-
畲药地稔(地菍)是野牡丹科植物地稔(Melastoma dodecandrum Lour.)的新鲜或干燥全草,临床常用于带状疱疹、盆腔炎、风湿骨痛等病症的治疗,是宫炎平片和紫地宁血散等中成药的重要组成[1]。现代药理学研究[2-3]表明,地稔提取液具有清除氧自由基、抑制人红细胞膜脂质过氧化、提高小鼠血清超氧化物歧化酶活性等作用,有较强的抗氧化活性。常见的抗氧化活性测定方法有1,1-二苯基-2-苦腈基自由基(DPPH)法、2,2'-连氨-(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二氨盐法、铁离子自由基法等,操作烦琐、费时[4]。近年来,基于DPPH的在线色谱分析法[5]大大提高了抗氧化活性的分析效率,但完成测定仍普遍需要30 min以上的时间。光谱技术具有快速、简便等优势。目前,已有研究将食品的光谱学特征与抗氧化活性直接关联,建立了茶叶、冬枣等抗氧化活性的快速预测方法[6-9],但采用紫外光谱技术快速预测地稔的抗氧化活性尚未见文献报道。课题组前期已建立了基于近红外光谱的地稔水提液抗氧化活性快速预测方法[10]。在前期基础上,本研究进一步建立了基于紫外光谱和偏最小二乘(partial least squares, PLS)回归算法的地稔水提液抗氧化活性快速预测方法,并开发了应用软件。采集待测地稔水提液的紫外光谱后,通过软件中的预测功能可在2 s内得到抗氧化活性的快速预测结果。本研究可为进一步完善地稔抗氧化活性的快速预测方法提供依据。
-
DPPH(Sigma-Aldrich公司)。无水乙醇(分析纯,浙江省无锡市展望化工试剂有限公司)。去离子水由Smart2pure超纯水系统制备(Thermo,美国)。共收集10批地稔药材,经浙江省中医药研究院俞忠明副主任中药师鉴定为地稔(Melastoma dodecandrum Lour.),阴干密封保存。紫外光谱采集采用2450系列紫外-可见分光光度仪(岛津,日本)。DPPH自由基清除活性吸光度测定采用SpectraMax 190酶标仪(Molecular Devices,美国)。
-
称取地稔药材各约5.0 g,分别加入料液比为1∶25~1∶45的去离子水,浸泡30 min,加热回流提取1.5~3.5 h,抽滤后的提取液水浴浓缩后转移至50 ml量瓶,用去离子水定容,共得到34批地稔水提液,采用DPPH法测定其抗氧化活性。地稔水提液的制备条件和抗氧化活性测定方法见文献[10]。
移取地稔水提液40 μl,加入去离子水3960 μl,10000 r/min离心后取上清液,制得样品溶液。用1 cm光程的石英比色皿采集紫外光谱。光谱扫描波长范围为190~600 nm,波长间隔为1 nm,扫描速度为快速。每次分析前用去离子水校正仪器基线。
-
以抗氧化活性为Y,以紫外光谱矩阵为X,通过留一法交叉验证确定最优主成分数,建立X对Y的PLS回归模型。采用校正集相关系数(Rcal)、拟合均方根误差(RMSEE)、交叉验证均方根误差(RMSEcv)、验证集相关系数(Rval)和预测均方根误差(RMSEP)对模型的准确性和预测能力进行评价[11]。首先,比较不同起始波长和终止波长的建模结果,优化光谱波长范围。继而比较原始光谱和光谱经中心化、标准化、Savitsky-Golay(SG)平滑结合一阶导数、SG平滑结合二阶导数、多源散射校正、标准正则变换等预处理后的建模结果,优化光谱预处理方法。最后,基于最优PLS回归模型开发应用软件。数据处理采用SIMCA-P+软件(版本12.0,Umetrics AB,瑞典)。应用软件开发采用Visual Basic软件(版本6.0,Microsoft,美国)。
-
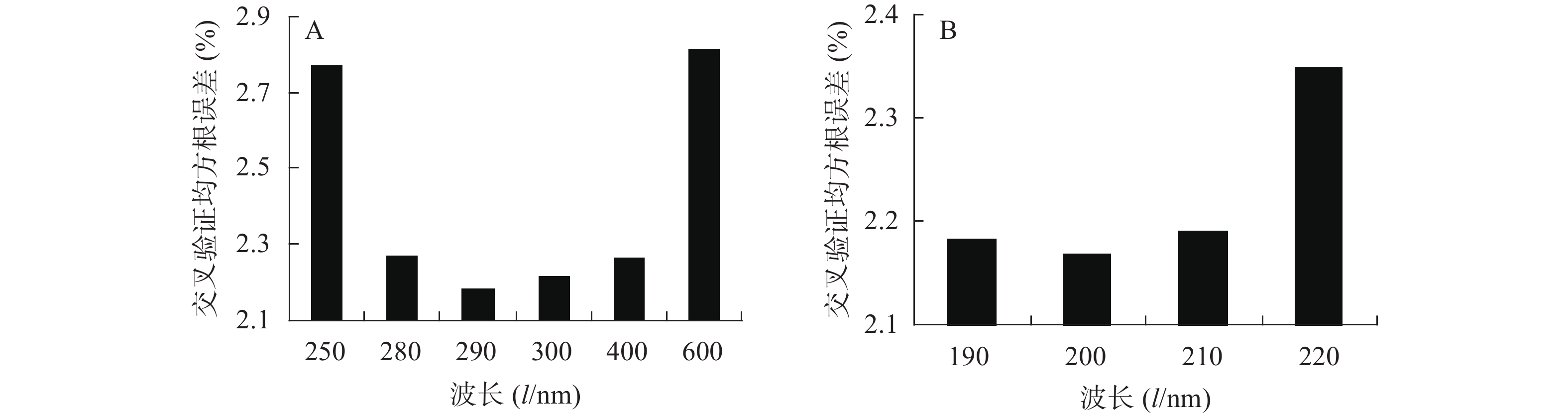
地稔水提液的抗氧化活性范围为83.4%~98.9%。样品溶液的紫外光谱见图1。随机选择24个样品作为校正集,剩下10个样品作为验证集。采用校正集样品,以抗氧化活性为Y,以190 nm为起始波长,分别以250、280、290、300、400、600 nm为终止波长,将紫外光谱经标准化处理后建立PLS回归模型,优化终止波长,见图2A。结果表明,以290 nm为终止波长所建模型的RMSEcv最小。以抗氧化活性为Y,分别以190、200、210、220 nm为起始波长,以290 nm为终止波长,将紫外光谱经标准化处理后建立PLS回归模型,优化起始波长,见图2B。结果表明,当起始波长为200 nm时所建模型的RMSEcv最小。综上所述,本研究选择200~290 nm为最优波长范围。
-
以抗氧化活性为Y,采用200~290 nm的紫外光谱,比较原始光谱和光谱经不同预处理后的建模结果,优化光谱预处理方法,结果见表1。综合考虑Rcal、RMSEE、RMSEcv等,本研究选择标准化为最优光谱预处理方法。
预处理方法 主成分数 校正集 验证集 校正集相关系数 拟合均方根误差 交叉验证均方根误差 验证集相关系数 预测均方根误差 原始光谱 3 0.716 40.9 40.7 0.567 47.2 中心化 3 0.883 2.23 2.21 0.901 1.83 标准化* 3 0.887 2.20 2.17 0.868 2.08 SG平滑结合一阶导数 3 0.734 40.5 39.0 0.647 44.3 SG平滑结合二阶导数 1 0.756 4.05 4.27 0.786 3.68 多元散射校正 1 0.110 4.50 4.72 0.302 3.77 标准正则变换 1 0.141 4.49 4.66 0.325 3.73 SG平滑结合一阶导数+中心化 3 0.898 2.09 2.13 0.722 3.33 SG平滑结合二阶导数+中心化 3 0.879 2.26 2.47 0.655 3.75 多元散射校正+中心化 1 0.110 4.50 4.41 0.302 3.77 标准正则变换+中心化 1 0.141 4.49 4.34 0.325 3.73 SG平滑结合一阶导数+标准化 1 0.840 95.0 95.4 0.757 91.1 SG平滑结合二阶导数+标准化 4 0.911 2.01 2.18 0.721 3.55 多元散射校正+标准化 1 0.520 3.87 4.03 0.582 3.28 标准正则变换+标准化 1 0.535 3.88 4.02 0.582 3.28 注:*最优PLS回归模型。 -
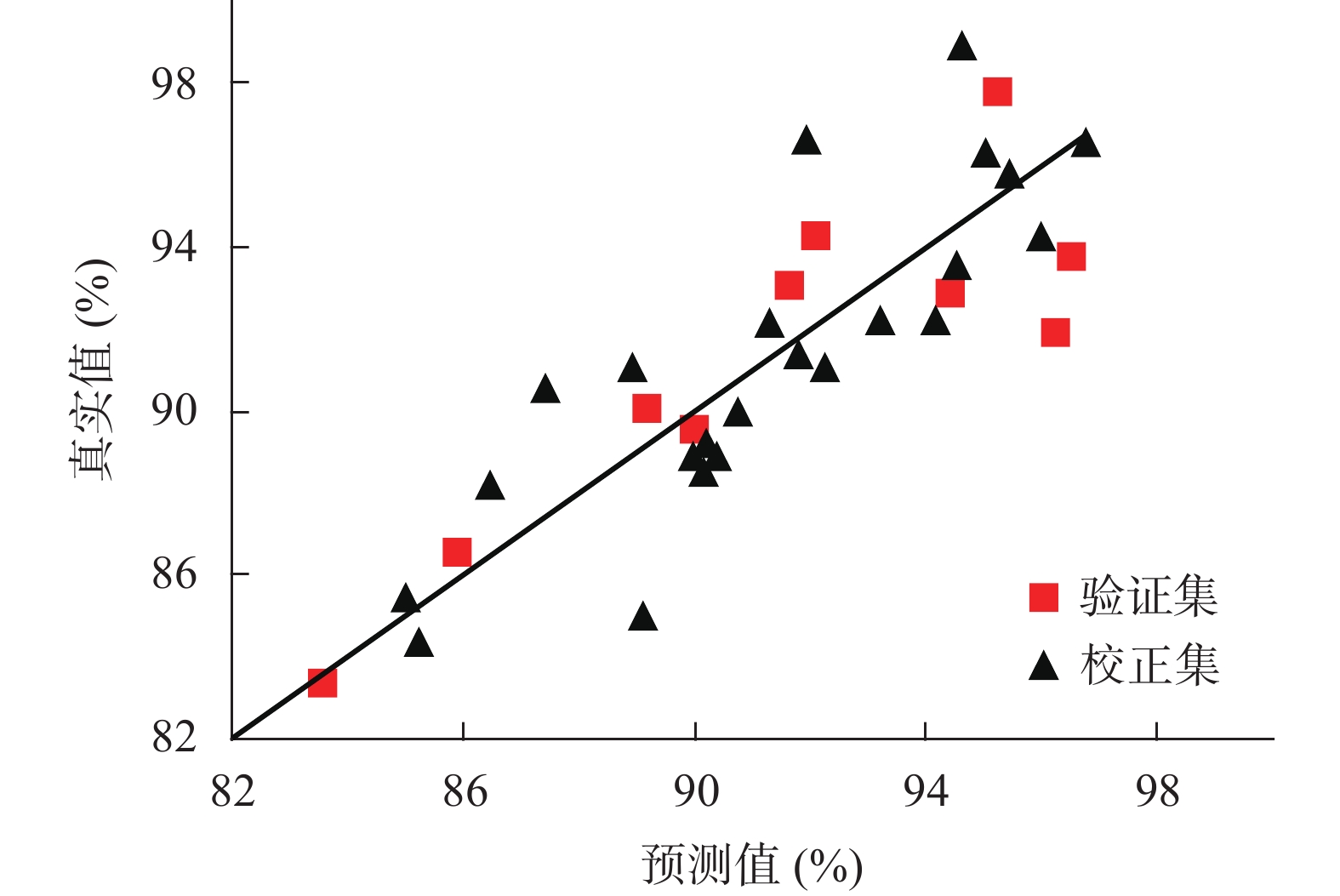
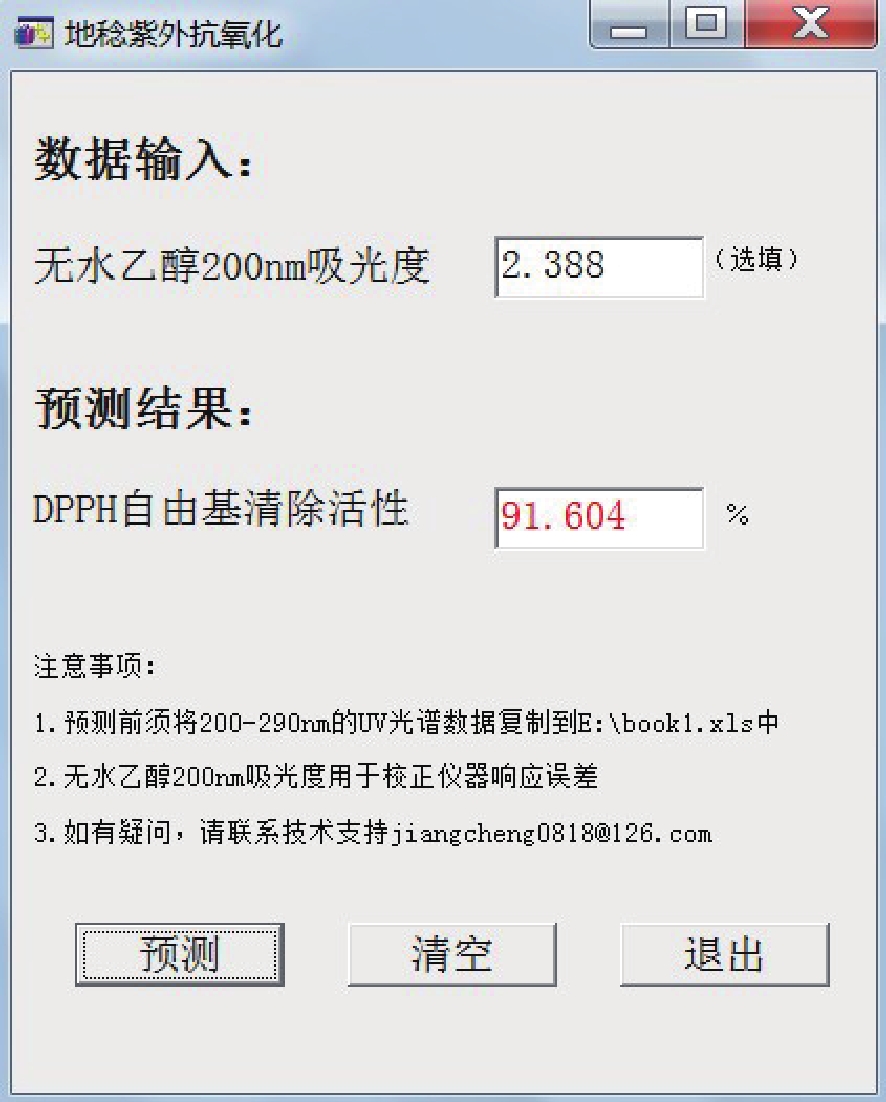
采用200~290 nm的紫外光谱,经标准化预处理后建立最优PLS回归模型,校正集预测值与真实值之间的相关图(图3),Rcal、RMSEE、RMSEcv分别为0.887、2.20%、2.17%。基于最优PLS回归模型开发应用软件,将所建预测模型嵌套入软件。软件双击即可打开,操作界面见图4。采用该应用软件,通过2个步骤即可实现待测地稔水提液抗氧化活性的快速预测。步骤1:将待测地稔水提液稀释后,采集紫外光谱,检测波长为200~290 nm。步骤2:通过软件中的预测功能将紫外光谱数据自动代入模型,在2 s内实现地稔水提液抗氧化活性的快速预测。
-
采用所开发的软件预测验证集样品的抗氧化活性。对比验证集抗氧化活性的预测值和真实值,验证本方法的准确性。验证集预测值与真实值之间的相关图见图3,预测回收率见表2。结果显示,验证集抗氧化活性的预测值和真实值差异较小,Rval、RMSEP分别为0.868、2.08%,平均预测回收率为(100.1±2.3)%,表明该方法的预测准确度较高。
编号 预测值 真实值 预测回收率 平均预测回收率 1 91.6 93.1 98.4 100.1±2.3 2 95.2 97.8 97.3 3 94.4 92.9 101.6 4 96.2 92.0 104.6 5 96.5 93.8 102.9 6 83.5 83.4 100.1 7 90.0 89.6 100.4 8 92.1 94.3 97.6 9 85.9 86.6 99.2 10 89.2 90.1 98.9 -
地稔是我国的民间常用药,在畲族等少数民族民众中广泛应用,具有较好的临床价值,但仍缺少有效的质量控制方法。现代药理学研究表明,地稔提取液有较强的抗氧化活性,但不同采收时间、不同部位地稔的质量有较大的差异[12-13]。因此,建立地稔抗氧化活性的快速预测方法对其质量控制具有重要意义。
目前,将光谱技术应用于食品、中药等抗氧化活性的快速预测已有较多文献报道[6-9, 14],但多以近红外光谱为主。紫外光谱是一种基于分子中价电子能级跃迁的电子光谱技术,具有快速、简便、绿色、灵敏度高等优势。目前,紫外光谱技术已广泛应用于中药活性成分的快速预测[15-17],但在中药抗氧化活性的快速预测方面仍罕见文献报道。课题组前期研究表明,地稔水提液紫外光谱的吸光度与其活性成分没食子酸、阿魏酸、芦丁、槲皮素、木犀草素、山奈酚的含量具有相关性[11]。另有研究表明,地稔水提液的抗氧化活性与多种活性成分的含量呈浓度依赖性[18]。基于上述结果,推测地稔水提液紫外光谱的吸光度可能与其抗氧化活性具有相关性。鉴于此,本研究通过探索地稔水提液紫外光谱与抗氧化活性的相关性,建立了基于紫外光谱的地稔水提液抗氧化活性快速预测方法。为了增加模型在不同紫外光谱仪间的适用性,本方法可选择性采用无水乙醇200 nm的吸光度进行校正[11]。采用本方法,抗氧化活性预测值与真实值的Rcal、RMSEE、RMSEcv分别为0.887、2.20%、2.17%,Rval、RMSEP分别为0.868、2.08%,平均预测回收率为(100.1±2.3)%,可为地稔水提液抗氧化活性的快速预测提供依据。
本方法简单、绿色,无需掌握复杂的回归参数和手动计算方法,也不需要耗费有机试剂,只需将待测地稔水提液用去离子水稀释后,采集并存储200~290 nm的紫外光谱,通过所开发的应用软件即可快速得到抗氧化活性的预测结果。本方法分析时间较短(每采集一张紫外光谱的时间小于1 min,软件预测时间小于2 s),而采用常规方法或在线色谱法测定DPPH自由基清除率至少需30 min。本研究可为进一步完善地稔的质量控制方法提供依据。
Rapid prediction of antioxidant activity in aqueous extract solutions of melastoma dodecandrum by ultraviolet spectroscopy
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202101016
- Received Date: 2021-01-12
- Rev Recd Date: 2021-07-13
- Available Online: 2022-01-20
- Publish Date: 2022-01-25
-
Key words:
- Melastoma dodecandrum /
- aqueous extract solution /
- antioxidant activity /
- ultraviolet spectroscopy /
- partial least squares regression
Abstract:
| Citation: | JIANG Cheng, XU Pingcui, WU Renjie, ZHANG Xiaoqing, CHEN Liping, WANG Nani. Rapid prediction of antioxidant activity in aqueous extract solutions of melastoma dodecandrum by ultraviolet spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2022, 40(1): 48-52. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202101016 |









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: