-
河豚毒素(tetrodotoxin,TTX)是一种存在于河豚、蝾螈、斑足蟾等动物中的天然毒素,其选择性作用于电压门控钠离子通道(voltage-gated sodium channels,VGSCs),可强效阻滞神经、肌肉兴奋传导,导致神经和肌肉的麻痹,甚至死亡[1]。基于VGSCs在体内的广泛分布和作用,TTX的药用价值也备受关注,尤其在麻醉、镇痛、戒断等方面,一直是研究的热点[2-6]。TTX对多种疼痛尤其是炎性疼痛和神经病理性疼痛表现出优异的镇痛效果,临床试验也表明,TTX在治疗无法控制的中、重度癌症相关疼痛方面有良好的疗效,且不会产生耐药性和成瘾性,具有较好的应用前景[7-8]。然而,目前对TTX的急性镇痛研究较少,有报道认为TTX对急性疼痛的镇痛效应较弱[7,9]。但也有研究表明,TTX在小鼠甩尾实验、醋酸扭体实验中有显著镇痛效应。为明确TTX的急性镇痛效应,本研究拟通过4种急性疼痛模型,即扭体实验、福尔马林刺激实验、热板实验和甩尾实验,进一步评估TTX对急性疼痛的镇痛效果,为其安全、合理应用提供实验支持。
HTML
-
ICR小鼠,体重18~22 g,Wistar大鼠,雄性,体重150~180 g,购自北京华阜康生物科技股份有限公司,实验动物合格证号:SCXK(京)2019-0008。动物经适应性饲养4~7 d后开始进行实验。
-
TTX(批号:E2011088,上海阿拉丁试剂有限公司);盐酸吗啡(批号:20110601,青海制药厂有限公司);花生四烯酸检测试剂盒(批号:202101,江苏雨桐生物科技有限公司);冰醋酸(批号:C10309476,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司);甲醛溶液(福尔马林,批号:030430,北京化学试剂公司)。
-
DK-S28型电热恒温水浴锅(上海精宏实验设备有限公司);YLS-6B智能热板仪(济南益延科技发展有限公司);5424R型离心机(德国Eppendorf公司);Synergy HTX酶标仪(美国BioTeK公司)。
-
小鼠70只,雌雄各半,随机分为7组,每组10只,实验前禁食12 h,自由饮水。给药组分别肌内注射0.5、1、2、4、8 μg/kg的TTX或1 mg/kg吗啡,对照组肌内注射等体积的生理盐水,给药后40 min,小鼠腹腔注射0.6%的醋酸溶液(0.1 ml/10 g),记录15 min内的扭体次数,以小鼠出现腹部内凹、躯干与后肢伸张、臀部高起等行为为扭体反应阳性。计算各组疼痛抑制率,公式为:
-
受试大鼠进行“疼痛反应累积分值”预筛实验,试验时,在大鼠左后肢足趾部皮下注射2.5%的福尔马林溶液50 μl后,分别观察1 ~10 min(Ⅰ相)和10 ~40 min(Ⅱ相)内大鼠的疼痛反应。表现为舔、咬、抖足为3分,提足为2分,轻触地面但不负重行走时跛行为1分,正常负重,行走自如为0分。记录各时间段出现上述各级反应的秒数乘以相应反应的分值,以乘积之和为疼痛反应累积分值,公式为:疼痛反应累积分值=跛行时间×1+提足时间×2+舔咬抖足时间×3。选择累积分值评分相近的动物进行实验。
动物恢复7 d,然后重新分组,每组10只,进行正式实验,给药组分别肌内注射0.5 ~8 μg/kg的TTX或1 mg/kg吗啡,对照组注射等体积生理盐水,给药40 min后,在大鼠右后肢足趾部皮下注射2.5%的福尔马林溶液50 μl,再次观察I相和II相疼痛反应,并计算各组的疼痛反应累积分值和疼痛抑制率。疼痛抑制率计算公式为:
-
受试动物均进行“基础痛阈”预筛实验,实验时,将小鼠尾下部垂直浸入(52±0.5)℃的恒温水浴中,浸入长度为3 cm左右,以尾回缩出水面的潜伏期为测痛指标,给药前间隔5 min测定2次,以其均值作为基础痛阈。选择基础痛阈相近(3~7 s)的动物作为合格动物进行实验。筛选后动物恢复24 h,重新分成7组,每组10只,进行正式实验。小鼠肌内注射TTX(0.5~8 μg/kg)、吗啡(1 mg/kg)或等体积生理盐水,给药后40 min,进行痛阈测定,间隔5 min测定2次,以其均值作为给药后痛阈。为防止尾部烫伤,若痛阈超过14 s则停止水浴,以14 s计算。疼痛抑制率计算公式为:
-
受试小鼠为雌性,均进行“基础痛阈”预筛实验,实验时,将小鼠放在预热至(55±0.5)℃金属板上,恒温,以小鼠舔足反应或跳跃反应的潜伏期为痛阈指标。每只动物测定间隔5 min,测定2次,取其平均值作为基础痛阈值。选择基础痛阈相近(5~20 s)的小鼠进行正式试验。筛选后小鼠恢复24 h以上,重新分为7组,每组10只,进行正式实验。小鼠肌内注射TTX(0.5~8 μg/kg)、吗啡(1 mg/kg)或等体积生理盐水,给药40 min后,进行痛阈测定。间隔5 min测定2次,以其均值作为给药后痛阈值。为防止足部烫伤,若痛阈值超过40 s则停止测定,以40 s计算。疼痛抑制率计算公式为:
-
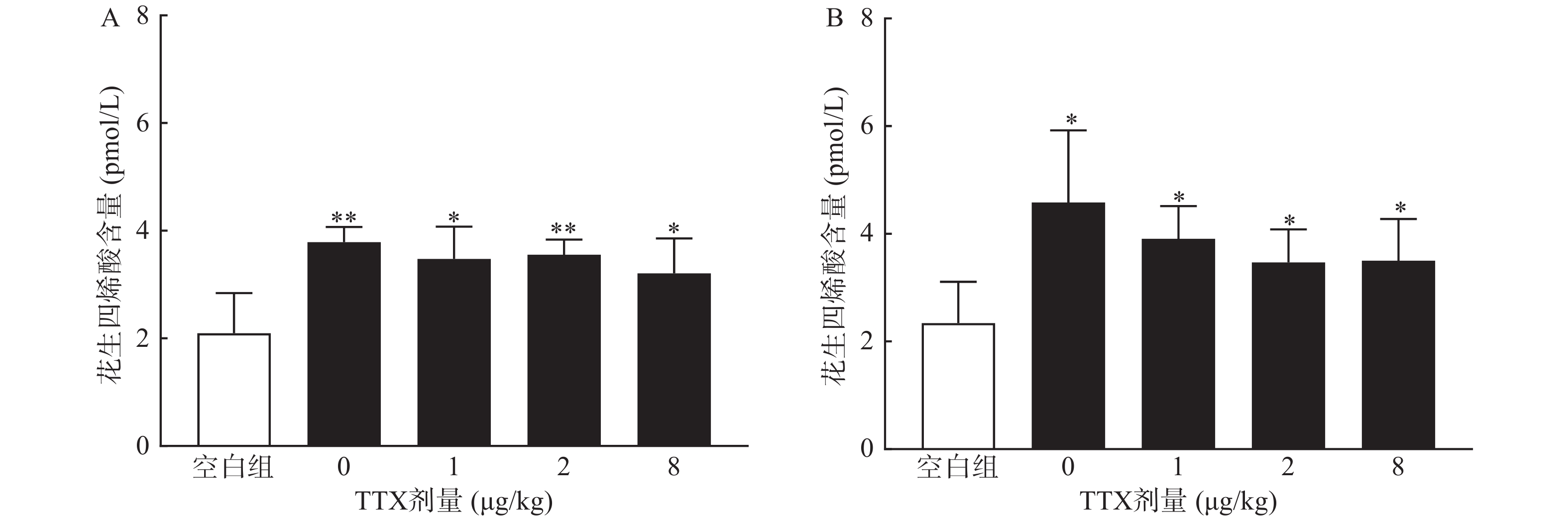
为进一步阐明TTX对醋酸扭体和福尔马林疼痛模型的镇痛机制,进行血清相关炎性介质的测定。将小鼠分为5组:空白对照组(只注射生理盐水),醋酸对照组(肌内注射生理盐水40 min后,腹腔注射0.6%的醋酸),TTX组(肌内分别注射1、2、8 μg/kg TTX 40 min后,腹腔注射0.6%的醋酸),每组10只,待测定镇痛效应后,小鼠眼眶取血;大鼠分组参照小鼠,注射生理盐水或TTX 40 min后足底注射福尔马林,待测定镇痛效应后,眼内眦取血;血液静置30 min后,3 000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液,用花生四烯酸Elisa试剂盒测定血清中花生四烯酸含量。
-
实验数据以(
$\bar x $ ±s)表示。用SPSS15.0统计分析软件进行统计学处理,组间差异采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)和t检验,以P<0.05为差异有显著性。
1.1. 实验动物
1.2. 药物与试剂
1.3. 仪器
1.4. 方法
1.4.1. 小鼠醋酸扭体实验
1.4.2. 大鼠福尔马林刺激实验
1.4.3. 小鼠甩尾实验
1.4.4. 小鼠热板实验
1.4.5. 血清花生四烯酸检测
1.5. 统计学分析
-
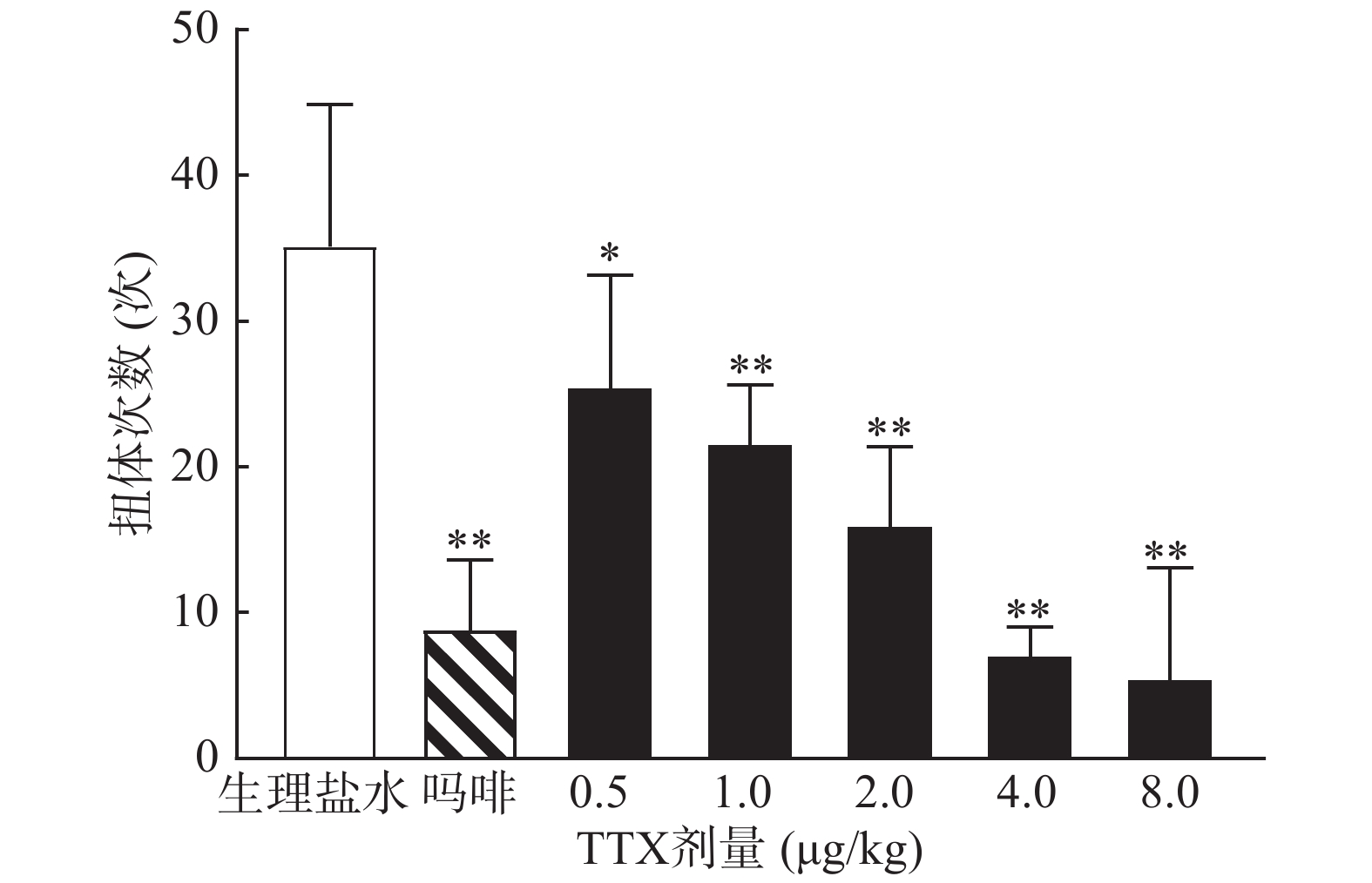
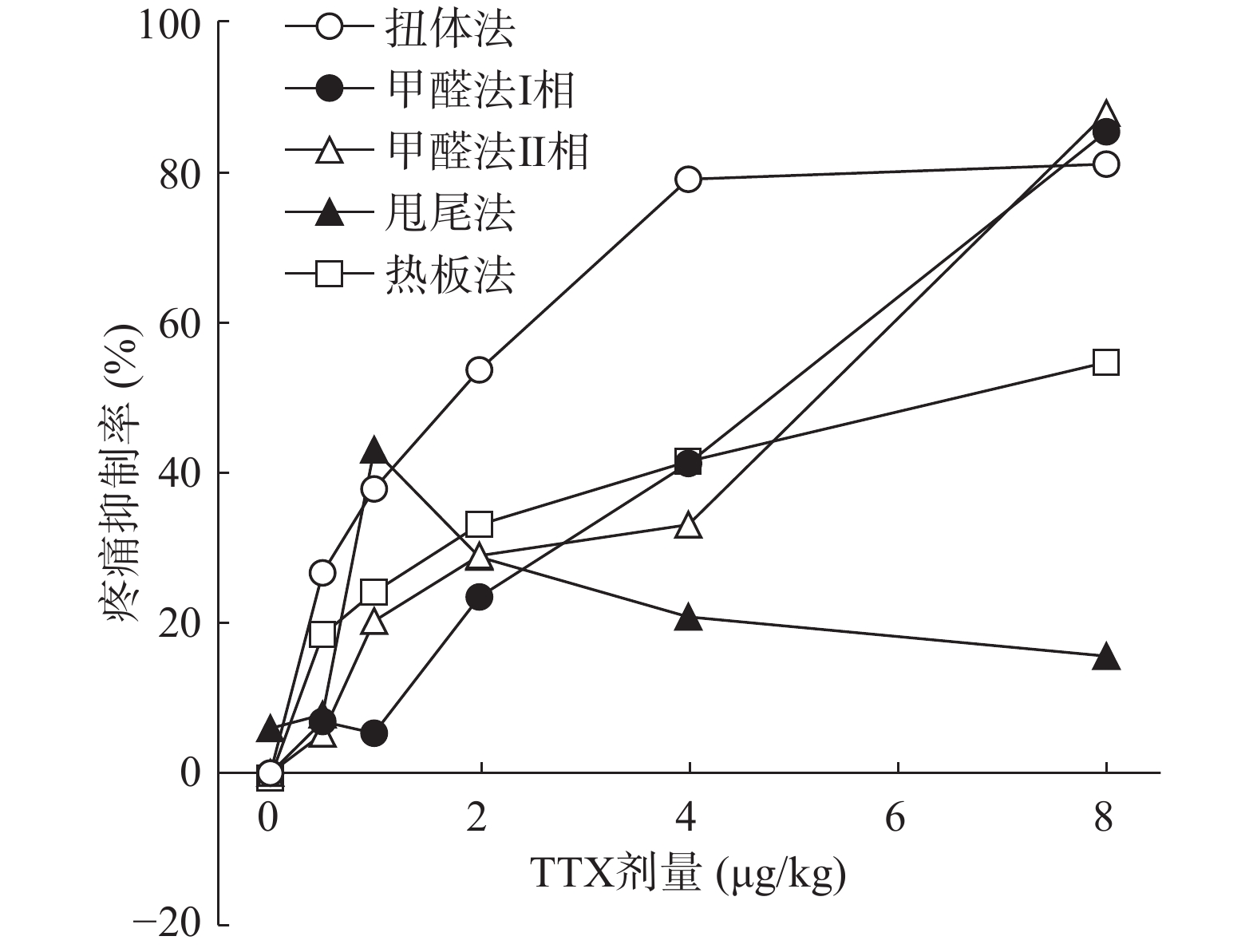
0.6%的醋酸可诱导小鼠扭体反应,15 min内平均扭体次数为(35.1±9.8)次,如图1所示。1 mg/kg盐酸吗啡显著抑制醋酸诱导的扭体反应,0.5~8 μg/kg的TTX呈剂量依赖性地降低醋酸诱导的小鼠扭体次数,最高抑制率约为81.26%。TTX抑制醋酸诱导疼痛效应的半数效应剂量(ED50)为1.51 μg/kg,95%置信区间(CI)为1.16 ~1.93 μg/kg,表明TTX对醋酸诱导的小鼠扭体疼痛模型具有较好的镇痛效果。
-
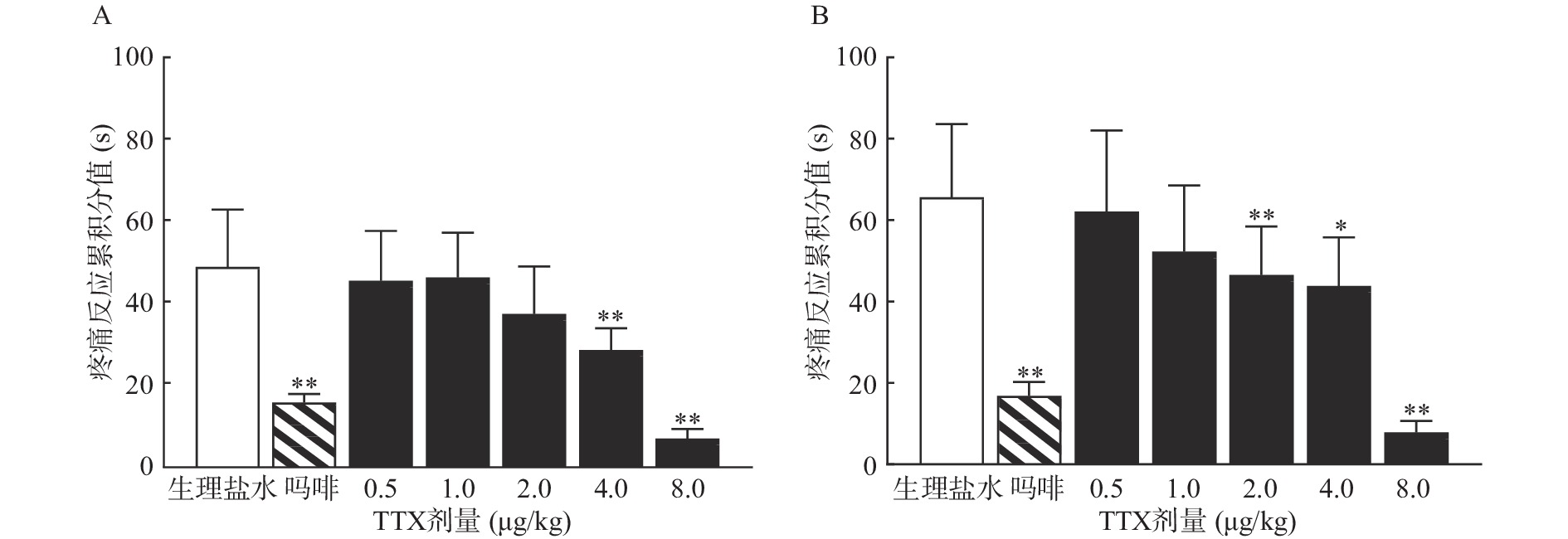
TTX 4 μg/kg和8 μg/kg剂量组对福尔马林致大鼠Ⅰ相疼痛反应累积分值与生理盐水组相比有显著差异(P<0.01),当TTX给药剂量为2~8 μg/kg 时,对福尔马林致大鼠Ⅱ相疼痛反应累积分值与阴性对照组相比有显著差异(P<0.05或P<0.01)(图2)。结果表明,吗啡及TTX对福尔马林致大鼠Ⅰ相、Ⅱ相疼痛反应均有明显的镇痛作用,TTX的最高疼痛抑制率分别为85.58%、88.05%。TTX抑制福尔马林致大鼠Ⅰ相、Ⅱ相疼痛反应的ED50值(95% CI)分别为4.12 μg/kg(3.22~5.25 μg/kg)、4.00 μg/kg(2.18 ~9.12 μg/kg)。
-
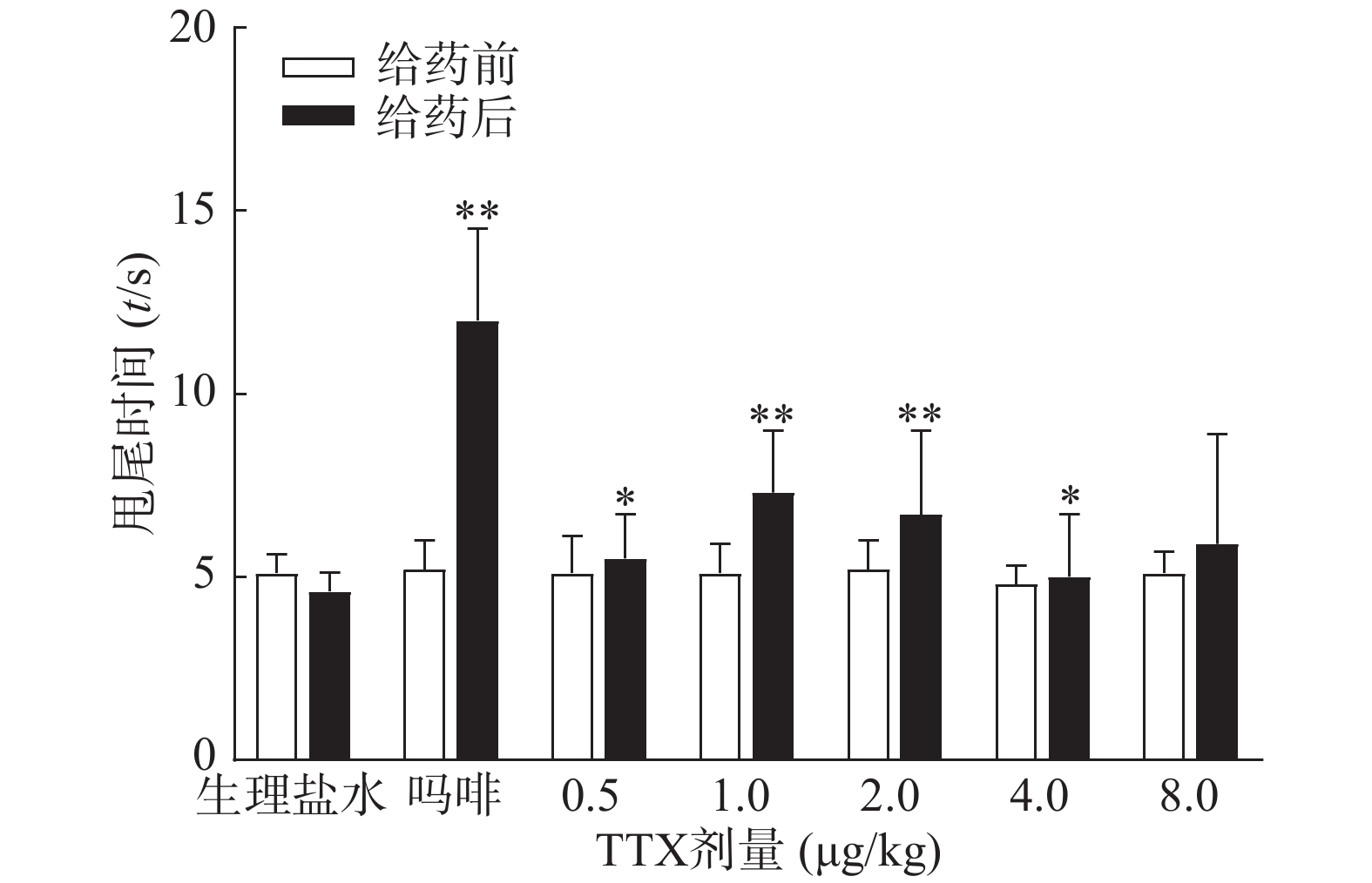
图3结果显示,1 mg/kg吗啡显著延长小鼠的甩尾时间,TTX在0.5~8 μg/kg的剂量范围,1 μg/kg镇痛效果达峰值,最高疼痛抑制率仅为25.0%,随着给药剂量增加,其镇痛效应并未提高,表明TTX对小鼠甩尾疼痛模型的镇痛效应较弱。
-
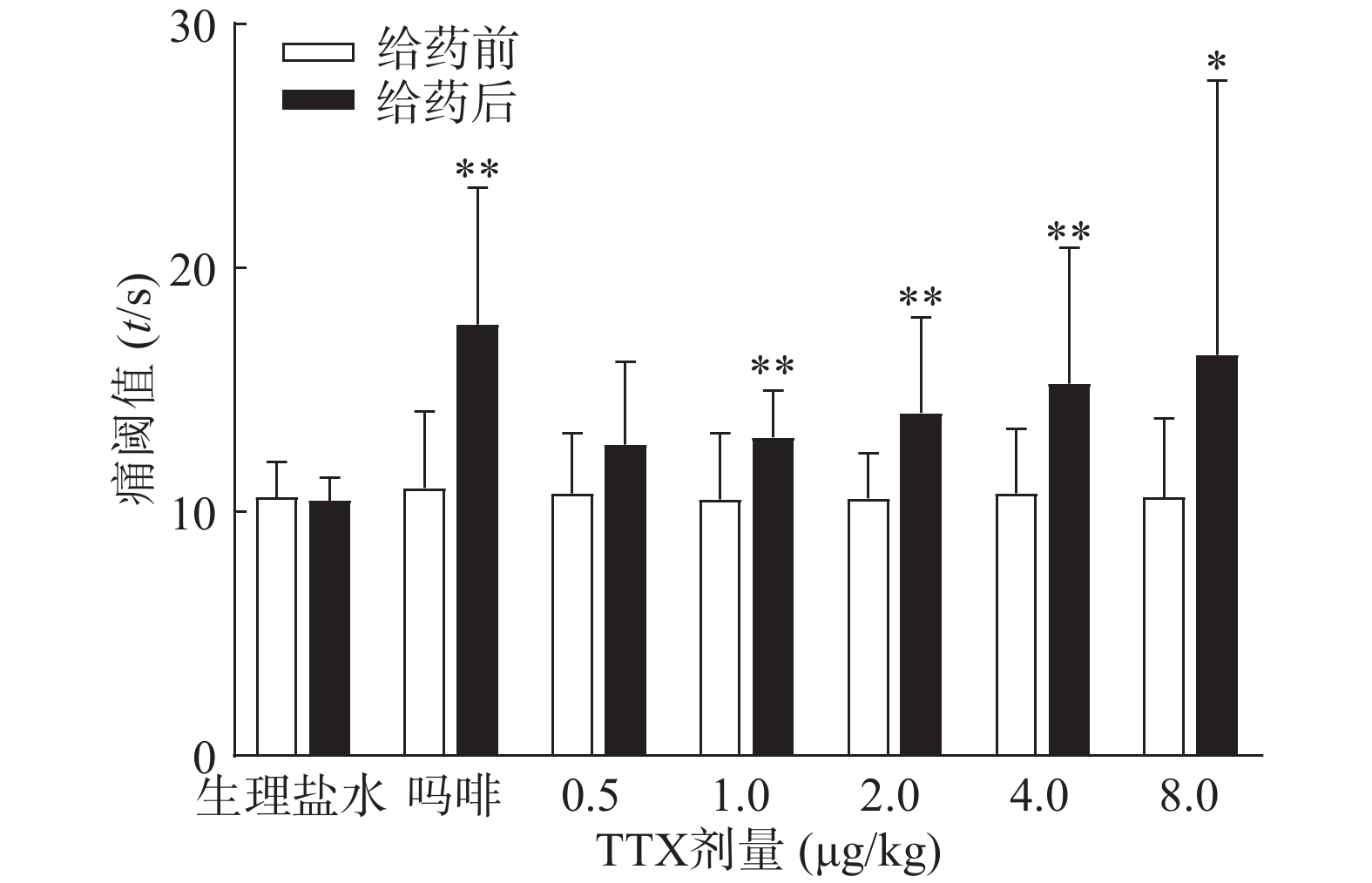
吗啡可显著延长小鼠热板时间(P<0.01),TTX在0.5 ~8 μg/kg的给药剂量范围,0.5 μg/kg剂量组与给药前相比无显著性差异,其余各剂量组可明显增加小鼠的痛阈值(P<0.05或P<0.01)(图4),但疼痛抑制率最高仅为19.79%,镇痛效应偏低,表明TTX对小鼠热板疼痛模型的镇痛效应较弱。
将4种模型计算得到的疼痛抑制率作图,如图5所示,TTX对动物扭体及福尔马林疼痛模型具有较好的镇痛效果,疼痛抑制率可达80%以上。在甩尾和热板模型上,TTX虽表现出一定的镇痛效果,但疼痛抑制率较低,整体镇痛效果偏弱。
-
对动物血清测定结果显示,与正常空白对照小鼠对比,腹腔注射0.6%的醋酸可显著提高血清中炎性介质花生四烯酸的水平(P<0.01),然而,TTX各剂量组血清花生四烯酸含量与醋酸对照组(TTX 0 μg/kg剂量组)比较,未有显著改变(P>0.05)。2.5%的福尔马林能显著升高大鼠血清花生四烯酸的含量(P<0.05),但TTX各剂量组未表现出对花生四烯酸的显著抑制作用(图6)。
2.1. TTX对小鼠醋酸扭体疼痛模型的镇痛作用
2.2. TTX对福尔马林诱导大鼠疼痛模型的镇痛作用
2.3. TTX对小鼠甩尾疼痛模型的镇痛作用
2.4. TTX对小鼠热板疼痛模型的镇痛作用
2.5. TTX对血清花生四烯酸的影响
-
目前,机体内已发现9种VGSCs亚型(Nav1.1~Nav1.9),根据对TTX的敏感性,又分为TTX敏感型钠通道和TTX非敏感型钠通道。其中Nav1.1、Nav1.2、Nav1.3、Nav1.4、Nav1.6和Nav1.7属于TTX敏感型钠通道,纳摩尔浓度的TTX即可抑制其电流。因此,TTX是已知毒性最大的神经毒素之一,其小鼠口服、皮下注射和腹腔注射的半数致死剂量分别为532、12.5和10.7 μg/kg,对人类的毒性剂量尚不明确[9]。本研究中应用的TTX剂量为0.5~8 μg/kg,各剂量组肌内注射后未观察到明显不良反应,且实验过程中及实验后14 d内无动物死亡。目前,报道的与疼痛相关的TTX敏感型钠通道有Nav1.1、Nav1.7、Nav1.3。近期的一项研究发现,激活脊根神经节Nav1.1通道会提升机械超敏小鼠的疼痛行为,且不会引起神经炎症[10]。Nav1.3通道参与外周和中枢神经系统对各种损伤的疼痛信号传导,应用Nav1.3反义核苷酸降低通道的表达,会减轻大鼠和小鼠的坐骨神经和脊髓损伤的疼痛反应[11-12]。Nav1.7通道在疼痛敏感性形成方面起重要作用,炎症反应如各种损伤、截肢或外科手术,导致Nav1.7的过度表达,Nav1.7基因敲除的小鼠对机械和热创伤性疼痛痛阈降低[2]。
TTX对多种疼痛尤其是炎症性疼痛和神经病理性疼痛的镇痛效应得到了广泛验证。低剂量TTX可显著降低脊神经结扎动物的疼痛行为,剂量依赖性地抑制角叉菜胶引起的机械性痛觉过敏、热痛觉过敏以及化疗药物诱导的神经病理性疼痛[7, 9]。近期研究也发现,TTX可有效抑制辣椒素等刺激诱发的内脏痛[13]。然而,TTX在急性疼痛治疗效果方面存在较大争议。本研究与其他研究结果都显示,TTX可有效抑制醋酸诱导的小鼠扭体次数[14-16]。Marcil等[16]的研究表明,TTX腹腔注射不能抑制福尔马林诱导的大鼠Ⅰ相疼痛反应,且只有高剂量TTX(6 μg/kg)显著抑制Ⅱ相疼痛反应。而徐英等[15]研究通过肌内注射TTX,可显著降低2.5%福尔马林注射后5 min内的疼痛反应。本研究结果也表明,TTX对福尔马林刺激引起的Ⅰ相和Ⅱ相疼痛均有较强的镇痛作用。
TTX对两种模型镇痛作用的机制可能与TTX的炎性疼痛抑制作用相关。小鼠扭体模型中,腹腔注射醋酸可刺激脏层和壁层腹膜,引起深部较大面积较长时间的炎性疼痛;足底皮下注射福尔马林引起的反应分为2个时相:0~10 min出现者为Ⅰ相(早期相),10 ~60 min出现的反应为Ⅱ相(迟发相)。Ⅰ相反应主要是刺激C纤维所致,Ⅱ相反应有炎症机制参与[17]。因此,为进一步明确TTX的镇痛效应与化学物质导致的炎性疼痛是否相关,本研究进行了血清花生四烯酸的测定,结果显示,醋酸和福尔马林均能显著提高动物血清中的花生四烯酸的水平,表明两者诱导的疼痛反应有炎性机制参与,但TTX并不能降低血清花生四烯酸水平,推测其可能是通过阻断炎性介质介导的疼痛反应产生镇痛效果,但不抑制炎性介质的产生或释放。
在急性物理性疼痛方面,虽然有研究显示TTX对热板和甩尾模型具有一定镇痛效应,但对两种模型的镇痛效应不一致,可能与足底和尾部的神经分布数量、类型差异相关[14]。然而,也有报道表明,皮下注射1~6 μg/kg TTX对热刺激、冷刺激及机械刺激导致的急性疼痛的抑制作用并不明显[18-20]。本研究发现,TTX通过肌内注射途径给药,对小鼠热板和甩尾疼痛模型镇痛效应较弱,TTX可能对热刺激引起的急性疼痛的镇痛作用较弱,但此结论还需要通过更多的给药途径和疼痛模型进一步验证和阐明。
本研究分别通过化学诱导和物理刺激方法,建立了4种急性疼痛模型并评估TTX的镇痛作用,结果表明TTX对醋酸和福尔马林诱导的化学诱导疼痛模型具有良好的镇痛效果,其作用可能与阻断化学物质诱导的炎性疼痛相关;而对热诱导(热板和热水)的物理刺激疼痛模型的镇痛效果较弱。本研究结果为TTX的安全、合理应用提供了进一步的实验支持。










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: