来抑制PD-1/PD-L1的表达;还可调节肠道菌群,丰富菌群多样性来抑制PD-1/PD-L1的作用。此外,中药活性小分子还可影响PD-1/PD-L1的翻译后修饰与亚细胞定位。例如,通过破坏PD-L1的糖基化修饰和二聚化阻碍其转运到癌细胞膜表面,从而改善肿瘤微环境中的免疫抑制。尽管如此,仍然还有许多中药活性小分子的作用机制没有完全地阐明,需要进一步的研究和探索。
Research progress on active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicine as inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 of cancer immune checkpoint
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202208079
- Received Date: 2022-08-19
- Rev Recd Date: 2023-03-12
- Publish Date: 2023-05-25
-
Key words:
- active small molecules of traditional Chinese medicine /
- tumor microenvironments /
- PD-1 /
- PD-L1
Abstract: Tumor immunotherapy has become a new cancer treatment which has been expected to eliminate tumors. Immune checkpoint inhibitors, especially programmed death-1 (PD-1) and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) antibodies, have achieved significant clinical efficacy in the treatment of solid tumors. But biologics possess disadvantages such as strong immunogenicity and high cost. Therefore, the discovery of small molecule drugs as immune checkpoint inhibitors may overcome the shortcomings of biologics and become a new challenge for future tumor immunotherapy. The active small molecules from traditional Chinese medicine that inhibit the expression of PD-1/PD-L1 and their regulatory effects on the tumor immune microenvironment were reviewed in this paper.
| Citation: | HUANG Fengai, ZHANG Junping. Research progress on active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicine as inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 of cancer immune checkpoint[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2023, 41(5): 277-283, 290. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202208079 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: