-
替考拉宁是一种糖肽类抗生素,临床上主要用于治疗各种严重的革兰阳性菌感染,包括不能用青霉素类和头孢菌素类其他抗生素者。该药的血药浓度与临床疗效密切相关,对于重症感染患者,监测血药浓度可以提高治愈率[1]。临床一般检测其在血浆中的稳态谷浓度,而在不同疾病中,替考拉宁谷浓度需达到对应的目标值才能满足治疗要求,但由于替考拉宁成分复杂,患者在常规剂量使用过程中低于目标谷浓度的发生率很高,因此,对替考拉宁进行血药浓度监测很有必要[2-4]。替考拉宁血浆谷浓度的检测方法目前主要为高效液相色谱(HPLC)法,需要专职人员进行,很多单位尚无条件进行检测。因此,寻找替考拉宁谷浓度的临床预测指标,探讨其与替考拉宁谷浓度的关系,就显得尤为重要。替考拉宁血浆蛋白结合率高,与白蛋白的结合率为 90%~95%,消除半衰期长,除 2%~3% 经肝脏代谢外,大部分以原型经肾脏排泄。肾功能的变化必然对替考拉宁谷浓度产生明显影响,既往研究也显示肌酐清除率会对替考拉宁谷浓度产生明显影响[5-7]。胱抑素C是一种能灵敏反映肾小球滤过率变化的内源性标志物[8],其血中浓度由肾小球滤过率决定,不受炎症反应、肌肉、性别等的影响。本研究主要探讨胱抑素C水平与替考拉宁血浆稳态谷浓度的关系,以期为临床替考拉宁的合理应用提供依据。
-
本研究收集2017年10月−2020年7月在陆军军医大学第一附属医院进行替考拉宁血药浓度监测患者。患者纳入标准:①年龄≥18岁;②住院患者;③替考拉宁谷浓度为稳态谷浓度。排除标准:①孕妇;②未监测肝肾功能者;③血液透析者。本研究经本院伦理委员会批准(批号:KY2020109)。
-
患者每日经静脉滴注给予替考拉宁(给药剂量为200~800 mg,qd,根据患者疗效和不良反应以及血药浓度监测结果对给药剂量进行调整;患者疗程为7~67 d),最早于第6剂(替考拉宁谷浓度达稳态)给药前30 min,用EDTA管采集静脉血4 ml,3 500 r/min室温离心5 min,取出血浆按下述高效液相色谱(HPLC)法测定其谷浓度。替考拉宁对照品溶液:取替考拉宁对照品适量,精密称定(20.00 mg)后置于10 ml棕色量瓶中,用超纯水溶解并稀释至刻度,混匀,即得。哌拉西林钠对照品溶液:取哌拉西林钠对照品(内标)适量,精密称定(15.43 mg)后置于100 ml棕色量瓶中,用甲醇溶解并稀释至刻度,混匀,即得。色谱柱:Diamonsil C18(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 µm);柱温:40 ℃;流动相:0.01 mol/L磷酸二氢钠-乙腈(76∶24,V/V);流速:1.6 ml/min;紫外检测波长为240 nm;进样量:20 µl。取待测血浆0.4 ml,加入50 µl内标甲醇液(150 µg/ ml),涡旋混匀30 s,随后再加入乙腈0.6 ml,涡旋混匀1 min,13 000 r/min,离心5 min,取出上清液0.9 ml加入0.4 ml二氯甲烷,涡旋混匀1 min,13 000 r/min,离心5 min,上清液20 µl进样测定。
空白血浆中加入替考拉宁对照品溶液适量,再依次用空白血浆分别稀释成3.125、6.250、12.50、25.00、50.00、100.0 µg/ml系列浓度,处理后上液相色谱仪测定,记录色谱图,将替考拉宁(TA2-2)与内标的峰面积比值(R)对浓度(C)进行线性回归,得回归方程(n=6):R=0.6821C−2.186×10−2,r=0.9999,线性范围:3.125~100.0 µg/ml,本试验最低定量限为3.125 µg/ml,其5次测量值的RSD为2.57 %。
-
炎症指标、肾功能指标、肝功能指标及其他实验室检查指标均由本院检验科测定。胱抑素C的检测采用胶乳增强免疫比浊法测定。质控品按其说明书进行操作,每天进行一次质控实验。试剂空白吸光度:波长546 nm,光径10 mm,测得吸光度值A≤1.5000。线性范围:0.2~8 mg/L范围内线性相关系数r≥0.995,0.2~2.0 mg/L范围内绝对偏差≤0.2 mg/L,2.0~8 mg/L范围内相对偏差≤10.0%。准确度:相对偏差≤10.0%。分析灵敏度:样本浓度为1.0 mg/L时,吸光度差值为0.0060~0.0600。
-
收集患者的人口统计学资料,包括患者性别、年龄、感染类型和病原菌,给药剂量、给药方式、替考拉宁谷浓度,与替考拉宁谷浓度监测同一时间点的炎症指标降钙素原(PCT),肾功能指标血肌酐和胱抑素C,肝功能相关指标谷丙转氨酶(ALT)、天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)、总蛋白、白蛋白、胆红素、直接胆红素,以及葡萄糖水平等。
-
采用SPSS 18.0统计软件进行分析。对计数资料行χ2检验;对连续性变量先进行正态分布检验,对不符合正态分布的变量,以中位数(第25百分位数,第75百分位数)表示。不同胱抑素C水平下替考拉宁谷浓度不符合正态分布,行 Mann-Whitney检验;Logistic回归分析替考拉宁谷浓度不达标(<15 µg/ml)的影响因素,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
-
共入组98例患者141个谷浓度,其中男65例、女33例,年龄19~94(52.2±16.2)岁,60岁以上者32例(32.0%)。患者肺部感染57例,粒细胞缺乏伴感染14例,腹腔感染12例,感染性心内膜炎4例,其他11例;感染检出病原菌有耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌、肺炎克雷伯菌、铜绿假单胞菌、鲍氏不动杆菌、粪肠球菌、大肠埃希菌和嗜麦芽窄食单胞菌等。入组患者的炎症指标PCT的均值为2.09,说明患者的感染程度较重。患者的实验室检查指标情况见表1。
表 1 患者的实验室检查指标
指标 中位数(第25,
第75百分位数)范围 ALT(U/L) 7.60(3.45,22.42) 3.2~339.4 AST(U/L) 21.30(12.50,45.40) 5.4~624.6 总蛋白(g/L) 60.05(54.52,67.28) 42.3~103.8 白蛋白(g/L) 32.00(28.30,35.15) 20.8~43.9 胆红素(mol/L) 19.70(13.10,44.20) 4.8~698.78 直接胆红素(mol/L) 7.00(5.36,9.63) 1.0~437.8 血肌酐(mol/L) 66.04(46.00,98.60) 22.6~482.9 胱抑素C(mg/L) 1.22(0.91,1.94) 0.45~6.37 降钙素原(ng/ml) 0.61(0.26,2.07) 0.02~20.98 注:表中括弧中数据为四分位中位数。 -
患者替考拉宁谷浓度为11.51(8.35,19.07)µg/ml,范围为3.57~41.93 µg/ml,谷浓度<15 µg/ml者95例次(67.38 %)。替考拉宁给药剂量为400 mg时,谷浓度<15 µg/ml的百分比为80.90 %(72/89);替考拉宁给药剂量为800 mg时,谷浓度<15 µg/ml的百分比为42.86 %(18/42);两种给药剂量比较,差异有统计学意义(χ2=19.205,P<0.01)。
-
胱抑素C浓度>1.05 mg/L时,替考拉宁谷浓度明显高于胱抑素C浓度在0.3~1.05 mg/L时(Z=-2.636,P=0.008),见表2。
表 2 不同胱抑素C水平下替考拉宁谷浓度
胱抑素C(mg/L) 替考拉宁浓度(µg/ml) 替考拉宁浓度范围(µg/ml) ≤1.05 8.68(6.34,11.79) 3.57~26.47 >1.05 11.37(8.96,20.52) 3.73~41.93 注:表中括弧中数据为四分位中位数。 -
炎症指标PCT,肝功能相关指标总蛋白、白蛋白、胆红素、直接胆红素和葡萄糖水平与替考拉宁谷浓度不相关(P>0.05)。血肌酐浓度与替考拉宁谷浓度呈正相关(P<0.01),胱抑素C浓度与替考拉宁谷浓度呈正相关(P<0.05),见表3。
表 3 各指标与替考拉宁谷浓度的相关性
指标名称 r值 P值 胱抑素C(mg/L) 0.225 0.036 血肌酐(mol/L) 0.248 0.009 降钙素原(ng/ml) 0.048 0.706 总蛋白(g/L) 0.032 0.746 白蛋白(g/L) 0.140 0.134 胆红素(mol/L) −0.025 0.798 直接胆红素(mol/L) −0.041 0.670 葡萄糖(mmol/L) 0.084 0.426 -
通过纳入替考拉宁谷浓度影响因素如患者性别、年龄、胱抑素C、血肌酐、ALT、AST、白蛋白、总蛋白、胆红素、直接胆红素进行Logistic回归分析,结果显示,替考拉宁谷浓度不达标(<15 µg/ml)的影响因素是患者年龄、胱抑素C和白蛋白水平(P<0.05),见表4。
表 4 替考拉宁谷浓度不达标影响因素的Logistic回归分析
因素 OR值 95%CI P值 胱抑素C 1.529 1.001~2.336 0.049 白蛋白 1.154 1.025~1.299 0.018 年龄 0.952 0.917~0.989 0.012 -
替考拉宁的血药浓度与临床疗效间存在较强的相关性,研究显示,治疗严重感染时,替考拉宁有效血谷浓度不应<10 mg/L,但目前临床使用中却发现其血药浓度达标率普遍偏低[3-4, 9]。2017年,注射用替考拉宁说明书的变更获批,提出重度感染时,替考拉宁谷浓度应达到15~30 mg/L。因此,本研究以替考拉宁谷浓度<15 µg/ml为不达标,而本研究中不达标患者百分比为67.38%,值得引起重视。给予标准负荷剂量6 mg/kg的替考拉宁早期均不能达到目标谷浓度,不论患者肌酐清除率正常与否;给予高负荷剂量10 mg/kg替考拉宁的低肌酐清除率者早期可达目标谷浓度[10-11]。本研究中,替考拉宁给药剂量为800 mg时,其谷浓度达标的百分比明显高于替考拉宁给药剂量为400 mg时,提示临床上应提高替考拉宁负荷剂量的使用率。
近年来研究表明血清胱抑素C能更准确地评价患者肾功能[5]。正常情况下,胱抑素C在血清和血浆中的浓度为0.3~1.05 mg/L。当肾功能受损时,胱抑素C在血液中的浓度会升高。有研究考察了胱抑素C、肌酐清除率和肾小球滤过率3种评价指标对替考拉宁体内代谢的影响,结果显示胱抑素C是影响替考拉宁清除率最显著的协变量[12-13]。因此,本研究考察了胱抑素C水平与替考拉宁谷浓度的关系,结果显示,胱抑素C水平高于正常值上限时,替考拉宁谷浓度明显升高。另外,替考拉宁谷浓度不达标影响因素的Logistic回归分析结果显示,胱抑素C是替考拉宁谷浓度不达标的影响因素。
研究显示,肌酐清除率显著影响替考拉宁的谷浓度[4,7,11],但血肌酐对替考拉宁谷浓度的影响无统计学意义[4]。本研究中,血肌酐浓度越高,替考拉宁谷浓度越高,但血肌酐不是替考拉宁谷浓度不达标的影响因素。有研究显示,白蛋白为影响替考拉宁清除率的主要因素[7]。本研究中,白蛋白水平虽与替考拉宁谷浓度不存在相关性,与相关研究相符[5],但白蛋白是替考拉宁谷浓度不达标的影响因素。另有研究显示,替考拉宁谷浓度与剂量的比值与炎症指标超敏 C 反应蛋白成负相关[6],本研究考察了另一炎症指标PCT与替考拉宁谷浓度的相关性,结果显示PCT与替考拉宁谷浓度不存在相关性。分析原因可能与影响替考拉宁谷浓度的其他因素,如年龄、性别、体重指数、给药剂量和肾功能差异等有关;也可能与PCT和C反应蛋白虽然同是炎症指标,但二者产生的机制,发挥的生理作用和临床预测价值不同有关。
本研究的不足之处:由于每例患者替考拉宁谷浓度监测次数多为1~2次,本研究未考察替考拉宁谷浓度与疗效的相关性,而只是考察了替考拉宁谷浓度的影响因素。终上所述,本研究结果显示,替考拉宁给药剂量为400 mg时,谷浓度不达标<15 µg/ml的百分比明显高于替考拉宁给药剂量为800 mg时,提示临床上应提高替考拉宁负荷剂量的使用率。胱抑素C浓度高于正常值上限时替考拉宁谷浓度明显升高,是替考拉宁谷浓度不达标的影响因素,提示除肌酐清除率外,无条件进行替考拉宁血药浓度监测的单位,可以考虑将胱抑素C作为替考拉宁剂量调整的参考指标。
Study on the relationship between cystatin C level and the plasma trough concentration of teicoplanin
-
摘要:
目的 探讨胱抑素C水平与替考拉宁血浆谷浓度的关系,为临床替考拉宁的合理应用提供依据。 方法 回顾性分析2017年10月至2020年7月我院收治的使用替考拉宁患者的临床资料。考察替考拉宁血浆谷浓度的分布情况,比较不同胱抑素C水平下替考拉宁血浆谷浓度,Logistic回归分析替考拉宁谷浓度不达标(<15 µg/ml)的影响因素。 结果 共入组98例患者,141个谷浓度,其中男65例、女33例,年龄19~94(52.2±16.2)岁。替考拉宁血浆谷浓度为11.51 (8.35,19.07) µg/ml,范围为3.57~41.93 µg/ml,谷浓度<15 µg/ml者95例次(67.38%)。胱抑素C浓度高于正常值上限(>1.05 mg/L)时,替考拉宁谷浓度为11.37 (8.96,20.52) µg/ml,明显高于胱抑素C浓度在正常范围内的8.68 (6.34,11.79) µg/ml(Z=−2.636,P<0.05)。Logistic回归分析显示胱抑素C水平为替考拉宁谷浓度不达标的影响因素(OR=1.529,95% CI=1.001~2.336,P<0.05)。 结论 胱抑素C浓度高于正常值上限时替考拉宁谷浓度明显升高,是替考拉宁谷浓度不达标的影响因素,临床上可以考虑将其作为替考拉宁剂量调整的参考指标。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the relationship between cystatin C level and the plasma trough concentration of teicoplanin, so as to provide a reference for the rational application of teicoplanin in clinical practice. Methods The clinical data of the patients receiving teicoplanin, who admitted to our hospital from October 2017 to July 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. The distribution of teicoplanin concentration, the difference of teicoplanin concentration under different cystatin C level, and influence factors for teicoplanin concentration (<15 µg/ml) were analyzed. Results A total of 98 patients including 65 males and 33 females, aged 19 to 94 (52.2±16.2) years old, with 141 trough concentrations were enrolled. The trough concentration of teicoplanin was 11.51 (8.35, 19.07) µg/ml, and the range was 3.57-41.93 µg/ml. 95 cases (67.38%) had teicoplanin concentration <15 µg/ml. When the concentration of cystatin C was >1.05 mg/L, the trough concentration of teicoplanin were 11.37 (8.96, 20.52) µg/ml, significantly higher than those when the concentration of cystatin C was in normal [8.68 (6.34, 11.79) µg/ml, Z=−2.636, P<0.05]. Logistic regression analysis showed that cystatin C level was the influencing factor for teicoplanin trough concentration does not meet the standard (OR=1.529, 95%CI=1.001-2.336, P<0.05). Conclusion The concentration of teicoplanin is significantly increased when the cystatin C level is higher than the normal. Cystatin C level is the influence factor for teicoplanin trough concentration not meeting the standard. The cystatin C level may be considered as a reference for teicoplanin dosage adjustment in clinical practice. -
Key words:
- teicoplanin /
- infection /
- therapeutic drug monitoring /
- cystatin C
-
药品的调剂发放是门诊药房药师工作中非常重要的组成部分,门诊药师的药学服务工作也都围绕着药品的调剂发放展开。随着医药科技发展,门诊处方量不断增加,以及药品集中采购带来的药品更替增加,都给门诊药品的调剂发放带来了巨大的压力。
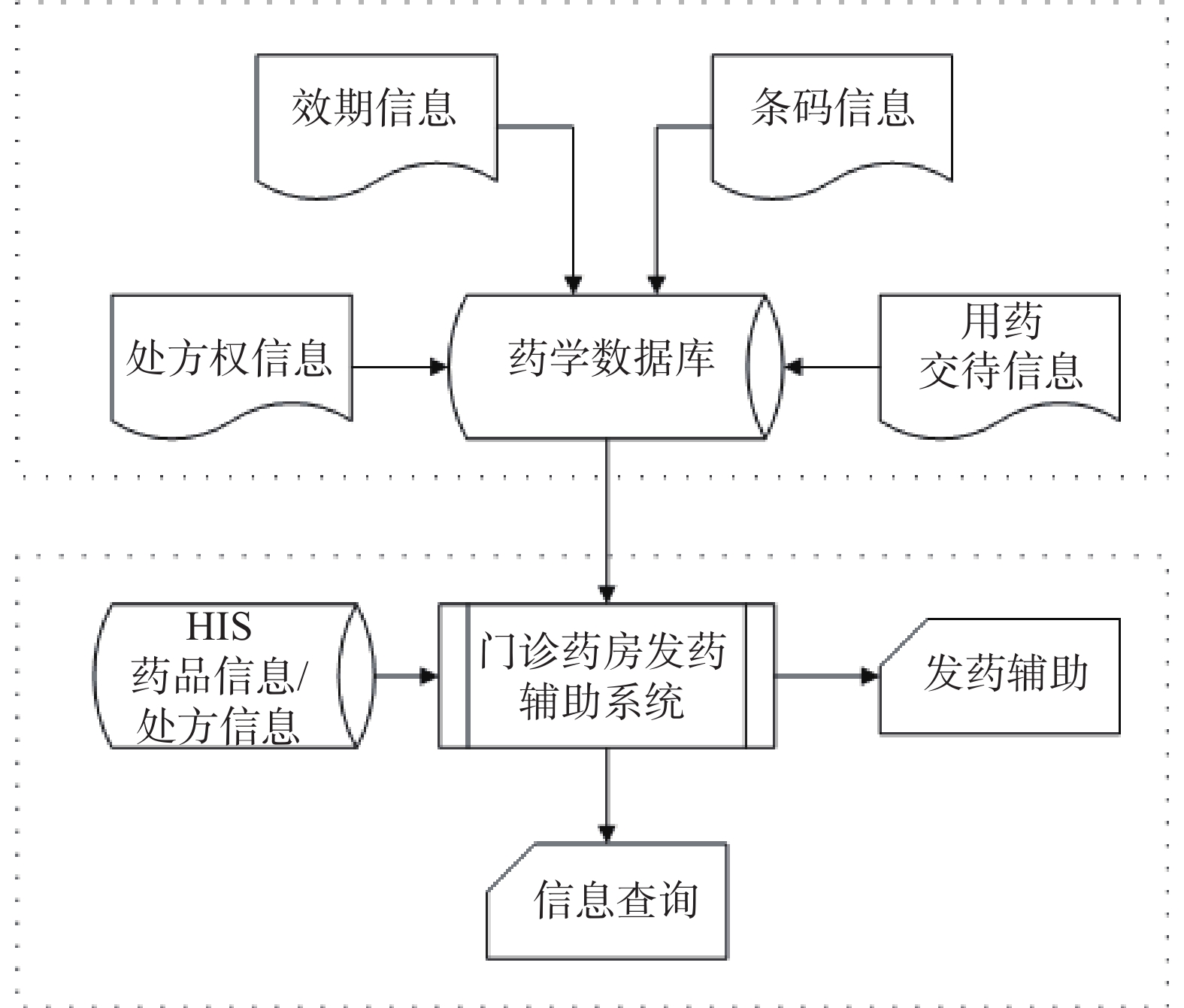
笔者所在医院是一所大型综合性医院,工作日平均门诊量在10 000人次左右,日均处方4 000张以上,每个发药窗口日均处方量500张以上,窗口药师工作压力巨大,极易出错。“军卫一号”发药系统自1997年在本院开始使用至今,软件老旧,功能不足。为适应我院的实际情况,提高工作效率,改善工作质量,特开发了“门诊发药辅助系统”。该系统充分利用各类条形码便捷输入的特点,在药品核对、处方权管理、效期管理、用药交待等多个环节辅助药师工作,可以有效降低差错,提高效率,增强药品管控能力。现将本系统的设计与使用情况做简要介绍。
1. 系统设计
1.1 系统环境
以医院信息系统(HIS)为数据基础,结合MS SqlServer 2008数据库管理系统作为数据储存平台,以Windows XP以上操作系统为开发及运行平台,Delphi和DotNet作为开发语言,构建了客户端(C/S)形式的应用程序。
1.2 系统结构
系统主要分后台数据维护和前台发药辅助两部分。后台数据维护部分负责对条形码、处方权、效期等提示信息进行维护,前台发药辅助部分提供即时的信息显示和查询功能。详细结构见图1。
2. 系统功能
条形码识别是该系统构建的核心。药品包装上的条形码一般有商品码和监管码两种[1]。2012年开始国家提出了对药品电子监管信息平台的建设工作,2016年国家又出台了《关于推动食品药品生产经营者完善追溯体系的意见》,虽然药品追溯体系的建立一波三折,但是至今国家药品监管码仍然已经覆盖了超过80%的中国药品企业和95%的国家重点关注品种[2]。本系统采用商品码和监管码并行查询的方式,对患者、处方和药品进行识别。
2.1 数据维护部分
条码信息、处方权信息和效期信息统一由数据维护程序录入系统。①药师通过程序的条码录入模块查询HIS储存的药品信息,然后扫描药盒上的商品码和监管码,把条码与相应的药品匹配。②负责管理处方权登记的药师可通过程序的处方权管理模块搜索HIS中储存的医生信息,在程序中设置医生所拥有的处方权限。③负责库存管理药师可通过程序的效期管理模块查询药品信息,并对药品的效期信息进行维护。
用药交待模块的数据直接从门诊用药咨询登记系统读取,平时由门诊咨询药师在咨询登记过程中根据咨询的情况随时维护,保证资料库中有最新、最简洁、最常用的药品信息直接为前台药师提供帮助。
2.2 发药辅助部分
由于原“军卫一号”发药系统的源代码无法修改,并且在现有的工作条件下,窗口药师工作繁忙,无法抽出时间进行过多的输入操作,所以系统把患者ID、条形码监管码等信息输入统一在一个输入口,通过系统后台监控药师扫码过程,做到功能无缝切换。药师只需扫描一次条码,系统即可查询并显示该患者当日所有就诊科室开具的多个处方信息。
2.2.1 药品核对
药品核对部分的工作流程见图2。
原有的发药流程中,药师只能依据经验,逐一核对患者的取药单据、电脑信息、处方和药品。引入新的“门诊发药辅助系统”后,药师只需扫描患者手中收据或者取药凭条上包含患者ID号信息的条码,发药系统搜索定位到该患者处方。此时辅助系统接收到扫描信息,自动完成输入焦点切换、查询并显示处方明细等一系列操作。药师直接扫描药品包装上的商品码或监管码进行药品核对。对于品种正确的药品,系统弹出显示框放大该药品信息,药师进一步核对药品数量。如果处方中没有该药品,则系统弹出提示告知药师确认。以往的药品核对工具只能对药品品种进行核对,缺乏对药品数量的敏感性[3]。该系统通过放大及颜色刺激的方式对数量做出提示,既可避免逐盒扫描药品对发药速度的影响,又可在一定程度上降低人工核对导致的数量差错。
显示的处方明细中以不同的字体颜色和底色向药师提示不同的情况。背景灰色表示该药品未录入条码,背景黄色表示该药品已扫码发放,红色字体表示该药品信息有异常。协助药师快速了解处方药品情况,提高发药效率。
2.2.2 处方权管理
处方权限的提示集成在扫码显示的处方明细界面中。显示的信息包括了医生的姓名及所在科室。文字为绿色则提示该医生有麻精药品处方权限,可以开具特殊药品处方,进一步点击医生姓名可显示HIS中储存的医生签名图片;文字为红色则提示该医生没有进行过麻精药品处方权限登记,如果开具特殊药品,需要有权限的医师在处方上再次签字确认。由于门诊医生人数众多,流动量大,该功能可帮助药师快速确定医生权限,不需要查阅处方权登记本,把更多精力放在对处方合理性的审核上。
2.2.3 效期管理
药品的效期提示同样集成在处方明细界面中,直接以颜色作为标识。如果辅助系统查询到处方中的某种药品包含近效期药品,则以醒目的绿色字体提示药师,药师需要仔细核对药品每个最小包装,确认是否可以正常发放。
2.2.4 用药交待
药品辅助咨询的信息以提示框的形式在处方明细界面供药师查询显示。药品信息以蓝色字体显示,则提示该药品包含提示信息。药师双击该药名即可弹出提示框显示该药品的储存方式、注意事项、用法用量、相互作用等需要提示患者的信息或者患者经常提问的信息,进一步强化药师的药学服务能力。
3. 应用效果
为考察发药辅助系统的实际应用效果,并对系统功能的进一步改进提供帮助,笔者针对门诊药师重点关注的调配差错、发药效率和对药师的影响等方面进行调查分析。
3.1 对调配差错影响
门诊药房作为与患者直接沟通的窗口,差错的出现对于患者影响的意义巨大,直接影响患者是否能安全有效的使用药物,影响患者对医院药学服务的信任程度。但是由于药品数量多,药师工作压力大,且存在药名相似、包装相似、一品多规等多种干扰因素,总是难以避免产生人为的调剂差错。据统计,美国每年用药差错中58%是由于药名、包装相似引起的品种差错[4],国内的报告中品种差错也达到了40%左右[5-6]。使用该系统后,对于品种差错,系统会自动提示错误,相当于在发药环节增加了计算机核对步骤,由原来的双核对增加到了三核对,同时高亮的已发药品显示还能帮助药师检查是否有漏发、多发的情况,可以有效降低药师发药的差错。在辅助系统稳定工作1年后,笔者对系统使用前后1年内的发药差错情况进行统计分析,差错数据来源除由患者找回的发药差错外,还包括在盘点过程中发现账物不符并排除其他情况后推断为发药差错的差错。其中数量差错包括多发、少发、漏发等情况,品种差错包括由于药名相似、剂型相似或包装相似等引起的差错,其他为患者拿错,遗落等原因引起的差错,所有差错均是经核实并登记的发药差错。结果如表1。
表 1 发药辅助系统使用前后发药差错对比差错类型 系统使用前 系统使用后 例数 占比(%) 例数 占比(%) 数量差错 41 49 15 60 品种差错 33 39 4 16 其他 10 12 6 24 总计 84 100 25 100 总差错率(‰)(差错数/年处方数) 0.107 0.027 3.2 对发药效率的影响
启用发药辅助系统后,药师在发药过程中增加了扫码环节,单个药品核对用时有所增加。但经过笔者对所在单位门诊发药高峰时段(10:00-11:30)使用发药辅助系统前后单个患者平均取药时间进行统计。结果显示使用发药辅助系统后,患者取药消耗的时间反而有所减少。高峰时段患者总取药时间中位数由原来的8 min 52 s,缩短到了现在的6 min 21 s。综合考虑药师发药时的各种情况,在当前调配量过剩的情况下,虽然发药扫码过程消耗了额外的时间,但是药师在系统的辅助下,只要逐品种扫码发放药品,核对数量,不需要额外花精力去确认药品是否漏发或发重,可以更快的核对处方、核对药品,在患者多科室看病,开具药品品种较多时,效果尤其明显。处方权提示和用药交代提供的内容帮助药师更快的应对发药过程中出现的情况,有效的提高了总体工作效率。
3.3 药师评价
通过对门诊药师开展系统使用情况的问题调研,反馈的情况统计如表2。
表 2 发药辅助系统药师反馈意见汇总(n=32)药师反馈意见 赞同人数 赞同人数占比(%) 系统可减少差错 30 94 系统可提高效率 23 72 有助于增强事件处理能力 20 63 增加了工作量 3 9 系统有助于药师工作 32 100 药师普遍认为该辅助系统有助于减少差错、降低发药药师的工作压力。通过对反馈问题的深入了解,主要不认可的问题在于部分年龄比较大的药师,经验丰富,工作更依赖于自身经验,对于新引入的计算机软件有一定的排斥心理,需要更多的时间逐渐适应系统操作。另外有个别药品外包装既没有商品码,也没有监管码,无法识别,只能人工核对药品信息。
4. 讨论
2015年国家食药总局就要求“2016年1月1日后生产的药品制剂应做到全部赋码”,2019年4月19日,国家药品监督管理局正式发布了《药品信息化追溯体系建设指导》和《药品追溯码编码要求》两项药品信息化追溯体系标准,编码规则确定了20位溯源码前7位为药品标识码或者符合ISO相关国际标准,但至今仍有部分药品既无监管码也没有商品码。笔者对所在医院门诊药房现有919种药品进行了统计,有58%的药品包装有商品码,有73%的药品包装印有监管码,条码总计覆盖了79%的药品。按药品消耗量计算,可扫码药品占门诊总发药量的93.8%。不能扫码的药品主要为医院制剂、针剂和部分瓶装普药。如果把这些药品全部纳入扫码,需要额外做大量的工作。对于医院制剂,可以与制剂部门沟通在药品包装上加印自制的条形码,其他药品需要在实际工作中仔细核对,进一步结合工作研究出既不影响效率又能提高准确率的方案。
应用该发药辅助系统后,总的差错数量大幅减少,数量差错也有明显减少,但品种差错仍然存在。主要原因是虽然辅助系统提供了多一层核对,但是药师过于依赖该系统,弱化了自身的核对,造成错误。同时高强度的工作也是导致药师注意力不集中,出现发药差错的影响因素。
门诊发药辅助系统功能涵盖了药师发药工作的多个环节,功能全面。系统以发药核对为核心功能,既整合了处方权管理、效期管理和药学服务等功能模块,同时各个模块之间又相对独立,可根据需求逐步添加。处方权管理模块在麻精药品管理中引入了信息化控制,能够进一步规范麻精药品的使用,确保制度落实。咨询辅助模块在协助药师回答患者问题的同时,也强化了药师的业务能力,有助于提高药师地位。药师咨询能力的提升,也有助于减少医患纠纷的发生[7]。
市售的大型发药系统虽然发药准确率可达到万分之二,但是设备引进及维护费用巨大,且对药房环境条件、药品剂型、包装等有诸多限制[8]。整个扫码发药过程中只需要在每个窗口添加条码扫描设备,维护简单,无需过多的硬件或资金投入。该程序的使用,用较低的成本优化了药学服务,提高了发药准确率,对药学服务的发展具有重要意义。
-
表 1 患者的实验室检查指标
指标 中位数(第25,
第75百分位数)范围 ALT(U/L) 7.60(3.45,22.42) 3.2~339.4 AST(U/L) 21.30(12.50,45.40) 5.4~624.6 总蛋白(g/L) 60.05(54.52,67.28) 42.3~103.8 白蛋白(g/L) 32.00(28.30,35.15) 20.8~43.9 胆红素(mol/L) 19.70(13.10,44.20) 4.8~698.78 直接胆红素(mol/L) 7.00(5.36,9.63) 1.0~437.8 血肌酐(mol/L) 66.04(46.00,98.60) 22.6~482.9 胱抑素C(mg/L) 1.22(0.91,1.94) 0.45~6.37 降钙素原(ng/ml) 0.61(0.26,2.07) 0.02~20.98 注:表中括弧中数据为四分位中位数。 表 2 不同胱抑素C水平下替考拉宁谷浓度
胱抑素C(mg/L) 替考拉宁浓度(µg/ml) 替考拉宁浓度范围(µg/ml) ≤1.05 8.68(6.34,11.79) 3.57~26.47 >1.05 11.37(8.96,20.52) 3.73~41.93 注:表中括弧中数据为四分位中位数。 表 3 各指标与替考拉宁谷浓度的相关性
指标名称 r值 P值 胱抑素C(mg/L) 0.225 0.036 血肌酐(mol/L) 0.248 0.009 降钙素原(ng/ml) 0.048 0.706 总蛋白(g/L) 0.032 0.746 白蛋白(g/L) 0.140 0.134 胆红素(mol/L) −0.025 0.798 直接胆红素(mol/L) −0.041 0.670 葡萄糖(mmol/L) 0.084 0.426 表 4 替考拉宁谷浓度不达标影响因素的Logistic回归分析
因素 OR值 95%CI P值 胱抑素C 1.529 1.001~2.336 0.049 白蛋白 1.154 1.025~1.299 0.018 年龄 0.952 0.917~0.989 0.012 -
[1] 沈琮, 陈文倩, 张相林. 替考拉宁治疗药物监测进展[J]. 中国医院用药评价与分析, 2019, 19(7):890-894,896. [2] ZHOU L J, GAO Y Q, CAO W, et al. Retrospective analysis of relationships among the dose regimen, trough concentration, efficacy, and safety of teicoplanin in Chinese patients with moderate-severe Gram-positive infections[J]. Infect Drug Resist,2018,11:29-36. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S146961 [3] 何丹, 董娜, 朱怀军, 等. 基于替考拉宁群体药物代谢动力学模型的个体化给药研究进展[J]. 临床药物治疗杂志, 2020, 18(5):38-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3384.2020.05.008 [4] 梁培, 郭晓芳. 重症感染患者替考拉宁血药谷浓度68例次监测分析[J]. 实用药物与临床, 2018, 21(5):553-556. [5] 张荣格, 张瑞霞, 张弋. 替考拉宁的血药浓度监测及影响因素分析[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2019, 54(8):654-658. [6] 吕佩瑜, 邓方斌, 林玮玮, 等. 替考拉宁在中国成人患者中的群体药动学研究[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2020, 55(8):616-622. [7] 李芳, 蔡乐, 毛智, 等. 重症感染患者负荷剂量替考拉宁的血药浓度监测[J]. 临床药物治疗杂志, 2019, 17(11):44-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3384.2019.11.010 [8] DHARNIDHARKA V R, KWON C, STEVENS G. Serum cystatin C is superior to serum creatinine as a marker of kidney function: a meta-analysis[J]. Am J Kidney Dis,2002,40(2):221-226. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2002.34487 [9] 周丽娟, 刘嘉, 曹巍, 等. 替考拉宁血药浓度监测对肺炎患者用药方案的指导意义探讨[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2017, 37(8):771-775. [10] 胡萨萨, 尤海生, 金建霞, 等. 中性粒细胞缺乏伴发热患者应用替考拉宁抗感染的剂量监测及优化[J]. 河北医药, 2019, 41(23):3654-3658. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2019.23.035 [11] 王冉冉, 马婧, 黄晓会. 重症感染患者替考拉宁血药谷浓度不达标的相关因素分析[J]. 中国药师, 2020, 23(3):494-496. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-049X.2020.03.021 [12] KASAI H, TSUJI Y, HIRAKI Y, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in hospitalized elderly patients using cystatin C as an indicator of renal function[J]. J Infect Chemother,2018,24(4):284-291. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2017.12.002 [13] KOZONO A, HIRAKI Y, ADACHI R, et al. Comparison of predictive accuracy of teicoplanin concentration using creatinine clearance and glomerular filtration rate estimated by serum creatinine or cystatin C[J]. J Infect Chemother,2016,22(5):314-318. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2016.01.024 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 罗敏,陈欢,赵福坤,苏穆,王远敏. 决策树支持下SmartDose在神经外科万古霉素个体化用药中的应用. 遵义医科大学学报. 2023(06): 605-611 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 杨浩,熊雄,刘长江. 骨科术后患者万古霉素峰谷浓度的影响因素及群体药动学预测比较. 中国医院药学杂志. 2023(24): 2722-2728 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(2)
-





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载: 

