-
定量核磁共振技术(qNMR)在现代化学、生物医药、食品科学等领域中扮演着至关重要的角色[1, 2]。其原理是基于核磁共振现象,当将含有1H、13C、19F、31P等特定磁性核的样品置于外加磁场中,并施加一定的频率射频脉冲时,特定磁性核会吸收能量并进入激发态。当这些原子核回到基态时,会释放出能量,产生NMR信号[3]。通过分析这些信号的强度,可以定量分析样品中目标分子[4, 5]。与传统的化学分析方法相比,qNMR技术具有准确度高、操作简便、无需标记和高通量检测等优点,已相继被《美国药典》、《欧洲药典》、《中国药典》收录,并广泛应用于多个领域[6]。如用于药物成分的定量分析,检测食品中的添加剂和污染物,监测环境中的有害物质,评估环境污染程度。此外,qNMR还在代谢组学、材料科学等领域中有着重要的应用[7, 8]。
核磁共振磷谱是一种核磁共振分析方法。其用于鉴定含磷化合物的结构,定量分析含磷化合物的含量,或监测含磷化合物动力学及其在生物体中的代谢过程[9]。由于31P原子核天然丰度为100 %,旋磁比较高,化学位移范围宽,使得31P-NMR成为研究含磷化合物极为有效的工具[10, 11]。通过分析31P-NMR谱图,可以获得关于磷化合物的分子结构、化学环境等重要信息[12]。
磷酸氢钙咀嚼片是一种以磷酸氢钙为主要原料,蔗糖、淀粉、硬脂酸镁为辅料制成的补钙类药品,具有参与骨骼形成、骨组织重建、降低毛细血管通透性等药理作用,广泛应用于儿童生长发育的促进和钙质补充。现行中国药典采用乙二胺四醋酸二钠滴定法测定磷酸氢钙片剂中的磷酸氢钙的含量[13, 14],但该法干扰因素多、灵敏度低、操作复杂。本研究建立了一种核磁共振磷谱定量(31P-qNMR)测定磷酸氢钙咀嚼片中磷酸氢钙含量的方法,相比于现有测定方法,操作简单,且专属性强,快速准确。
-
仪器:600 MHz NMR(Bruker,AVANCE II)、分析天平(Shimadzu,AUW220D)、5 mm 同轴核磁管(Wilmad,535-pp-7)。
样品与试剂:某公司磷酸氢钙咀嚼片、重水(Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, Ins)、六甲基磷酰三胺(Adamas,含量≥98.0%,)、磷酸氢钙对照品(中国食品药品检定研究院,批号100410-201802)、稀盐酸(Adamas,分析纯)。
-
取20片磷酸氢钙咀嚼片,精密称定后研细,精密称取细粉适量(约相当于含磷酸氢钙0.60 g)于100 ml量瓶中,加入10 ml 0.1 mol/L盐酸溶液,超声5 min后加入重水10 ml,用水稀释至刻度,摇匀后过滤。制得含磷酸氢钙浓度约为6 mg/ml的供试品溶液,精密量取260 μl于同轴核磁管外管。
-
精密量取40 mg六甲基磷酰三胺于5 ml量瓶中,加入0.5 ml重水后,用水稀释至刻度,摇匀,精密量取220 μl于同轴核磁管内管。
-
精密称定磷酸氢钙对照品5.009 6 g于100 ml量瓶中,加10 ml 0.1 mol/L 稀盐酸溶解后定容,摇匀后得浓度为50.096 mg/ml的磷酸氢钙对照品储备液,稀释至适当浓度后精密量取260 μl于同轴核磁管外管。
-
精密量取260 μl待测样品、220 μl内标物溶液分别置于同轴核磁管外管和内管,进行数据采集。采用zgpg30脉冲序列在25 ℃下获取31P-NMR谱。具体实验参数设置如下:谱宽频率(SWH)= 39 682.5 Hz,采样点数(TD)= 65 K,采样时间(AQ)= 0.825 s,采样次数(NS)= 128,空扫次数(DS)= 4,增益(RG)= 1 150,其他实验参数均采用仪器推荐参数。采用Topspin3.1 软件进行数据处理。
-
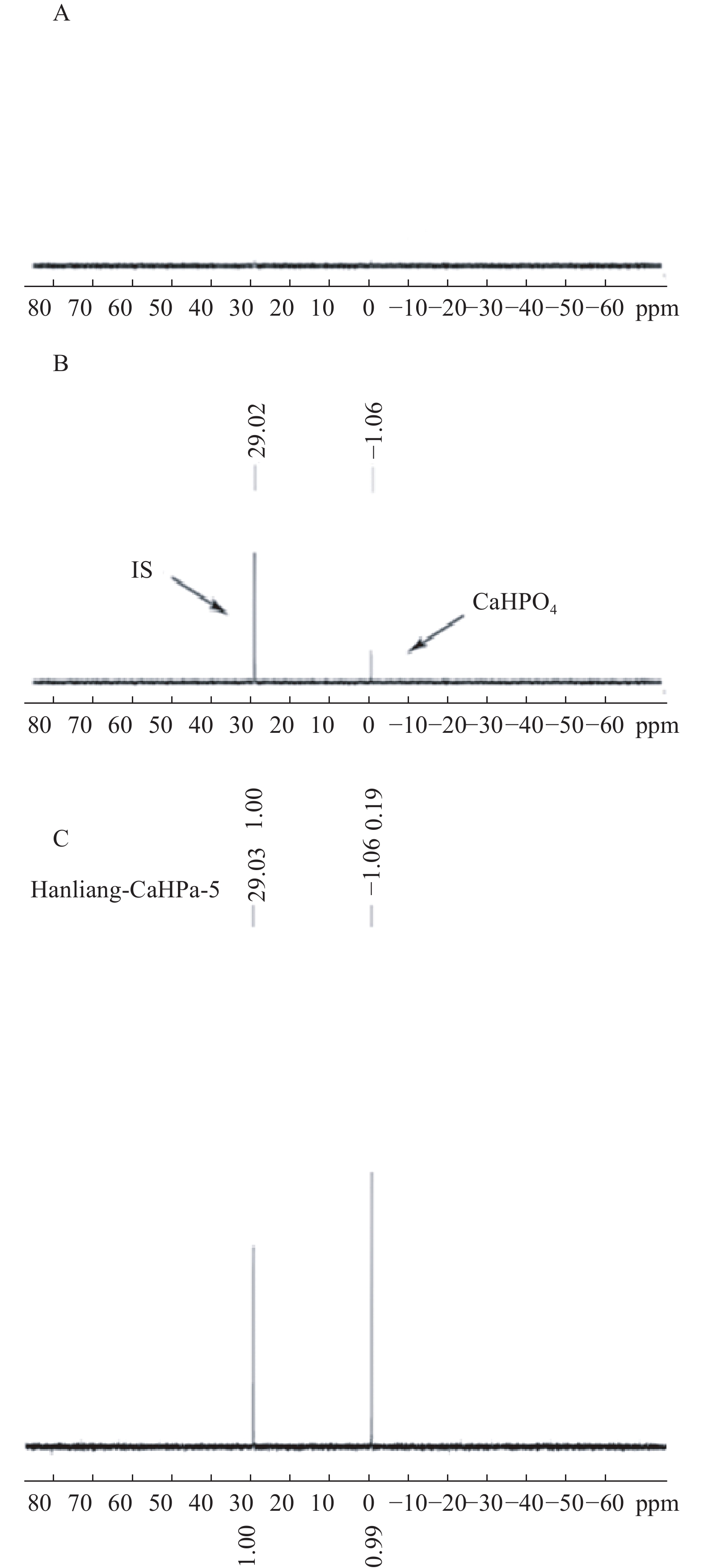
按“2.1”项对空白辅料、对照品、和实测样品进行处理后进样,图1表明辅料及溶剂成分对被测组分的测定没有干扰,且磷酸氢钙的化学位移为δ 1.06,内标的化学位移为δ 29.02,内标对药物的测定也没有干扰。
-
量取9.0、7.0、5.0、3.0、1.0 ml磷酸氢钙对照品储备液置于50 ml量瓶中,稀释至刻度,制成含磷酸氢钙对照品浓度为9.018、7.014、5.010、3.006、1.002 mg/ml 的标准曲线溶液。分别量取260 μl标准曲线溶液于同轴核磁管外管,按照“2.2”项下方法测定31P NMR谱。以磷酸氢钙对照品响应信号和内标响应信号比为纵坐标,标准曲线系列溶液浓度为横坐标(mg/ml)进行线性回归,计算得回归方程为:A=0.004 3+0.183 6C,表明磷酸氢钙在1.0~9.0 mg/ml 范围内线性范围较好,r=0.999 9。
-
按“2.1”项下重复精密称取6份片剂细粉,经相同处理后,按“2.2”项下进行检测,记录响应信号面积,根据工作曲线法计算其含量,得磷酸氢钙咀嚼片中磷酸氢钙含量为98.7 %,RSD为0.098 %,表明该方法重复性满足要求。
-
精密称定磷酸氢钙对照品1.002 g于100 ml量瓶中,加入10 ml 0.1 mol/L 盐酸溶解后加水至刻度线,摇匀后得浓度为10.02 mg/ml的磷酸氢钙对照品储备液。
移液管精密移取供试品储备液2.00 ml于5 ml容量瓶中,分别精确加入10.02 mg/ml对照品溶液0.75、1.00、1.25 ml,加水稀释至刻度线后得到低、中、高3种浓度的回收率测定溶液,每种浓度平行配制3份,测定并计算加样回收率,得平均回收率为98.02 %、98.16 %、98.47 %,RSD分别为 0.31 %、0.68 %、0.62 %(n=9),证明该方法准确度较好。
-
取同一样品溶液分别在0、4、8、12 h下进行测定,记录供试品信号峰面积,计算样品中磷酸氢钙含量。4次测量的信号峰面积的RSD值仅为0.26 %,表明供试品溶液在室温下放置12 h稳定性较好。
-
分别精密量取5份供试品溶液260 μl于同轴核磁管外管,按照“2.2”项下方法测定31P NMR谱图并计算样品中待测组分磷酸氢钙的含量,结果表明样品中磷酸氢钙平均含量为98.19 %,RSD = 0.10 %。
-
内标物的选择是定量核磁共振方法建立的关键,31P-qNMR定量检测中内标物质应选择结构稳定、不与待测样品发生反应、内标物信号峰与待测样品信号峰分离度高等特点。常见的磷核磁共振定量内标物有六甲基磷酰三胺(HMDA)、磷酸、甲基膦酸、亚甲基二磷酸等。其中,六甲基磷酰三胺易溶于氘代溶剂,且化学性质稳定,化学位移值约为δ 29.01,与待测物磷酸氢钙分离度好,无重叠,故本实验选取六甲基磷酰三胺作为内标物。经过方法学考察后,表明磷酸氢钙在1.0~9.0 mg/ml范围内线性相关,低、中、高3种浓度的加样回收率结果为98.0 %、98.1 %和98.4 %。本研究建立了一种精密度高、专属性强的含磷药物的含量检测方法,且无需自身对照物、前处理简便、检测速度快,为含磷药品质量控制提供了新的策略。
Determination of phosphorus content in calcium hydrogen phosphate tablets by 31P-qNMR
-
摘要:
目的 建立一种高精密度和高专属性的核磁共振磷谱定量方法(31P-qNMR),用于检测磷酸氢钙咀嚼片中含磷药物的含量。 方法 使用六甲基磷酸酰胺作为内标,采集磷酸氢钙咀嚼片剂溶液的磷谱数据。研究磷酸氢钙在浓度范围1.0~9.0 mg/ml内的线性关系,并进行加样回收率和重复性实验。 结果 磷酸氢钙与内标的峰面积比在1.0 ~9.0 mg/ml范围内显示出良好的线性关系,回归方程为A = 0.0043 +0.1836 C。低、中、高3种浓度的加样回收率分别为98.0 %、98.1 %、98.4 %,相对标准偏差(RSD)分别为0.31 %、0.68 %、0.62 %(n = 9)。测定得到的磷酸氢钙咀嚼片中磷酸氢钙的平均含量为98.1 %。结论 成功建立了一种精密度高且专属性强的磷酸氢钙咀嚼片含量检测方法。该方法无需自身对照物,前处理过程简便,检测速度快,为含磷药品质量控制提供了新的技术支撑。 Abstract:Objective To establish a high-precision and high-specificity quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance phosphorus spectrometry method(31P-qNMR)for detecting the phosphorus content in calcium hydrogen phosphate chewable tablets. Methods Hexamethyl phosphoramide was used as an internal standard, phosphorus spectrum data of calcium hydrogen phosphate chewable tablets solution was collected. The linear relationship of calcium hydrogen phosphate within the concentration range of 1.0 to 9.0 mg/ml was studied, and sample recovery rate and repeatability experiments were conducted. Results Calcium hydrogen phosphate and the internal standard demonstrated a good linear relationship within the concentration range of 1.0 to 9.0 mg/ml, with a regression equation A = 0.0043 +0.1836 C. The recovery rates for low, medium, and high concentrations were 98.0%, 98.1%, and 98.4%, respectively, with relative standard deviations(RSD)of 0.31%, 0.68%, and 0.62%, respectively(n= 9). The average content of calcium hydrogen phosphate in the chewable tablets was determined to be 98.1%.Conclusion This study successfully established a high-precision and highly specific method for quantifying the content of calcium hydrogen phosphate in chewable tablets, which did not require a self-reference substance, was simple in sample preparation, and had a fast detection speed. The method could provide a new technical support for the quality control of phosphorus-containing drugs. -
Key words:
- 31P-NMR /
- q-NMR /
- content determination /
- calcium hydrogen phosphate
-
[1] CHEN Z, LIAN X F, ZHOU M C, et al. Quantitation of L-cystine in food supplements and additives using 1H qNMR: method development and application[J]. Foods, 2023, 12(12):2421. doi: 10.3390/foods12122421 [2] KIM H C, BAEK K H, LEE Y E, et al. Using 2D qNMR analysis to distinguish between frozen and frozen/thawed chicken meat and evaluate freshness[J]. NPJ Sci Food, 2022, 6(1):44. doi: 10.1038/s41538-022-00159-x [3] MA H, PEDERSEN C M, ZHAO Q, et al. NMR analysis of the Fischer-Tropsch wastewater: Combination of 1D selective gradient TOCSY, 2D DOSY and qNMR[J]. Anal Chim Acta, 2019, 1066:21-27. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.04.007 [4] IWASAKI D, KANAZAWA M, KAWAMOTO F, et al. A new single-reference quantitative method using liquid chromatography with relative molar sensitivity based on 1H-qNMR for khellactone esters from Peucedanum japonicum root extract[J]. Food Chem, 2023, 427:136647. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136647 [5] SCETTRI A, SCHIEVANO E. Quantification of polyols in sugar-free foodstuffs by qNMR[J]. Food Chem, 2022, 390:133125. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133125 [6] WELLS R J, HOOK J M, AL-DEEN T S, et al. Quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance (QNMR) spectroscopy for assessing the purity of technical grade agrochemicals: 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D)and sodium 2, 2-dichloropropionate (Dalapon sodium)[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2002, 50(12):3366-3374. doi: 10.1021/jf0114379 [7] GIANCASPRO G, ADAMS K M, BHAVARAJU S, et al. The qNMR Summit 5.0: Proceedings and Status of qNMRTechnology[J]. Anal Chem, 2021, 93(36):12162-12169. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c02056 [8] MUSIO B, RAGONE R, TODISCO S, et al. A community-built calibration system: The case study of quantification of metabolites in grape juice by qNMR spectroscopy[J]. Talanta, 2020, 214:120855. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120855 [9] 黄挺, 吴华鑫. 氟磷谱定量核磁共振法进展综述[J]. 计量科学与技术, 2023, 67(5):9-15. doi: 10.12338/j.issn.2096-9015.2023.0095 [10] KOMOROSKI R A, HOLDER J C, PAPPAS A A, et al. 31P NMR of phospholipid metabolites in prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2011, 65(4):911-913. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22677 [11] DEELCHAND D K, NGUYEN T M, ZHU X H, et al. Quantification of in vivo 31P NMR brain spectra using LCModel[J]. NMR Biomed, 2015, 28(6):633-641. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3291 [12] 黎玲玲, 邹亚娟, 吴节莉, 等. 31P核磁共振内标法测定甘油磷酸胆碱的含量[J]. 药物分析杂志, 2017, 37(11):1933-1936. [13] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典: 二部: 2020年版[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 1914. [14] 郭国宁. 磷酸氢钙中钙含量的测定方法[J]. 无机盐工业, 2001, 33(3):41-42,2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2001.03.016 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李新露,黄劼,董凌莉,钟继新. 二肽基肽酶4抑制剂在风湿免疫病中的潜在作用. 医药导报. 2023(02): 166-172 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载:


