-
脑卒中是危害人类健康的主要疾病之一。根据国家卫健委最新颁布的《中国脑卒中防治指导规范(2021年版)》显示:脑卒中已成为我国居民第一大死因。缺血性脑卒中是最常见的脑卒中类型,占我国脑卒中的69.6%~70.8%。我国住院急性缺血性脑卒中患者发病后1个月内病死率为2.3%~3.2%,发病后1年内病死率为14.4%~15.4%,死亡/残疾率为33.4%~33.8%[1],缺血性脑卒中的致死率和致残率相当高。对于缺血性脑卒中的治疗,我们熟知的静脉溶栓、抗血小板、抗凝、降纤、扩容等方法,都是旨在改善脑血液循环,并非针对脑神经细胞的保护[2]。目前针对神经保护的药物较少,且疗效与安全性尚未被临床广泛接受。美国心脏病协会/美国卒中协会发布的《2019年急性缺血性卒中患者早期管理指南》中表示:目前没有任何假定具有神经保护作用的药物或非药物治疗能够证明改善缺血性脑卒中的预后[3]。国内最新脑卒中诊治指南也认为神经保护剂的疗效与安全性尚需要更多高质量临床试验来进一步证实[1]。目前的神经保护药物尚不能解决脑卒中患者遗留神经功能障碍的问题。
菸花苷是课题组从传统活血化瘀中药红花中研发的治疗急性脑缺血性脑卒中的中药1类新药,化学结构式如图1。课题组前期的研究表明,菸花苷对于动物缺血性脑卒中急性期具有预防和治疗作用[4],但是,菸花苷对脑缺血的长期治疗效果尚未见报道,其抗脑缺血作用机制的研究也有待进一步深入。本实验通过观察菸花苷对于大鼠长期生存率、神经系统功能、体重及脑神经元的影响,进一步探讨菸花苷对缺血性脑卒中的长期治疗效果及可能的作用机制。
-
SPF级健康雄性Wistar大鼠,购自上海斯莱克实验动物有限公司,体重(250±20)g,手术开始前于清洁级动物房适应性饲养1周,自由进食、饮水,温度(25±2) ℃,相对湿度40%~60%,人工照明模拟昼夜变化。实验过程中,严格遵循动物伦理原则,遵守动物福利、动物保护的相关规定。
-
菸花苷注射液(菸花苷含量为10 mg/ml)及菸花苷注射液空白制剂,均由苏中药业集团股份有限公司提供。
-
通用型组织固定液(上海博光生物科技有限公司);氯化钠注射液(辰欣药液股份有限公司);尼氏染色液、苏木素伊红(HE)染色试剂盒(上海博谷生物科技有限公司);水合氯醛、氯化钠、无水乙醇、二甲苯(AR级)(国药集团化学试剂有限公司)。
-
手术器械(上海医疗器械有限公司);线栓(平顶山豫顺生物科技有限公司);蠕动泵(上海之信仪器有限公司);Direct-Pure RO(上海迪发仪器仪表有限公司);荧光显微镜(日本Olympus公司);EG1160一体式石蜡包埋机、ASP200S全自动脱水机、RM2235切片机、HI1210水浴摊片机、HI1220烘片机(德国Leica公司)。
-
取健康雄性Wistar大鼠,体重(250±20)g,分为假手术组、模型组、菸花苷组。其中假手术组大鼠10只,模型组和菸花苷组各20只。菸花苷组在手术当天缺血后1 h,以10 mg/kg的剂量尾静脉注射给药,手术后第2~7天,每天给药1次,此后每隔日给药1次。模型组以相同的给药方法给予相同体积的菸花苷注射液空白制剂。
-
选用MCAO法进行缺血性脑卒中模型的造模,参考相关文献中的MCAO的方法[5-7],并结合本实验室改进措施,最终选用如下方式进行操作:术前将大鼠禁食8 h,按大鼠体重以350 mg/kg的剂量,用10%的戊巴比妥钠腹腔注射麻醉,仰卧位固定于手术台上。沿颈部正中线切开皮肤,钝性分离腺体、筋膜及其他皮下组织,分离并暴露左侧颈总动脉(CCA),继而分离颈外动脉(ECA)和颈内动脉(ICA)。用细线结扎CCA近心端及ECA基部。动脉夹暂时夹闭ICA,用显微剪沿CCA近心端斜向上45°剪一小口,将直径约0.26 mm的线栓小心插入CCA血管腔中,用提前布于CCA下方的细线微微固定(结扎过紧会造成进线困难,太松则易造成出血),在血管放松的前提下,向前轻推最终沿着ICA插入颅内,插入深度距ECA与ICA分叉处大约18 mm。缺血2 h后将线栓轻轻拉出,造成再灌注损伤,此时注意拔栓速度不宜过快以免造成血管痉挛,随后扎紧CCA远心端,缝合伤口。术后置大鼠于俯卧位,且稍稍抬高大鼠颈部。整个手术过程中室温维持在25 ℃左右,并用保暖灯及电热毯保持大鼠体温恒定在37 ℃左右。假手术组大鼠分离暴露血管,并不插入线栓,也不结扎任何血管。术后待大鼠清醒后,放置单笼饲养观察。
-
从手术后第1天开始,由不参与整个实验的研究者观察手术后各组大鼠在第1、2、3、5、7、10、15、20、25、30天的行为学表现,评分并记录。每只大鼠的行为学检查在3~5 min内完成。行为学评分参照文献中的经典评分方法[8-10],具体如下:
(1)轻轻将大鼠的尾部提起,至地面的垂直距离约0.5 m高,观察前肢情况,是否有内收或者内旋现象。正常实验鼠的两前肢平衡对称,向下向前伸出。根据严重程度评分,最严重者为4分,正常为0分。
(2)将大鼠放于平稳的地板上,推左肩向对侧移动,再推右肩向对侧移动,观察大鼠抗推动的能力。正常大鼠左右两侧的抗推动能力相当,若大鼠左侧抗推动能力下降,最严重为3分,正常为0分。
(3)将大鼠的左右前肢轻轻放于较大的金属网上,观察左右前肢抓金属网的肌肉张力。正常大鼠的左右前肢抓金属网的力量明显且对称。若大鼠左前肢张力下降,最严重为3分,正常为0分。
每只受试的大鼠,根据以上标准打分并累加,满分为10分。
-
手术前记录各组大鼠体重作为起始体重。手术后,在每天的相同时段(相差不超过1h),将各组大鼠放于体重计上,待示数稳定5 s后,立刻记下体重数。由不参与整个实验的研究者记录手术后菸花苷组与模型组在第1、2、3、5、7、10、15、20、25、30天的体重。每只大鼠的体重记录在1~3 min内完成。
-
手术30 d后,按大鼠体重以350 mg/kg的剂量,用10%的戊巴比妥钠腹腔注射麻醉。迅速打开胸腔,暴露心脏,用针头从心尖部位插入左心室,剪开右心耳,针头另一端连接生理盐水,打开灌流泵,使生理盐水通过血液循环将血液排出。待灌入150 ml左右生理盐水,且流出的液体几乎为无色时,立刻将灌注液改为通用型组织固定液(4%多聚甲醛),此时注意速度为先快后慢。灌流时若大鼠全身不停抽动则代表4%多聚甲醛已进入全身循环,待灌入150 ml左右固定液即可停止。将脑完整取出,在4%多聚甲醛中固定48 h。
-
用ASP200S全自动脱水机进行脱水处理,再用EG1160一体式石蜡包埋机进行包埋。临用前,切取3~5 mm厚的石蜡切片附于载玻片上,用新鲜的二甲苯脱蜡2次,每次10 min。随后依次放入无水乙醇5 min;放入90%乙醇、70%乙醇、蒸馏水各2 min。
-
将上述脱蜡后的石蜡切片参照试剂盒说明书进行如下操作:在37 ℃的烘箱中,用尼氏染色液染色7 min。随后,用蒸馏水洗涤 2 次,每次5 s,再用95%乙醇洗涤5 s,至此完成尼氏染色。
-
将脱蜡后的石蜡切片参照试剂盒说明书进行如下操作:用苏木素染色液染色6 min。浸于足够的蒸馏水中冲去多余的染色液,这个过程大约持续10 min,再放于新鲜的蒸馏水内数秒钟润洗一遍。然后,用1%盐酸酒精溶液分化数秒(一般不超过5 s)。蒸馏水洗涤5 min后,Scott液返蓝处理50 s,蒸馏水再次洗涤3 min,进入伊红染色液中染色8 min,至此完成HE染色。
-
将上述过程中的尼氏染色、HE染色的切片分别用70%乙醇洗涤后,用95%乙醇脱水3次,每次3 min。入二甲苯透明5 min,共计2次。中性树胶封片。
-
利用软件SPSS 18.0进行统计学分析,所得计量数据以(
$ \bar{x} $ ±s)表示,两组间数据比较采用Student t检验;生存资料以生存曲线表示,采用Log-rank (Mantel-Cox)检验。P<0.05具有统计学意义。 -
观察30 d内脑缺血损伤后大鼠的生存情况,发现手术后,模型组和菸花苷组大鼠均出现不同程度的死亡情况。菸花苷组大鼠于第8天开始,存活的数目趋于稳定,模型组于第16天开始,无新增的死亡大鼠。截止到第30天观察结束时,假手术组生存率为100%,模型组生存率为30.4%,菸花苷组生存率为70%,较之模型组,菸花苷组的生存率显著升高(P<0.05),结果见图2。
-
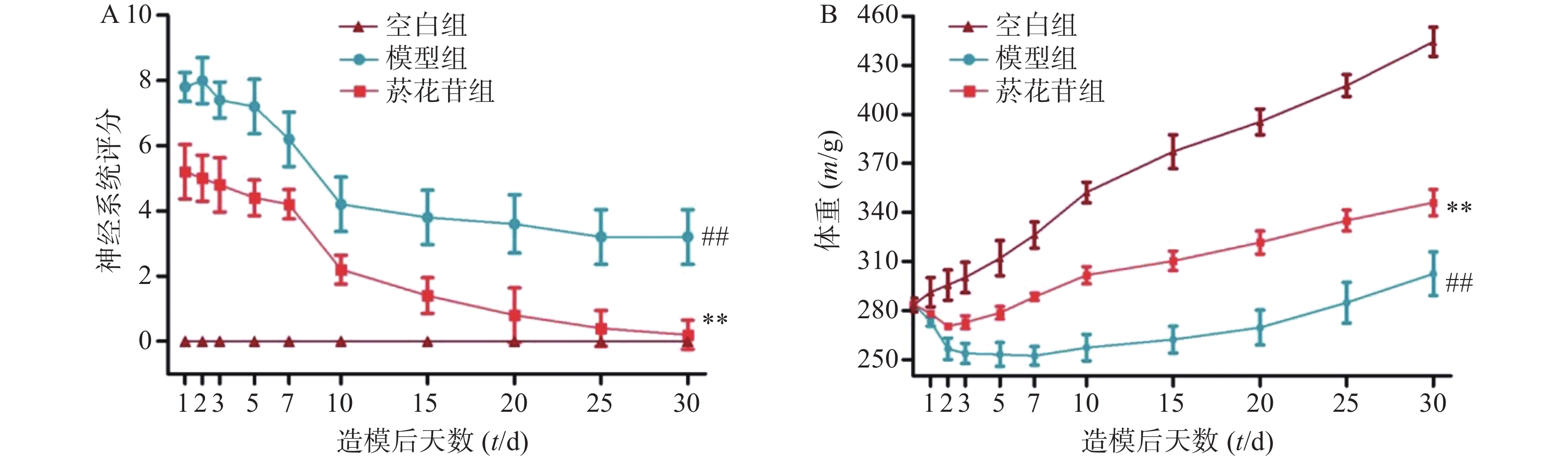
由图3A可知,在手术后的各个观察时间点,假手术组的行为学评分均为0,一直未出现神经功能损伤的体征。与模型组相比,菸花苷组在测评的各个时间点神经功能损伤较轻,具有显著的统计学意义(P<0.01),且整个观察过程中,菸花苷组大鼠的行为学得分不断降低,神经功能趋向好转。
由图3B可知,在体重变化方面,手术后,假手术组大鼠体重一直保持持续增长状态。术后第1天,模型组与菸花苷组大鼠的体重有不同程度的下降,菸花苷组大鼠在术后第3天开始恢复体重增长状态,模型组从术后第10天开始恢复体重增长状态。在初始体重差别不大的情况下,较之模型组,菸花苷组在术后各个时间点观察得到的体重数值均明显高于模型组大鼠的体重数值(P<0.01)。
-
由图4A可知,假手术组皮层和海马区的细胞大小均一,结构清晰,胞浆丰富,核质比例适中,CA1区的锥体细胞和DG区的颗粒细胞排列整齐紧密,CA3区锥体细胞体积较之CA1区的略大,排列稍松散但整齐。模型组的神经元大小不一,胞质不规则淡染,胞核皱缩变形,部分细胞脱失明显,CA1区锥体细胞和DG区的颗粒细胞排列松散,CA3区锥体细胞排列散乱,表明造模后神经细胞受损严重。与模型组相比,菸花苷组的神经元虽也出现了细胞淡染,大小不均,部分胞体肿胀,CA1区及DG区排列稍显混乱,但整体的形态接近正常,病理损伤明显减轻。
由图4B可知,假手术组皮层和海马区的尼氏体大且多,“虎斑”也不在少数,呈深蓝色,表明神经元功能良好。模型组整体淡染,皮层的尼氏体大大减少,海马区尼氏体极少,表明造模后神经元功能受到损伤。与模型组相比,菸花苷组皮层尼氏体数目更多,个体更大,染色较均匀,海马区尼氏体虽多为颗粒状,个体稍小,但数目明显增多,说明神经元蛋白合成有所增加,较为活跃。
-
正如“卒中治疗学术产业圆桌会议”中对神经保护药物的研究所提出的那样[11]:较为理想的神经保护类药物的实验室阶段研究,应该在至少两个不同实验室中展开,运用在至少两种动物身上,兼顾在永久缺血模型和短暂局灶性缺血模型,既要考察短期内的组织和功能上的结果,也需要考察长期作用的影响。在本研究中,我们在前期证明菸花苷对急性永久性缺血模型和短暂局灶性缺血模型均具有良好的保护作用的基础上[12-13],通过建立大鼠脑缺血再灌注模型,从功能和组织层面证明了菸花苷对缺血性脑卒中的长期保护作用。
长期生存率是药效结果最直观的体现,体重可以反映出大鼠在发生缺血性脑卒中后整体的预后情况,而行为学的变化可以间接反应出大鼠神经系统的功能。我们通过连续30 d观察实验大鼠的生存率、行为学以及体重变化,发现造模后给予菸花苷显著地提高了大鼠生存率,并能逐渐降低行为学得分,改善神经功能,体重也在术后第3天开始恢复增长状态。这些结果表明菸花苷可以改善缺血性脑卒中的预后,促进神经系统的远期功能恢复。
海马区是大脑中负责记忆与学习的重要区域,与认知功能密切相关,也是研究卒中后认知障碍等脑卒中并发症的重点关注区域,其中CA1区的神经元对脑缺血缺氧较为敏感,容易受到损伤,而CA3区及DG区的神经元则相对耐受[14]。尼氏体是神经元胞体和树突内的嗜碱性颗粒或小斑块,由游离的核糖体和粗面内质网构成,对缺血变化非常敏锐[15]。病理组织学研究表明,菸花苷给药后大鼠海马区的尼氏体数目有所增加,蛋白合成更为活跃,脑组织恢复更好,整体趋向正常。提示菸花苷对神经细胞结构和功能具有长期保护作用。
综上所述,菸花苷对缺血性脑卒中大鼠具有长期保护作用,可维持神经细胞结构功能处于相对良好的状态,并能促进神经系统远期功能的恢复,可以作为一种潜在的神经保护剂,其作用机制有待进一步研究。
Long-term protective effects of the nicotiflorin on ischemic stroke rats
-
摘要:
目的 探讨菸花苷对缺血性脑卒中大鼠的长期保护作用。 方法 建立大鼠脑缺血模型,观察菸花苷对于大鼠长期生存率、神经系统功能、体重及脑神经元的影响。 结果 菸花苷可以显著提高脑缺血大鼠的长期生存率,促进大鼠体重增加,减轻脑组织病理损伤,维持脑神经元形态及神经系统功能。 结论 菸花苷具有明显的对缺血性脑卒中大鼠的长期保护作用,其作用机制可能与保护脑神经元结构和功能有关。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the long-term protective effects of the nicotiflorin on ischemic stroke rats. Methods Ischemic stroke model in rats was established for this study. The effects of nicotiflorin on long-term survival rate, nervous system function, body weight and brain neurons in rats were observed. Results The nicotiflorin had significantly improved the long-term survival rate of cerebral ischemia rats, which also promoted weight gain, alleviated pathological damage of brain tissue, maintained morphology of brain neurons and function of nervous system. Conclusion The nicotiflorin has obvious long-term protective effect on ischemic stroke rats and the mechanism may be related to the protection of the structure and function of brain neurons. -
Key words:
- nicotiflorin /
- ischemic stroke /
- neuroprotection /
- pathology
-
脑卒中是危害人类健康的主要疾病之一。根据国家卫健委最新颁布的《中国脑卒中防治指导规范(2021年版)》显示:脑卒中已成为我国居民第一大死因。缺血性脑卒中是最常见的脑卒中类型,占我国脑卒中的69.6%~70.8%。我国住院急性缺血性脑卒中患者发病后1个月内病死率为2.3%~3.2%,发病后1年内病死率为14.4%~15.4%,死亡/残疾率为33.4%~33.8%[1],缺血性脑卒中的致死率和致残率相当高。对于缺血性脑卒中的治疗,我们熟知的静脉溶栓、抗血小板、抗凝、降纤、扩容等方法,都是旨在改善脑血液循环,并非针对脑神经细胞的保护[2]。目前针对神经保护的药物较少,且疗效与安全性尚未被临床广泛接受。美国心脏病协会/美国卒中协会发布的《2019年急性缺血性卒中患者早期管理指南》中表示:目前没有任何假定具有神经保护作用的药物或非药物治疗能够证明改善缺血性脑卒中的预后[3]。国内最新脑卒中诊治指南也认为神经保护剂的疗效与安全性尚需要更多高质量临床试验来进一步证实[1]。目前的神经保护药物尚不能解决脑卒中患者遗留神经功能障碍的问题。
菸花苷是课题组从传统活血化瘀中药红花中研发的治疗急性脑缺血性脑卒中的中药1类新药,化学结构式如图1。课题组前期的研究表明,菸花苷对于动物缺血性脑卒中急性期具有预防和治疗作用[4],但是,菸花苷对脑缺血的长期治疗效果尚未见报道,其抗脑缺血作用机制的研究也有待进一步深入。本实验通过观察菸花苷对于大鼠长期生存率、神经系统功能、体重及脑神经元的影响,进一步探讨菸花苷对缺血性脑卒中的长期治疗效果及可能的作用机制。
1. 实验材料
1.1 动物
SPF级健康雄性Wistar大鼠,购自上海斯莱克实验动物有限公司,体重(250±20)g,手术开始前于清洁级动物房适应性饲养1周,自由进食、饮水,温度(25±2) ℃,相对湿度40%~60%,人工照明模拟昼夜变化。实验过程中,严格遵循动物伦理原则,遵守动物福利、动物保护的相关规定。
1.2 药物
菸花苷注射液(菸花苷含量为10 mg/ml)及菸花苷注射液空白制剂,均由苏中药业集团股份有限公司提供。
1.3 试剂
通用型组织固定液(上海博光生物科技有限公司);氯化钠注射液(辰欣药液股份有限公司);尼氏染色液、苏木素伊红(HE)染色试剂盒(上海博谷生物科技有限公司);水合氯醛、氯化钠、无水乙醇、二甲苯(AR级)(国药集团化学试剂有限公司)。
1.4 器械与设备
手术器械(上海医疗器械有限公司);线栓(平顶山豫顺生物科技有限公司);蠕动泵(上海之信仪器有限公司);Direct-Pure RO(上海迪发仪器仪表有限公司);荧光显微镜(日本Olympus公司);EG1160一体式石蜡包埋机、ASP200S全自动脱水机、RM2235切片机、HI1210水浴摊片机、HI1220烘片机(德国Leica公司)。
2. 实验方法
2.1 脑缺血损伤模型
2.1.1 分组及给药
取健康雄性Wistar大鼠,体重(250±20)g,分为假手术组、模型组、菸花苷组。其中假手术组大鼠10只,模型组和菸花苷组各20只。菸花苷组在手术当天缺血后1 h,以10 mg/kg的剂量尾静脉注射给药,手术后第2~7天,每天给药1次,此后每隔日给药1次。模型组以相同的给药方法给予相同体积的菸花苷注射液空白制剂。
2.1.2 缺血性脑卒中模型的造模
选用MCAO法进行缺血性脑卒中模型的造模,参考相关文献中的MCAO的方法[5-7],并结合本实验室改进措施,最终选用如下方式进行操作:术前将大鼠禁食8 h,按大鼠体重以350 mg/kg的剂量,用10%的戊巴比妥钠腹腔注射麻醉,仰卧位固定于手术台上。沿颈部正中线切开皮肤,钝性分离腺体、筋膜及其他皮下组织,分离并暴露左侧颈总动脉(CCA),继而分离颈外动脉(ECA)和颈内动脉(ICA)。用细线结扎CCA近心端及ECA基部。动脉夹暂时夹闭ICA,用显微剪沿CCA近心端斜向上45°剪一小口,将直径约0.26 mm的线栓小心插入CCA血管腔中,用提前布于CCA下方的细线微微固定(结扎过紧会造成进线困难,太松则易造成出血),在血管放松的前提下,向前轻推最终沿着ICA插入颅内,插入深度距ECA与ICA分叉处大约18 mm。缺血2 h后将线栓轻轻拉出,造成再灌注损伤,此时注意拔栓速度不宜过快以免造成血管痉挛,随后扎紧CCA远心端,缝合伤口。术后置大鼠于俯卧位,且稍稍抬高大鼠颈部。整个手术过程中室温维持在25 ℃左右,并用保暖灯及电热毯保持大鼠体温恒定在37 ℃左右。假手术组大鼠分离暴露血管,并不插入线栓,也不结扎任何血管。术后待大鼠清醒后,放置单笼饲养观察。
2.2 行为学观察
从手术后第1天开始,由不参与整个实验的研究者观察手术后各组大鼠在第1、2、3、5、7、10、15、20、25、30天的行为学表现,评分并记录。每只大鼠的行为学检查在3~5 min内完成。行为学评分参照文献中的经典评分方法[8-10],具体如下:
(1)轻轻将大鼠的尾部提起,至地面的垂直距离约0.5 m高,观察前肢情况,是否有内收或者内旋现象。正常实验鼠的两前肢平衡对称,向下向前伸出。根据严重程度评分,最严重者为4分,正常为0分。
(2)将大鼠放于平稳的地板上,推左肩向对侧移动,再推右肩向对侧移动,观察大鼠抗推动的能力。正常大鼠左右两侧的抗推动能力相当,若大鼠左侧抗推动能力下降,最严重为3分,正常为0分。
(3)将大鼠的左右前肢轻轻放于较大的金属网上,观察左右前肢抓金属网的肌肉张力。正常大鼠的左右前肢抓金属网的力量明显且对称。若大鼠左前肢张力下降,最严重为3分,正常为0分。
每只受试的大鼠,根据以上标准打分并累加,满分为10分。
2.3 体重观察
手术前记录各组大鼠体重作为起始体重。手术后,在每天的相同时段(相差不超过1h),将各组大鼠放于体重计上,待示数稳定5 s后,立刻记下体重数。由不参与整个实验的研究者记录手术后菸花苷组与模型组在第1、2、3、5、7、10、15、20、25、30天的体重。每只大鼠的体重记录在1~3 min内完成。
2.4 灌流取材固定
手术30 d后,按大鼠体重以350 mg/kg的剂量,用10%的戊巴比妥钠腹腔注射麻醉。迅速打开胸腔,暴露心脏,用针头从心尖部位插入左心室,剪开右心耳,针头另一端连接生理盐水,打开灌流泵,使生理盐水通过血液循环将血液排出。待灌入150 ml左右生理盐水,且流出的液体几乎为无色时,立刻将灌注液改为通用型组织固定液(4%多聚甲醛),此时注意速度为先快后慢。灌流时若大鼠全身不停抽动则代表4%多聚甲醛已进入全身循环,待灌入150 ml左右固定液即可停止。将脑完整取出,在4%多聚甲醛中固定48 h。
2.5 脑组织病理切片观察
2.5.1 石蜡切片
用ASP200S全自动脱水机进行脱水处理,再用EG1160一体式石蜡包埋机进行包埋。临用前,切取3~5 mm厚的石蜡切片附于载玻片上,用新鲜的二甲苯脱蜡2次,每次10 min。随后依次放入无水乙醇5 min;放入90%乙醇、70%乙醇、蒸馏水各2 min。
2.5.2 尼氏染色
将上述脱蜡后的石蜡切片参照试剂盒说明书进行如下操作:在37 ℃的烘箱中,用尼氏染色液染色7 min。随后,用蒸馏水洗涤 2 次,每次5 s,再用95%乙醇洗涤5 s,至此完成尼氏染色。
2.5.3 HE染色
将脱蜡后的石蜡切片参照试剂盒说明书进行如下操作:用苏木素染色液染色6 min。浸于足够的蒸馏水中冲去多余的染色液,这个过程大约持续10 min,再放于新鲜的蒸馏水内数秒钟润洗一遍。然后,用1%盐酸酒精溶液分化数秒(一般不超过5 s)。蒸馏水洗涤5 min后,Scott液返蓝处理50 s,蒸馏水再次洗涤3 min,进入伊红染色液中染色8 min,至此完成HE染色。
2.5.4 脱水、透明、封片
将上述过程中的尼氏染色、HE染色的切片分别用70%乙醇洗涤后,用95%乙醇脱水3次,每次3 min。入二甲苯透明5 min,共计2次。中性树胶封片。
2.6 统计分析
利用软件SPSS 18.0进行统计学分析,所得计量数据以(
$ \bar{x} $ ±s)表示,两组间数据比较采用Student t检验;生存资料以生存曲线表示,采用Log-rank (Mantel-Cox)检验。P<0.05具有统计学意义。3. 实验结果
3.1 菸花苷对缺血性脑卒中大鼠长期生存率的影响
观察30 d内脑缺血损伤后大鼠的生存情况,发现手术后,模型组和菸花苷组大鼠均出现不同程度的死亡情况。菸花苷组大鼠于第8天开始,存活的数目趋于稳定,模型组于第16天开始,无新增的死亡大鼠。截止到第30天观察结束时,假手术组生存率为100%,模型组生存率为30.4%,菸花苷组生存率为70%,较之模型组,菸花苷组的生存率显著升高(P<0.05),结果见图2。
3.2 菸花苷对缺血性脑卒中大鼠30 d内行为学及体重的影响
由图3A可知,在手术后的各个观察时间点,假手术组的行为学评分均为0,一直未出现神经功能损伤的体征。与模型组相比,菸花苷组在测评的各个时间点神经功能损伤较轻,具有显著的统计学意义(P<0.01),且整个观察过程中,菸花苷组大鼠的行为学得分不断降低,神经功能趋向好转。
由图3B可知,在体重变化方面,手术后,假手术组大鼠体重一直保持持续增长状态。术后第1天,模型组与菸花苷组大鼠的体重有不同程度的下降,菸花苷组大鼠在术后第3天开始恢复体重增长状态,模型组从术后第10天开始恢复体重增长状态。在初始体重差别不大的情况下,较之模型组,菸花苷组在术后各个时间点观察得到的体重数值均明显高于模型组大鼠的体重数值(P<0.01)。
3.3 菸花苷对缺血性脑卒中大鼠神经元的影响
由图4A可知,假手术组皮层和海马区的细胞大小均一,结构清晰,胞浆丰富,核质比例适中,CA1区的锥体细胞和DG区的颗粒细胞排列整齐紧密,CA3区锥体细胞体积较之CA1区的略大,排列稍松散但整齐。模型组的神经元大小不一,胞质不规则淡染,胞核皱缩变形,部分细胞脱失明显,CA1区锥体细胞和DG区的颗粒细胞排列松散,CA3区锥体细胞排列散乱,表明造模后神经细胞受损严重。与模型组相比,菸花苷组的神经元虽也出现了细胞淡染,大小不均,部分胞体肿胀,CA1区及DG区排列稍显混乱,但整体的形态接近正常,病理损伤明显减轻。
由图4B可知,假手术组皮层和海马区的尼氏体大且多,“虎斑”也不在少数,呈深蓝色,表明神经元功能良好。模型组整体淡染,皮层的尼氏体大大减少,海马区尼氏体极少,表明造模后神经元功能受到损伤。与模型组相比,菸花苷组皮层尼氏体数目更多,个体更大,染色较均匀,海马区尼氏体虽多为颗粒状,个体稍小,但数目明显增多,说明神经元蛋白合成有所增加,较为活跃。
4. 讨论
正如“卒中治疗学术产业圆桌会议”中对神经保护药物的研究所提出的那样[11]:较为理想的神经保护类药物的实验室阶段研究,应该在至少两个不同实验室中展开,运用在至少两种动物身上,兼顾在永久缺血模型和短暂局灶性缺血模型,既要考察短期内的组织和功能上的结果,也需要考察长期作用的影响。在本研究中,我们在前期证明菸花苷对急性永久性缺血模型和短暂局灶性缺血模型均具有良好的保护作用的基础上[12-13],通过建立大鼠脑缺血再灌注模型,从功能和组织层面证明了菸花苷对缺血性脑卒中的长期保护作用。
长期生存率是药效结果最直观的体现,体重可以反映出大鼠在发生缺血性脑卒中后整体的预后情况,而行为学的变化可以间接反应出大鼠神经系统的功能。我们通过连续30 d观察实验大鼠的生存率、行为学以及体重变化,发现造模后给予菸花苷显著地提高了大鼠生存率,并能逐渐降低行为学得分,改善神经功能,体重也在术后第3天开始恢复增长状态。这些结果表明菸花苷可以改善缺血性脑卒中的预后,促进神经系统的远期功能恢复。
海马区是大脑中负责记忆与学习的重要区域,与认知功能密切相关,也是研究卒中后认知障碍等脑卒中并发症的重点关注区域,其中CA1区的神经元对脑缺血缺氧较为敏感,容易受到损伤,而CA3区及DG区的神经元则相对耐受[14]。尼氏体是神经元胞体和树突内的嗜碱性颗粒或小斑块,由游离的核糖体和粗面内质网构成,对缺血变化非常敏锐[15]。病理组织学研究表明,菸花苷给药后大鼠海马区的尼氏体数目有所增加,蛋白合成更为活跃,脑组织恢复更好,整体趋向正常。提示菸花苷对神经细胞结构和功能具有长期保护作用。
综上所述,菸花苷对缺血性脑卒中大鼠具有长期保护作用,可维持神经细胞结构功能处于相对良好的状态,并能促进神经系统远期功能的恢复,可以作为一种潜在的神经保护剂,其作用机制有待进一步研究。
-
-
[1] 国家卫生健康委脑卒中防治工程委员会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国脑卒中防治指导规范(2021年版) . (2021-08-27). http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/index.shtml. [2] 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2018, 51(9):666-682. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2018.09.004 [3] POWERS W J, RABINSTEIN A A, ACKERSON T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American heart association/American stroke association[J]. Stroke,2019,50(12):e344-e418. [4] 王业晴, 夏玉叶, 唐颖, 等. 菸花苷对全脑缺血再灌注模型大鼠的脑保护作用[J]. 药学服务与研究, 2017, 17(2):109-113. [5] BELAYEV L, KHOUTOROVA L, ATKINS K D, et al. Robust docosahexaenoic acid-mediated neuroprotection in a rat model of transient, focal cerebral ischemia[J]. Stroke,2009,40(9):3121-3126. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.555979 [6] CHEN J L, YE X C, YAN T, et al. Adverse effects of bone marrow stromal cell treatment of stroke in diabetic rats[J]. Stroke,2011,42(12):3551-3558. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.627174 [7] HASEGAWA Y, SUZUKI H, SOZEN T, et al. Activation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 by FTY720 is neuroprotective after ischemic stroke in rats[J]. Stroke,2010,41(2):368-374. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.568899 [8] SUZUKI Y, CHEN F, NI Y C, et al. Microplasmin reduces ischemic brain damage and improves neurological function in a rat stroke model monitored with MRI[J]. Stroke,2004,35(10):2402-2406. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000140628.00927.1a [9] DESLAND F A, AFZAL A, WARRAICH Z, et al. Manual versus automated rodent behavioral assessment: comparing efficacy and ease of bederson and garcia neurological deficit scores to an open field video-tracking system[J]. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis, 2014, 6: 7-14. DESLAND F A, AFZAL A, WARRAICH Z, et al. Manual versus automated rodent behavioral assessment: comparing efficacy and ease of bederson and garcia neurological deficit scores to an open field video-tracking system[J]. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis, 2014, 6:7-14. [10] PANG X M, LI T X, FENG L X, et al. Ellagic acid-induced thrombotic focal cerebral ischemic model in rats[J]. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods,2014,69(3):217-222. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2014.01.001 [11] Stroke Therapy Academic Industry R. Recommendations for standards regarding preclinical neuroprotective and restorative drug development[J]. Stroke,1999,30:2752-2758. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.30.12.2752 [12] LI R P, GUO M L, ZHANG G, et al. Nicotiflorin reduces cerebral ischemic damage and upregulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase in primarily cultured rat cerebral blood vessel endothelial cells[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2006,107(1):143-150. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.04.024 [13] LI R P, GUO M L, ZHANG G, et al. Neuroprotection of nicotiflorin in permanent focal cerebral ischemia and in neuronal cultures[J]. Biol Pharm Bull,2006,29(9):1868-1872. doi: 10.1248/bpb.29.1868 [14] SCHMIDT-KASTNER R, FREUND T F. Selective vulnerability of the Hippocampus in brain ischemia[J]. Neuroscience,1991,40(3):599-636. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90001-5 [15] HU H H, LI S J, WANG P, et al. An L-type calcium channel agonist, bay K8644, extends the window of intervention against ischemic neuronal injury[J]. Mol Neurobiol,2013,47(1):280-289. doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8362-x -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:


