-
滇南金线兰Anoectochilus burmannicus Rolfe ex Downie为兰科(Orchidaceae)金线兰属植物,主要分布于我国云南南部至西南部,缅甸、老挝、泰国也有分布 [1]。滇南金线兰与同属植物金线兰A. roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl的植物形态相似,主要含内酯苷、黄酮、多糖、挥发油等成分[2-3]。金线兰是福建特色中药金线莲的基原植物,具有保肝、降血糖、免疫调节、抗类风湿性关节炎、抗骨质疏松、抗氧化等生物活性[4-9]。滇南金线兰水提物具有抗炎和胰岛素抵抗作用[10],其他方面的药理活性研究鲜见报道。课题组在前期金线莲资源调查过程中发现,民间常把滇南金线兰当作金线莲使用。虽然滇南金线兰和金线兰都含有内酯苷、黄酮和多糖类成分,但是二者中这些成分的含量是否有显著差异?滇南金线兰能否替代金线兰,当作金线莲使用?这些问题都还有待进一步的研究。因此,为确保临床用药的准确性,本文对滇南金线兰原植物进行鉴定,就植物形态特征、显微特征等进行观察描述,旨在为该药的准确鉴别,以及进一步的开发利用提供参考。
-
SZ61体视显微镜(日本奥林巴斯);数码相机[AV205S富士胶片(中国)投资有限公司]、XS-2100生物显微镜(日本尼康公司)。
-
水合氯醛、甘油、盐酸、F.A.A 固定液、间苯三酚、甲醇、乙醇等均为国产分析纯试剂。滇南金线兰采自云南西双版纳,由福建中医药大学药学院吴岩斌副研究员鉴定为兰科金线兰属滇南金线兰Anoectochilus burmannicus Rolfe ex Downie。
-
取滇南金线兰新鲜植株进行植株形态观察,用数码相机拍照,同时对其花进行解剖,在体视显微镜下观察拍照,并描述其特征。取滇南金线兰新鲜植株,对其根、根茎、叶(过中脉)部位按常规石蜡制片法制作石蜡切片,在光学显微镜下观察并拍照。撕取新鲜植株叶的上、下表皮进行表面制片,观察其表面观特征。新鲜植株干燥后研成细粉,用水合氯醛透化装片,在光学显微镜下观察并拍照。
-
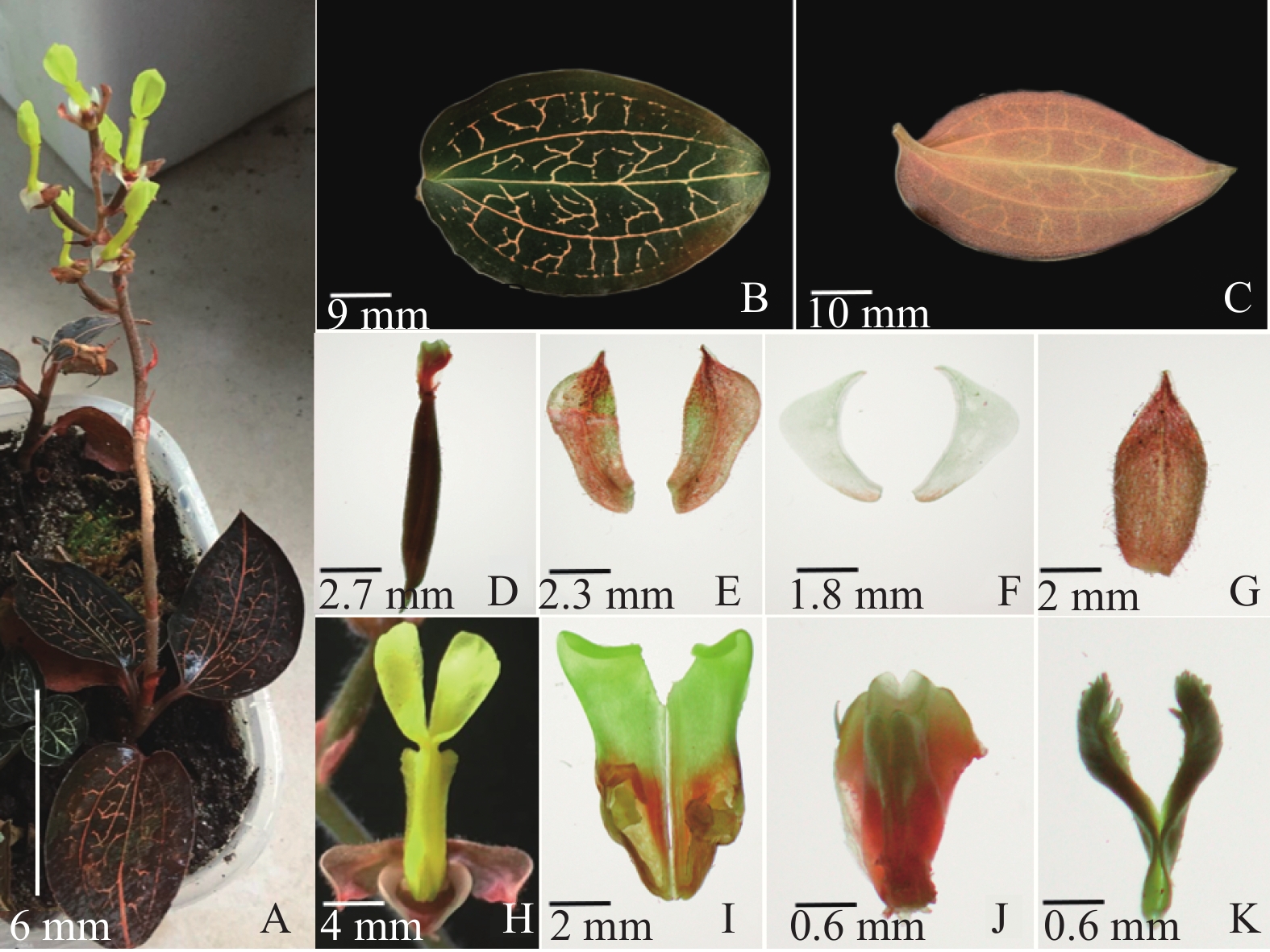
植株高10~35 cm。根状茎肉质,匍匐,茎上部直立或斜升,圆柱形,深绿色。叶2~6片,互生,叶片卵形或卵状披针形,先端急尖,基部斜歪,全缘,边缘银白色,长4~10 cm,宽2.5~5.5 cm,上面黑绿色,具金红色带绢丝光泽的美丽网脉,有5条弧形主脉,边缘2条主脉不明显,背面淡紫红色,叶柄下部扩大成抱茎的鞘。总状花序具1~8朵花;苞片淡红色,卵状披针形,长1.8~4.0 mm,宽1.8~2.0 mm,先端渐尖,背面被短柔毛;子房圆柱形,不扭转,连花梗长10 mm;花较大,不倒置(唇瓣位于上方),萼片3枚,浅红褐色,两侧萼片肾形,中萼片倒卵形,凹陷呈舟状,先端近钝,与花瓣粘合呈兜状;花瓣斜歪的半卵形,白色;唇瓣黄色,呈Y字形,前部明显扩大并2裂,裂片狭长圆形或狭倒披针形,中部收狭成长10 mm左右、其边缘具狭翅,基部凹陷呈圆锥状距,内具2枚肉质的胼胝体;蕊柱短。花期9~12月(见图1)。
-
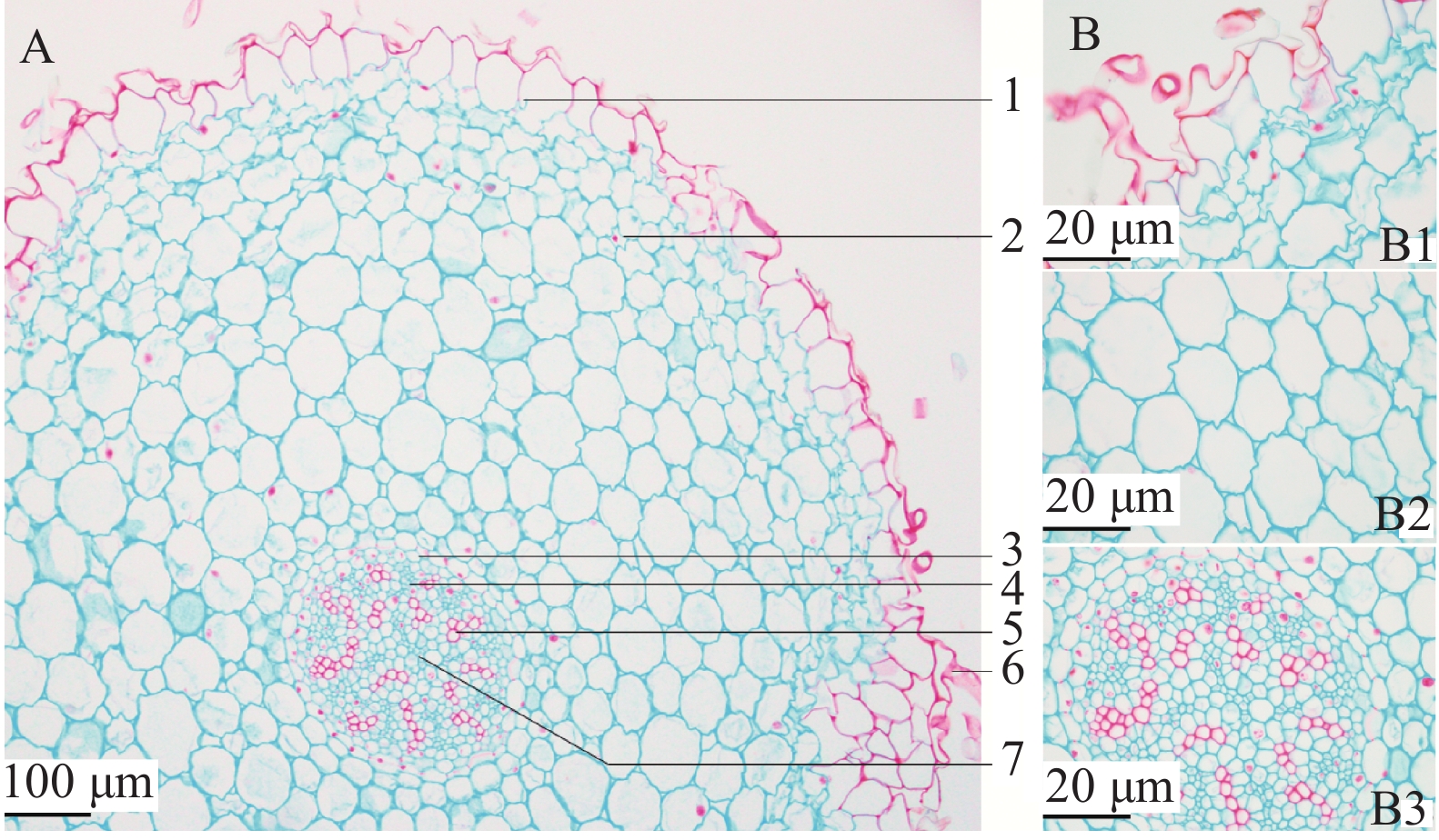
呈类圆形,表皮为不规则的类方形,外有略栓质化根被,排列紧密,皮层宽广,约占横切面的6/7左右。外皮层为2~3层形状不规则细胞组成,排列较紧密;中皮层常见含有草酸钙针晶的黏液细胞,细胞排列疏松;内皮层由一层长方形细胞组成,具明显增厚的凯氏点。中柱鞘较明显,韧皮部与木质部相间排列,呈辐射状维管束,无形成层,木质部导管多类圆形,纵列或3~11个成群;中央为髓部,导管向髓部发展,髓部不明显(见图2)。
-
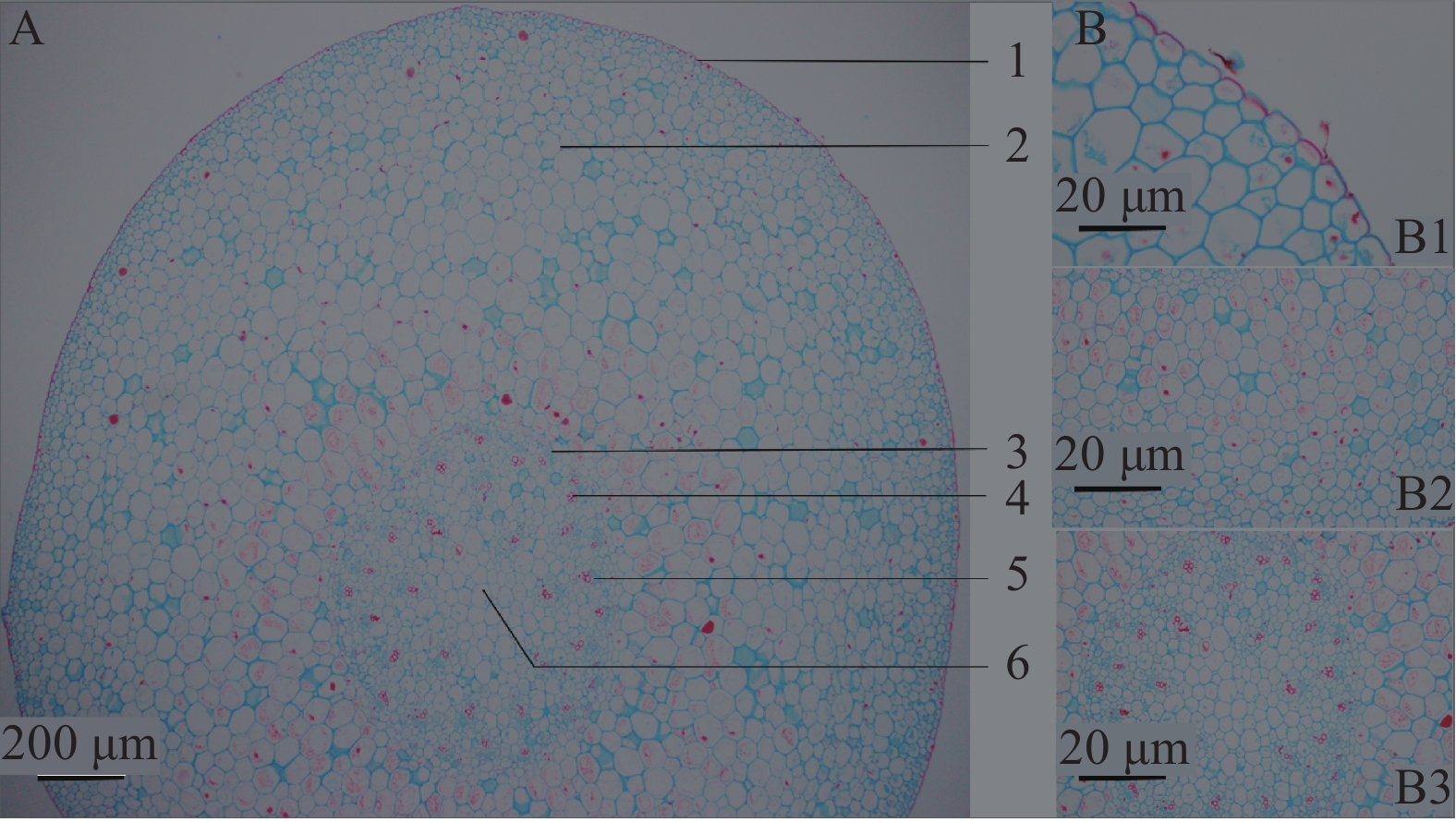
呈类圆形,表皮为1层类圆形细胞组成,细胞外切向壁角质化加厚,排列紧密;皮层宽广,约占横切面的5/7左右,由类圆形薄壁细胞组成,皮层中部至维管柱以外薄壁细胞,偶见草酸钙针晶分布,内皮层明显,由一层排列紧密的长椭圆形细胞组成,具凯氏带;维管柱内27~32个有限外韧型维管束无序散在;木质部由多类圆形导管组成,纵列或2~4个成群,髓部不明显(见图3)。
-
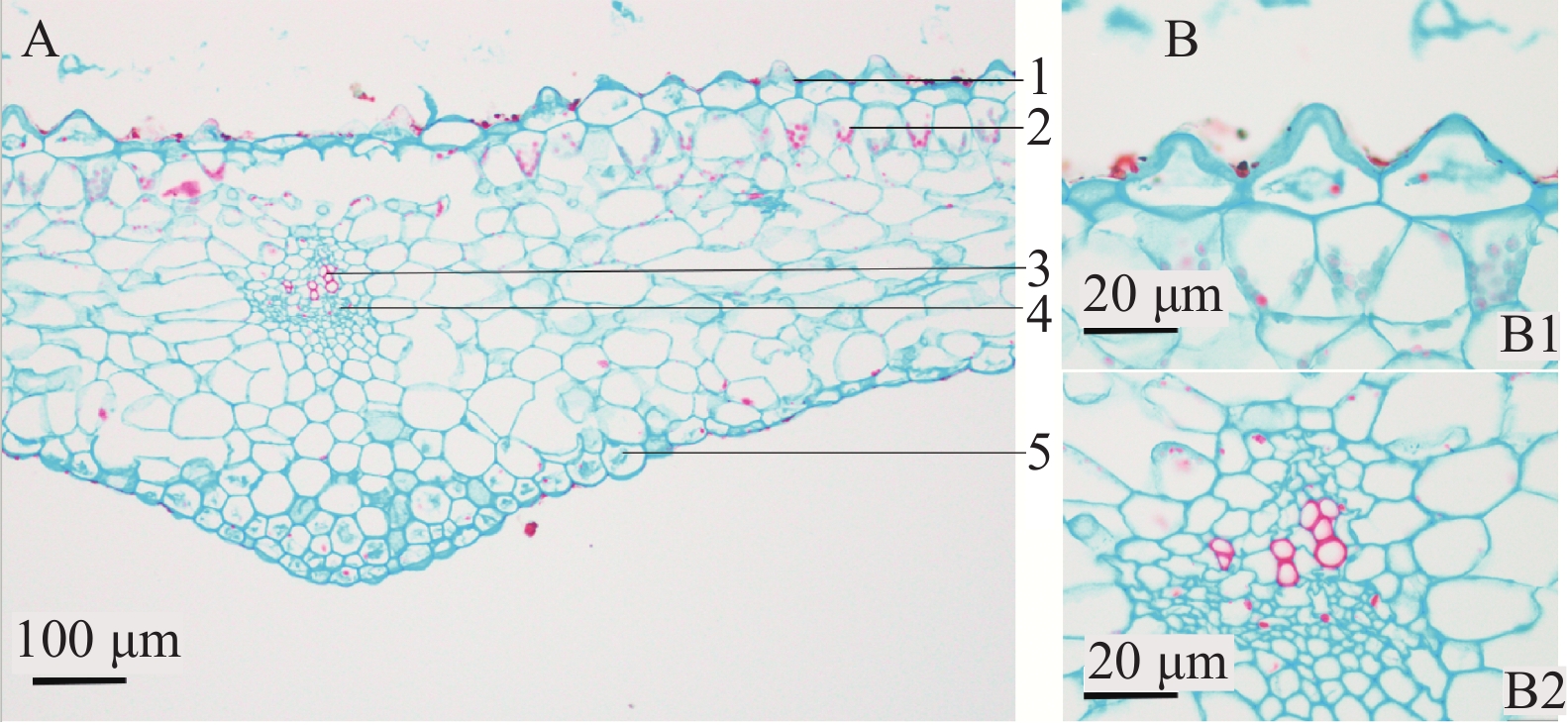
上表皮细胞乳突状突起,排列紧密,具角质层,未见气孔;叶肉中栅栏组织与海绵组织分化不明显,但靠近上表皮的细胞中存在较多叶绿体,主脉下方微凸,维管束1个,为有限外韧型,中脉木质部导管2~4个成束。下表皮细胞排列紧密,可见气孔分布(见图4)。
-
上表皮细胞类圆形,大小相近,未见气孔器。下表皮细胞多为不规则多角形,气孔众多,以不定式气孔为主,副卫细胞2~5个,偶见直轴式、不等式气孔(见图5)。
-
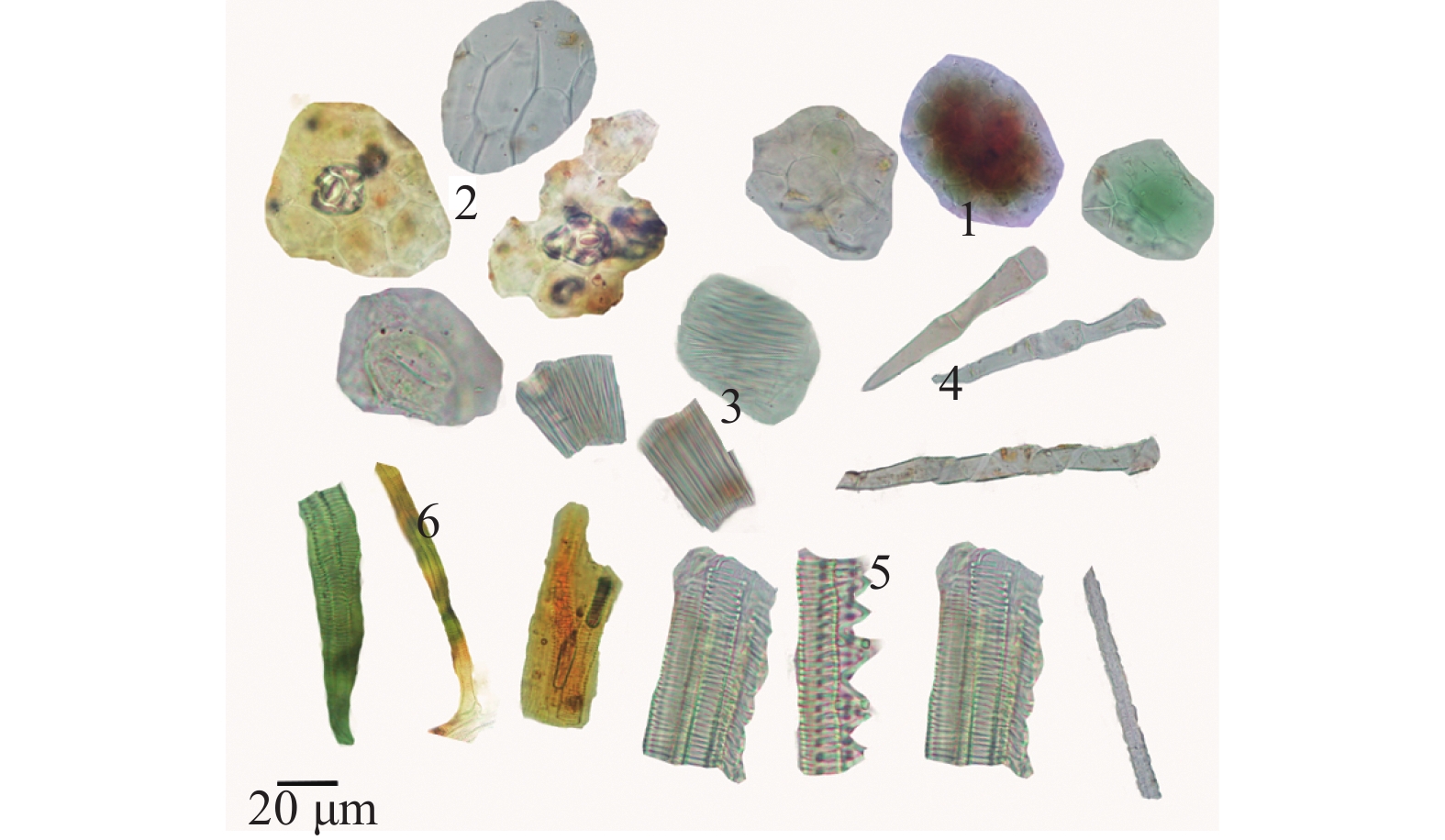
粉末棕褐色。导管多见螺纹。草酸钙针晶束众多,直径40~60 μm,聚集成束或散在。管胞多见螺纹,较少网纹。根毛基部较多为平直,其壁较薄,多破碎,有的扭曲成螺旋状,有的平直。叶的上表面细胞呈类椭圆形。叶下表皮碎片,细胞类长方形,多见气孔,主要为不定式(见图6)。
-
将实验观察结果与相关文献进行对比[11-13],发现滇南金线兰和金线兰原植物形态、组织构造及粉末显微特征虽有相似之处,但也有所区别。不同之处在于滇南金线兰根茎较粗大、叶片较大,全缘,叶边缘为银白色,叶上表面有5条弧形主脉,边缘2条主脉不明显,叶脉较稀疏,叶基部斜歪,唇瓣黄色,前部明显扩大并2裂,裂片狭长圆形或狭倒披针形,中部收狭成长10 mm左右、其边缘具狭翅;金线兰根茎较小,叶片较小,叶边缘邹波状,叶上表面有5条弧形主脉,叶脉较密集,唇瓣白色,前部扩大并2裂,裂片近长圆形或近楔状长圆形,中部收狭成长4~5 mm的爪,其两侧各具6~8条长约4~6 mm的流苏状细裂条。可以凭借以上鉴别点对滇南金线兰进行准确鉴定,避免与金线兰混淆。
Plant pharmacognostic and microscopic identification of Anoectochilus burmannicus
-
摘要:
目的 对滇南金线兰进行生药鉴定,明确其原植物形态和显微特征。 方法 采用生药学鉴定方法,观察滇南金线兰的原植物形态、组织构造及粉末显微特征。 结果 叶片呈卵形或卵状披针形,具金红色叶脉,花不倒置,唇瓣黄色,呈Y字形,前部明显扩大并2裂,裂片狭长圆形或狭倒披针形,中部收狭成长10 mm左右、其边缘具狭翅。显微结构中,根、茎横切面中皮层明显,具草酸钙针晶、黏液细胞等;叶横切面上表皮细胞乳突状,下表皮气孔类型多样,以不定式气孔为主。粉末中可见草酸钙针晶和导管。 结论 滇南金线兰的生药鉴定为其资源开发利用提供了参考依据。 Abstract:Objective To identify the crude drugs of Anoectochilus burmannicus, and clarify its original plant pharmacognostical and microscopic characteristics. Methods The pharmacognostical identification method was used to observe the original plant, tissue structure and microscopic characteristics of A. burmannicus. Results Leaves were ovate or ovate elliptic with golden-red veins. Non-inverted yellow flowers had Y-shaped and yellow labellum, which were anteriorly enlarged and 2-lobed. The lobes were narrowly oblong or narrowly oblanceolate. The middle part of labellum was narrow to form a 10 mm long structure with margin narrowly winged. In the microscopic structure, the cortex is obvious in the cross sections of root and stem, together with needle crystals of calcium oxalate and mucous cells. The upper epidermal cells on the cross section of the leaves were papilloid in shape, whereas diverse stomas existed among the lower epidermal cells, with anomocytic stomas as the major type. Needle crystals of calcium oxalate and conduits can be found in the powder. Conclusion These data provide a reference for the identification and resource development and utilization of A. burmannicus. -
近年来随着医药行业的快速发展,治疗药物监测愈益成为临床药物治疗工作的一项重要内容,也是个体化用药指导的重要手段之一。治疗药物监测[1](therapeutic drug monitoring,TDM),其目的是通过测定血液中或其他体液中药物的浓度并利用药动学的原理相应调整药物剂量,使给药方案个体化,以提高药物的疗效,避免或减少毒副反应;同时也为药物过量中毒的诊断和处理提供实验室依据,简而言之就是对药物浓度的评估[2]。药物治疗窗(therapeutic drug window)指药物产生最小治疗效应与机体能耐受的最小中毒反应间的血药浓度范围,是TDM的临床用药依据。目前临床上开展TDM的药物涉及多种类、多监测方法,但TDM的治疗窗和血样却没有很好的分析、归纳及总结。前期课题组研究表明[3-4],高原环境对药物代谢酶、转运体的活性及蛋白表达均有一定的影响,导致高原环境下药动学参数发生变化,而药动学参数是指导临床合理用药的重要理论依据,直接关系到给药的剂量及给药时间,那么高原低氧环境对临床常用监测药物的代谢是否会产生影响?本文将对临床上常用的治疗监测药物种类、治疗窗、以及检测血样进行归纳和总结,分析高原环境下对临床常用监测药物代谢的影响,一方面有利于指导临床合理用药、毒性反应评估、引导个体化用药;另一方面,为本课题组进一步研究高原环境下开展TDM提供理论指导。
1. TDM药物种类及治疗窗
随着TDM研究的不断深入,王菁等人[5]归纳了临床上遴选TDM遵循的八条原则。即行TDM的药物具有自身治疗指数低、治疗窗窄、毒性较大、非线性药动学特征和个体差异较大,以及联合用药时会发生相互作用,导致血药浓度变化等特点。目前,需TDM的药物种类主要包括免疫抑制剂,如他克莫司(FK506)、环孢霉素(CsA);抗菌药,如万古霉素、替考拉宁;平喘药,如氨茶碱;抗癫痫药,如丙戊酸(VPA)、卡马西平(CBZ)、苯巴比妥;心血管系统药物,如地高辛;抗心律失常药物,如普鲁卡因胺、利多卡因、奎尼丁;抗肿瘤药,如甲氨蝶呤(MTX);抗抑郁药,如丙咪嗪、阿米替林、碳酸锂,等等。由于这些药物个体差异大,容易在同等剂量出现毒副反应或达不到相应的疗效,因此,临床上需要做TDM。使监测药物的血药浓度控制在治疗窗内,是保证患者安全、有效的用药关键。以下将临床上常用TDM药物的治疗窗及血样进行分类(表1)。
表 1 临床常用治疗监测药物的治疗窗类别 代表药物 血样 治疗窗 免疫抑制剂 他克莫司 全血 5−10 ng/ml 环孢霉素 全血 150−400 ng/ml 抗菌药 万古霉素 血清 10−15 μg/ml 替考拉宁 血浆 ρmin≥10 μg/ml(非复杂感染) 20−60 μg/ml(深部复杂感染) 平喘药 氨茶碱 血清 10−20 mg/ml 血浆 55−110 μmol/L 抗癫痫药 丙戊酸 血清 50−100 μg/ml 苯巴比妥 血清 10−40 μg/ml 卡马西平 血清 4−12 μg/ml 心血管系统药物 地高辛 血清 0.8−2.0 ng/ml 并非所有的药物都需要做血药浓度监测,一些有显著效果指标的药物,如降压药(如硝苯地平、厄贝沙坦、卡托普利等),其临床的治疗效果可以直接通过测定患者血压数值来反映降压的程度,进而根据血压数值调整用药的剂量;新型广谱唑类药物艾沙康唑(isavuconazole)目前也不需要TDM[6]。对于上述治疗窗宽、安全范围广的药物进行血药浓度监测和药代动力学参数的研究并没有多少实际意义。
进行监测的药物血样[7]主要有全血、血浆及血清等,监测血样的确定主要根据药物与血浆蛋白、红细胞结合率,以及游离状态来决定,以便更好的评价血药浓度,指导临床个体用药剂量。当药物主要与血液中红细胞结合时,监测的血样一般选择全血;药物与血浆蛋白结合率高时,主要以游离态来发挥作用时,选择血清为监测的血样结果会更加准确。例如,免疫抑制剂他克莫司、环孢霉素,监测的血样为全血,因为多数他克莫司与血液中红细胞结合,少数与血浆中的脂蛋白结合[8-9];环孢霉素也在血浆中与血浆蛋白和红细胞的结合率高[10]。由于他克莫司、环孢霉素与红细胞有较高的结合率,因此,必须以全血为血样,以保证监测的浓度结果更加可靠、准确、稳定,但在测定全血时干扰物质较多,全血处理也要有严格的要求[雅培公司所产的全自动免疫分析仪(型号:AR i1000SR)在测定血样前需加入全血沉淀试剂];而抗癫痫药丙戊酸的监测血样为血清,因为丙戊酸80%~90%处于与血浆蛋白结合状态,主要以游离态发挥作用[11],因此,丙戊酸以血清来评价血药浓度。研究表明[12],在血清中加入适量的高丰度蛋白质去除试剂乙腈,不仅能够有效沉淀蛋白,减少对血药浓度的影响,还能减弱加入内标提取液引起的乳化现象,使临床监测更加简便、经济。
2. 高原环境对TDM药物代谢的影响
高原环境具有低氧、低温、低气压、高辐射等基本特点,其中低氧是影响药物代谢的主要因素,低氧环境中药物蛋白结合率、器官血流量、代谢酶及转运体的表达及功能均会发生变化[13-14]。而这些变化会导致高原环境下药动学参数的改变,而药动学参数是指导临床合理用药的重要理论依据,直接关系到给药的剂量及间隔。TDM药物的代谢与血浆蛋白结合率、局部器官的血流量、代谢酶及转运体有直接的关系,也就是说高原环境的特殊性对TDM代谢也会有很大的影响,这些因素影响会使TDM药物的血药浓度发生改变,进而导致药动学参数发生变化,使高原人群的用药剂量存在风险。因此探究高原环境下TDM代谢发生的变化,对保证高原人群安全、合理、有效的用药具有重大意义。
2.1 高原环境对TDM血浆蛋白结合率的影响
药物与血浆蛋白结合率是影响药物在体内分布的重要因素,蛋白结合率高的药物在体内消除慢,作用维持时间长。药物进入循环后首先与血浆蛋白成为结合型药物,未被结合的药物称为游离型药物,两种类型的药物处于动态的平衡状态,仅游离型药物才能转运到作用部位产生药理效应。药物的血浆蛋白结合率会严重影响机体对药物的分布、排泄和代谢,从而影响药物作用强度和持续时间,加大了不良反应的发生率。高原环境对不同药物的血浆蛋白结合率具有不同的影响。如呋塞米、美托洛尔的蛋白结合率无显著性差异;而醋甲唑胺、普萘洛尔蛋白结合率显著性增高[15]。
临床上常用的监测药物种类多,不同药物在高原环境中血浆蛋白结合率不同,导致药物临床药效不同。课题组前期研究表明[16],监测药物氨茶碱平原组与高原组Wistar大鼠血浆蛋白结合率分别为37.05%和74.17%,急进高原组的血浆蛋白结合率比平原组显著高37.12%,具有较高的血浆蛋白结合率,导致药物的浓度增大,体内驻留时间缩短,若按照平原给药的标准很有可能发生不良反应。高原环境对TDM药物的血浆蛋白结合率的影响会使体内药物浓度发生改变,进而导致TDM药动学参数的变化。
2.2 高原环境对局部器官血流量的影响
人体脏器的血流量分布以肝最多,肾、脑、脾、心次之。肝是代谢药物的主要场所,进入高原机体对器官的血流增多,红细胞对血管的黏附也增强[17],血液黏稠度会增高,肾血流量减少,尿量减少,导致药物在体内的蓄积;脾是重要的免疫器官,其血流量显著增加到6.70±1.84(P<0.01)[18],使脾脏过负荷,导致脾肿大生理功能下降。
高原环境对器官血流量的影响,导致TDM药物的排泄发生变化。如地高辛在体内消除主要是以原型药经肾小球滤过或肾小管分泌排泄,尿中排出量为用量的50%~70%,仅约10%左右在肝代谢,另有7%左右处于肠肝循环。因此,高原环境中,地高辛经尿液的排出量减少,造成其在体内造成大量的蓄积,毒副作用也随之产生,即主要经肾排泄的TDM药物(VPA、苯巴比妥),在高原低氧的状态下应对可能产生的毒副反应进行监测,防止不良反应的发生。高原环境对器官血流量产生的影响,导致TDM药物的排泄发生改变。
2.3 高原环境对TDM代谢酶的影响
大多数药物代谢主要在肝脏中进行,肝细胞中的药物代谢酶会参与药物的代谢,肝脏微粒体酶系(细胞色素P450酶系)是促进药物转化的主要酶系统。CYP450酶系是一个基因超家族,临床中90%以上经肝脏代谢的药物是经过CYP450酶系亚酶代谢的,已有大量研究表明高原低氧导致酶的活性或表达降低,影响机体对大部分药物的生物转化率及清除率,减缓药物在体内的代谢,可能增加药物的毒副作用。
治疗监测药物的代谢也需要代谢酶的参与。如免疫抑制剂、环孢霉素主要通过CYP3A4和CYP3A5代谢[19-20];氨茶碱通过CYP1A2代谢[21];抗癫痫药丙戊酸的代谢过程受到尿苷二磷酸葡萄糖醛酸基转移酶(UGT酶)和细胞色素酶(CYP)影响[22];苯巴比妥在肝脏中主要被CYP2C9代谢,而CYP2C19和CYP2E1代谢较少[23]。课题组前期研究表明[3-4, 24-25],在高原低氧环境中,上述药物的代谢亚酶CYP3A4、CYP3A5、CYP1A2、CYP2C9及 UGT的mRNA与蛋白表达均下降,导致酶活性降低,这会使体内TDM药物的代谢减慢,半衰期延长,甚至使体内的药物浓度过大,造成药物及其代谢物在体内的大量蓄积,直接关系到患者用药的剂量及间隔。因此,高原环境对不同代谢酶的影响,TDM药物的代谢参数也将发生变化。
2.4 高原环境对TDM转运体的影响
药物转运体是转运药物透过细胞膜进入体内和产生药效的关键因素,其广泛分布在小肠绒毛上皮细胞、肾小管上皮细胞、肝细胞,其在药物代谢的各个环节中发挥着重要的作用。同一个转运体可在多个正常器官和组织中表达,而同一个组织和器官也可表达多个转运体。药物转运体分两类:ABC族转运蛋白和SLC族载体转运蛋白。P-糖蛋白(P-gp)是人体重要的ABC族外运蛋白,其存在于肝、肾、小肠、胎盘屏障和血脑屏障等组织器官中,其主要功能是将药物摄取或外排出细胞,从而影响体内代谢的各个过程。Rohwer等[26]总结了不同肿瘤细胞中P-gp 的变化,发现低氧诱导因子使转运体蛋白高表达,从而影响化疗药物的疗效。本课题组[4,27-28]研究了高原实地低氧环境中大鼠体内转运体的变化情况,高原低氧组小肠组织中P-gp mRNA与蛋白的相对表达水平分别下调50.80%和71.30%(P<0.05),高原低氧会导致小肠中P-gp的表达下调,使其底物的外排减少,增加其底物在肠道的吸收;肝脏中P-gp mRNA与蛋白的相对表达量分别上调了1.15倍和1.33倍;肾脏中分别上调了49.0%和1.83倍;高原组(海拔4 010 m)与平原组比,大鼠血脑屏障(BBB)组织中P-gp mRNA与蛋白相对表达量分别显著上调了2.18倍和2.58倍(P<0.05),随着表达量的升高,介导药物的外排增多,进入脑内的药量减少,疗效减弱。这些研究表明高原低氧条件下各组织中P-gp表达量均会发生明显的变化,影响药物在体内各组织的转运,代谢发生变化。
临床常用TDM:他克莫司、环孢霉素、卡马西平、丙戊酸都是P-gp的底物药物[29],也会受到高原环境的影响,导致药物在不同组织中发生不同的变化。如,抗癫痫药丙戊酸、苯巴比妥、卡马西平需要通过血脑屏障来发挥作用,高原环境会使这类药物进入脑内的药量减少、导致药效大大减弱。如果沿用平原的给药标准那么很有可能无法达到预期疗效。因此,必要研究TDM药物在高原低氧环境下的代谢变化,保证高原人群用药安全性和有效性。
2.5 高原环境中TDM药代参数的改变
高原环境对器官血流量及药物血浆蛋白结合率、代谢酶、转运体的活性及蛋白表达均有一定的影响,这些将导致高原环境下药动学参数发生变化,而药动学参数是临床用药剂量及间隔的重要依据。如大鼠灌胃给予氨茶碱剂量为3.6 mg/200 g,高原组氨茶碱体内消除减慢、Tmax显著减小(高原组0.44±0.191;平原组0.887±0.196),药物半衰期和滞留时间延长(高原组2.944±0.694;平原组2.365±0.448),Cmax增大到1.22倍,AUC增到1.35倍[20]。这些表明氨茶碱在高原低氧环境中生物利用度升高,那么人体中其用药剂量应适当的降低,防止体内浓度过高。若明确高原环境下TDM药物的药代参数,用药的剂量也会有所明确,以确保TDM药物的疗效。
3. 总结与展望
高原低氧环境中不仅使器官的血流量发生改变,而且严重影响TDM血浆蛋白结合率、代谢酶和药物转运体,使监测血药浓度值存在误差;药动学参数也会发生改变,而药代参数的改变会导致TDM剂量受到影响。目前,TDM的监测及代谢研究多在低海拔地区进行,而高原低氧环境下TDM的代谢鲜有文献报道。高原人群TDM的用药剂量及间隔是否可以沿用平原用药标准?因此,高原环境下TDM药物代谢是一个亟待解决的问题,更是临床有效性和安全性用药的重要前提。解决这问题将为高原临床治疗监测药物提供参考,在保证高原人群合理用药、减少毒副反应发生、提高生活质量等方面具有重大意义。
-
[1] 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志 第十七卷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006. [2] WU Y B, PENG M C, ZHANG C, et al. Quantitative determination of multi-class bioactive constituents for quality assessment of ten Anoectochilus, four Goodyera and one Ludisia species in China[J]. Chin Herb Med,2020,12(4):430-439. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2020.07.002 [3] 陈阿虹, 钱丽萍, 陈婉清, 等. 滇南开唇兰挥发油化学成分比较研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2018, 29(12):2877-2880. [4] ZENG B, SU M, CHEN Q, et al. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of polysaccharides from Anoectochilus roxbur-ghii[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2016,153:391-398. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.067 [5] ZHANG J G, LIU Q, LIU Z L, et al. Antihyperglycemic activity of Anoectochilus roxburghii polysaccharose in diabetic mice induced by high-fat diet and streptozotocin[J]. J Ethnopharmacol,2015,164:180-185. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.050 [6] 郑小香, 李萍, 潘晓丽, 等. 金线莲多糖对小鼠脾淋巴细胞体外增殖、细胞周期及分泌IL-2、IFN-γ的影响[J]. 中国食品学报, 2017, 17(6):47-52. [7] GUO Y, YE Q, YANG S, et al. Therapeutic effects of polysaccharides from Anoectochilus roxburghii on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2019,122:882-892. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.015 [8] HSIAO H B, LIN H, WU J B, et al. Kinsenoside prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss and suppresses osteoclastogenesis by regulating classical NF-κB pathways[J]. Osteoporos Int,2013,24(5):1663-1676. doi: 10.1007/s00198-012-2199-z [9] 刘青, 刘珍伶, 周娟. 金线莲多糖的体外抗氧化活性[J]. 华侨大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 31(6):718-720. [10] BUDLUANG P, PITCHAKARN P, TING P, et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-insulin resistance activities of aqueous extract from Anoectochilus burmannicus[J]. Food Sci Nutr,2017,5(3):486-496. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.416 [11] 郑丽香. 金线莲的资源调查及生药学研究[D]. 福州: 福建中医药大学, 2018. [12] 易骏, 吴建国, 张秀才, 等. 不同植物基原金线莲生药鉴别[J]. 中草药, 2015, 46(23):3570-3576. [13] 林美珍, 陈育青, 陈美燕, 等. 金线莲与台湾金线莲显微结构比较[J]. 亚热带植物科学, 2016, 45(3):279-282. -





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载: