-
菊花为菊科植物菊花的干燥头状花序,是一种常见的药食两用的花卉,具有清热、明目、疏风、解毒之功效[1-2]。根据经典的记载,中国栽培菊花历史已有3000多年。汉朝《神农本草经》记载:“菊花久服能轻身延年”。现代药理学研究表明,菊花具有抗菌、抗病毒、抗氧化、抗炎以及保肝等作用[3-12],因此,常作为保健饮品服用。安徽黄山是菊花的重要产地,拥有黄山金丝皇菊、黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊等多个品种,其中皇菊的黄酮含量极高,富含多种氨基酸、维生素和微量硒元素,具有重要的药用价值;而道地黄山贡菊更是菊花中的上等品,“白边黄芯绿屁股”,处于四大药菊之首。本研究主要对以上四种菊化品种进行研究,对比其抗氧化及抗炎活性,为菊花抗氧化和抗炎品种的开发提供参考和借鉴。
-
4种菊花(黄山金丝皇菊、黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊)来源于黄山市产品质量检验研究院;总抗氧化能力检测试剂盒(ABTS法)、总抗氧化能力检测试剂盒(FRAP法)、1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼试剂盒(DPPH法)购自Solarbio;双报告基因检测试剂盒购自Promega;LPS购自美国Sigma公司;SD大鼠,雄性,体重180~220g,购自上海斯莱克实验动物中心。
-
4种不同菊花经粉碎机粉碎并过60目筛,各取100 g,加入1000 ml去离子水浸泡12 h,然后加热回流提取2 h,过滤去除滤渣,滤液用旋转蒸发仪(60 ℃)蒸发去除溶剂,然后经真空干燥彻底去除水分[13]。由于4种菊花水提物得率基本一致(约17%),因此后续用相同质量的水提物表征同等质量的菊花。
-
将等体积的ABTS溶液和氧化剂溶液混合配置成ABTS工作母液,室温避光存放24 h。使用前,把ABTS工作液用PBS稀释30~50倍,要求ABTS工作液的吸光度减去相应的PBS空白对照后,A734为0.7±0.05,对应的A405在1.4左右。称取菊花粗提物粉末100 mg,用适量蒸馏水充分溶解。同时,用蒸馏水将10 mmol/L Trolox标准溶液稀释成0.15、0.3、0.6、0.9、1.2和1.5 mmol/L。于96孔板的每个检测孔中加入200 μl ABTS工作液,空白对照孔中加入10 μl蒸馏水;标准曲线检测孔中加入10 μl各浓度Trolox标准溶液;样品检测孔中加入10 μl样品溶液,轻轻混匀。室温孵育2~6 min后测定A734。根据标准曲线计算样品的总抗氧化能力[14]。
-
将TPTZ稀释液与TPTZ溶液充分混匀再加入检测缓冲液,从而配制成FRAP工作液。称取菊花粗提物粉末100 mg,用适量蒸馏水充分溶解。称取27.8 mg本试剂盒提供的 FeSO4•7H2O,溶解并定容到1 ml,此时浓度即为100 mmol/L。取适量100 mmol/L FeSO4溶液用蒸馏水稀释至0.15、0.3、 0.6、 0.9、 1.2和1.5 mmol/L。于96孔板的每个检测孔中加入180 μl FRAP工作液,空白对照孔中加入5 μl蒸馏水;标准曲线检测孔中加入5 μl各浓度FeSO4标准溶液;样品检测孔中加入5 μl样品溶液,轻轻混匀。室温孵育2~6 min后测定A593。根据标准曲线计算样品的总抗氧化能力[14]。
-
称取菊花粗提物粉末100 mg,用适量蒸馏水充分溶解。同时,用蒸馏水将10 mmol/L Trolox标准溶液稀释成0.15、0.3、0.6、0.9、1.2和1.5 mmol/L。于96孔板的每个检测孔中加入190 μl DPPH工作液,空白对照孔中加入10 μl蒸馏水;标准曲线检测孔中加入10 μl各浓度Trolox标准溶液;样品检测孔中加入10 μl样品溶液,混匀后室温避光静置30 min,测定A515。根据标准曲线计算样品的总抗氧化能力[14]。
-
Raw264.7细胞以适当密度接种于96孔板,实验分别设置空白组、LPS刺激组和不同药物浓度处理组,每组分别设置3个复孔。细胞过夜贴壁,利用转染试剂共转染报告基因质粒pNF-κB-Luc 和pRL-SV40,转染6 h后换液。转染24 h后加药,药物孵育2 h后加入LPS(终浓度1 μg/ml)刺激6 h,双报告基因法检测NF-κB转录活性。
-
取SD大鼠48只,随机分为6组,分别为空白组、模型组、菊花水提物给药组(2 g/ kg,相当于菊花11.76 g/kg)。各组大鼠连续灌胃给药3 d,模型组给予相同体积的生理盐水,第4天于每只大鼠右后足垫皮下注射1.0%角叉菜胶100 μl,致炎后灌胃给予相应药物,分别在致炎前和致炎后1、2、4 h,测量大鼠致炎侧足容积,计算足趾肿胀率和肿胀抑制率[15-16]。按下式计算小鼠足趾肿胀率和抑制率:肿胀率=(致炎后足趾体积-致炎前足趾体积)/致炎前足趾体积×100%, 抑制率= (模型组足趾肿胀率-给药组足趾肿胀率)/模型组足趾肿胀率×100%。
-
数据以(
$\bar x $ ±s)表示,单因素方差分析(One way ANOVA)比较各组差异,以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。 -
ABTS、FRAP和DPPH线性方程以及相关系数见表1。
表 1 ABTS、FRAP、DPPH的线性方程及相关系数
项目 方程 相关系数 ABTS Y=0.662 4X+0.715 3 r=0.999 5 FRAP Y=0.298 5X+0.060 r=0.999 4 DPPH Y=0.459 8X−0.023 8 r=0.998 9 从表1可以看出,ABTS、FRAP以及DPPH测定方法具有很好的线性。
-
ABTS法检测菊花水提物总抗氧化能力,结果显示,4种菊花的抗氧化能力存在明显差异,其中,黄山金丝皇菊抗氧化能力最强,为(0.481±0.052) mmol/g(总抗氧化能力用TEAC标准溶液表示),其次是黄山皇菊,为(0.402±0.043) mmol/g,然后依次是黄山贡菊(0.369±0.031)mmol/g和黄山黄菊(0.287±0.014)mmol/g。FRAP和DPPH检测以上四种菊花水提物抗氧化能力,结果与ABTS法类似,黄山金丝皇菊抗氧化能力最强,其次依次是黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊。综上,可以得出结论:黄山金丝皇菊水提物抗氧化能力最强,其次是黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊(表2)。
表 2 4种菊花抗氧化能力
名称/抗氧化
能力FRAP(mmol FeSO4/g) ABTS(mmol Trolox/g) DPPH(mmol Trolox/g) 黄山金丝皇菊 0.504±0.049 0.481±0.052 0.359±0.025 黄山皇菊 0.421±0.036 0.402±0.043 0.305±0.033 黄山贡菊 0.347±0.028## 0.369±0.031 0.277±0.041# 黄山黄菊 0.270±0.017###,** 0.287±0.014## 0.208±0.019##,* *P<0.05,**P<0.01,与黄山皇菊比较;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,###P<0.001,与黄山金丝皇菊比较。 -
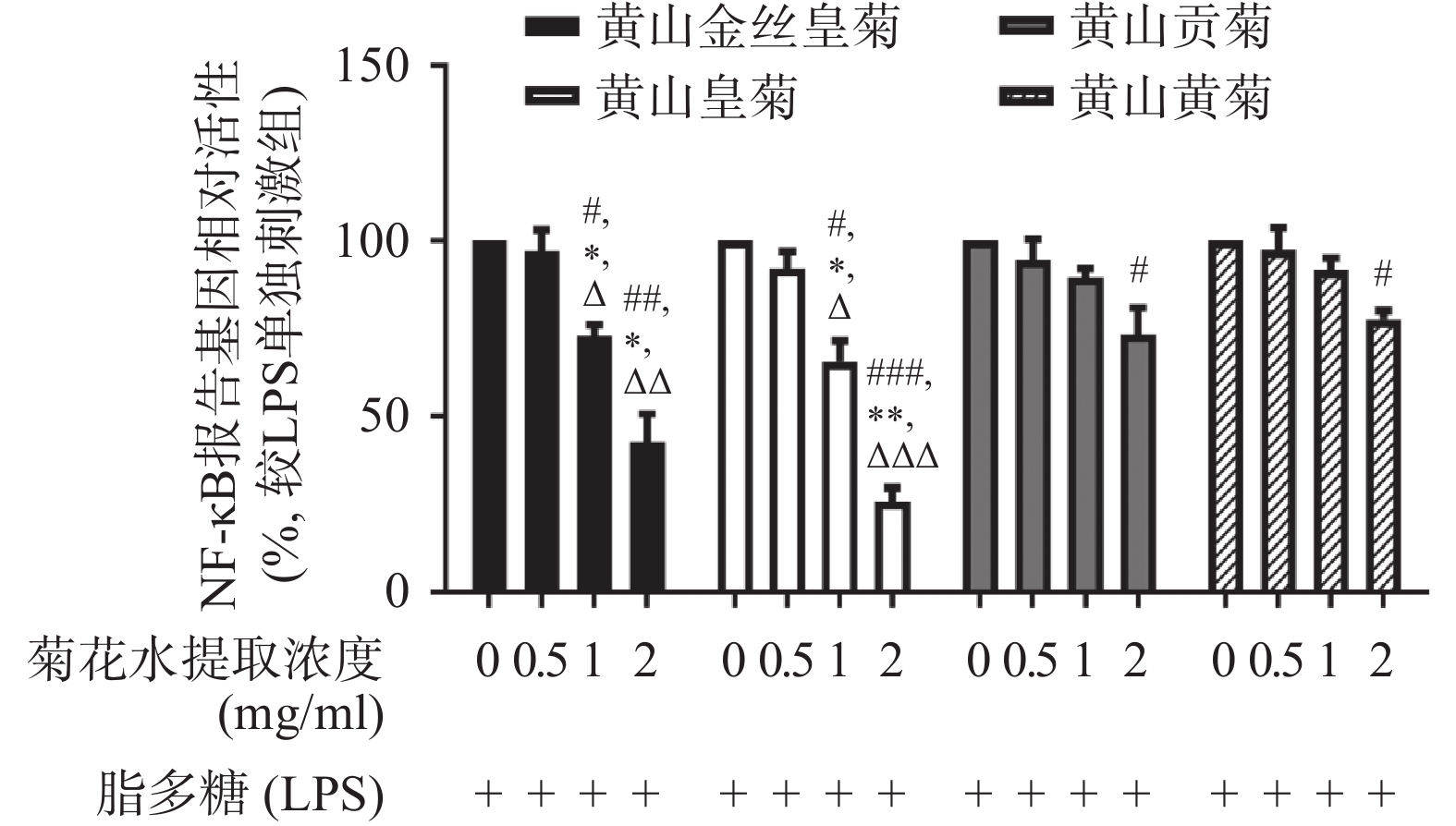
利用双报告基因的方法检测4种菊花水提物对Raw264.7细胞 NF-κB转录活性的影响,结果显示4种菊花水提物均能够一定程度的抑制LPS诱导的NF-κB的转录活性。相同作用浓度下,黄山皇菊NF-κB抑制活性最强,其次依次是黄山金丝皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊。结果表明黄山皇菊抗炎作用最强,其次是黄山金丝皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊(图1)。
-
为了进一步确认4种菊花提取物的抗炎活性,我们构建了角叉菜胶致大鼠足肿胀模型。大鼠足趾肿胀率和肿胀抑制率如表3所示,1 h时间点,给予菊花水提物处理的各组大鼠足趾肿胀均低于模型对照组,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。2 h时间点,黄山皇菊和黄山金丝皇菊对足趾肿胀仍然具有抑制作用,而黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊抑制作用消失; 组间比较,黄山皇菊足趾肿胀抑制作用优于黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊(P<0.05)。4 h时间点,各组对足趾肿胀的抑制作用消失。综上结果表明,黄山皇菊的抗炎活性最好,其次是黄山金丝皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊,该结论与NF-κB报告基因结果一致。
表 3 角叉菜胶致大鼠急性炎症模型结果(x±s,n=8)
组别 1 h 2 h 4 h 肿胀率(%) 抑制率(%) 肿胀率(%) 抑制率(%) 肿胀率(%) 抑制率(%) 模型组 41.6±
4.5− 52.5±
10.7− 45.1±
8.2− 黄山金丝皇菊 31.5±
5.9#24.3 42.3±
7.1#19.5 44.9±
8.80.5 黄山皇菊 28.9±
5.9##30.6 38.9±
7.8#,*,ΔΔ26.0 46.4±
10.0−2.8 黄山贡菊 31.8±
6.3#23.7 50.0±
11.74.8 46.4±
8.3−2.8 黄山黄菊 33.3±
6.2#20.1 51.0±
7.32.9 44.9±
8.80.6 *P<0.05,与黄山贡菊比较;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,与模型组比较;ΔΔP<0.01,与黄山黄菊比较。 -
本研究采用ABTS、FRAP和DPPH 这3种方法测定了4种黄山菊花水提物的抗氧化活性,并通过报告基因法和大鼠足肿胀模型评估了其抗炎活性。结果表明,4种菊花表现出不同的抗氧化活性和抗炎活性,其中黄山金丝皇菊的抗氧化能力最强,其次是黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊;而黄山皇菊的抗炎活性最强,其次是黄山金丝皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊。菊花中黄酮类化合物具有清除自由基和超氧阴离子的能力,其抗氧化能力与黄酮类化合物含量有关;而菊花中的抗炎成分相对复杂,包含多糖、黄酮类化合物(如木犀草素、槲皮素及黄芩苷等)、有机酸(如绿原酸)和挥发油等,4种不同菊花在抗炎及抗氧化方面的活性差异可能与上述成分的差异有关[2,17-18]。尽管不同菊花品种在抗氧化和抗炎活性方面存在差异,但是均表现出良好的药用及食用价值,人们在日常生活中可以根据使用目的的不同进行选择,如考虑通过饮用菊花茶起到抗氧化目的,可以优先选用金丝皇菊,而如果考虑菊花抗炎作用,则可以考虑黄山皇菊。综之,4种黄山道地菊花提取物均表现出一定的抗氧化活性及抗炎活性,常饮之有保健功效。
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of four kinds of Huangshan chrysanthemum
-
摘要:
目的 探究4种黄山菊花品种水提物的抗氧化和抗炎活性。 方法 采用ABTS、FRAP和DPPH 3种方法测定黄山金丝皇菊、黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊4种菊花水提物的抗氧化活性,并通过NF-κB报告基因法和大鼠足肿胀模型评估其抗炎活性。 结果 ABTS、FRAP和DPPH结果显示,4种菊花水提物均具有抗氧化作用,其中黄山金丝皇菊作用最强,其次是黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊。NF-κB报告基因和大鼠足肿胀模型结果显示,4种菊花提取物均能够一定程度的抑制LPS诱导的NF-κB转录活性和缓解角叉菜胶致大鼠足趾肿胀程度,其中,黄山皇菊作用最为显著,其次是黄山金丝皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊。 结论 4种黄山菊花品种的水提物均表现出一定的抗氧化及抗炎活性,其抗氧化活性由强到弱依次为黄山金丝皇菊、黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊,抗炎活性由强到弱依次为黄山皇菊、黄山金丝皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of four kinds of Huangshan chrysanthemum. Methods ABTS, FRAP and DPPH were used to detect the antioxidant activities of Huangshan golden silk chrysanthemum, Huangshan chrysanthemum, Huangshan gongju, and Huangshan dendranthema. Their anti-inflammatory activities were evaluated by NF-κB reporter gene assay and rat foot swelling models. Results The outcomes of ABTS, FRAP and DPPH showed that the water extracts of four kinds of chrysanthemum all had certain antioxidant activities and the activities of Huangshan golden silk chrysanthemum were strongest, followed by Huangshan chrysanthemum , Huangshan gongju , and Huangshan dendranthema. Results of NF-κB reporter gene assay and rat foot swelling models showed that four extracts of chrysanthemum morifolium could inhibit the transcription of NF-κB induced by LPS and alleviate foot swelling of rat induced by carrageenan, with the strongest activity of Huangshan chrysanthemum, followed by Huangshan golden silk chrysanthemum, Huangshan gongju, and Huangshan dendranthema. Conclusion The antioxidant activities of Huangshan golden silk chrysanthemum were strongest, followed by Huangshan chrysanthemum, Huangshan gongju, and Huangshan dendranthema. The anti-inflammatory activities of Huangshan chrysanthemum were strongest, followed by Huangshan golden silk chrysanthemum, Huangshan gongju, and Huangshan dendranthema. -
Key words:
- antioxidation /
- anti-inflammation /
- chrysanthemum /
- feet swelling
-
结直肠癌(CC)发生率占所有肿瘤发生率的第3位,病死率仅次于肺癌,属于下消化系统恶性肿瘤[1]。目前,结肠癌的治疗主要采用多学科的综合治疗模式[2]。包括5-氟尿嘧啶、奥沙利铂与贝伐珠单抗等的组合[3-5]。然而,这些常规的化疗方案可能造成患者不耐受以及骨髓等的抑制。因此,寻找新的有效的药物对于现今结肠癌治疗具有重要意义。
紫杉醇(PTX)是一种广谱抗肿瘤活性的化疗药物,来源于太平洋紫杉树皮(红豆杉)[6,7]。临床试验结果表明,PTX在几种癌症治疗中有较好的活性,包括:乳腺癌、皮肤恶性肿瘤、非小细胞肺癌以及卵巢癌等[8,9]。然而,由于结肠癌中过表达的P糖蛋白(P-gp)引起了多重耐药性(MDR),导致PTX对结肠癌临床治疗效果不甚理想[10]。此外,PTX生物半衰期短,其一代药物Taxol以聚氧乙烯蓖麻油为表面活性剂,具有引起患者过敏反应的风险,从而限制了PTX临床疗效的发挥[11]。因此,迫切需要对PTX进行结构改进与剂型设计,改善其药物递送效率,提高生物利用度[12]。
脂肪酸作为生物膜和生物信号分子的重要成分,参与了细胞能量产生、代谢的过程。由于肿瘤细胞增殖快速,需要大量的细胞合成物质和能量的供应,因此,患有恶性肿瘤的患者其脂肪酸合成也较快。其中,肿瘤细胞因为迅速繁殖对含有16个碳原子的棕榈酸(PA)为主的脂肪酸需求量大,因此利用PA进行修饰有利于药物被肿瘤细胞摄取[13,14]。再者,研究发现,由PA修饰的紫杉醇,能降低其对P-gp的亲和力,避免了PTX进入肿瘤细胞后的外排,提高紫杉醇对于结肠癌治疗的有效性[15]。
此外,作为一种成熟的药物载体,脂质体(Lip)在体内可被降解、无毒性和免疫原性,能够增强药物在体内的稳定性,从而可以减少给药剂量、降低毒副作用,并且其表面具有可修饰性[16],例如,采用聚乙二醇磷脂(PEG-DSPE)修饰的脂质体因其空间位阻效应可延长其在体内的循环时间[17]。同时结合肿瘤组织的增强通透性和滞留效应(EPR),使药物通过被动靶向递送到靶部位[18]。
结合以上背景,本研究首先通过棕榈酸酯与紫杉醇共价键结合构建紫杉醇棕榈酸酯(PTX-PA),并建立基于高效液相(HPLC)的定量分析方法,旨在降低其对P-gp的亲和力,避免PTX进入肿瘤细胞后被外排,从而改善紫杉醇毒性较大、生物半衰期短、成药性差等问题,提高紫杉醇对于结肠癌治疗的有效性。其次,我们将PTX-PA包载进PEG修饰的脂质体构建紫杉醇棕榈酸酯的脂质体(PTX-PA/Lip),以实现其长循环,增加PTX的疗效、降低其毒副作用。最后,采用工艺筛选与单因素处方优化的方法制备最佳PTX-PA/Lip,为PTX-PA的制剂学研究奠定基础[19]。
1. 仪器与材料
1.1 仪器
高效液相色谱仪(安捷伦科技有限公司,美国);十万分之一电子天平(MS105DU,梅特勒托利多公司,瑞士);超滤管(30 kD,密理博公司,美国);低温高速离心机(Eppendorf-200,艾本德公司,德国);高压均质机(NanoGenizer,美国);Zeta-sizer Nano粒度仪(Nano-ZS,马尔文公司,英国)。
1.2 试剂与材料
紫杉醇购自江苏红豆杉生物科技股份有限公司,纯度≥98%;棕榈酸购自中国医药集团上海化学试剂公司,纯度≥99%;蛋黄卵磷脂(PC98-T)、胆固醇、DSPE-PEG 2000均购自上海艾韦特医药科技有限公司;1-(3-二甲氨基丙基)-3-乙基碳二亚胺(EDC)、4-二甲氨基吡啶(DMAP)、乙酸乙酯、二氯甲烷、无水乙醇、石油醚均购自中国医药集团上海化学试剂公司,分析纯;乙酸乙酯、PC-98T蛋黄卵磷脂(上海艾韦特医药科技有限公司);胆固醇(上海艾韦特医药科技有限公司);二氯甲烷、DSPE-PEG 2000(上海艾韦特医药科技有限公司);无水乙醇、石油醚购自中国医药集团上海化学试剂公司;甲醇购自美国默克公司,色谱纯。
2. 方法
2.1 PTX-PA的制备与纯化
PTX-PA前药由PTX与PA发生酯化反应合成,其合成过程如下[20,21]:精密称取PTX 0.85 g,加入无水二氯甲烷 30 ml。依次加入精密称取的EDC 0.19 g、DMAP 0.15 g和PA 0.31 g,在氮气保护下室温搅拌反应12 h。反应结束后,用5%柠檬酸水溶液、饱和食盐水洗涤3遍,旋蒸除去有机溶剂,即得PTX-PA粗品。采用石油醚和乙酸乙酯通过柱层析法对PTX-PA进行分离、纯化。洗脱完成后,将产物旋蒸去除有机溶剂,得到的白色固体即为PTX-PA,样品经核磁共振氢谱、碳谱确定为PTX-PA,样品纯度98.5%。
2.2 基于HPLC定量检测的方法学建立[22]
2.2.1 最大吸收波长测定与色谱条件设定
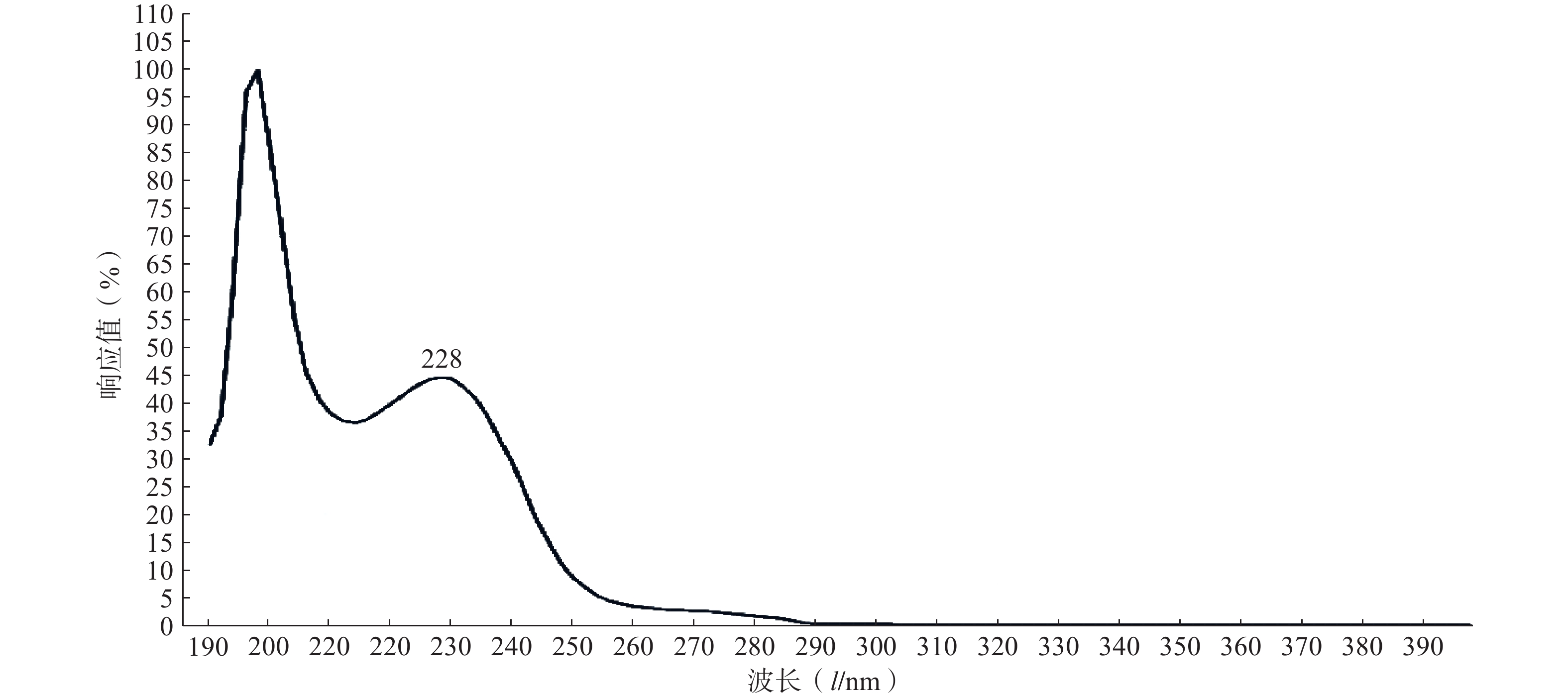
精密取适量的PTX-PA粉末,采用甲醇溶解,定容,通过全波长(190~400 nm)扫描测定其紫外最大吸收波长λmax。
本实验采用Agilent Eclipse plus C18色谱柱(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm),流动相采用甲醇/水(95∶5,V/V),进样量20 μl,流速1.0 ml/min。
2.2.2 样品溶液配制
空白溶液的配制:精密量取不含药的空白脂质体1 ml加入适量的甲醇溶液,超声,用甲醇定容至25 ml,0.45 μm的微孔滤膜过滤,滤液即为空白溶液。
对照品溶液的配制:精密称取PTX-PA 粉末50 mg,用甲醇溶解并定容至50 ml,过滤,即得PTX-PA对照品储备溶液。
供试品溶液的配制:精密量取1 ml PTX-PA/Lip,加入适量甲醇溶解、超声破乳、定容至25 ml,过滤,滤液即为供试品溶液。
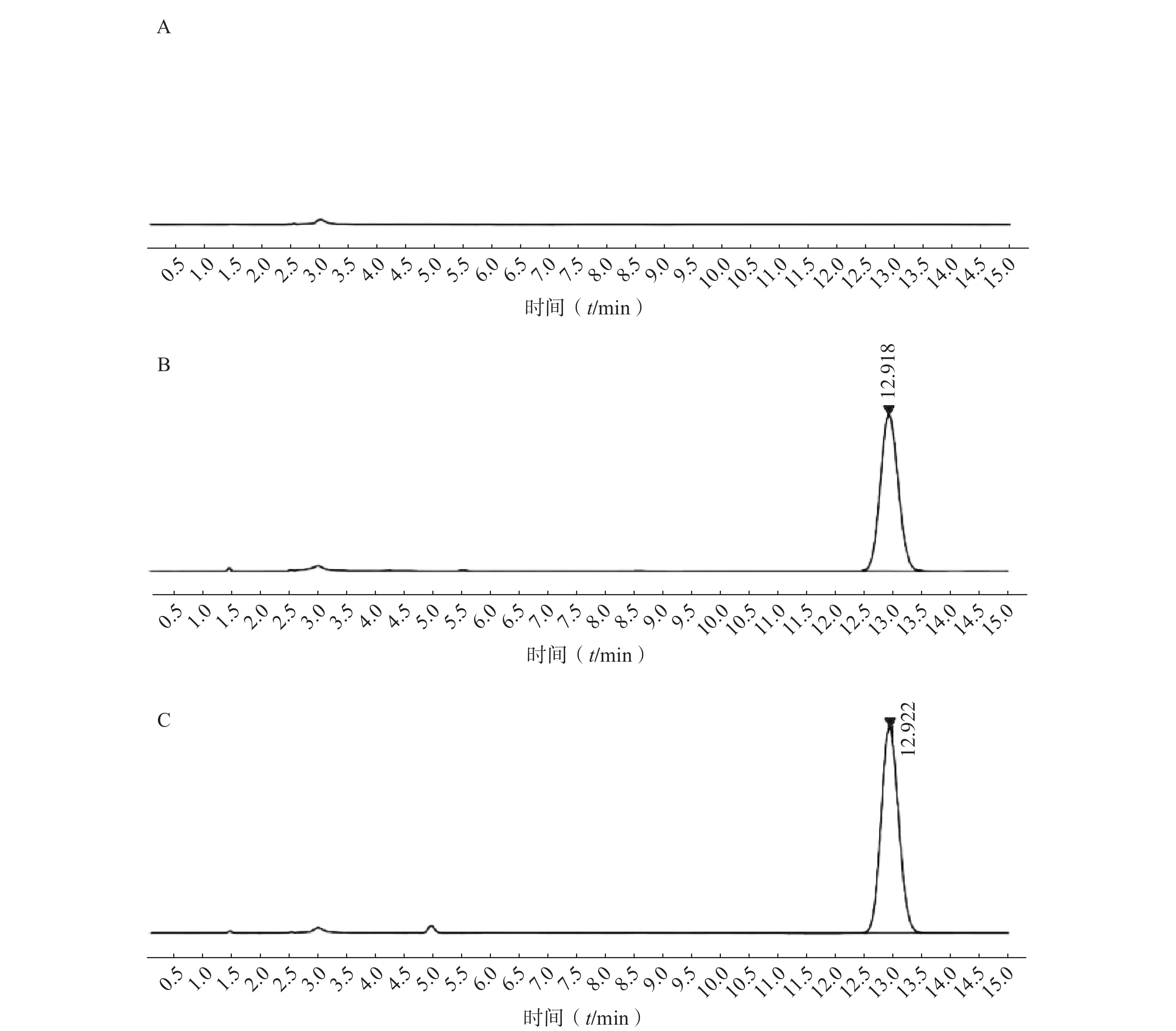
2.2.3 专属性考察
分别取适量空白溶液、对照品溶液和供试品溶液,用流动相稀释至适当的浓度后,按照“色谱条件”中建立的高相液相参数进行进样分析。
2.2.4 线性关系考察
精密量取适量PTX-PA对照品储备液依次稀释为浓度1、5、10、25、50、100 μg/ml的PTX-PA系列浓度。按照“色谱条件”中的高效液相参数进行进样分析(n=5),并记录不同浓度的PTX-PA的色谱峰面积。以浓度(C)为X轴、峰面积(A)为Y轴进行回归。
2.2.5 精密度考察
日内精密度考察:精密吸取3种不同浓度(5、25、100 μg/ml)的 PTX-PA对照品溶液,对同一浓度溶液连续进样5次,每次10 µl,按照“2.2.1”项下色谱条件进行分析,记录各个浓度吸收峰面积。
日间精密度考察:精密吸取3种不同浓度(5、25、100 μg/ml)的 PTX-PA对照品溶液,对同一浓度溶液连续进样5 d,每天1次,每次10 µl,按照“2.2.1”项下色谱条件进行分析,记录第0、1、2、3、4天的吸收峰面积,计算样品浓度,考察仪器的日间精密度。
2.2.6 重复性与稳定性
空白脂质体超声破乳,配制成3种不同浓度(1、10、100 μg/ml),连续进样5次,每次10 µl,记录各吸收峰面积,考察重复性。精密吸取浓度为50 μg/ml的 PTX-PA供试品溶液,于0、2、4、6、8、12、24 h进样测定,每次进样10 µl,记录各紫外吸收峰面积,考察样品的稳定性。
2.2.7 加样回收率考察
空白脂质体超声破乳,分别加入浓度为1 mg/ml的PTX-PA溶液0.5、2.5、5 ml,采用流动相稀释定容至100 ml,分别进样,并结合PTX-PA的理论浓度(5、25、50 μg/ml)进行加样回收率的计算与分析。
2.3 紫杉醇棕榈酸酯脂质体PTX-PA/Lip的制备
2.3.1 PTX-PA/Lip的制备方法的选择
(1) 薄膜分散法
精密称取PTX-PA 20 mg、蛋黄卵磷脂350 mg、胆固醇5 mg和DSPE-PEG2000 25 mg,加入适量的二氯甲烷使其充分溶解。然后旋蒸除去有机溶剂,使圆底烧瓶底部形成一层均匀透明的薄膜,再加入预热至同等温度的重蒸水10 ml,震荡、水化,得PTX-PA/Lip粗品。将得到的粗品经探头超声(1 min)、过滤处理后,即得PTX-PA/Lip纳米给药系统[19]。
(2) 高压均质法
将薄膜分散法制得的PTX-PA/Lip粗品置于高压均质机中,经3次均质处理后(均质压力12 000 psi),即得PTX-PA/Lip纳米给药系统[23,24]。
(3)挤出法
将薄膜分散法制得的PTX-PA/Lip粗品置于挤出器中,使分别经过孔径为0.2、0.1、0.05 μm的聚碳酸酯膜,即得PTX-PA/Lip纳米给药系统[25-27]。
2.3.2 处方工艺筛选
(1)磷脂种类的选择
采用薄膜分散法考察不同磷脂制备的PTX-PA/Lip,包括:氢化磷脂(HSPC)、蛋黄卵磷脂(PC98-T)、蛋黄磷脂(EPCS)、二棕榈酸磷脂酰胆碱(DPPC),以形态、粒径、包封率为指标进行评价。
(2)磷脂和药物/胆固醇比例的考察
分别以磷脂和药物的质量比(5∶1、10∶1、20∶1、30∶1、40∶1)/PC98-T和胆固醇的质量比(4∶0.05、4∶0.1、4∶0.2、4∶0.3、4∶0.4、4∶0.5)为自变量制备PTX-PA/Lip脂质体,考察不同处方的粒径、粒径分布、包封率,确定处方中磷脂与药物/胆固醇的质量比。
(3)药物和DSPE-PEG2000比例的考察
以PTX-PA和DSPE-PEG2000的质量比(1∶0.5、1∶1、1∶1.5、1∶2、1∶2.5)为自变量,考察其用量对制剂的外观澄明度、纳米粒子大小等是否产生影响。
(4)薄膜蒸发法的温度考察
将旋转蒸发仪温度分别设置为35、40、45、50、55 ℃,考察薄膜蒸发过程中温度对PTX-PA/Lip形态、粒径、包封率等的影响。
(5)探头超声时间的考察
以探头超声PTX-PA/Lip粗品的时间为自变量,考察不同超声时间(30、60、90、180、240 s)对PTX-PA/Lip纳米制剂形态、纳米粒子大小的影响。
2.4 统计学分析
数据采用IBM SPSS Statistics 27.0进行统计分析,采用单因素方差分析ANOVA进行显著性检验与评价。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 基于PTX-PA的HPLC定量检测方法学建立
3.1.1 最大吸收波长的选择
实验结果如图1所示,选用PTX-PA的最大吸收波长为228 nm为测定波长。
3.1.2 专属性考察
如图2所示,本章所建立的色谱条件对PTX-PA检测具有专属性,溶剂以及样品中的辅料对PTX-PA的检测不产生干扰。
3.1.3 线性关系考察
按照2.2.4方法进行回归,得PTX-PA的吸收峰面积-浓度在1~100 μg/ml的浓度范围内为线性方程:A=15.14 C+10.81(r=0.999 8)。
3.1.4 精密度考察
按照2.2.5方法进行精密度考察,结果如表1所示,日内与日间精密度各时间点峰面积的RSD均小于3%,表明仪器的日内与日间精密度符合测定要求。
表 1 PTX-PA的精密度考察结果(n=5)理论浓度(μg/ml) 实测浓度(μg/ml) RSD(%) 日内 5.00 4.98±0.13 2.65 25.00 25.30±0.55 2.18 100.00 99.66±1.11 1.11 日间 5.00 4.99±0.11 2.31 25.00 25.50±0.57 2.23 100.00 100.65±1.38 1.37 3.1.5 重复性与稳定性
按照2.2.6方法进行研究,精密吸取3种不同浓度的 PTX-PA溶液,连续进样5次并记录各吸收峰面积。各浓度峰面积RSD均<3%,表明仪器符合检测检测要求。此外,稳定性结果表明,样品溶液峰面积的RSD为0.81%,表明制备的PTX-PA溶液在24 h内稳定。
3.1.6 加样回收率
按照2.2.7方法计算加样回收率,结果如表2所示:低、中、高3个浓度的加样回收率均在95%~105%之间,且RSD分别为2.39%、1.80%、2.34%,表明本实验建立的高效液相色谱定量方法可用于PTX-PA的含量测定。
表 2 PTX-PA的加样回收率测试结果(n=5)理论浓度(μg/ml) 检测浓度(μg/ml) 回收率(%) RSD(%) 5 5.02±0.12 100.4 2.39 25 24.98±0.45 99.92 1.80 50 50.01±1.17 100.02 2.34 3.2 紫杉醇棕榈酸酯脂质体的制备及处方优化
3.2.1 PTX-PA/Lip制备方法的选择
采用不同方法制备的PTX-PA/Lip表征结果如表3所示,按照2.4方法进行统计学分析,3种制备方法的包封率无显著性差异,但采用薄膜分散法制备的PTX-PA/Lip粒径与PDI更小。因此,本研究优选薄膜分散法来构建PTX-PA/Lip。
表 3 3种常规制备方法对PTX-PA/Lip粒径、粒径分布、包封率的影响制备方法 粒径(l/nm) PDI 包封率(%) 薄膜分散法 76.76±3.39 0.104±0.02 79.38±2.00 高压均值法 125.11±5.32 0.139±0.03 78.87±2.00 挤出法 128.87±4.92 0.239±0.05 81.38±1.11 3.2.2 处方工艺筛选
(1)磷脂种类的选择
按照2.3.2(1)制备的PTX-PA/Lip表征结果如表4所示,以PC98-T为膜材制备的纳米给药系统粒径小、外观澄明、粒径分布均匀、包封率较高,因此选择PC98-T作为本研究中的磷脂。
表 4 磷脂种类对脂质体的外观形态、颗粒大小、药物包封率的影响磷脂种类 外观 粒径(l/nm) PDI 包封率(%) PC98-T 半透明 76.76±3.39 0.104±0.02 79.38±2.00 HSPC 有沉淀 177.86±5.39 0.532±0.08 59.06±1.32 EPCS 半透明 135.12±5.65 0.108±0.03 73.23±1.15 DPPC 有沉淀 158.26±4.11 0.669±0.05 53.27±2.68 (2)磷脂和药物比例的考察
按照2.3.2(2)项下确定处方中药物和磷脂的用量,其结果如表5所示,磷脂PC98-T和药物的质量比大于10时,制备的PTX-PA/Lip外观澄明度、粒子大小、粒径分散系数等参数无显著性差别。随着磷脂浓度不断增加,药物的包封率不断增加,当PC98-T和PTX-PA的质量比为20∶1时,脂质体对药物的包封率最高,后期考虑到经济成本,将PC98-T和PTX-PA的质量比定为20∶1。
表 5 磷脂和药物质量比对脂质体的外观澄明度、颗粒大小、对药物包封率的影响磷脂∶药物 外观 粒径(l/nm) PDI 包封率(%) 5∶1 略透明 134.62±2.95 0.364±0.04 58.15±1.73 10∶1 有沉淀 90.29±4.66 0.151±0.04 71.56±1.60 20∶1 半透明 84.58±1.33 0.11±0.02 83.50±0.92 30∶1 半透明 86.06±2.71 0.09±0.05 73.44±4.44 40∶1 有沉淀 88.86±1.91 0.199±0.05 68.37±11.08 (3)磷脂和胆固醇比例的考察
按照2.3.2(2)方法研究,结果如表6所示,随着胆固醇用量增多,制剂变浑浊,粒径增大,载药量显著降低。因此,胆固醇不加入本制剂的处方中。
表 6 磷脂和胆固醇质量比对脂质体外观澄明度、颗粒大小、对药物包封率的影响磷脂∶胆固醇 外观 粒径(l/nm) PDI 包封率(%) 4∶0.05 半透明 115.37±4.48 0.200±0.07 71.57±1.28 4∶0.1 半透明 160.16±3.15 0.251±0.01 61.08±3.13 4∶0.2 半透明 182.75±2.43 0.217±0.04 54.97±0.95 4∶0.3 乳白色 241.90±12.09 0.697±0.12 54.11±1.64 4∶0.4 乳白色 255.33±8.27 0.700±0.138 48.84±0.78 (4)药物和DSPE-PEG2000比例的考察
按照2.3.2(3)方法研究,其结果如表7所示,DSPE-PEG2000对包封率没有显著性影响,但当DSPE-PEG2000含量不断增加时,纳米粒子的颗粒大小先降低,当药物与DSPE-PEG2000质量比小于1∶1.5时,粒径无显著性变化,因此,药物与DSPE-PEG2000的质量比选择1∶1.5。
表 7 PTX-PA和DSPE-PEG2000的质量比对脂质体外观、粒径、药物包封率的影响药物∶DSPE-
PEG2000外观 粒径(l/nm) PDI 包封率(%) 2∶1 半透明 82.86±2.15 0.107±0.01 90.48±0.49 1∶1 半透明 78.16±2.05 0.351±0.38 90.41±0.34 1∶1.5 半透明 72.23±2.60 0.110±0.02 89.66±1.25 1∶2 半透明 74.64±1.81 0.140±0.04 90.90±2.93 1∶2.5 半透明 75.38±2.10 0.097±0.04 89.48±0.67 (5)薄膜蒸发法的温度考察
按照2.3.2(4),采用不同温度制备纳米制剂表征结果如表8所示,在筛选的5个温度中,当温度为45 ℃时,脂质体粒径最小、粒径分散性好、包封率最高,因此,本研究选用45 ℃作为薄膜蒸发温度。
表 8 温度对PTX-PA/Lip外观、粒径、包封率的影响温度(T/ ℃) 外观 粒径(l/nm) PDI 包封率(%) 35 略透明 159.42±2.42 0.545±0.08 54.94±1.85 40 半透明 105.93±6.13 0.269±0.03 73.98±1.60 45 半透明 76.97±2.50 0.105±0.049 91.13±1.45 50 半透明 91.93±2.60 0.181±0.05 80.27±2.13 55 半透明 112.23±6.37 0.233±0.06 74.15±2.12 (6)探头超声时间的考察
按照2.3.2(5)方法进行研究,结果如表9所示:处理时间较短时,纳米粒径较大,颗粒大小分布不均匀;随着超声处理的延长,粒径减小,包封率也提高;超声时间过长,脂质体结构破坏,导致药物泄露、包封率降低。因此将探头超声处理时间定为90 s。
表 9 超声处理对脂质体的外观澄明度、颗粒大小、对药物包封率的影响超声时间(t/s) 外观 粒径(l/nm) PDI 包封率(%) 30 沉淀 278.09±4.73 0.857±0.10 42.83±2.76 60 半透明 113.21±11.16 0.485±0.04 54.96±2.41 90 半透明 78.13±2.78 0.055±0.02 92.74±0.77 180 半透明 123.17±8.39 0.430±0.08 76.29±1.76 240 沉淀 261.85±4.94 0.915±0.20 50.42±2.74 3.3 紫杉醇棕榈酸酯脂质体PTX-PA/Lip的理化性质表征
综上研究,采用的最优处方和制备工艺如下:精密称取PTX-PA 20 mg、PC98-T 400 mg、DSPE-PEG2000 30 mg,加入适量二氯甲烷溶解,接着45 ℃旋蒸去除有机溶剂,再向圆底烧瓶底部薄膜中加入10 ml重蒸水(预热至同等温度),震荡、水化,得PTX-PA/Lip粗品,最后粗品探头超声(90 s)、过滤(0.22 μm),得最终样品PTX-PA/Lip纳米给药系统。
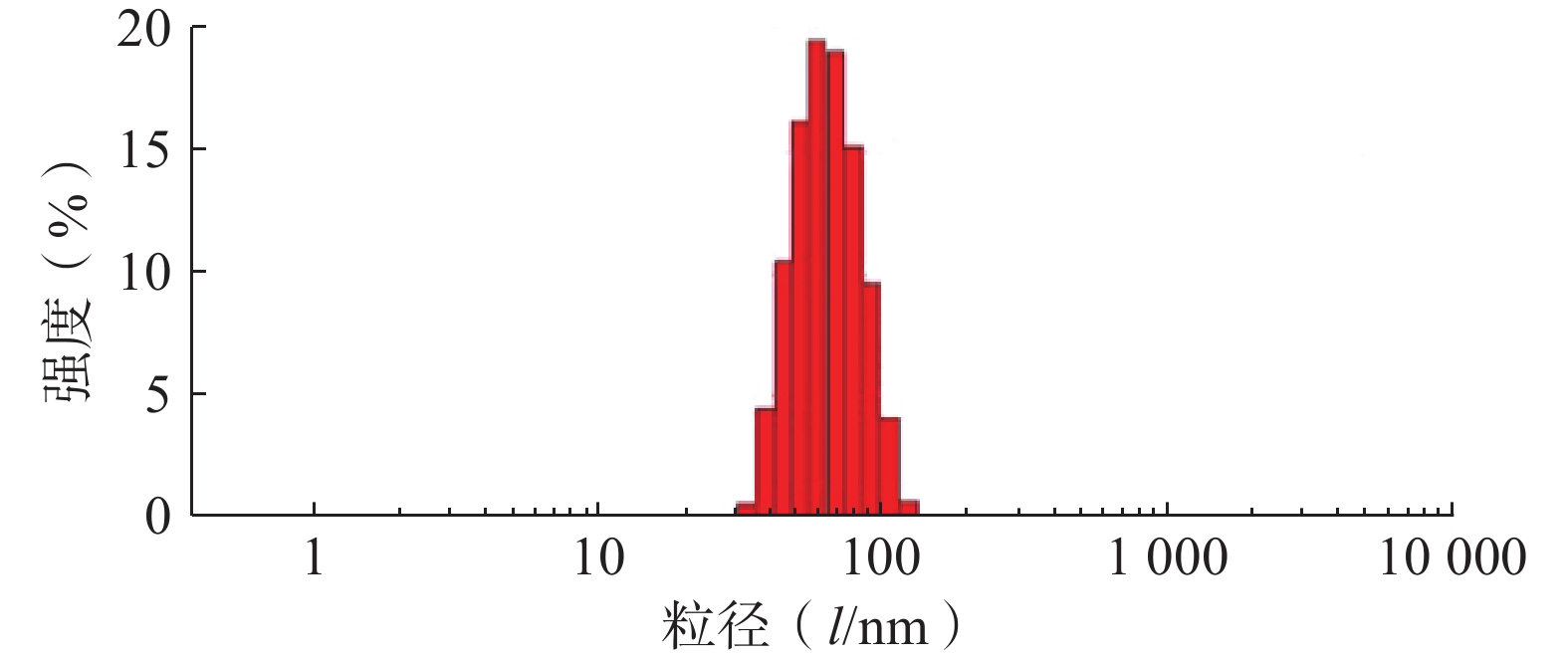
采用Zeta-sizer Nano粒度仪测定最优PTX-PA/Lip的粒径、PDI与zeta电位。结果如图3所示,制备的PTX-PA/Lip脂质体粒径大小为(62.75±1.81) nm,PDI为(0.076±0.020),Zeta电位为(−15.9±0.21) mV,表明制备的PTX-PA/Lip纳米给药系统粒径较小、分布均匀、具有良好的分散性。
4. 总结
本实验合成紫杉醇前药——紫杉醇棕榈酸酯PTX-PA,建立PTX-PA的HPLC定量测定方法,经一系列方法学验证,表明其符合PTX-PA定量分析要求,为后续试验奠定了基础。本实验采用薄膜分散法制备PTX-PA脂质体,工艺简便,技术成熟,并通过单因素筛选对PTX-PA脂质体进行处方优化。本文基于纳米技术成功制备出棕榈酸修饰的紫杉醇脂质体,增强了紫杉醇在靶细胞的递送,为PTX-PA后续的药效学研究奠定基础。
-
表 1 ABTS、FRAP、DPPH的线性方程及相关系数
项目 方程 相关系数 ABTS Y=0.662 4X+0.715 3 r=0.999 5 FRAP Y=0.298 5X+0.060 r=0.999 4 DPPH Y=0.459 8X−0.023 8 r=0.998 9 表 2 4种菊花抗氧化能力
名称/抗氧化
能力FRAP(mmol FeSO4/g) ABTS(mmol Trolox/g) DPPH(mmol Trolox/g) 黄山金丝皇菊 0.504±0.049 0.481±0.052 0.359±0.025 黄山皇菊 0.421±0.036 0.402±0.043 0.305±0.033 黄山贡菊 0.347±0.028## 0.369±0.031 0.277±0.041# 黄山黄菊 0.270±0.017###,** 0.287±0.014## 0.208±0.019##,* *P<0.05,**P<0.01,与黄山皇菊比较;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,###P<0.001,与黄山金丝皇菊比较。 表 3 角叉菜胶致大鼠急性炎症模型结果(x±s,n=8)
组别 1 h 2 h 4 h 肿胀率(%) 抑制率(%) 肿胀率(%) 抑制率(%) 肿胀率(%) 抑制率(%) 模型组 41.6±
4.5− 52.5±
10.7− 45.1±
8.2− 黄山金丝皇菊 31.5±
5.9#24.3 42.3±
7.1#19.5 44.9±
8.80.5 黄山皇菊 28.9±
5.9##30.6 38.9±
7.8#,*,ΔΔ26.0 46.4±
10.0−2.8 黄山贡菊 31.8±
6.3#23.7 50.0±
11.74.8 46.4±
8.3−2.8 黄山黄菊 33.3±
6.2#20.1 51.0±
7.32.9 44.9±
8.80.6 *P<0.05,与黄山贡菊比较;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,与模型组比较;ΔΔP<0.01,与黄山黄菊比较。 -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典[S]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2022, 323. [2] 王德胜, 黄艳梅, 石岩, 等. 菊花化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2018, 46(23):9-11,17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2018.23.003 [3] 张健, 李友宾, 钱大玮, 等. 菊花化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2006, 17(10):1941-1942. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2006.10.107 [4] YANG W S, KIM D, YI Y S, et al. AKT-targeted anti-inflammatory activity of the methanol extract of Chrysanthemum indicum var albescens[J]. J Ethnopharmacol,2017,201:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.03.001 [5] YANG L, AOBULIKASIMU·NUERBIYE, CHENG P, et al. Analysis of floral volatile components and antioxidant activity of different varieties of Chrysanthemum morifolium[J]. Molecules,2017,22(10):1790. doi: 10.3390/molecules22101790 [6] XUE G M, LI X Q, CHEN C, et al. Highly oxidized guaianolide sesquiterpenoids with potential anti-inflammatory activity from Chrysanthemum indicum[J]. J Nat Prod,2018,81(2):378-386. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00867 [7] LI Y F, YANG P Y, LUO Y H, et al. Chemical compositions of chrysanthemum teas and their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties[J]. Food Chem,2019,286:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.02.013 [8] MING K, CHEN Y, SHI J T, et al. Effects of Chrysanthemum indicum polysaccharide and its phosphate on anti-duck hepatitis a virus and alleviating hepatic injury[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2017,102:813-821. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.04.093 [9] ZHAO W H, ZENG C, JIA Q Q, et al. Effects of the Kunlun snow chrysanthemum polysaccharides on acetaminophen-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis using animal model[J]. Pak J Pharm Sci,2018,31(3):985-990. [10] KIM K J, KIM Y H, YU H H, et al. Antibacterial activity and chemical composition of essential oil of Chrysanthemum boreale[J]. Planta Med,2003,69(3):274-277. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-38479 [11] KUANG C L, LV D, SHEN G H, et al. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activities of volatile oil extracted from Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat[J]. J Food Sci Technol,2018,55(7):2786-2794. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3203-1 [12] LEE J S, KIM H J, LEE Y S. A new anti-HIV flavonoid glucuronide from Chrysanthemum morifolium[J]. Planta Med,2003,69(9):859-861. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-43207 [13] 宋雷, 绽春蕊, 杨世英, 等. 杭黄菊提取物的体外抗菌活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2015, 27:455-458. doi: 10.16333/j.1001-6880.2015.03.017 [14] 杨璐齐, 陈冠林, 俞憬, 等. 6种菊花抗氧化活性及总酚含量的研究[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2017, 38(18):6-10. [15] 白小军, 杨锋, 呼睿, 等. 消肿止痛膏对足肿胀模型大鼠足肿胀度的影响[J]. 陕西中药, 2017, 38(8):1144-1145. [16] 肖百全, 朱少璇, 杨威, 等. 角叉菜胶致大鼠足肿胀模型探讨及其机制研究[J]. 中国实用医药, 2008, 3(23):63-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7555.2008.23.037 [17] 张晓媛, 段立华, 赵丁. 菊花化学成分及药理作用的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2008, 19(7):1702-1704. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2008.07.075 [18] 瞿璐, 王涛, 董勇喆, 等. 菊花化学成分与药理作用的研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究, 2015, 1:98-104. -





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



