-
河豚毒素是一种钠通道阻滞剂,可以导致人类中毒和死亡[1]。河豚毒素不仅存在于河豚科的河豚中,而且在海洋和陆地环境的多种生物中均有发现[2-4]。河豚毒素作用时具有选择性,其与心肌NaV通道缺乏亲和力,且无法穿透血脑屏障,这些特性使其成为麻醉和镇痛药物设计的有吸引力的候选者[5]。河豚毒素的毒理作用在神经性、急性和炎症性疼痛模型中得到证实[6-8]。在远低于半数致死剂量(LD50)的浓度下,河豚毒素对神经系统的急性和瞬时作用使其在最低浓度时即可达到预期结果[9]。然而,河豚毒素的高毒性引发人们对其安全性问题的关注,本文利用斑马鱼模型研究河豚毒素的急性毒性,旨在为评价河豚毒素的安全性提供依据。
-
河豚毒素[中洋生物科技(上海)股份有限公司,批号:2020102307],用醋酸盐缓冲液配制成10.0 mmol/L母液,冷藏避光储存。斑马鱼饲养于28 ℃的养鱼用水中(水质:每1 L反渗透水中加入200 mg速溶海盐,电导率为450~550 μS/cm,pH为6.5~8.5,硬度为50~100 mg/L CaCO3),由杭州环特生物科技股份有限公司养鱼中心繁殖提供,实验动物使用许可证号为:SYXK(浙)2012-0171,饲养管理符合国际AAALAC认证(编号:001458)的要求。野生型AB品系斑马鱼,以自然成对交配繁殖方式进行,年龄为受精后2 d(2 dpf)。
-
随机选取2 dpf野生型AB品系斑马鱼于6孔板中,每孔(实验组)均处理30尾斑马鱼。分别水溶给予河豚毒素(浓度为0.125、0.250、0.500、1.00、2.00、4.00、8.00、16.0、32.0、64.0 µmol/L),同时设置正常对照组和溶剂对照组,每孔容量为3 ml。28 ℃处理72 h,每天统计各实验组的斑马鱼死亡数量并及时移除。
-
实验结束后,在解剖显微镜下观察并记录斑马鱼心脏、循环系统、出血及血栓、脑、下颌、眼睛、肝脏、肾脏、肠道、躯干/尾/脊索、肌肉/体节、身体着色、体长等变化情况,采集典型毒性器官照片。以各器官的毒性发生率评价河豚毒素样品对斑马鱼的急性毒性,并鉴别毒性靶器官。
-
用Origin 8.0统计学软件绘制“浓度-死亡率”效应曲线,并计算河豚毒素对斑马鱼的MNLC和LC10。
-
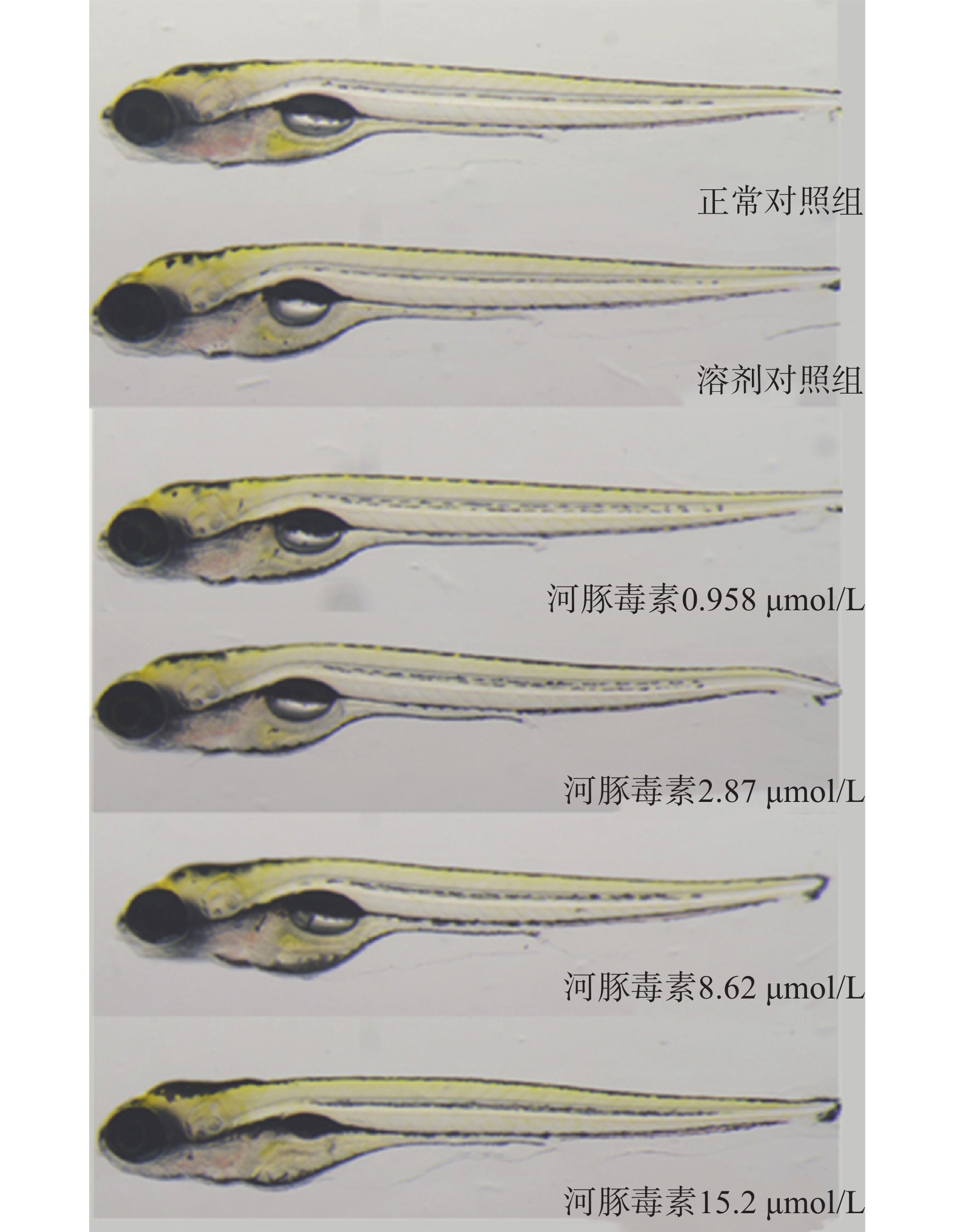
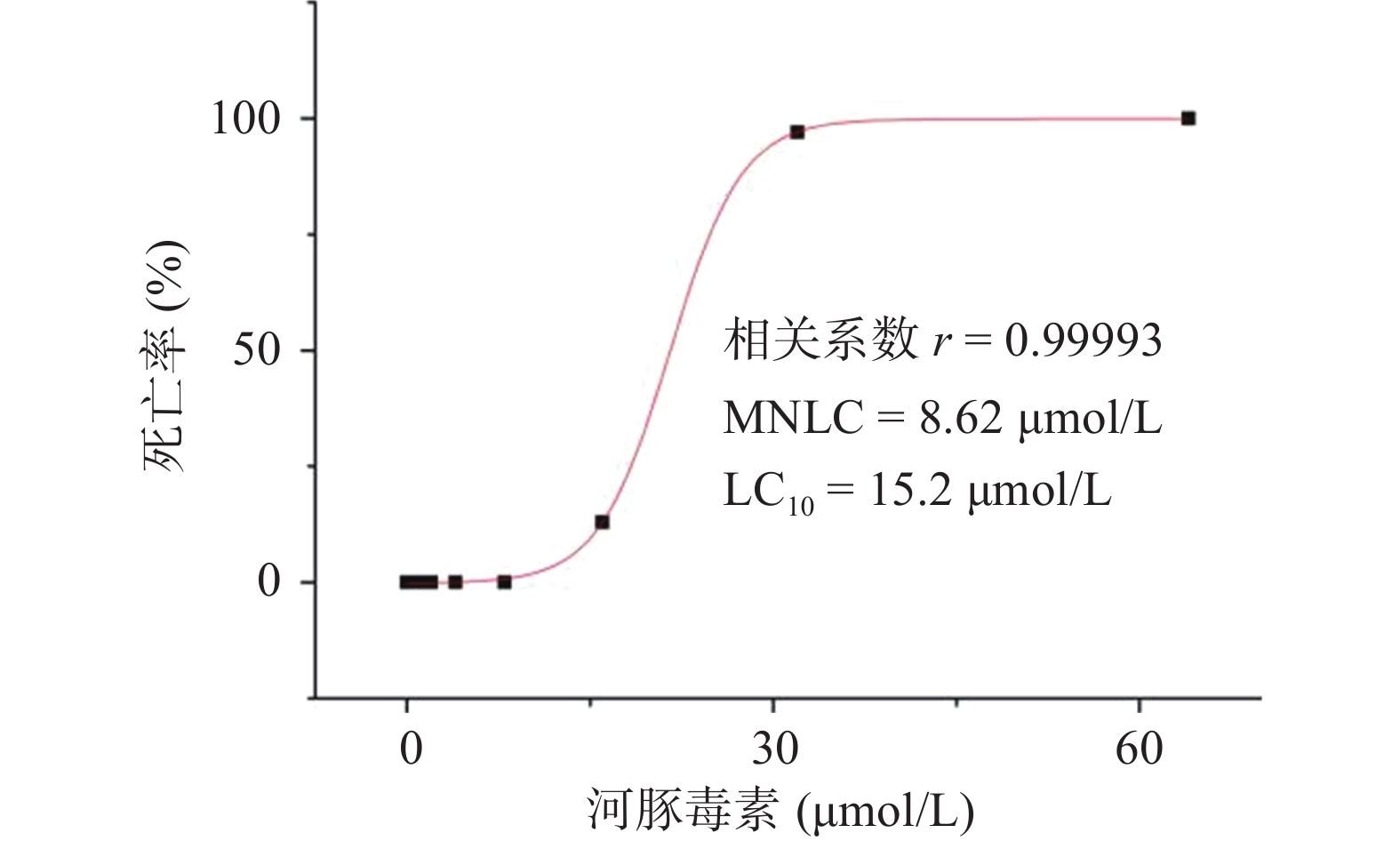
研究结果显示,正常对照组和溶剂对照组斑马鱼的死亡率均为0;0.125~8.00 µmol/L的河豚毒素处理后斑马鱼的死亡率均为0;当河豚毒素的浓度达到16.0 µmol/L时,斑马鱼死亡4尾,死亡率为13%,当河豚毒素的浓度达到32.0 µmol/L时,斑马鱼死亡29尾,死亡率为97%,而当河豚毒素的浓度达到64.0µmol/L时,斑马鱼死亡30尾,死亡率为100%。经Origin 8.0软件模拟得出河豚毒素对斑马鱼急性毒性MNLC为8.62 μmol/L,LC10为15.2 µmol/L,详见图1。
-
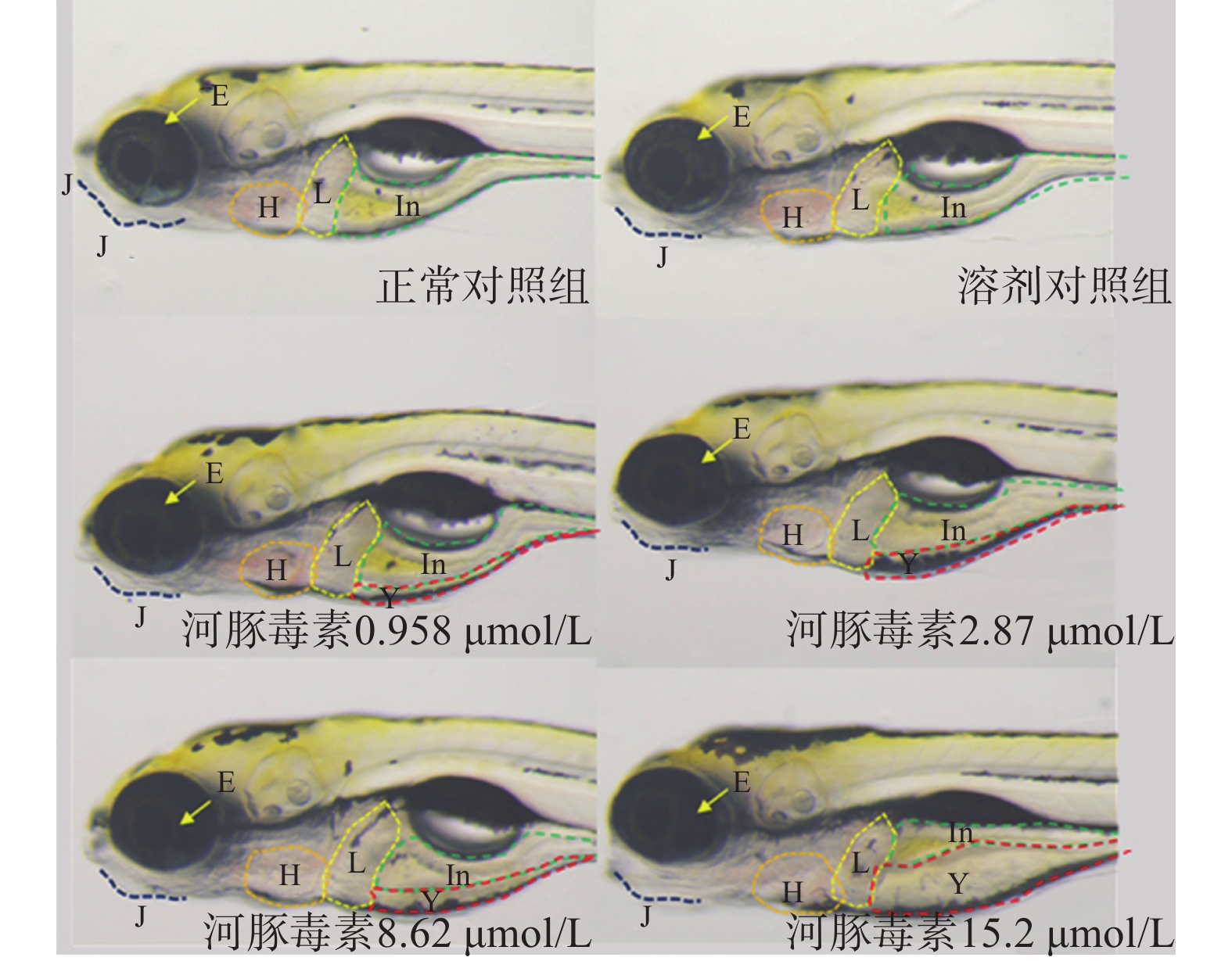
在本实验条件下浓度摸索过程中,16.0 μmol/L及以上浓度诱发心包水肿和心律异常,河豚毒素处理后72 h出现部分或全部死亡。如表1和图2、图3所示,河豚毒素急性毒性靶器官是心脏和肝脏,当河豚毒素的浓度达到0.958 µmol/L及以上时,斑马鱼表现出卵黄囊吸收延迟。当河豚毒素的浓度达到2.87 µmol/L及以上时斑马鱼表现出心律异常和肠腔异常。当河豚毒素浓度达到8.62 µmol/L及以上时斑马鱼表现出心包水肿。不同浓度的河豚毒素均未发现躯干/尾/脊索、肌肉/体节、身体着色以及体长生长等异常。
表 1 河豚毒素急性毒性发生率统计(n=30)
毒性类型 正常对照组 溶剂对照组 河豚毒素浓度(μmol/L) 0.958 2.87 8.62 15.2 心脏 心包水肿 - - - - 7(2/30) 13(4/30) 房室缺失 - - - - - - 心律异常 - - - 7(2/30) 7(2/30) 17(5/30) 循环系统 血流变慢 - - - - - - 循环缺失 - - - - - - 出血及血栓 - - - - - - 脑 畸形 - - - - - - 下颌 短小 - - - - - - 眼睛 眼变小 - - - - - - 肝脏 缺失 - - - - - - 肝肿大 - - - - - - 肝变性 - - - - - - 卵黄囊吸收延迟 - - 80(24/30) 80(24/30) 87(26/30) 93(28/30) 肾脏 水肿 - - - - - - 肠道 肠腔异常 - - - 7(2/30) 13(4/30) 13(4/30) 躯干/尾/脊索 弯曲 - - - - - - 肌肉/体节 肌肉变性 - - - - - - 身体着色 异常 - - - - - - 体长变短 - - - - - 死亡 - - - - - 注:“-”表示未见明显异常 -
河豚毒素是一种致命的神经毒素,作为一种选择性Na+通道阻滞剂,其在生物医学中的应用引起了广泛关注[10]。日本传统医学中曾使用河豚鱼来治疗麻风病患者的神经痛,后来河豚毒素被发现、提取和纯化,并用于抑制破伤风患者的痉挛[11]。近年来,在双壳贝类中也发现了河豚毒素。例如,2011年在新西兰发现一种蛤类中的河豚毒素(0.8 mg/kg)[12],2014年英国学者发现贻贝和太平洋牡蛎样本中的河豚毒素(0.003~0.12 mg/kg)[13]。这些证据表明,河豚毒素对于食品安全来说具有一定的威胁,因此,国际食品和药品监管机构将河豚毒素作为一种新的风险。
在本研究中我们通过使用MNLC和LC10这两个指标,以评估河豚毒素对斑马鱼的急性毒性。研究发现,当河豚毒素的浓度达到16.0 μmol/L时,斑马鱼出现了心包水肿和心律异常,导致部分或者全部的斑马鱼死亡。有研究证实,选择性激活河豚毒素敏感的神经元钠通道可以安全地增加心脏收缩力[14]。还有研究结果显示,河豚毒素的肌肉内给药改变了肝脏中参与各种信号通路的肝脏基因的表达[15]。由此可见,河豚毒素对斑马鱼具有明显的心脏和肝脏毒性,且其毒性随着河豚毒素浓度的升高而增强。
目前,尚无针对河豚毒素的解毒剂,一旦摄入河豚毒素,严重中毒者可发生心力衰竭甚至死亡[16]。多年前有研究者收治了5例河豚毒素中毒者,患者出现了肾脏损害,表现为多尿,经过治疗后仍有患者死亡[17]。在日本,监管规定了河豚毒素的摄入浓度不得超过2 mg/kg[11]。目前,关于河豚毒素急性毒性的可用数据非常少,而且现有的大部分数据都缺乏足够的实验细节。有研究者发现,在昆明小鼠腹膜内(ip)、皮下(sc)和胃内(ig)注射的中位致死剂量(LD50)分别为10.7、12.5、532 μg/kg[18]。我们在斑马鱼模型中研究发现,河豚毒素对斑马鱼急性毒性MNLC为8.62 μmol/L,LC10为15.2 µmol/L,急性毒性靶器官是心脏和肝脏,主要表现为心包水肿、心律异常和卵黄囊吸收延迟,毒性出现浓度为0.958 µmol/L。
本研究还存在一定的不足。作为一种常用于药物毒性评价的模式生物,斑马鱼具有易养殖、繁殖快、成本低等优势,但斑马鱼被用于药物毒性检测时易存在假阳性和假阴性。因此,本研究的结论还需要在其他动物模型中进一步研究。
The acute toxicity of tetrodotoxin to zebra fish
-
摘要:
目的 研究河豚毒素对斑马鱼的急性毒性。 方法 在斑马鱼中用最大非致死浓度(MNLC)和10%致死浓度(LC10)测定和评估河豚毒素的急性毒性。 结果 经Origin 8.0软件模拟,得出河豚毒素对斑马鱼急性毒性MNLC为8.62 μmol/L,LC10为15.2 μmol/L。在本实验条件下,16.0 μmol/L及以上浓度河豚毒素可诱发斑马鱼心包水肿和心律异常,终点时出现部分或全部死亡。河豚毒素的急性毒性靶器官是心脏和肝脏,主要表现为心包水肿、心律异常和卵黄囊吸收延迟,毒性出现浓度为0.958 μmol/L。 结论 河豚毒素对斑马鱼具有一定的心脏和肝脏毒性,且其毒性与河豚毒素的浓度相关。 Abstract:Objective To study the acute toxicity of tetrodotoxin to zebra fish. Methods The maximum non-lethal concentration (MNLC) and 10% lethal concentration (LC10) determinations were used to assess the acute toxicity of tetrodotoxin. Results According to the simulation calculation of Origin 8.0 software, the MNLC was 8.62 µmol/L and 15.2 µmol/L for LC10. Under the experimental conditions, tetrodotoxin at a concentration of 16.0 µmol/L and above induced pericardial edema and arrhythmia, leading to the death of zebra fish. The target organs for acute toxicity of tetrodotoxin were the heart and liver. The main manifestations were pericardial edema, arrhythmia, and delayed yolk sac absorption. The toxicity appeared at a concentration of 0.958 µmol/L. Conclusion Tetrodotoxin has heart and liver toxicity to zebra fish, and its toxicity is dose-dependent. -
Key words:
- tetrodotoxin /
- zebra fish /
- acute toxicity
-
肺型氧中毒是长期吸入高浓度氧气导致的肺部损伤,表现为肺组织充血、水肿、炎性浸润等,其中以多型核白细胞为主[1]。活化的多型核白细胞可以激活氧化酶,进而产生和释放大量的炎症介质和氧自由基,进一步介导级联式扩大的炎症反应对肺部造成损伤[2]。在饱和潜水或重型减压病患者进行加压治疗时,肺型氧中毒已成为最常见的并发症[3]。然而,目前关于高压氧(HBO)诱导的肺型氧中毒发生机制缺乏深入的探讨。
山莨菪碱(ANI)是一种毒蕈碱(M)受体阻滞剂,新斯的明(NEO)是一种临床常见的胆碱酯酶抑制剂。我们课题组前期研究发现ANI和NEO以500∶1的比例组成复方,简称新斯莨菪碱,能协同地激活α7nAChR,并减轻二者联用所致的不良反应。研究表明激活α7nAChR受体在感染性休克[4]、类风湿关节炎[5]、挤压综合征[6]、脑卒中[7]等动物模型上均发挥保护作用。然而,在HBO诱导的肺型氧中毒的发生、发展过程中,新斯莨菪碱是否可以用于肺型氧中毒的治疗?其治疗作用的病理生理机制是什么?这些都尚未阐明。
铁死亡是一种以细胞内铁依懒性的活性氧(ROS)异常增高,导致细胞内ROS的生成和降解失衡为特征的细胞死亡方式[8]。高浓度氧暴露条件下生成的大量ROS,一方面可直接对肺细胞产生损害,另一方面可参与炎症反应,促进炎症细胞渗透聚集,使各种致炎因子的表达增多,进一步加重肺的急性炎症反应[9]。
本文探究了新斯莨菪碱对HBO诱导的肺型氧中毒是否具有保护效应,并在此基础上,阐明铁死亡在新斯莨菪碱治疗HBO诱导的肺型氧中毒中的作用,以期为肺型氧中毒的临床防治提供新的理论指导和思路。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 实验动物
雄性C57BL/6小鼠,6~8周龄,小鼠购自上海斯莱克公司。所有小鼠均饲养于22℃,昼夜循环12 h的独立饲养系统中。小鼠自由饮食、自由饮水。所有实验均经海军军医大学实验动物伦理委员会批准并按照指南进行。
1.2 仪器和试剂
小型实验动物氧舱(RDC150-300-6,海军军医大学);台式高速冷冻离心(SCILOGEX);7500RT-PCR 仪器(Applied Biosystems 公司);激光共聚焦显微镜(日本Olympus公司);酶标仪(瑞士Tacan 公司);高速组织研磨仪(上海净信实业发展有限公司);Trizol、BCA 法蛋白定量试剂盒(美国GLPBIO公司);苏木精-伊红(上海Sangon Biotech公司);戊巴比妥(上海国药集团化学试剂公司);RT-PCR试剂盒(日本Takara公司);组织铁检测试剂盒(北京Solarbiog公司);伊文思蓝(美国Sigma-Aldrich公司);MDA、GSH检测试剂盒(上海Beyotime公司);Perls stain、抗谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4(GPX4)抗体、抗β-actin抗体(英国Abcam公司);驴抗兔/驴抗鼠二抗、Odyssey 扫膜仪(LI-COR公司)。
1.3 实验方法
1.3.1 肺型氧中毒模型的制备
将小鼠置于动物加压舱内,先用纯氧冲洗舱5 min,然后将压力在5 min内调至舱内为100% O2、2.5 ATA,维持6 h,在暴露过程中保持 0.5 L/min的连续氧流量,每1~2 h调整气阀进行快速通气,同时舱内放置碱石灰以避免呼吸产生的CO2在舱内蓄积。动物实验分组如下:①正常组:腹腔注射给予生理盐水10 ml/kg,常压饲养;②模型组:HBO暴露前30 min给予生理盐水10 ml/kg,2.5 ATA暴露6 h;③新斯莨菪碱组:HBO暴露前30 min给予ANI(25 mg/kg)+NEO(50 μg/kg),2.5 ATA 暴露6 h。
1.3.2 HE染色
使用戊巴比妥钠麻醉并处死小鼠,解剖取小鼠左肺组织于4%多聚甲醛中固定,然后用石蜡包埋并切成5 μm的薄片。在 200倍光学显微镜下观察组织炎症、水肿或其他损伤。组织学评分:0分为正常组织学;1分代表轻度白细胞浸润和毛细血管充血;2分代表轻度白细胞浸润、血管周围水肿、肺结构部分破坏和出血;3分代表强烈的白细胞浸润和肺结构破坏。
1.3.3 伊文思蓝染色
HBO暴露6 h后,将小鼠固定,尾静脉注射1%伊文思蓝(50 mg/kg)后放回笼中自由活动,约30 min处死动物,用PBS灌流后取肺组织,用滤纸擦干肺组织表面水分并对肺组织进行拍照。每100 mg肺组织加入2 ml甲酰胺,55℃孵育18 h,反应结束后10 000×g 离心30 min后取上清液,并在630、740 nm处测量吸光度。
1.3.4 肺组织湿干比
将小鼠麻醉处死后,取新鲜左肺组织,滤纸擦干表面血迹后称重记为湿重,随后将肺组织置于60℃干燥箱中,每日测量肺组织重量,直至肺组织重量不再变化,此时肺组织重量为干重。肺含水量(%)=(湿重−干重)/湿重×100%。
1.3.5 肺泡灌洗液蛋白含量测定
用1 ml预冷PBS经气管插管灌洗肺3次,收集混合的支气管肺泡灌洗液(BALF),将收集到的BALF以1 500 r/min 离心10 min获得其上清液,BCA法测定试剂盒定量BALF中总蛋白。
1.3.6 非血红素铁含量测定
30 mg肺组织在冷PBS中清洗,在冰上用匀浆器在铁测定缓冲液中匀浆,在4℃以16 000×g离心10 min,收集上清液用铁检测试剂盒进行组织铁含量测定。
1.3.7 普鲁士蓝染色
戊巴比妥钠麻醉处死小鼠,取新鲜肺组织于4%多聚甲醛中固定,固定48 h后进行梯度脱水,二甲苯置换,浸蜡;包埋、切片(厚度为5 μm)。将石蜡切片脱蜡后用Prussian Blue Stain(等体积的亚铁氰化钾溶液和盐酸溶液混合,制成铁染色工作液)染色15 min,洗涤,然后用核固红溶液染色5 min,洗涤,封片后在Olympus光学显微镜下观察染色切片。
1.3.8 丙二醛(MDA)的测定
取100 μg肺组织于300 μl PBS溶液中,匀浆机研磨后,以12 000 r/min离心10 min后取上清液待测。所有试剂盒均按照制造商的说明书使用,按检测工作液与上清2∶1配好检测体系后100℃水浴15 min,冷却后于532 nm处测吸光度。
1.3.9 谷胱甘肽(GSH)的测定
取100 μg肺组织,与700 μl蛋白去除试剂S溶液混匀,匀浆机研磨后以12 000 r/min,离心10 min后取上清液进行总谷胱甘肽测定。所有试剂盒均按照制造商的说明书使用,25℃反应60 min即可测得氧化性谷胱甘肽(GSSG)含量,还原GSH含量=总谷胱甘肽含量−GSSG×2 。
1.3.10 实时定量PCR
动物出舱后,解剖取肺组织,使用TRIzol试剂提取组织总RNA并逆转录成cDNA,进行PCR扩增,采用2–ΔΔCT分析目的基因的相对表达量,引物序列见表1。
表 1 实时定量PCR引物序列引物名称 引物序列(5′—3′) IL-6(F) CCAGAAACCGCTATGAAGTTCC IL-6(R) GTTGGGAGTGGTATCCTCTGTGA IL-1β(F) GTTCCCATTAGACAACTGCACTACAG IL-1β(R) GTCGTTGCTTGGTTCTCCTTGTA TNF-α(F) CCCCAAAGGGATGAGAAGTTC TNF-α(R) CCTCCACTTGGTGGTTTGCT GAPDH(F) GTATGACTCCACTCACGGCAAA GAPDH(R) GGTCTCGCTCCTGGAAGATG 注:F: 正向引物; R: 反向引物。 1.3.11 Western blot
提取肺组织蛋白,BCA法测定蛋白浓度。十二烷基硫酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶(SDS-PAGE)电泳分离蛋白质,然后转移到硝酸纤维素膜上,与GPX4、β-肌动蛋白共孵育。最后,根据情况将膜与驴抗兔或驴抗鼠二抗孵育,使用Odyssey 扫膜仪获取图像,通过Image J 软件对条带进行定量分析。
1.4 统计学处理
实验数据的分析以及数据处理均使用GraphPad Prism 8.0 软件进行。所有值以(
$ \bar{x}\pm s $ )表示,多组间比较用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)并 Bonferroni 检验,P<0.05 视为差异具有统计学意义。2. 结果
2.1 新斯莨菪碱保护了 HBO暴露引起的肺组织损伤
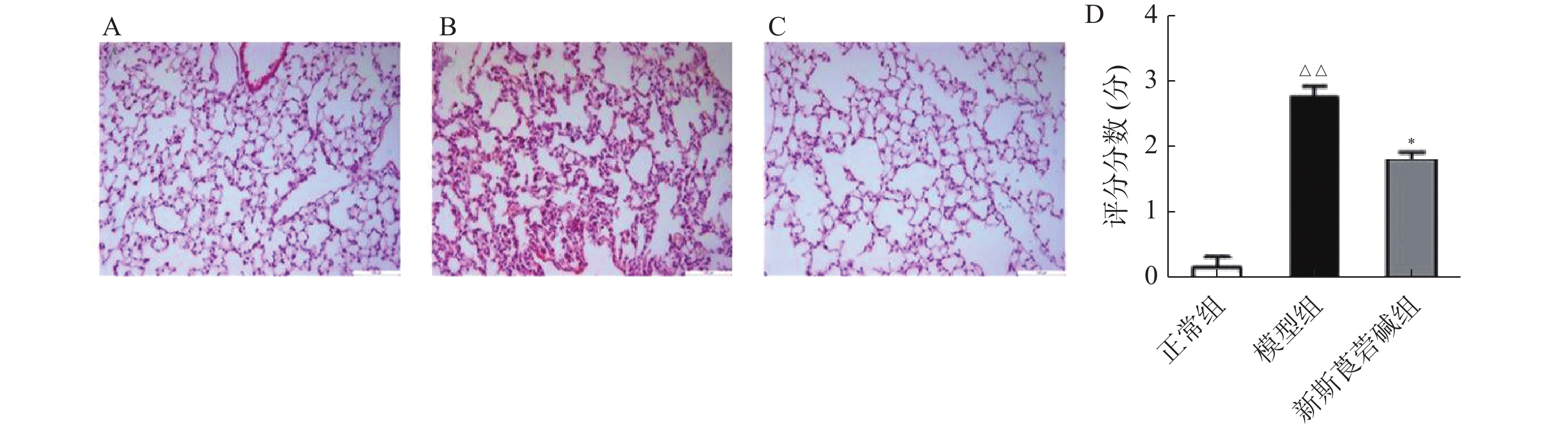
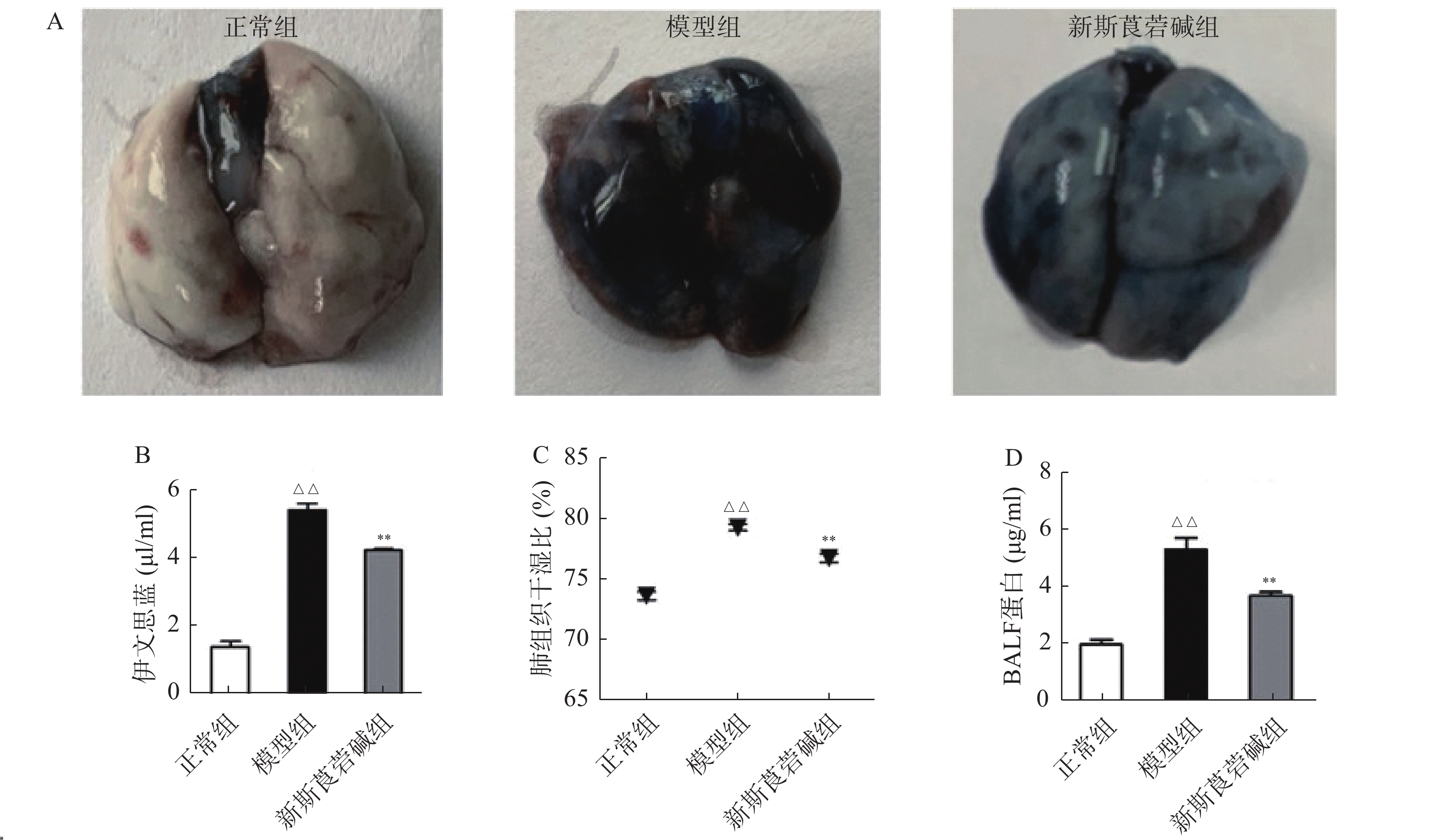
首先,探究HBO暴露后对肺组织的病理损伤情况以及新斯莨菪碱对HBO诱导的肺损伤的作用。将C57BL/6小鼠置于2.5 ATA的高压氧舱中暴露6 h建立肺型氧中毒模型,然后通过HE染色观察肺组织结构变化,如图1所示。正常组小鼠肺泡肺泡壁结构完整,间隔无增厚,肺泡腔内无渗出物;HBO暴露后,肺泡间隔出现水肿、增厚,肺泡腔内可见红细胞渗出,肺间质见大量炎性细胞浸润(图1B);给予新斯莨菪碱治疗后,肺水肿明显减轻,肺泡内炎性细胞浸润以及红细胞渗出减少,肺组织病理损伤减轻(图1C~D)。以上结果表明新斯莨菪碱治疗能减轻肺型氧中毒后肺组织的病理损伤。
2.2 新斯莨菪碱改善肺组织渗透性
从图2可以看出,模型组伊文思蓝染色加深,表明HBO暴露后肺渗透性增加,而新斯莨菪碱治疗后上述情况明显改善(图2A~B)。与正常组相比,模型组肺组织湿干比重明显增加,而新斯莨菪碱治疗后能够显著降低肺湿干比(图2C)。此外,HBO暴露后肺泡灌洗液中蛋白含量升高,新斯莨菪碱治疗能够有效减少肺泡灌洗液中蛋白的渗出(图2D)。这些结果表明,新斯莨菪碱治疗能够有效改善肺型氧中毒后的肺水肿及肺组织渗出。
2.3 新斯莨菪碱抗炎、抗氧化应激作用
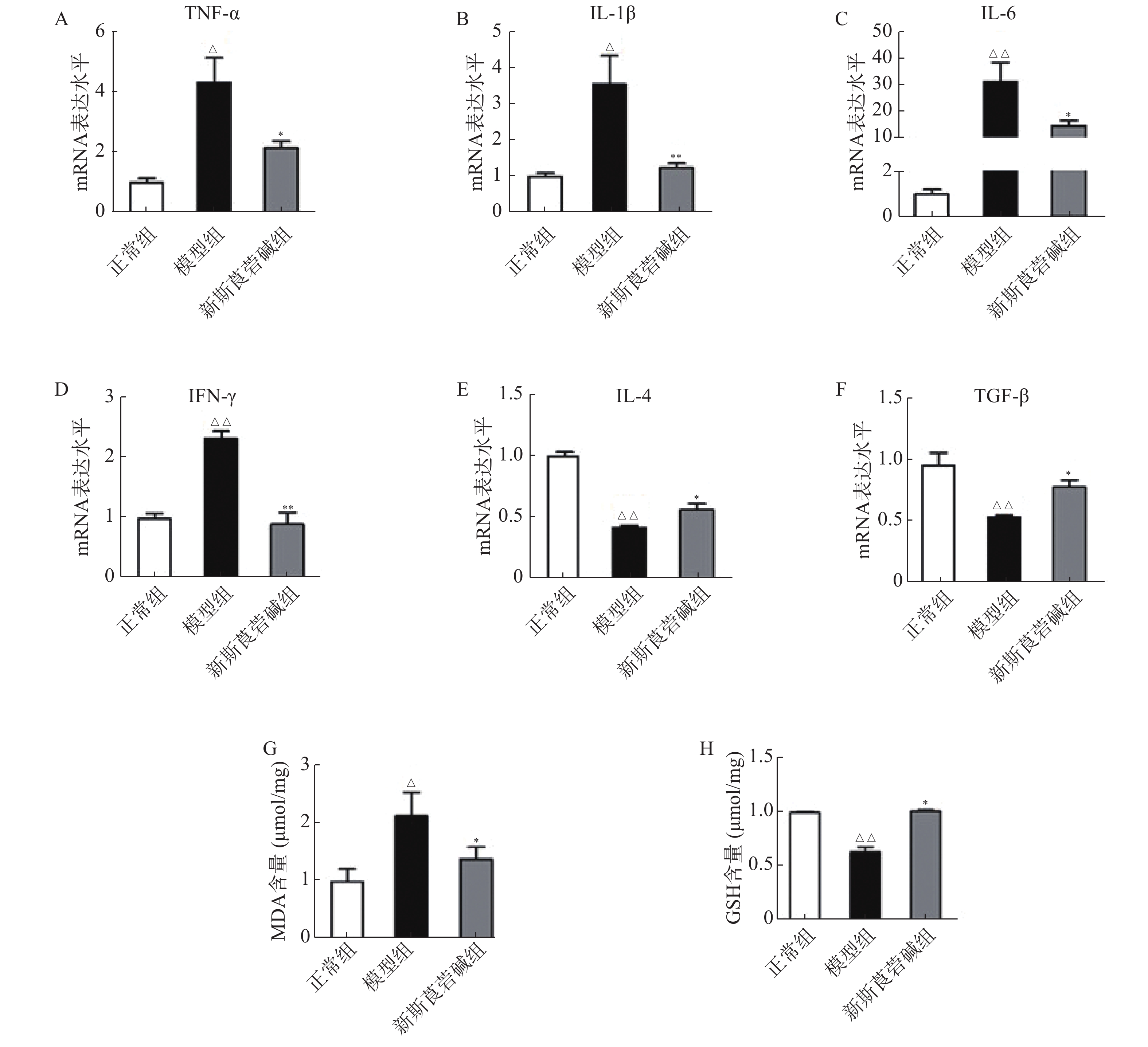
从图3中可以看出,HBO暴露后,肺组织中促细胞因子,如TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6和IFN-γ的mRNA显著增高,抗炎因子IL-4及TGF-β则显著降低,而新斯莨菪碱能显著降低促炎因子的表达,同时提高抗炎因子的水平(图3A~F)。HBO暴露后肺组织氧化指标MDA升高,而抗氧化指标GSH降低,给予新斯莨菪碱治疗后,能明显逆转上述变化(图3G~H)。由此说明,新斯莨菪碱能降低HBO诱导的肺型氧中毒引起的炎症反应及氧化应激水平。
2.4 新斯莨菪碱减轻铁死亡
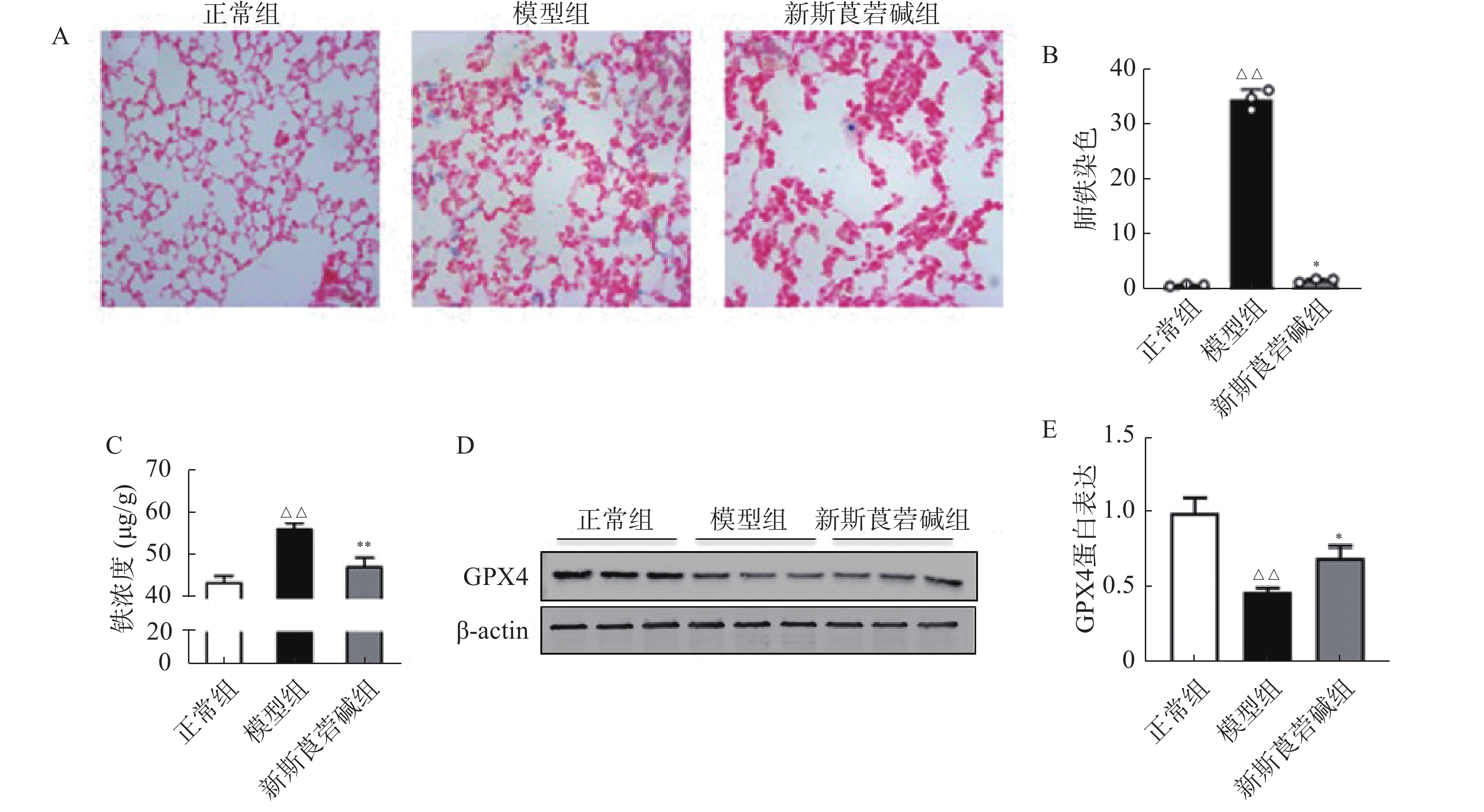
铁元素是维持正常生理活动所必需的,但过量的铁会产生对细胞有害的自由基。在病理状态下,铁蛋白的破坏导致细胞内游离铁的增高,脂质过氧化反应和游离铁的增高会导致细胞的铁死亡。如图4所示,HBO暴露后普鲁士蓝染色可见肺组织中铁含量增高,对肺组织铁离子含量进行检测得到了同样的结果(图4A~C)。GPX4是一种重要的抗氧化酶,HBO暴露后GPX4的表达降低(图4D~E),导致机体抗氧化应激能力减弱,对细胞有害的自由基无法被有效清除。而新斯莨菪碱治疗后可以改善GPX4的表达,降低肺组织铁含量,从而减少细胞铁死亡的发生,对肺组织起到保护作用。
3. 讨论
HBO已被广泛用于多种疾病的治疗以及潜水作业中,并发挥了难以替代的作用[10]。然而,在饱和潜水或重型减压病患者加压治疗以及临床上用于治疗新生儿呼吸窘迫时,HBO诱导的肺损伤已成为最常见的并发症[11]。研究发现,当HBO环境持续存在时,将出现小气道功能障碍,表现为肺活量降低、气体扩散功能减弱和肺顺应性降低[12]。与之前的报道一致,本研究结果表明,与正常组相比,模型组的肺组织损伤显著加重;伊文思蓝染色显示HBO暴露后染色加深,肺湿/干比增加,同时肺泡灌洗液中的蛋白含量也显著增加,新斯莨菪碱治疗后这些变化被显著抑制,这些结果初步表明新斯莨菪碱与HBO诱导的肺型氧中毒的发生密切相关。
ANI属于传出自主神经M受体阻断剂,阻断M受体引起交感神经优势。NEO是一种可逆性胆碱酯酶抑制剂,可有效延长乙酰胆碱的作用时间,同时激活胆碱能抗炎通路[11]。Sun等[4]研究证实,两药物联合使用,不仅可以加强胆碱能抗炎通路的炎症抑制作用,还可降低NEO的不良反应,达到协同增强作用。本课题组前期的研究发现ANI和NEO联合使用,能够通过阻断巨噬细胞上的毒蕈碱型受体,使更多的乙酰胆碱作用于α7尼古丁乙酰胆碱受体,进而对胆碱能抗炎通路起到双向活化调节作用,进一步加强了对炎症反应的抑制作用[7]。本研究发现新斯莨菪碱能够显著降低肺组织中促炎因子TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6和IFN-γ的表达。由此说明,新斯莨菪碱可减轻HBO导致的肺部炎症反应。
肺型氧中毒包括高压力损伤和高浓度氧损伤,目前认为ROS 及其代谢产物介导的生化紊乱是导致肺型氧中毒发生发展的主要因素。HBO环境下会产生大量氧自由基,可能导致细胞因子释放和炎症反应的增加,而异常的炎症反应可加剧肺损伤[13]。研究发现,HBO 暴露后肺组织中氧化指标MDA 显著升高、抗氧化指标 GSH 则显著降低,而给新斯莨菪碱治疗能明显改善肺组织氧化损伤情况。
铁死亡作为一种新发现的细胞死亡方式,其释放出内源性损伤相关分子(DAMPs)与炎症和氧化应激之间存在着诸多途径的交互作用。GPX4作为铁死亡的核心调控因子,近年来受到广泛关注。研究表明GPX4的缺乏或功能丧失会加剧铁死亡的发生,并促使细胞进一步受到氧化应激的影响[14]。Kang等[15]的研究发现在LPS诱导的脓毒症模型中,敲除GPX4导致脂质过氧化的加剧并进一步促进铁死亡的发生。本研究发现,HBO暴露后肺组织中铁含量增高、GPX4的表达量降低,而新斯莨菪碱治疗后可以逆转这些变化。
综上所述,新斯莨菪碱可能通过激活胆碱能抗炎通路,从而抑制炎症的和氧化应激的发生,进而减少了肺组织中游离铁的含量,最终抑制细胞铁死亡。下一步我们将通过体外实验,进一步验证在HBO诱导的肺型氧中毒模型中,新斯莨菪碱是否通过抑制铁死亡的产生从而减轻肺组织的损伤情况,以期为防治HBO诱导的肺型氧中毒提供新的策略。
-
表 1 河豚毒素急性毒性发生率统计(n=30)
毒性类型 正常对照组 溶剂对照组 河豚毒素浓度(μmol/L) 0.958 2.87 8.62 15.2 心脏 心包水肿 - - - - 7(2/30) 13(4/30) 房室缺失 - - - - - - 心律异常 - - - 7(2/30) 7(2/30) 17(5/30) 循环系统 血流变慢 - - - - - - 循环缺失 - - - - - - 出血及血栓 - - - - - - 脑 畸形 - - - - - - 下颌 短小 - - - - - - 眼睛 眼变小 - - - - - - 肝脏 缺失 - - - - - - 肝肿大 - - - - - - 肝变性 - - - - - - 卵黄囊吸收延迟 - - 80(24/30) 80(24/30) 87(26/30) 93(28/30) 肾脏 水肿 - - - - - - 肠道 肠腔异常 - - - 7(2/30) 13(4/30) 13(4/30) 躯干/尾/脊索 弯曲 - - - - - - 肌肉/体节 肌肉变性 - - - - - - 身体着色 异常 - - - - - - 体长变短 - - - - - 死亡 - - - - - 注:“-”表示未见明显异常 -
[1] ZIMMER T. Effects of tetrodotoxin on the mammalian cardiovascular system[J]. Mar Drugs, 2010, 8(3): 741-762. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20411124/ [2] BIESSY L, BOUNDY M J, SMITH K F, et al. Tetrodotoxin in marine bivalves and edible gastropods: a mini-review[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 236: 124404. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31545201/ [3] TAMELE I J, SILVA M, VASCONCELOS V. The incidence of tetrodotoxin and its analogs in the Indian Ocean and the red sea[J]. Mar Drugs, 2019, 17(1): 28. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30621279/ [4] MAGARLAMOV T Y, MELNIKOVA D I, CHERNYSHEV A V. Tetrodotoxin-producing bacteria: detection, distribution and migration of the toxin in aquatic systems[J]. Toxins, 2017, 9(5): 166. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28513564/ [5] NIETO F R, COBOS E J, TEJADA M Á, et al. Tetrodotoxin (TTX) as a therapeutic agent for pain[J]. Mar Drugs, 2012, 10(2): 281-305. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22412801/ [6] MATTEI C. Tetrodotoxin, a candidate drug for Nav1.1-induced mechanical pain? [J]. Mar Drugs, 2018, 16(2): E72. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29470418/ [7] SALAS M M, MCINTYRE M K, PETZ L N, et al. Tetrodotoxin suppresses thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in a rat full thickness thermal injury pain model[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2015, 607: 108-113. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26424077/ [8] QIU F, JIANG Y G, ZHANG H, et al. Increased expression of tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels Nav1.8 and Nav1.9 within dorsal root Ganglia in a rat model of bone cancer pain[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2012, 512(2): 61-66. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22342308/ [9] NEWMAN D J, CRAGG G M. Drugs and drug candidates from marine sources: an assessment of the current “state of play”[J]. Planta Med, 2016, 82(9-10): 775-789. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26891002/ [10] JAL S, KHORA S S. An overview on the origin and production of tetrodotoxin, a potent neurotoxin[J]. J Appl Microbiol, 2015, 119(4): 907-916. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26178523/ [11] LAGO J, RODRÍGUEZ L P, BLANCO L, et al. Tetrodotoxin, an extremely potent marine neurotoxin: distribution, toxicity, origin and therapeutical uses[J]. Mar Drugs, 2015, 13(10): 6384-6406. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26492253/ [12] MCNABB P S, TAYLOR D I, OGILVIE S C, et al. First detection of tetrodotoxin in the bivalve Paphies australis by liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry with and without precolumn reaction[J]. J AOAC Int, 2014, 97(2): 325-333. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24830143/ [13] TURNER A D, POWELL A, SCHOFIELD A, et al. Detection of the pufferfish toxin tetrodotoxin in European bivalves, England, 2013 to 2014[J]. Euro Surveill, 2015, 20(2): 21009. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25613778/ [14] KIRCHHOF P, TAL T, FABRITZ L, et al. First report on an inotropic peptide activating tetrodotoxin-sensitive, “neuronal” sodium currents in the heart[J]. Circ Heart Fail, 2015, 8(1): 79-88. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25424392/ [15] MATSUMOTO T, FEROUDJ H, KIKUCHI R, et al. DNA microarray analysis on the genes differentially expressed in the liver of the pufferfish, Takifugu rubripes, following an intramuscular administration of tetrodotoxin[J]. Microarrays (Basel), 2014, 3(4): 226-244. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27600346/ [16] 王敏, 臧奎, 尚福泰, 等. 河豚毒素中毒致心跳呼吸骤停1例[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2014, 15(1): 54-55. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ZZLC201401024&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [17] 张桦, 赵剑. 河豚毒素中毒致急性肾脏损害5例报告[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2002, 22(5): 303. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=SYNK200205028&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [18] 徐勤惠, 黄凯, 高莉莎, 张翰, 荣康泰. 河豚毒素对小鼠和家兔的毒性研究[J]. 卫生研究, 2003, 32(4): 371-374. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=WSYJ200304022&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ -





 下载:
下载:
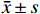
 下载:
下载: