-
西红花,为鸢尾科多年生植物番红花(Crocus sativus L.)的干燥柱头,具有活血化瘀、凉血解毒、解郁安神等功效 [1]。番红花是三倍体不育植物,只能通过被称为球茎的块状球茎无性繁殖。西红花的产量和品质与球茎大小直接相关 [2]。而球茎中包含的有机酸、脂肪酸、萜类等化合物 [3]与球茎生长代谢过程密切相关,并在很大程度上影响球茎的大小。然而,目前球茎中内源性代谢物的分析方法均需要将样本进行匀浆后检测,这就会造成空间信息的丢失,无法实现原位分析。因此,利用新的技术手段研究番红花球茎中内源性代谢物的空间分布规律至关重要。
解吸电喷雾电离质谱成像(DESI-MSI)无需复杂的预处理步骤,可直接对样品进行可视化分析 [4]。目前已在解析植物内源性代谢物的空间定位方面显示出强大的分析能力。本研究通过优化切片厚度,建立了一种灵敏、高覆盖的质谱成像分析方法,以可视化番红花球茎中内源性代谢物在不同产地及同一产地不同部位的空间分布,实现了番红花球茎中黄酮、有机酸、氨基酸、类胡萝卜素和环烯醚萜苷的原位表征。为探究番红花全生命周期内的生长过程和开展番红花球茎种质筛选提供了新的技术支持。
-
1900-冷冻切片机(浙江益迪医疗科技有限公司);SYNAPT G2-Si HDMS质谱成像仪、HD Imaging 质谱成像数据分析软件 (Waters公司);标准级显微镜载玻片(上海泰坦科技股份有限公司)。
OCT 包埋剂(美国樱花SAKURA 公司);甲醇(HPLC级,美国Merck公司)。
-
番红花球茎分别购自上海崇明、浙江建德和安徽亳州西红花种植合作社,批号分别为20230901SH、20230830ZJ、20230830AH,经海军军医大学韩婷教授鉴定。将新鲜球茎置于冷冻切片机中预冷30 min之后,用OCT包埋剂固定于切片机样品托上。连续切片,分别制备成20、30、40、50 μm的切片,黏附于载玻片上,在室温下干燥20 min后备用。
-
将准备好的组织切片置于X轴和Y轴二维操控台上,使用SYNAPT G2-Si HDMS质谱成像仪在正离子模式下进行检测。检测的质荷比(m/z)范围设定为50~650;空间分辨率为200 μm;施加在电喷雾针上的电压为3.0 kV;电喷雾针与二维操控台的角度为38°;离子传输管温度为100 ℃;二维操控平台移动速度为200 μm/s。质谱成像原始数据文件利用HD imaging软件转化成图片,用总离子流图进行归一化。
-
组织切片是获得高质量质谱成像图像的关键步骤 [5]。组织切片的厚度会影响切片的完整性,如果碎裂就无法获得完整的空间分布图像 [6]。质谱成像在动物、人体内源性代谢物的可视化分布研究起步较早。对于哺乳动物组织,推荐5~20 μm作为检测低分子量的最优厚度 [7]。然而受限于植物组织富含水分,组织容易破碎的特点,难以制成薄片。为了获得高质量质谱图片,本研究进行了切片厚度的优化。在番红花球茎中,除了水分之外,淀粉是其干物质的重要组成之一 [8],因此切片时成形性较差,极易造成组织破碎、结构不完整。本研究选用在20~50 μm之间的浙江建德球茎,以10 μm为梯度,进行了4个不同的切片厚度探索。结果表明,切片厚度为20 μm时,顶芽部位存在大部分缺失,球茎部分也存在部分碎裂;30 μm和40 μm时,顶芽的部位切片完整,但球茎部分仍然不完整,其中40 μm球茎完整度好于30 μm;而50 μm切片整体完整度较高,能良好的呈现球茎和顶芽形态(图1)。因此本研究选择50 μm切片厚度进行后续质谱成像检测。
-
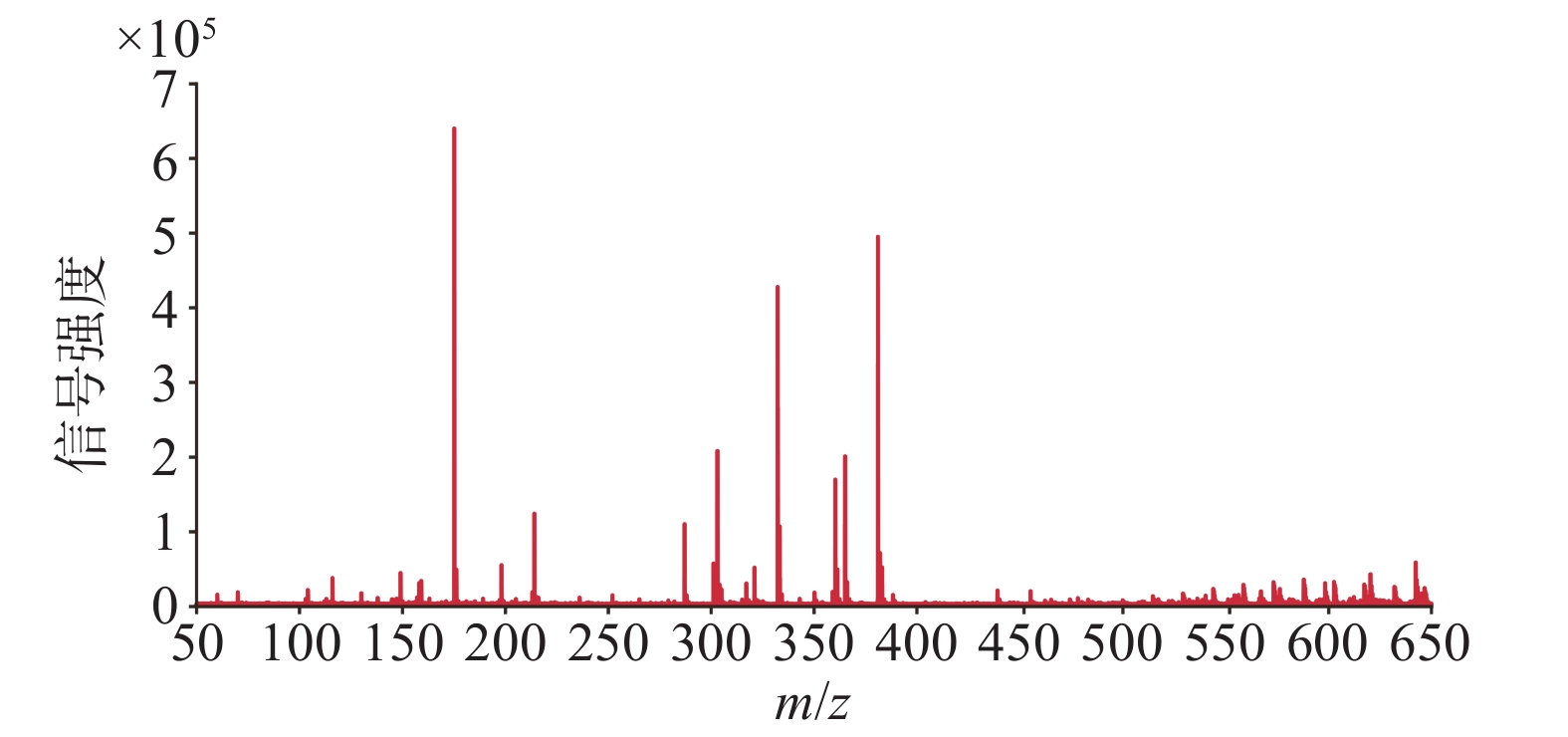
使用优化的条件直接进行DESI-MSI检测,获得球茎切片在正离子模式下的平均质谱图,如图2所示,可以观测到丰富的信号峰,其中,m/z 范围在150~400之间信号丰度较高,在450~650范围内也观察到不少代谢物,但是丰度较低。用总离子流图进行归一化后在HD imaging软件中提取质荷比,结合数据库和已报道文献检索,共获得了66种化合物的空间分布信息。其中,观察到代谢物在球茎的不同部位具有不同的分布特征。
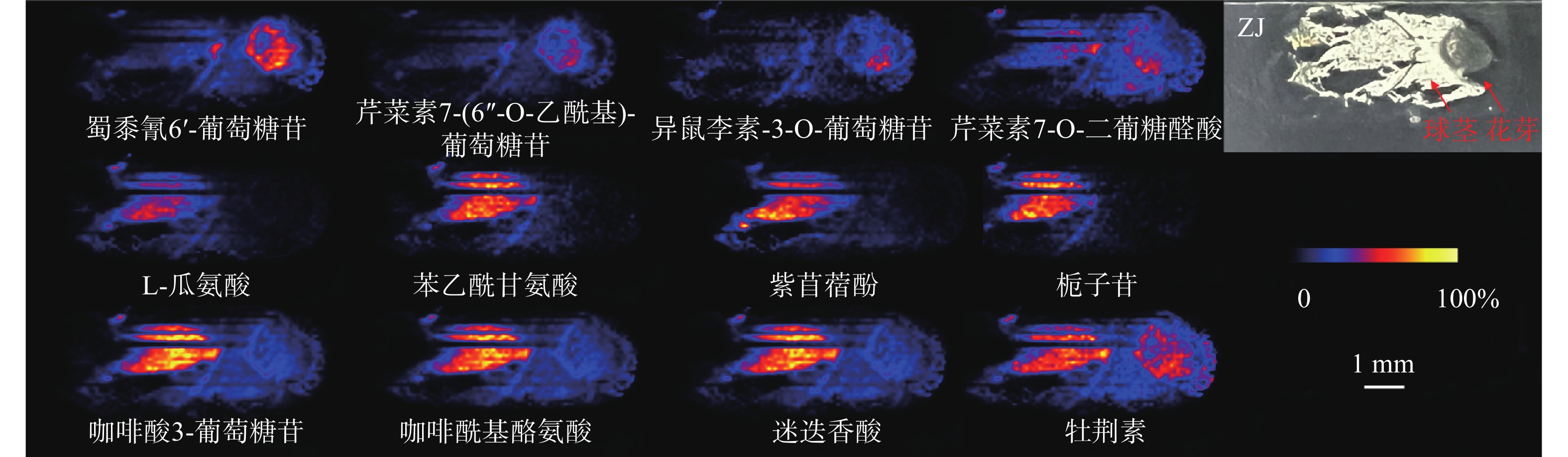
值得关注的是,芹菜素7-(6''-O-乙酰基)-葡萄糖苷、异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷、蜀黍氰苷6'-葡萄糖苷几乎只分布在顶芽中;芹菜素7-O-二葡糖醛酸同样主要分布在顶芽中,球茎部分也有少量分布(图3)。蜀黍氰苷是广泛分布于植物界的一种含氮化合物,通过在食草动物的组织破裂时释放氰化氢而起到化学防御作用 [9]。在萌发的高粱种子中,发现蜀黍氰苷主要积累在萌发的胚芽中 [10]。本研究中观察到蜀黍氰苷主要在番红花球茎萌发的顶芽中分布,与文献报道一致,其分布的特异性可能是由于对抗食草动物从而保护新兴的组织。黄酮类化合物作为中药成分的重要药效部分,具有一定的抗炎、抗氧化、抗细胞凋亡等作用 [11]。异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷在西红花中已有检测,本次发现其在顶芽中丰度较高,推测与芽承担运输功能有关。
在球茎中,主要观察到氨基酸和部分次生代谢物的分布,如L-瓜氨酸、苯乙酰甘氨酸、紫苜蓿酚和栀子苷等均只特异性分布在球茎中(图3)。氨基酸作为一种重要的初生代谢物,不仅在植物生长发育过程中发挥着不可或缺的角色,还是生物碱合成的重要前体 [12]。因球茎是番红花的营养器官,故氨基酸主要积累于球茎部位,为其生长提供所需物质和能量。
某些化合物在顶芽和球茎中均可以观察到,如咖啡酸3-葡萄糖苷、咖啡酰基酪氨酸、迷迭香酸和牡荆素(图3)。有趣的是,酪氨酸除了分布于球茎部分,在顶芽中也有不少分布。研究表明,酪氨酸参与植物色素合成且是生物碱合成的重要前体 [12],其在球茎和顶芽中均有分布,说明球茎在萌发过程中已经开始色素和生物碱合成的准备。
-
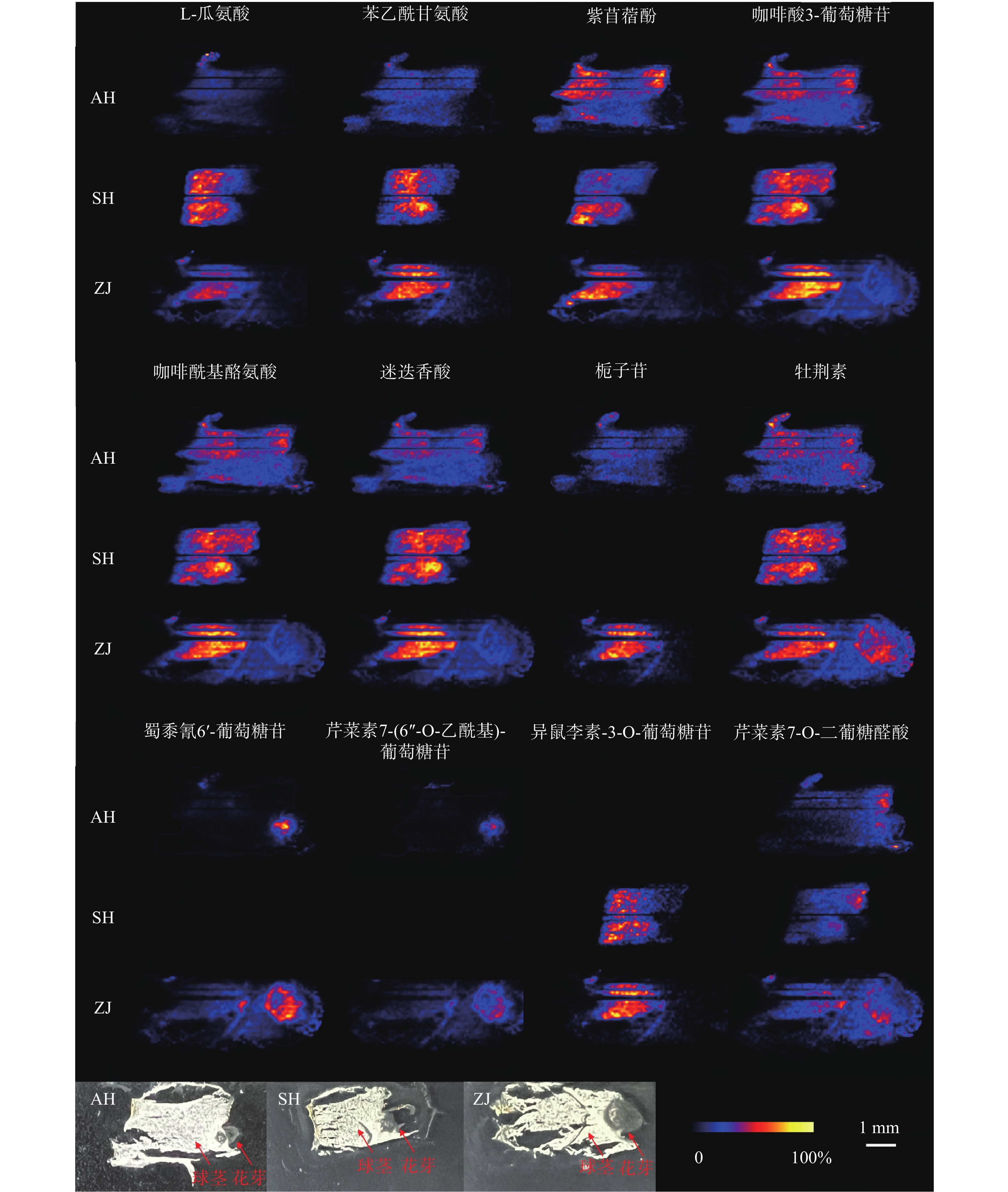
总体来说,大多数化合物都呈现出一致的分布规律。对于在球茎部位分布的化合物来说,在上海的球茎中丰度最高,浙江次之,安徽最低,但是浙江球茎检测到的化合物种类最多。此外,我们还观察到了某些化合物在不同产地具有不同的分布规律。如栀子苷、蜀黍氰苷6'-葡萄糖苷和芹菜素7-(6''-O-乙酰基)-葡萄糖苷在上海球茎中未观察到分布,而异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷在安徽球茎中未观察到分布(图4)。番红花喜凉怕酷热、怕严寒、喜湿润,对生长环境要求较高 [13]。上海崇明地处中国最大河流长江入海口,气候温和湿润,年平均气温16.5 ℃,年平均降雨量1128.9 mm;浙江建德年平均气温17.8 ℃,年降水量1905.1 mm,气候同样温暖湿润;而安徽亳州年平均气温14.9 ℃,属温带半湿润气候区,年平均降雨量仅831 mm。与安徽亳州相比,上海崇明和浙江建德的气候特点显然更适于番红花生长。同时,从光学照片可以发现,浙江球茎的顶芽分化早于上海和安徽球茎,这可能是浙江球茎内代谢物较为丰富的原因之一。
-
本文通过优化切片厚度,利用DESI质谱成像技术对不同产地番红花球茎内源性代谢物的分布特征进行了可视化研究,实现了黄酮、类胡萝卜素、氨基酸和有机酸的原位表征。不同化合物在球茎不同部位显示出不同分布,其中蜀黍氰苷6'-葡萄糖苷、异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷、芹菜素衍生物主要分布于顶芽中,而作为能量和物质供应的氨基酸则主要积累在球茎。此外,不同产地的番红花球茎也存在较大差异。从成像丰度来看,上海的球茎物质丰度较高,其次是浙江,安徽丰度最低。就化合物的分布规律而言,大部分代谢物在不同产地球茎中分布是一致的,但也观察到了一些差异。如栀子苷、蜀黍氰苷6'-葡萄糖苷和芹菜素7-(6''-O-乙酰基)-葡萄糖苷在上海未观察到分布,而异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷仅在上海和浙江产地观察到分布。我们推测,这可能是由于不同地域的温度、湿度等环境因素所致。本研究首次可视化了不同产地番红花球茎中不同物质在不同部位的分布特征,为探究番红花全生命周期内的生长过程和开展番红花球茎种质筛选提供了新的技术支持。
Analysis of tissue distribution of metabolites in Crocus sativus L. corms based on DESI mass spectrometry imaging technique
-
摘要:
目的 探究不同产地番红花球茎中内源性代谢物的分布特征。 方法 利用解吸电喷雾(DESI)质谱成像技术,通过优化样品前处理,建立了一种对番红花球茎内源性代谢物可视化分析的方法。 结果 实现了黄酮、有机酸、氨基酸、类胡萝卜素和环烯醚萜苷等代谢物的原位表征;L-瓜氨酸、苯乙酰甘氨酸、紫苜蓿酚和栀子苷等特异性分布在球茎中;芹菜素7-(6''-O-乙酰基)-葡萄糖苷、异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷、蜀黍氰苷6'-葡萄糖苷、芹菜素7-O-二葡糖醛酸主要分布在顶芽中;对于在球茎部位分布的化合物,产于上海的番红花球茎丰度最高,浙江次之,安徽最低。 结论 番红花球茎在不同产地及同一产地不同部位的代谢物分布存在显著差异,黄酮和黄酮衍生物如异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷、芹菜素衍生物主要分布于顶芽中,此外,天然植物保护剂蜀黍氰苷6'-葡萄糖苷也主要在顶芽分布,而作为能量和物质供应的氨基酸则主要积累在球茎。 Abstract:Objective To explore the distribution characteristics of endogenous metabolites in Crocus sativus L. corms from different origins. Methods A method based on desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging and optimized sample pretreatment was developed for directly visualize metabolites in C. sativus corms. Results In situ characterization of metabolites such as flavonoids, organic acids, amino acids, carotenoids, and cyclic enol ether terpene glycosides was achieved. L-Citruline, phenylacetylglycine, sativol, and geniposide were specifically distributed in the corms. Apigenin 7-(6''-O-acetyl)-glucoside, isorhamnetin-3-O-β-D-Glucoside, dhurrin 6'-glucoside, and Apigenin 7-O-diglucuronide were mainly distributed in the terminal bud. For compounds distributed in the corms, the highest abundance was found in corms from Shanghai, followed by Zhejiang and the lowest from Anhui. Conclusion The distribution of metabolites in different parts of C. sativus corms from different origins and the same origin varies significantly. Flavonoids and flavonoid derivatives such as isorhamnetin-3-O-β-D-Glucoside and apigenin derivatives are mainly distributed in the terminal buds, in addition, the natural plant protection agent dhurrin 6'-glucoside is also mainly distributed in the terminal corms, whereas amino acids, which are used as energy and material supplies, are mainly accumulated in the corms. -
西红花,为鸢尾科多年生植物番红花(Crocus sativus L.)的干燥柱头,具有活血化瘀、凉血解毒、解郁安神等功效 [1]。番红花是三倍体不育植物,只能通过被称为球茎的块状球茎无性繁殖。西红花的产量和品质与球茎大小直接相关 [2]。而球茎中包含的有机酸、脂肪酸、萜类等化合物 [3]与球茎生长代谢过程密切相关,并在很大程度上影响球茎的大小。然而,目前球茎中内源性代谢物的分析方法均需要将样本进行匀浆后检测,这就会造成空间信息的丢失,无法实现原位分析。因此,利用新的技术手段研究番红花球茎中内源性代谢物的空间分布规律至关重要。
解吸电喷雾电离质谱成像(DESI-MSI)无需复杂的预处理步骤,可直接对样品进行可视化分析 [4]。目前已在解析植物内源性代谢物的空间定位方面显示出强大的分析能力。本研究通过优化切片厚度,建立了一种灵敏、高覆盖的质谱成像分析方法,以可视化番红花球茎中内源性代谢物在不同产地及同一产地不同部位的空间分布,实现了番红花球茎中黄酮、有机酸、氨基酸、类胡萝卜素和环烯醚萜苷的原位表征。为探究番红花全生命周期内的生长过程和开展番红花球茎种质筛选提供了新的技术支持。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 仪器和试剂
1900-冷冻切片机(浙江益迪医疗科技有限公司);SYNAPT G2-Si HDMS质谱成像仪、HD Imaging 质谱成像数据分析软件 (Waters公司);标准级显微镜载玻片(上海泰坦科技股份有限公司)。
OCT 包埋剂(美国樱花SAKURA 公司);甲醇(HPLC级,美国Merck公司)。
1.2 样品收集和前处理
番红花球茎分别购自上海崇明、浙江建德和安徽亳州西红花种植合作社,批号分别为20230901SH、20230830ZJ、20230830AH,经海军军医大学韩婷教授鉴定。将新鲜球茎置于冷冻切片机中预冷30 min之后,用OCT包埋剂固定于切片机样品托上。连续切片,分别制备成20、30、40、50 μm的切片,黏附于载玻片上,在室温下干燥20 min后备用。
1.3 DESI质谱成像分析
将准备好的组织切片置于X轴和Y轴二维操控台上,使用SYNAPT G2-Si HDMS质谱成像仪在正离子模式下进行检测。检测的质荷比(m/z)范围设定为50~650;空间分辨率为200 μm;施加在电喷雾针上的电压为3.0 kV;电喷雾针与二维操控台的角度为38°;离子传输管温度为100 ℃;二维操控平台移动速度为200 μm/s。质谱成像原始数据文件利用HD imaging软件转化成图片,用总离子流图进行归一化。
2. 结果和讨论
2.1 切片厚度的优化
组织切片是获得高质量质谱成像图像的关键步骤 [5]。组织切片的厚度会影响切片的完整性,如果碎裂就无法获得完整的空间分布图像 [6]。质谱成像在动物、人体内源性代谢物的可视化分布研究起步较早。对于哺乳动物组织,推荐5~20 μm作为检测低分子量的最优厚度 [7]。然而受限于植物组织富含水分,组织容易破碎的特点,难以制成薄片。为了获得高质量质谱图片,本研究进行了切片厚度的优化。在番红花球茎中,除了水分之外,淀粉是其干物质的重要组成之一 [8],因此切片时成形性较差,极易造成组织破碎、结构不完整。本研究选用在20~50 μm之间的浙江建德球茎,以10 μm为梯度,进行了4个不同的切片厚度探索。结果表明,切片厚度为20 μm时,顶芽部位存在大部分缺失,球茎部分也存在部分碎裂;30 μm和40 μm时,顶芽的部位切片完整,但球茎部分仍然不完整,其中40 μm球茎完整度好于30 μm;而50 μm切片整体完整度较高,能良好的呈现球茎和顶芽形态(图1)。因此本研究选择50 μm切片厚度进行后续质谱成像检测。
2.2 代谢物在球茎不同部位中的分布特征
使用优化的条件直接进行DESI-MSI检测,获得球茎切片在正离子模式下的平均质谱图,如图2所示,可以观测到丰富的信号峰,其中,m/z 范围在150~400之间信号丰度较高,在450~650范围内也观察到不少代谢物,但是丰度较低。用总离子流图进行归一化后在HD imaging软件中提取质荷比,结合数据库和已报道文献检索,共获得了66种化合物的空间分布信息。其中,观察到代谢物在球茎的不同部位具有不同的分布特征。
值得关注的是,芹菜素7-(6''-O-乙酰基)-葡萄糖苷、异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷、蜀黍氰苷6'-葡萄糖苷几乎只分布在顶芽中;芹菜素7-O-二葡糖醛酸同样主要分布在顶芽中,球茎部分也有少量分布(图3)。蜀黍氰苷是广泛分布于植物界的一种含氮化合物,通过在食草动物的组织破裂时释放氰化氢而起到化学防御作用 [9]。在萌发的高粱种子中,发现蜀黍氰苷主要积累在萌发的胚芽中 [10]。本研究中观察到蜀黍氰苷主要在番红花球茎萌发的顶芽中分布,与文献报道一致,其分布的特异性可能是由于对抗食草动物从而保护新兴的组织。黄酮类化合物作为中药成分的重要药效部分,具有一定的抗炎、抗氧化、抗细胞凋亡等作用 [11]。异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷在西红花中已有检测,本次发现其在顶芽中丰度较高,推测与芽承担运输功能有关。
在球茎中,主要观察到氨基酸和部分次生代谢物的分布,如L-瓜氨酸、苯乙酰甘氨酸、紫苜蓿酚和栀子苷等均只特异性分布在球茎中(图3)。氨基酸作为一种重要的初生代谢物,不仅在植物生长发育过程中发挥着不可或缺的角色,还是生物碱合成的重要前体 [12]。因球茎是番红花的营养器官,故氨基酸主要积累于球茎部位,为其生长提供所需物质和能量。
某些化合物在顶芽和球茎中均可以观察到,如咖啡酸3-葡萄糖苷、咖啡酰基酪氨酸、迷迭香酸和牡荆素(图3)。有趣的是,酪氨酸除了分布于球茎部分,在顶芽中也有不少分布。研究表明,酪氨酸参与植物色素合成且是生物碱合成的重要前体 [12],其在球茎和顶芽中均有分布,说明球茎在萌发过程中已经开始色素和生物碱合成的准备。
2.3 代谢物在不同产地番红花球茎中的分布特征
总体来说,大多数化合物都呈现出一致的分布规律。对于在球茎部位分布的化合物来说,在上海的球茎中丰度最高,浙江次之,安徽最低,但是浙江球茎检测到的化合物种类最多。此外,我们还观察到了某些化合物在不同产地具有不同的分布规律。如栀子苷、蜀黍氰苷6'-葡萄糖苷和芹菜素7-(6''-O-乙酰基)-葡萄糖苷在上海球茎中未观察到分布,而异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷在安徽球茎中未观察到分布(图4)。番红花喜凉怕酷热、怕严寒、喜湿润,对生长环境要求较高 [13]。上海崇明地处中国最大河流长江入海口,气候温和湿润,年平均气温16.5 ℃,年平均降雨量1128.9 mm;浙江建德年平均气温17.8 ℃,年降水量1905.1 mm,气候同样温暖湿润;而安徽亳州年平均气温14.9 ℃,属温带半湿润气候区,年平均降雨量仅831 mm。与安徽亳州相比,上海崇明和浙江建德的气候特点显然更适于番红花生长。同时,从光学照片可以发现,浙江球茎的顶芽分化早于上海和安徽球茎,这可能是浙江球茎内代谢物较为丰富的原因之一。
3. 结论
本文通过优化切片厚度,利用DESI质谱成像技术对不同产地番红花球茎内源性代谢物的分布特征进行了可视化研究,实现了黄酮、类胡萝卜素、氨基酸和有机酸的原位表征。不同化合物在球茎不同部位显示出不同分布,其中蜀黍氰苷6'-葡萄糖苷、异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷、芹菜素衍生物主要分布于顶芽中,而作为能量和物质供应的氨基酸则主要积累在球茎。此外,不同产地的番红花球茎也存在较大差异。从成像丰度来看,上海的球茎物质丰度较高,其次是浙江,安徽丰度最低。就化合物的分布规律而言,大部分代谢物在不同产地球茎中分布是一致的,但也观察到了一些差异。如栀子苷、蜀黍氰苷6'-葡萄糖苷和芹菜素7-(6''-O-乙酰基)-葡萄糖苷在上海未观察到分布,而异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷仅在上海和浙江产地观察到分布。我们推测,这可能是由于不同地域的温度、湿度等环境因素所致。本研究首次可视化了不同产地番红花球茎中不同物质在不同部位的分布特征,为探究番红花全生命周期内的生长过程和开展番红花球茎种质筛选提供了新的技术支持。
-
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典(一部)2020年版[S]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020. [2] AHRAZEM O, RUBIO-MORAGA A, NEBAUER S G, et al. Saffron: its phytochemistry, developmental processes, and biotechnological prospects[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2015, 63(40):8751-8764. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03194 [3] MOHTASHAMI L, AMIRI M S, RAMEZANI M, et al. The genus Crocus L.: a review of ethnobotanical uses, phytoche-mistry and pharmacology[J]. Ind Crops Prod, 2021, 171:113923. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113923 [4] WISEMAN J M, IFA D R, SONG Q Y, et al. Tissue imaging at atmospheric pressure using desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) mass spectrometry[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2006, 45(43):7188-7192. doi: 10.1002/anie.200602449 [5] WANG X F, ZHANG L, XIANG Y H, et al. Systematic study of tissue section thickness for MALDI MS profiling and imaging[J]. Analyst, 2023, 148(4):888-897. doi: 10.1039/D2AN01739C [6] DONG Y H, LI B, MALITSKY S, et al. Sample preparation for mass spectrometry imaging of plant tissues: a review[J]. Front Plant Sci, 2016, 7:60. [7] SUGIURA Y, SHIMMA S, SETOU M. Thin sectioning improves the peak intensity and signal-to-noise ratio in direct tissue mass spectrometry[J]. J Mass Spectrom Soc Jpn, 2006, 54(2):45-48. doi: 10.5702/massspec.54.45 [8] 张永珊. 藏红花球茎生物学特性及繁育增殖初步研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2021. [9] YADAV M, SINGH I K, SINGH A. Dhurrin: a naturally occurring phytochemical as a weapon against insect herbivores[J]. Phytochemistry, 2023, 205:113483. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113483 [10] MONTINI L, CROCOLL C, GLEADOW R M, et al. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometry imaging of metabolites during Sorghum germination[J]. Plant Physiol, 2020, 183(3):925-942. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.01357 [11] WEN K M, FANG X C, YANG J L, et al. Recent research on flavonoids and their biomedical applications[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2021, 28(5):1042-1066. doi: 10.2174/0929867327666200713184138 [12] 王广苹, 韩翠婷, 葛珈铭, 等. 氮的吸收同化以及在药用植物组织培养中的应用[J]. 中药材, 2023(9):2353-2560. [13] 杨芙蓉, 冉家栋, 齐耀东, 等. 西红花全球生态适宜区预测及生态特征[J]. 中国现代中药, 2021, 23(9):1534-1541. -






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:


