-
表面增强拉曼光谱(surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, SERS)作为一种高效、快速、灵敏的分析手段,受到各个领域的广泛关注[1-2]。SERS技术在原有拉曼光谱的基础上将被测物质的信号提高了106~1014倍[3],并且,通过SERS技术可以获取被测物质详细的指纹图谱,是鉴别、检测结构类似物最有效的分析手段之一[4-5]。但是,利用单一的SERS技术对混合体系中的目标物进行检测是十分困难的。而通过联用其他分析手段可有效的弥补单一SERS技术检测的不足,提高SERS技术的检测能力和表征能力。本文将可以与SERS联用的技术方法进行系统地分类,并对联用的机理和优势进行阐述。
-
拉曼散射由印度著名物理学家C.V Raman首次发现,他通过实验证明,当一束光通过介质时,光子与物质分子可以发生弹性碰撞和非弹性碰撞两种形式。弹性碰撞只改变光子的运动方向,不损耗光子的能量,称之为瑞利散射;而非弹性碰撞在改变光子的运动方向的同时也会损耗光子自身能量,即散射光的频率发生变化,这种现象称之为拉曼散射,由此形成了以拉曼散射为基础的拉曼光谱技术。表面增强拉曼光谱是在拉曼光谱技术上发展起来的一种新型分析手段,主要利用粗糙金属(金、银、铜)表面吸附被测物质,使得被测物质信号急剧增强,极大地提高了检测的灵敏度[6-7]。目前,普遍公认的两种增强机理是:化学增强和电磁增强[2,8]。化学增强主要认为待测物质分子与粗糙金属表面发生了电荷转移的相互作用,但该作用对于物质信号增强作用较小。电磁增强主要认为入射光照射到粗糙金属表面,当光子频率与电子振动频率一致时,共振发生,金属表面磁场极大增强。因此,置于此磁场中的物质分子的拉曼信号也得到了大幅增强,甚至对单分子测定仍然具有较高的灵敏度和准确性[9]。SERS技术因其独特的指纹图谱特性,成功且广泛地应用在药品和食品分析[10-11]、农药残留检测[12]、环境监控[13]、生物样品测定[14-15]、细菌[16]以及细胞检测[17]等领域。
尽管SERS技术具有灵敏度高、检测速度快、样品需求量少等优点,但仍然有一些在实际应用中无法克服的缺点。例如,SERS不是一个分离手段,而真实样品往往不是单一组分,是多种物质的混合体系。因此,单独使用SERS技术对混合体系中的目标物质进行准确鉴别是一个巨大的挑战。同样,单纯依靠SERS技术获得的指纹图谱无法实现对未知物质精确表征。因此,SERS联合其他技术手段来对被测物质进行准确测定成为必然趋势。通过联用的方式,提高SERS在检测和表征方面的不足,实现对被测物质高效、灵敏、准确测定的目的。许多技术方法都可以与SERS技术联用,并且成功的应用在实际检测中[18-19]。其中联用后可以提高SERS检测能力的方法主要有:① 分离技术:包括萃取法、薄层色谱法、高效液相色谱法;② 捕捉技术:包括抗体、适配体,分子印迹法;③ 微流体技术。联用后可以提高SERS表征能力的方法主要有:质谱、核磁共振光谱、红外光谱以及原子力显微镜等。
-
在对样品进行SERS检测之前,首先利用分离技术处理被测体系,利用目标物质与复杂体系中其它杂质的理化性质的不同,分离提纯目标物,同时富集目标物含量,可以显著提高SERS检测的准确性和灵敏度。常见的分离技术主要有:萃取法、薄层色谱法、高效液相色谱法等。
-
萃取法主要是利用复杂体系中各组分在不同相中的溶解度差异,从而将目标物从一相转移到另一相的过程。萃取方式主要包括固-液、液-液、气-液的萃取等。萃取法操作简单、成本低、快捷,是传统的样品前处理方法之一[20]。将萃取法应用在SERS检测之前,利用萃取技术对复杂样品中的目标物进行提纯,同时,还可以富集被测目标物含量,将复杂体系单纯化,然后与增强试剂按照比例进行预处理,最后利用SERS技术进行分析测定,即可得到分析物详细的指纹图谱。如今。微萃取的发展,克服了传统萃取法样品需求量大的缺点,使得萃取-SERS联用可以更好地应用到食品、药品等各个领域[21]。但是萃取法同时也存在一些缺点,即无法分离混合体系中对于同一萃取相溶解度相近的物质。
-
薄层色谱法(TLC)隶属于平面色谱法,是指将固定相涂于玻璃板、铝箔等平面上,形成一层均匀的薄层后,将试样点在薄层板底端,然后放置到盛有适宜展开剂的玻璃容器内展开,从而实现将目标物与其它物质分离的目的。同时,利用各组分在薄层板上的比移值的不同,达到分离鉴别的目的。该方法具有分析速度快、操作简单、成本低、效率高、分析结果直观等优点[22-23]。TLC与SERS主要有两种联用模式。一种是将固定相和增强试剂同时涂于TLC板上,待试样经过TLC分离后,可直接利用SERS检测[24]。或者,TLC板仅由固定相组成,待样品经过展开剂分离后,将增强试剂均匀地喷涂于整个薄层板上,或喷涂在展开之后的样品点上,然后再采集该点SERS图谱,这样便可以获取具有高强度检测信号的被测物质详细的指纹图谱信息[25]。TLC-SERS联用可排除其他无关杂质的干扰,极大地提高SERS检测的灵敏度和准确性。自1977年提出至今,TLC-SERS联用方法因其操作简单、快速、高效等优势,广泛地应用在食品、药品、合成染料、生物样品分析等领域[26-28]。
-
尽管利用TLC可以快速分离复杂体系中不同组分的物质,但是相比于高效液相色谱法(HPLC),TLC的分离效能和稳定性相对较弱,无法分离体系中与目标物结构、极性十分相近的化合物。而HPLC是最常见的柱色谱之一,具有高效的固定相,同时采用高压输送流动相的方式,使得HPLC具有分离效能好、分析时间短、灵敏度高、适用范围广等优点[29-30]。但是在具有高密度峰的色谱中,单个峰的归属变得困难,仅仅依靠保留时间对复杂体系进行定性分析,往往得不到预期结果。所以,将具有良好分离效能的HPLC与SERS联用,就可以得到被测组分详细的结构信息。常见的联用方式,主要是被测组分流经色谱柱和检测器后与惰性金属溶胶溶液进行预处理后,再混合流入SERS测试流动池。此时,既可以对分离液进行不间断收集,采集各个时间段SERS图谱;也可以利用检测器分析结果,收集相对应的色谱峰的流出液,获取目标物的SERS峰,实现HPLC-SERS的离线检测。随着SERS检测系统的不断发展,HPLC-SERS联用可以直接利用SERS仪器代替HPLC中的检测器进行分析,真正实现“即流即测”动态检测的在线分析测定[31]。经过HPLC分离得到的试样组分纯度高,杂质少,为之后SERS检测到单一的、含量高纯物质信号提供保障。如今,HPLC-SERS联用技术成功的应用在痕量分析等各个领域中[24,32]。
-
SERS技术几乎不具有选择性,当混合体系中存在结构、性质十分相近,通过上述分离技术得不到良好区分时,就无法通过SERS采集到精准的目标物质图谱。所以,需要借助一些捕捉技术特异性地识别目标物质,从而将目标物质从被测体系中分离出来。因此,通过联用捕捉技术与SERS,实现对目标物质的选择性检测,缩短分析测定的时间。
-
抗体是一类可以特异性识别抗原,并与抗原以高亲和力、高选择性结合的蛋白质,是临床免疫分析的常用物质。通过抗体捕捉技术,可以检测特定分子如:蛋白质、细胞、细菌等生物分子的浓度,或者验证它们的存在[33-35]。经由特异性识别、捕捉的过程,可以将目标物从生物复杂体系中分离出来,同时排除待测体系中其他杂质的干扰。这样一种高选择性、高灵敏度的联用方式逐渐引起了人们广泛的关注。其中最常见的抗体捕捉技术与SERS的联用方式是:首先将抗体固定在磁珠上,这样固定好的抗体就会与混合体系中的抗原(目标物分子)特异性结合,然后标签分子(由惰性金属纳米颗粒和抗体组成,必要时也可加入信号分子)与上述被捕捉的抗原分子结合,形成“三明治”结构,然后利用磁珠将该结构从混合液中分离,这样便得到了单一的被测目标物。此时将该目标物与惰性金属溶胶液预处理后,即可利用SERS技术进行检测,得到抗原分子准确详细的指纹图谱[36-38]。该方法极大地排除了无关杂质的干扰,提高了分析方法的选择性,同时降低了被测物质的检测限。
-
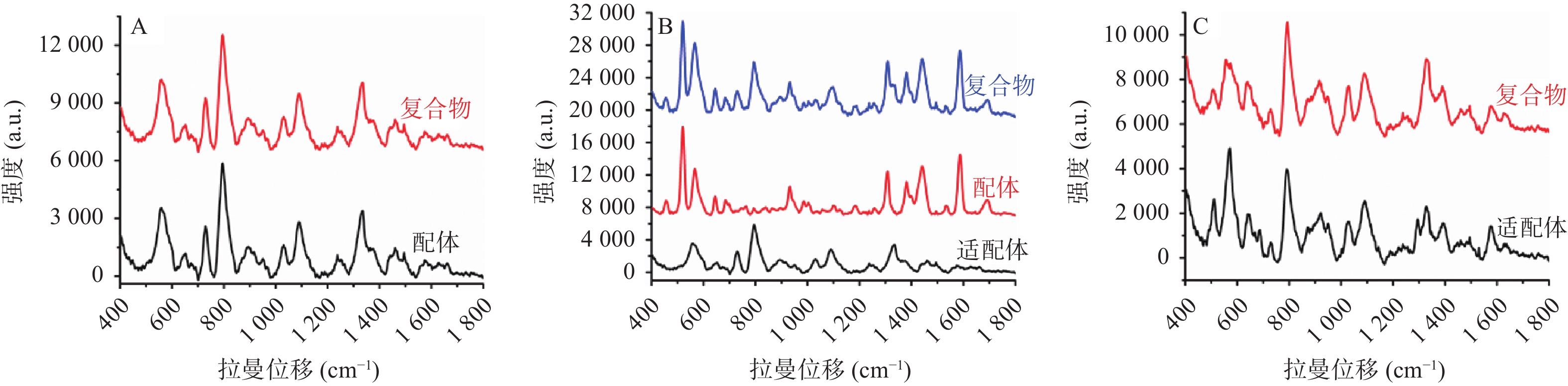
适配体通常是指具有特定空间结构的单链核酸序列,相比于抗体分子,适配体具有更好的热稳定性、盐耐受性,并且易合成储存、价格低廉等优点[39-40]。近年来,适配体被广泛地应用到药物、蛋白质、细胞、细菌等分子的分析检测领域中,是临床治疗诊断的常用手段。利用适配体对配体分子的高亲和力和高选择性,可以将配体分子从混合体系中识别并分离出来,分离得到的纯物质再与惰性金属溶胶液预混,然后进行SERS检测。检测结果通常分为以下3种情况:①大多数情况下,如适配体分子本身不产生拉曼信号,适配体捕捉到配体分子形成复合物后,通过SERS采集到的图谱均为配体分子的拉曼信号;②如适配体与配体分子均产生较强的拉曼信号,二者结合形成复合物后,通过SERS采集到的信号为二者之和,此时需要扣除适配体的背景信号以获取配体分子信息;③如配体分子并无拉曼特征峰,而适配体分子拉曼信号强烈,则可以通过配体与适配体结合后,适配体构象改变所引起的拉曼信号的改变来判断配体分子的存在(见图1)。通过捕捉适配体的方式与SERS检测联用,解决了SERS选择性差的问题,极大地提高了SERS检测的灵敏度和准确度,有助于获得目标物质准确的结构特征信息。该联用方法正广泛的应用在检测、传感、临床诊断和治疗等各个领域。
-
抗体和适配体在生物大分子的选择、识别方面具有突出优势,而在低分子量的小分子检测中,分子印迹技术优势显著。分子印迹技术是人工合成与目标分子特异性结合的功能单体,利用适当的交联剂使功能单体聚合,形成共聚物,然后再将目标分子脱去,这样聚合物中就形成能与目标分子高度互补的空间结构,类似于“锁-钥”结构,利用这种结构的互补性,可以重新与目标分子特异性结合,能够在复杂体系中准确、专一地识别和分离目标分子[41-43]。此时,将分离得到的目标物与惰性金属溶胶进行预处理,便可直接利用SERS技术采集详细的指纹图谱,获取目标物的化学结构特征。通过分子印迹技术合成的功能单体聚合物又称为分子印迹聚合物,该聚合物能够重复利用,稳定性好,排除体系中其他物质的干扰,与SERS技术联用后,可有效的提高SERS检测的选择性,并且可以对被测物质含量进行富集,极大地降低了SERS的检测限,是痕量物质检测首选的分析方法,已成功地应用在食品、药品掺杂分析等领域[44-46]。
-
微流体技术的发展使在微观尺寸下,对微量液体精确操控和处理成为可能[47-48]。在微流体通道里,被测样品溶液以恒定的速度均匀流动,解决了由于人工上样导致SERS检测结果不稳定、重现性差的问题,实现对被测样品实时监控的目的。微流体与SERS的联用可以通过“Y”型管道实现,被测样品溶液和惰性金属银胶溶液分别从“Y”型管道的两支流入,并成功在“Y”型管道中混合,经过一定时间的充分混合,最终流入SERS检测体系,便可以采集目标物SERS图谱[49-50]。当然,也可以将惰性金属纳米颗粒直接加入到通道里,这样当样品溶液流入后,就可以直接被SERS检测。若与多通道的微流体技术联用,则可以实现SERS的高通量检测,极大地缩短了检测时间,使检测流程程序化、精确化。因此微流体技术与SERS的联用,使得SERS检测更加稳定、实时、高效。
-
通过SERS图谱可以获得分析物详细的指纹图谱,但是当没有标准品作为对照时,仅仅依靠SERS图谱信息,对未知化合物进行鉴别、分析是十分困难的,需要借助其他技术,来弥补SERS图谱的不足,对未知分析物进行全面、准确地分析测定。与SERS联用后可以提高SERS表征能力的常用技术有:质谱、核磁共振光谱、红外光谱以及原子力显微镜。
-
质谱(MS)法主要是依靠多种离子化技术,将待测分子转化为气态离子形式,并得到一系列碎片离子,这些碎片离子按照质荷比(m/z)大小顺序排列,最终被记录形成图谱。MS法灵敏度高、分析速度快、信息量大,通过MS分析可以准确获取被测物的相对分子质量,是物质结构分析强有力的工具。然而。单一的MS分析无法区分光学异构体、几何异构体,以及确定取代基的位置等等。而SERS图谱虽然可以提供有关被测物详细的结构信息,但是物质分子结构与金属纳米颗粒表面无法产生强烈的共振效应,导致分子结构中的某些信息没有展现在SERS图谱中。Bei等以Ag纳米溶胶为介质,同时应用于SERS和MS检测,得到了罗丹明6G、对氨基苯硫酚和二羟基苯甲酸3种物质精确的结构信息[51]。因此,联用SERS-MS便可以同步获取目标化合物二维图像和物质组成信息,实现全面而准确地分析的目的[52]。
-
核磁共振(NMR)光谱是指在外加磁场作用下,原子核内部存在着不同能级,当用一定频率的射频照射样品分子时,原子核自旋能级跃迁,产生核磁共振,以共振信号强度和照射频率作图,即得核磁共振光谱图[53]。常用的NMR光谱主要有氢谱和碳谱,根据NMR光谱图提供的信息,可以预测被测物的分子基团、化学环境、反应状态和原子相对数量,广泛用于研究有机分子的性质。SERS在获取物质表面信号方面具有极高灵敏度,但是较强的物质往往会掩盖整体信号,使得SERS获取的被测物质的信号较为片面,而与NMR联合应用便可相互补充,弥补SERS在分子基团结构预测方面的不足。Cheng等曾利用SERS和NMR技术,成功对聚集诱导发光分子的分子内转动情况与光致发光之间的关联进行研究,并取得满意结果[54]。因此,NMR-SERS联用可以对被测物质进行详细、准确地预测和鉴别。
-
红外光谱(IR)是指物质分子吸收连续波长的红外光后,分子振动能级发生跃迁产生红外光谱图。吸收辐射的频率与化学键的振动或原子跃迁的能量相匹配,每一个物质都有自身特征的吸收峰,因此,IR图谱具有特征性和指纹性。根据IR图谱中吸收峰的位置、强度、形状可以判断被测物的基团、化学键类型等等。IR和SERS图谱都是分析、检测物质结构强有力的工具,但是由于两种技术原理不同,所以对于同一化学键或基团的表征能力有所区别。例如,红外光谱对水溶液具有强吸光度,会使被测样品的水溶液产生高强度背景信号,掩盖目标物的信号。而水溶液是弱的拉曼散射体,SERS光谱对水溶液几乎不显示,是红外光谱良好的补充技术,两者合用的目的主要是信息加和。Howbeer等利用SERS和IR光谱对自然界中的微生物进行鉴别区分,并得到了各类微生物详细全面的结构信息[55-56]。因此,将IR与SERS联用,取长补短,会比单独使用一种方法预测物质结构更加真实可靠。
-
原子力显微镜(atomic force microscopy, AFM)是一种可以根据显微探针受力情况计算得到被测物质分子结构表面高度,从而获得样品形态的三维信息的成像技术。AFM既可以在空气中工作,也可以在缓冲溶液等近生理条件下工作。具有高分辨率、样品无损、应用范围广、前处理简单等优势[57]。Ece等利用AFM和SERS技术对连接在去污剂耐受膜上的鼠诺如病毒进行研究,并对两者之间的相互作用情况进行分析。从SERS图谱解读病毒分子内部成键和结构信息,利用AFM对样品外部形态进行表征,如此,便可以对测定的物质有全面深入的了解[58]。
-
SERS因其灵敏度高、分析速度快、样品需求量小以及可以提供被测物质详细的指纹图谱等优点在物质检测、分析、结构预测等领域显示出巨大的应用前景。然而,SERS对于复杂样品体系显示出较弱的检测能力,以及单纯依靠SERS图谱无法准确预测分子的结构信息。因此,需要将SERS技术与其他技术手段联合应用,以增强SERS的检测能力和表征能力,实现对被测分子高选择性和高灵敏度的检测。
Overview of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy in combination with other detection techniques
-
摘要: 表面增强拉曼光谱(SERS)作为日渐成熟的分析检测技术,对自然界中许多单一物质具有鉴别检测,甚至是定量测定的能力。但在实际样品分析中,被测样品往往是多种物质的混合体系,单纯依靠SERS技术无法实现对混合体系各组成成分的准确表征。因此,SERS联用其他技术手段来对被测物质进行准确测定已成为必然趋势。通过联用的方式,提高SERS在检测和表征方面的不足,实现高效、灵敏、准确地测定被测物质的目的。
-
关键词:
- 表面增强拉曼散射光谱 /
- 联用 /
- 分析测定
Abstract: As an increasingly mature analytical technique, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy has the ability to identify, detect, and even quantitatively measure many single substances in nature. However, in the actual sample analysis, the tested samples were often a mixed system of various substances, and it was impossible to accurately characterize the components of the mixed system only by relying on SERS technology. Therefore, SERS combined with other techniques to accurately determine the measured substances has become an inevitable trend. Through the combination, the deficiency of SERS in detection and characterization was improved, and the purpose of efficient, sensitive and accurate determination of substances to be measured was achieved.-
Key words:
- surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy /
- combination /
- determination
-
[1] GARCIA-RICO E, ALVAREZ-PUEBLA R A, GUERRINI L. Direct surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) spectroscopy of nucleic acids: from fundamental studies to real-life applications[J]. Chem Soc Rev,2018,47(13):4909-4923. doi: 10.1039/C7CS00809K [2] PILOT R, SIGNORINI R, DURANTE C, et al. A review on surface-enhanced Raman scattering[J]. Biosensors,2019,9(2):57. doi: 10.3390/bios9020057 [3] ZONG C, XU M X, XU L J, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for bioanalysis: reliability and challenges[J]. Chem Rev,2018,118(10):4946-4980. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00668 [4] WU M R, LI H, LV D Y, et al. Dynamic-SERS spectroscopy for the in situ discrimination of xanthine analogues in ternary mixture[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem,2017,409(23):5569-5579. doi: 10.1007/s00216-017-0495-3 [5] ZHU Q X, CAO Y B, CAO Y Y, et al. Rapid on-site TLC-SERS detection of four antidiabetes drugs used as adulterants in botanical dietary supplements[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem,2014,406(7):1877-1884. doi: 10.1007/s00216-013-7605-7 [6] SMITH R, WRIGHT K L, ASHTON L. Raman spectroscopy: an evolving technique for live cell studies[J]. Analyst,2016,141(12):3590-3600. doi: 10.1039/C6AN00152A [7] BUTLER H J, ASHTON L, BIRD B, et al. Using Raman spectroscopy to characterize biological materials[J]. Nat Protoc,2016,11(4):664-687. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.036 [8] ZHANG Y, ZHAO S J, ZHENG J K, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) combined techniques for high-performance detection and characterization[J]. Trac Trends Anal Chem,2017,90:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2017.02.006 [9] NIE S, EMORY S R. Probing single molecules and single nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering[J]. Science,1997,275(5303):1102-1106. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5303.1102 [10] XIE X H, PU H B, SUN D W. Recent advances in nanofabrication techniques for SERS substrates and their applications in food safety analysis[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr,2018,58(16):2800-2813. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1341866 [11] LI P, HE H, LIN D Y, et al. Highly sensitive detection of an antidiabetic drug as illegal additives in health products using solvent microextraction combined with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Analyst,2019,144(24):7406-7411. doi: 10.1039/C9AN01688K [12] ZHANG D, LIANG P, YE J M, et al. Detection of systemic pesticide residues in tea products at trace level based on SERS and verified by GC-MS[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem,2019,411(27):7187-7196. doi: 10.1007/s00216-019-02103-7 [13] SONG D, YANG R, LONG F, et al. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) detection of environmental pollutants[J]. J Environ Sci (China),2019,80:14-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.07.004 [14] BARHOUMI A, ZHANG D M, TAM F, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of DNA[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2008,130(16):5523-5529. doi: 10.1021/ja800023j [15] MA H, TANG X F, LIU Y W, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering for direct protein function investigation: controlled immobilization and orientation[J]. Anal Chem,2019,91(14):8767-8771. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01956 [16] GAO W C, LI B, YAO R Z, et al. Intuitive label-free SERS detection of bacteria using aptamer-based in situ silver nanoparticles synthesis[J]. Anal Chem,2017,89(18):9836-9842. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01813 [17] HE X N, WANG Y N, WANG Y, et al. Accurate quantitative detection of cell surface sialic acids with a background-free SERS probe[J]. Talanta,2020,209:120579. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120579 [18] BROSSEAU C L, GAMBARDELLA A, CASADIO F, et al. Ad-hoc surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy methodologies for the detection of artist dyestuffs: thin layer chromatography-surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and in situ on the fiber analysis[J]. Anal Chem,2009,81(8):3056-3062. doi: 10.1021/ac802761v [19] LIAO W, LU X N. Determination of chemical hazards in foods using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy coupled with advanced separation techniques[J]. Trends Food Sci Technol,2016,54:103-113. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgs.2016.05.020 [20] ANSARI S A, MOHAPATRA P K. A review on solid phase extraction of actinides and lanthanides with amide based extractants[J]. J Chromatogr A,2017,1499:1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2017.03.035 [21] YU S H, LIU Z G, LI H W, et al. Combination of a graphene SERS substrate and magnetic solid phase micro-extraction used for the rapid detection of trace illegal additives[J]. Analyst,2018,143(4):883-890. doi: 10.1039/C7AN01547J [22] WANG J, RIOS A, LISOVA K, et al. High-throughput radio-TLC analysis[J]. Nucl Med Biol,2020,82-83:41-48. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2019.12.003 [23] HEMDAN ABOU-TALEB N, MAHMOUD EL-ENANY N, TAWFIK EL-SHERBINY D, et al. Digitally enhanced thin layer chromatography for simultaneous determination of norfloxacin and tinidazole with the aid of Taguchi orthogonal array and desirability function approach: Greenness assessment by analytical Eco-Scale[J]. J Sep Sci,2020,43(6):1195-1202. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201900997 [24] CIURA K, DZIOMBA S, NOWAKOWSKA J, et al. Thin layer chromatography in drug discovery process[J]. J Chromatogr A,2017,1520:9-22. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2017.09.015 [25] CHEN J, ABELL J, HUANG Y W, et al. On-chip ultra-thin layer chromatography and surface enhanced Raman spectrosco-py[J]. Lab Chip,2012,12(17):3096-3102. doi: 10.1039/c2lc40221a [26] HERMAN K, MIRCESCU N E, SZABO L, et al. In situ silver spot preparation and on-plate surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection in thin layer chromatography separation[J]. J Appl Spectrosc,2013,80(2):311-314. doi: 10.1007/s10812-013-9765-9 [27] TAN A L, ZHAO Y, SIVASHANMUGAN K, et al. Quantitative TLC-SERS detection of histamine in seafood with support vector machine analysis[J]. Food Control,2019,103:111-118. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.03.032 [28] GEIMAN I, LEONA M, LOMBARDI J R. Application of Raman spectroscopy and surface-enhanced Raman scattering to the analysis of synthetic dyes found in ballpoint pen inks[J]. J Forensic Sci,2009,54(4):947-952. doi: 10.1111/j.1556-4029.2009.01058.x [29] MARGHANY K A, ABDELSALAM R A, HADDAD G M. HPLC method transfer study for simultaneous determination of seven angiotensin II receptor blockers[J]. J Sep Sci,2020,43(8):1398-1405. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201900534 [30] NARUKAWA T, IWAI T, CHIBA K. Simultaneous speciation analysis of inorganic arsenic and methylmercury in edible oil by high-performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Talanta,2020,210:120646. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120646 [31] SHENG R S, NI F, COTTON T M. Determination of purine bases by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography using real-time surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Anal Chem,1991,63(5):437-442. doi: 10.1021/ac00005a010 [32] WANG W, XU M M, GUO Q H, et al. Rapid separation and on-line detection by coupling high performance liquid chromatography with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. RSC Adv,2015,5(59):47640-47646. doi: 10.1039/C5RA05562H [33] GAO Y L, HUANG X X, ZHU Y B, et al. A brief review of monoclonal antibody technology and its representative applications in immunoassays[J]. J Immunoassay Immunochem,2018,39(4):351-364. doi: 10.1080/15321819.2018.1515775 [34] LIU J, YU Q Q, ZHAO G Y, et al. A novel immunochromatographic assay using ultramarine blue particles as visible label for quantitative detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen[J]. Anal Chim Acta,2020,1098:140-147. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.11.037 [35] CHO I H, BHANDARI P, PATEL P, et al. Membrane filter-assisted surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy for the rapid detection of E. coli O157: H7 in ground beef[J]. Biosens Bioelectron,2015,64:171-176. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.08.063 [36] GUARROTXENA N, LIU B, FABRIS L, et al. Antitags: nanostructured tools for developing SERS-based ELISA analogs[J]. Adv Mater,2010,22(44):4954-4958. doi: 10.1002/adma.201002369 [37] PEKDEMIR M E, ERTÜRKAN D, KÜLAH H, et al. Ultrasensitive and selective homogeneous sandwich immunoassay detection by Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS)[J]. Analyst,2012,137(20):4834-4840. doi: 10.1039/c2an35471c [38] LI M, BANERJEE S R, ZHENG C, et al. Ultrahigh affinity Raman probe for targeted live cell imaging of prostate cancer[J]. Chem Sci,2016,7(11):6779-6785. doi: 10.1039/C6SC01739H [39] CHÁVEZ J L, LYON W, KELLEY-LOUGHNANE N, et al. Theophylline detection using an aptamer and DNA-gold nanoparticle conjugates[J]. Biosens Bioelectron,2010,26(1):23-28. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2010.04.049 [40] WANG G Q, WANG Y Q, CHEN L X, et al. Nanomaterial-assisted aptamers for optical sensing[J]. Biosens Bioelectron,2010,25(8):1859-1868. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2009.11.012 [41] LUO L H, ZHANG F, CHEN C Y, et al. Molecular imprinting resonance light scattering nanoprobes based on pH-responsive metal-organic framework for determination of hepatitis A virus[J]. Mikrochim Acta,2020,187(2):140. doi: 10.1007/s00604-020-4122-1 [42] SAYLAN Y, YILMAZ F, ÖZGÜR E, et al. Molecular imprinting of macromolecules for sensor applications[J]. Sensors (Basel),2017,17(4):E898. doi: 10.3390/s17040898 [43] YıLMAZ E, GARIPCAN B, PATRA H K, et al. Molecular imprinting applications in forensic science[J]. Sensors (Basel),2017,17(4):E691. doi: 10.3390/s17040691 [44] CHEN S N, DONG L J, YAN M, et al. Rapid and sensitive biomarker detection using molecular imprinting polymer hydrogel and surface-enhanced Raman scattering[J]. R Soc Open Sci,2018,5(1):171488. doi: 10.1098/rsos.171488 [45] GAO F, GRANT E, LU X N. Determination of histamine in canned tuna by molecularly imprinted polymers-surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Anal Chim Acta,2015,901:68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.10.025 [46] KAMRA T, XU C G, MONTELIUS L, et al. Photoconjugation of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman detection of propranolol[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces,2015,7(49):27479-27485. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b09500 [47] BOYD-MOSS M, BARATCHI S, DI VENERE M, et al. Self-contained microfluidic systems: a review[J]. Lab Chip,2016,16(17):3177-3192. doi: 10.1039/C6LC00712K [48] CHO Y, LEE S A, CHEW Y L, et al. Multimodal stimulation in a microfluidic device facilitates studies of interneurons in sensory integration in C. elegans[J]. Small,2020,16(10):e1905852. doi: 10.1002/smll.201905852 [49] HIDI I J, JAHN M, WEBER K, et al. Droplet based microfluidics: spectroscopic characterization of levofloxacin and its SERS detection[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys,2015,17(33):21236-21242. doi: 10.1039/C4CP04970E [50] WU L, WANG Z Y, ZONG S F, et al. Rapid and reproducible analysis of thiocyanate in real human serum and saliva using a droplet SERS-microfluidic chip[J]. Biosens Bioelectron,2014,62:13-18. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.06.026 [51] NIE B, MASYUKO R N, BOHN P W. Correlation of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and laser desorption-ionization mass spectrometry acquired from silver nanoparticle substrates[J]. Analyst,2012,137(6):1421-1427. doi: 10.1039/c2an15790j [52] CYRIAC J, LI G T, COOKS R G. Vibrational spectroscopy and mass spectrometry for characterization of soft landed polyatomic molecules[J]. Anal Chem,2011,83(13):5114-5121. doi: 10.1021/ac200118f [53] LUDWIG M, HIMMEL D, HILLEBRECHT H. GIAO versus GIPAW: comparison of methods to calculate 11B NMR shifts of icosahedral Closo-heteroboranes toward boron-rich borides[J]. J Phys Chem A,2020,124(11):2173-2185. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.9b06582 [54] FANG C, XIE Y J, JOHNSTON M R, et al. SERS and NMR studies of typical aggregation-induced emission molecules[J]. J Phys Chem A,2015,119(29):8049-8054. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.5b05478 [55] MUHAMADALI H, SUBAIHI A, MOHAMMADTAHERI M, et al. Rapid, accurate, and comparative differentiation of clinically and industrially relevant microorganisms via multiple vibrational spectroscopic fingerprinting[J]. Analyst,2016,141(17):5127-5136. doi: 10.1039/C6AN00883F [56] XIE Y F, LI P, ZHANG J, et al. Comparative studies by IR, Raman, and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of azodicarbonamide, biurea and semicarbazide hydrochloride[J]. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc,2013,114:80-84. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.05.055 [57] SHI Y, CAI M J, ZHOU L L, et al. Measurement of mechanical properties of naked cell membranes using atomic force microscope puncture test[J]. Talanta,2020,210:120637. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120637 [58] BONDŽIĆ A M, LESKOVAC A R, PETROVIĆ S Ž, et al. Conjugates of gold nanoparticles and antitumor gold(III) complexes as a tool for their AFM and SERS detection in biological tissue[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2019,20(24):E6306. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246306 -





 下载:
下载: