-
烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸(NAD)是一种经典辅酶,对线粒体电子转移反应至关重要,在许多生物学功能中起着关键作用[1]。烟酰胺单核苷酸(NMN)是NAD生物合成的关键中间体。NMN在心脑血管疾病、肝肾功能、血管和内皮功能,以及免疫和炎症、衰老等各类疾病治疗方面都具有相当强的潜力[2],常被人称为“万能药”。NMN能够通过口服、静脉注射、腹腔注射(小鼠)等多种给药途径进入体内,通常具有较高的安全性。在急性毒性实验中,小鼠连续7 d给予最大灌胃剂量和饱和浓度的NMN,每天1次,耐受性良好,除血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶略有升高外,其余生物标志物基本保持不变,而相同处理条件下的比格犬,会有轻度的肌酐和尿酸升高[3];在长期给药实验中,小鼠连续12个月给予100和300 mg/kg的NMN,均未出现不良反应[4]。在出血性休克治疗方面,对出血性休克大鼠模型,术前连续5 d的NMN饮水给药和术后静脉推注NMN均能缩短休克复苏时间和提高复苏后的存活率[5]。据报道[6-9],在炎症治疗方面,NMN及相关代谢产物烟酰胺核糖、烟酰胺都具有一定抗炎作用。
内毒素休克是由感染引起的全身炎症反应综合征,会导致各系统衰竭,包括循环系统、呼吸系统、血液系统,损害肝脏和肾脏功能[10]。相关研究显示,最佳的治疗时间在发病6 h内,能够提高患者的生存率,降低病死率[11]。目前临床内毒素休克以药物治疗为主(如血管活性药物、激素、抗菌素等)[12],同时辅以液体复苏、脑神经保护、吸氧等常规治疗。为便于对内毒素休克开展研究治疗,通常使用LPS进行内毒素休克动物造模,LPS是G-菌细胞壁外膜上的主要成分,也叫内毒素,能引起严重的炎症级联反应,是G-菌的主要致病成分之一[13]。
目前,NMN对内毒素休克的治疗作用尚未知。本研究旨在探究NMN对LPS诱导的内毒素休克小鼠模型的死亡率影响,为阐明NMN在内毒素休克治疗方面的作用提供线索。
-
烟酰胺单核苷酸[NMN,纯度≥95%,−25~−15 ℃保存,邦泰生物工程(深圳)有限公司];烟酰胺单核苷酸[NMN~,纯度≥95%,2~8 ℃保存,尚科生物医药(上海)有限公司];脂多糖(LPS,美国Sigma公司);BT25S精密电子天平[赛多利斯科学仪器(北京)有限公司];独立通风系统(上海鸣励实验室科技发展有限公司)。
-
SPF级8周龄雄性C57BL/6J小鼠(西普尔-必凯实验动物有限公司)。实验前在相对洁净的环境下使用独立通风系统,将动物适应性饲养2周。期间动物自由饮水、进食。笼具内温度22~26 ℃、湿度40%~70%,笼内维持正压20~25 Pa,每小时换气次数60~70次,室内明暗交替12 h(8:00~20:00照明)。
-
根据不同实验目的,将C57BL/6J小鼠随机分为给药组和对照组。腹腔注射LPS(10 mg/kg)进行内毒素休克造模,在造模前或者造模后进行NMN腹腔注射给药,给药方式分为单次给药和两次给药方式。具体分成5个实验:①造模后0.5 h给药,剂量为10、30、100、300 mg/kg;②造模前0.5 h给药,剂量为30、100、300、600 mg/kg;③造模后0.5 h和12 h两次给药,每次300 mg/kg;④造模后0.5 h和12 h分别用2种不同厂家的NMN给药,剂量为300 mg/kg;⑤造模前0.5 h用不同厂家的NMN给药,剂量为300 mg/kg。
-
使用Log-rank检验,对给药组和溶剂对照组的生存曲线进行比较,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义,使用GraphPad Prism8软件对数据进行统计分析。
-
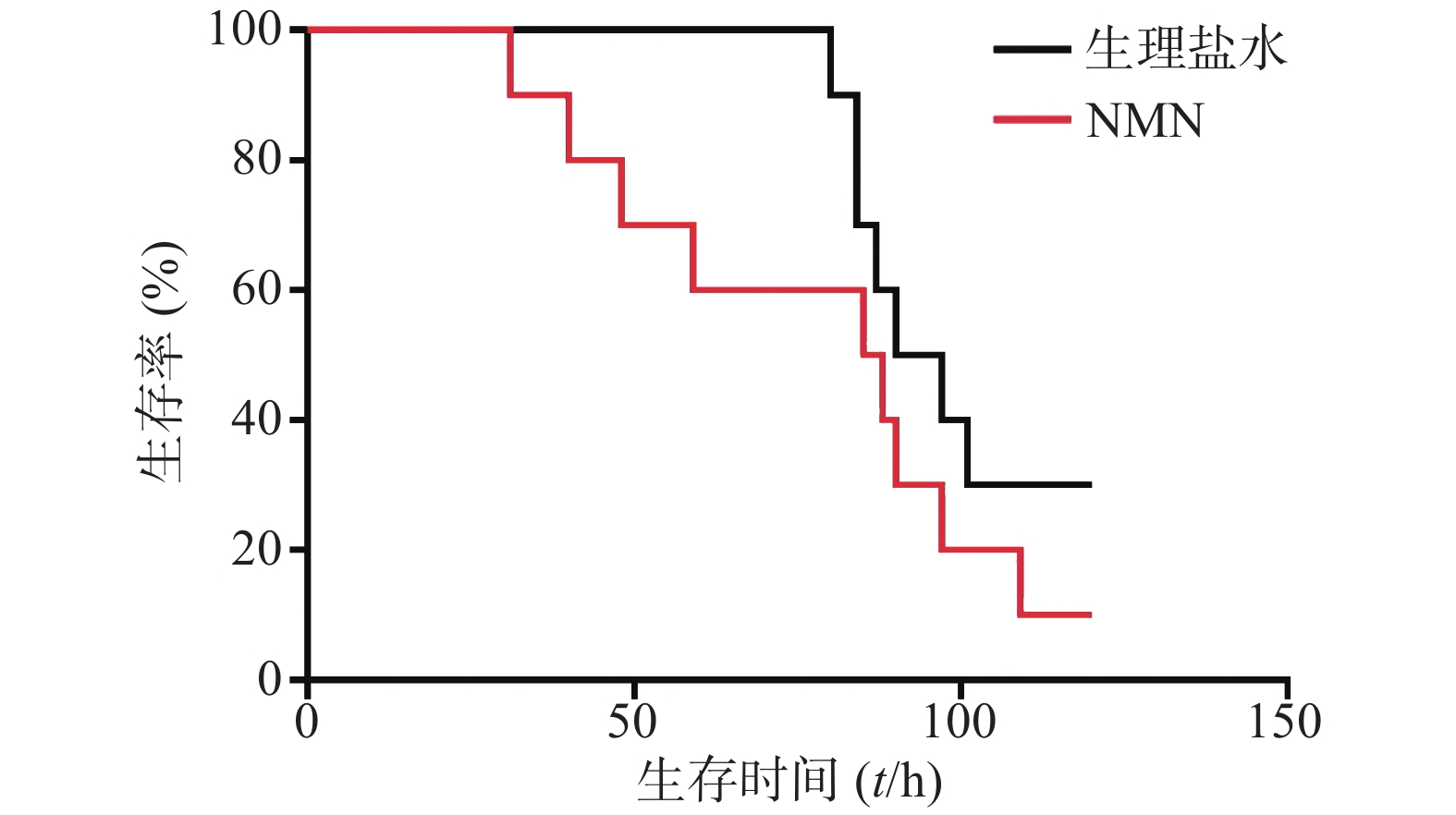
如图1所示,LPS造模后0.5 h给予300 mg/kg NMN组小鼠首次出现死亡的时间比生理盐水组更早,整个观察期间给药组小鼠死亡的总体趋势要稍快于生理盐水组,且在观察末期存活的动物数量略少。但两组生存曲线之间比较无统计学差异(P=0.2161)。因此,LPS造模后0.5 h给予300 mg/kg NMN不具有治疗内毒素休克的作用,甚至有轻微增加内毒素休克死亡率的趋势。
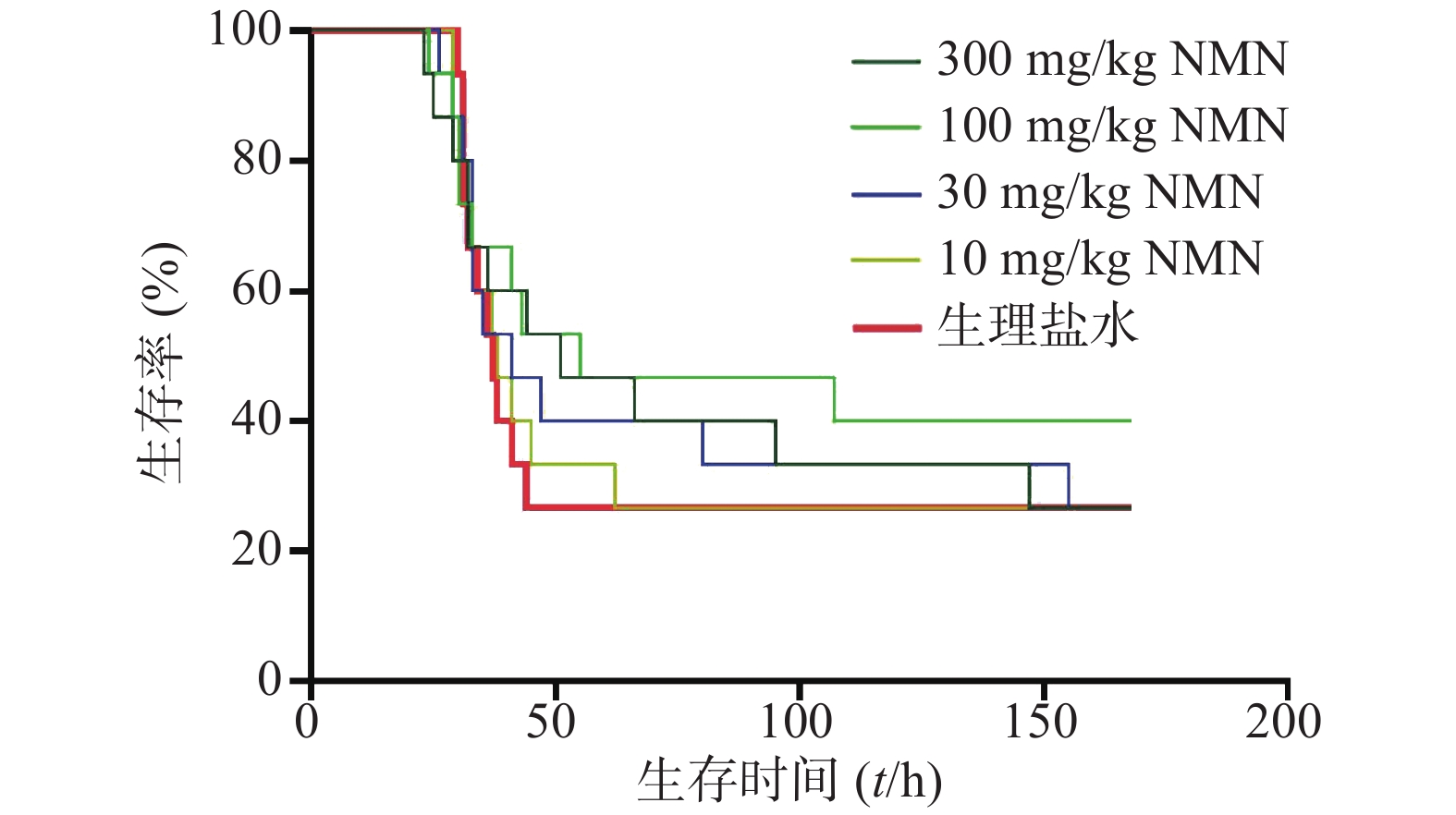
实验进一步考察了LPS造模后0.5 h给予多个不同剂量NMN对内毒素休克死亡率的影响,如图2所示,与生理盐水组相比,10、30、100、300 mg/kg NMN给药组的小鼠首次出现死亡的时间均接近,各组中位生存时间:300、100、30、10 mg/kg给药组分别为51、55、41和38 h,生理盐水组为37 h。整个观察期间NMN给药各组死亡速度较生理盐水组稍缓,其中放缓趋势最明显的是100 mg/kg剂量组,但均不具有统计学意义(P=0.4334),表明小鼠在LPS造模后0.5 h单次给予NMN不能改善内毒素休克死亡率或减缓死亡速度。
-
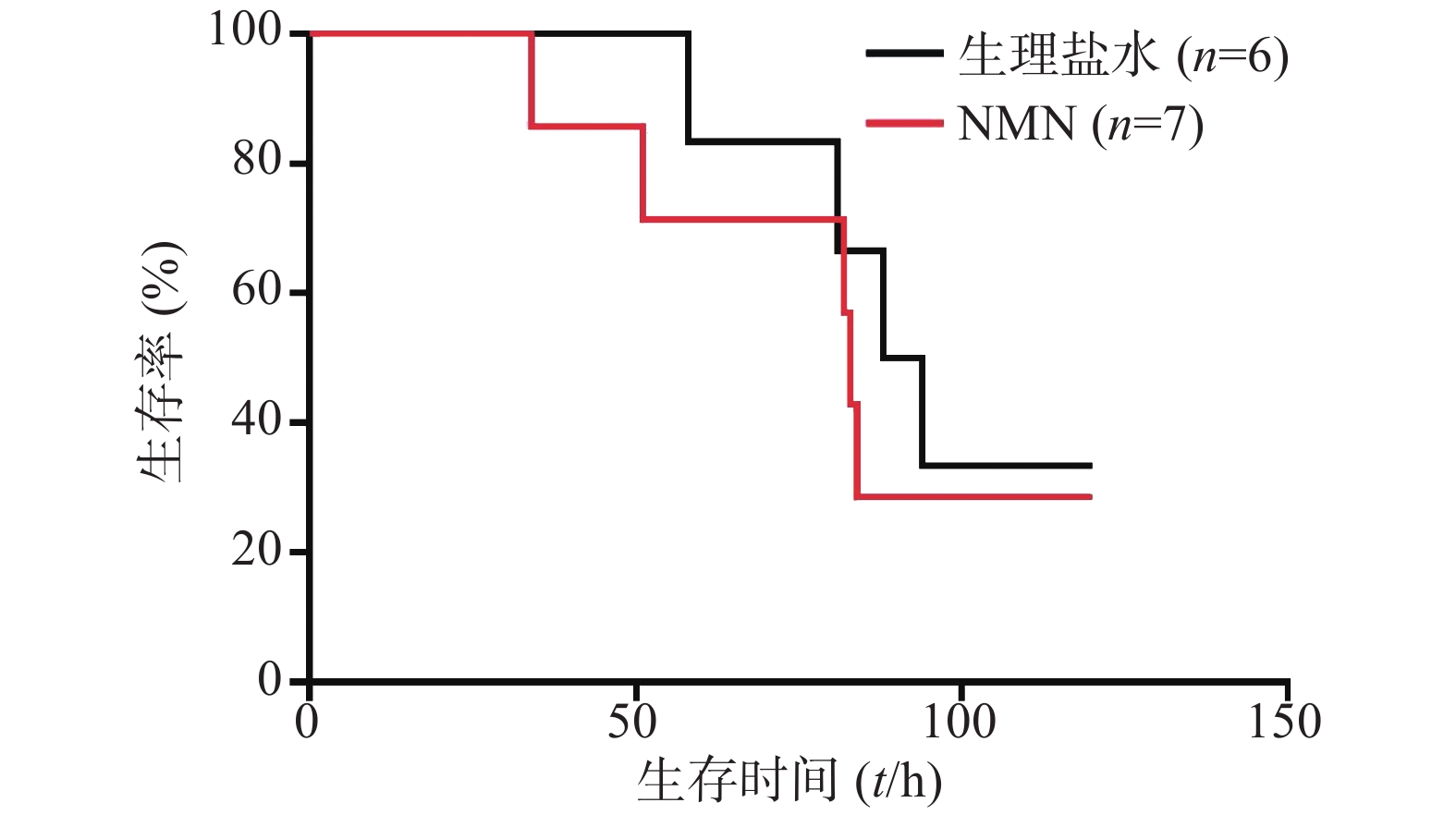
在LPS造模前0.5 h进行NMN给药。如图3所示,300 mg/kg NMN预防给药组小鼠首次出现死亡的时间稍早于生理盐水组,而2组死亡的总体趋势相近,前者的中位生存时间为83 h,后者为91 h,生存曲线比较无统计学差异(P=0.5946),故LPS造模前0.5 h给予300 mg/kg NMN不能改善内毒素休克小鼠的死亡率,不具有防治作用。
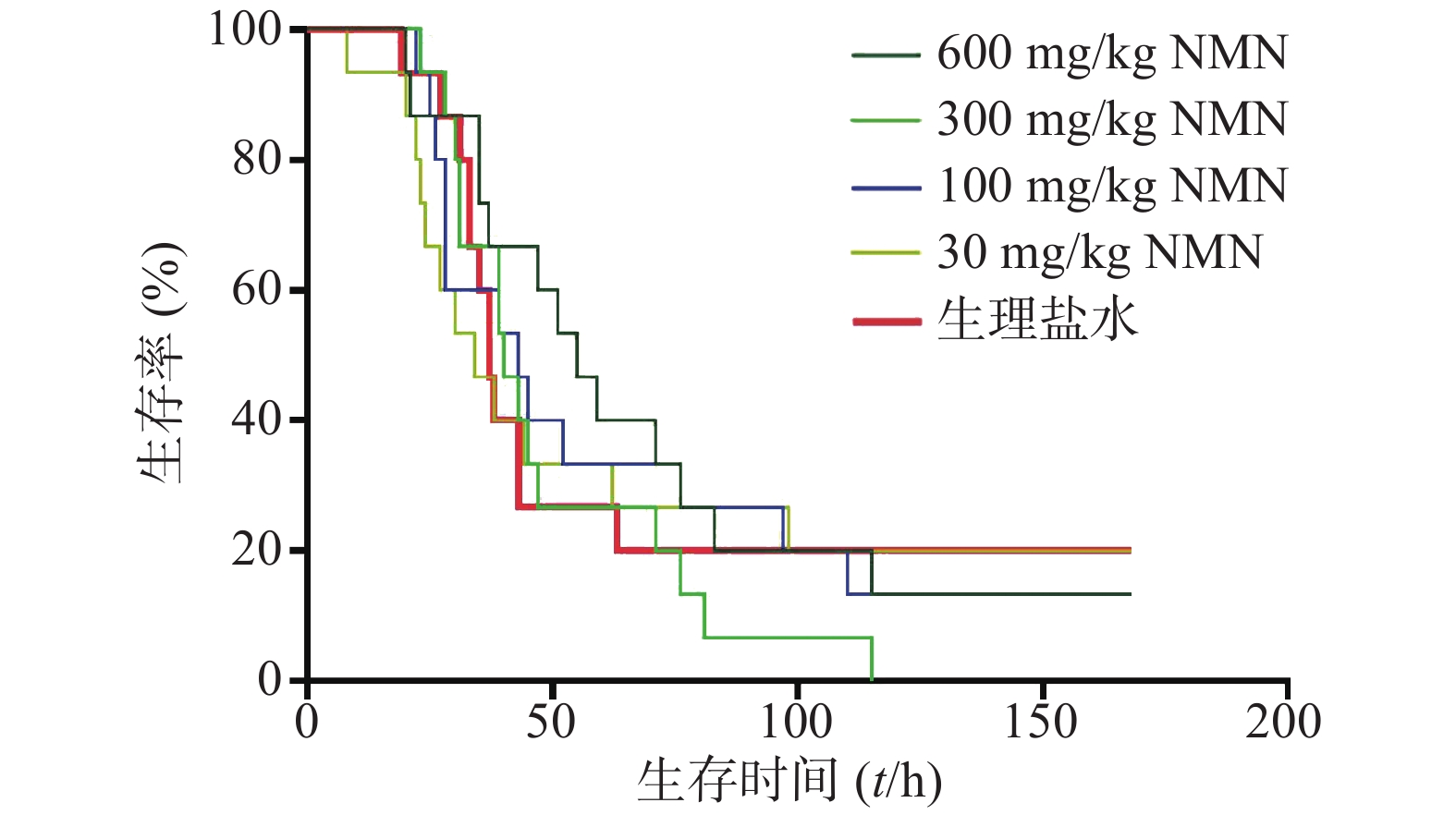
随后又进行多个不同剂量NMN单次预给药实验。如图4所示,NMN 30、100、300、600 mg/kg组与生理盐水组小鼠首次出现死亡的时间均相近,之后各组死亡趋势也类似,各组中位生存时间分别是:NMN给药组30 mg/kg为34 h、100 mg/kg为43 h、300 mg/kg为40 h、600 mg/kg为55 h,生理盐水组为37 h,各组生存曲线也无统计学意义。结果表明,在造模前进行NMN单次预给药对于LPS构建的内毒素休克模型无明显改善生存率的作用。
-
考虑到NMN在体内的代谢速度较快,能够迅速入血进入各个组织器官并代谢为活性分子NAD,而NAD被证明在多种炎症性疾病中具有保护作用,因此,观察NMN的2次给药是否对内毒素休克有治疗效果。
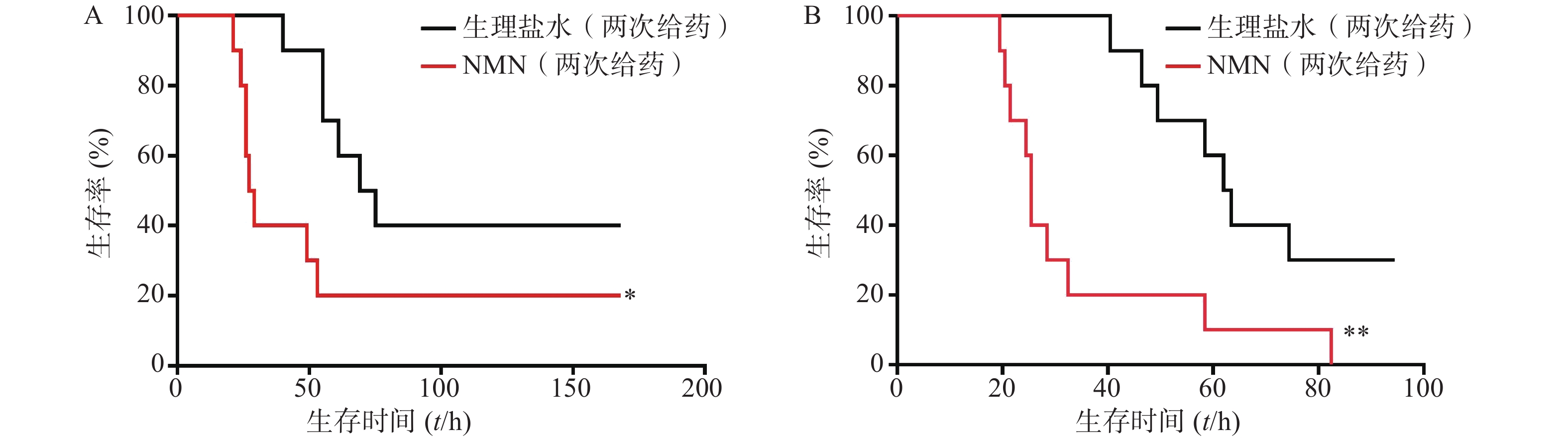
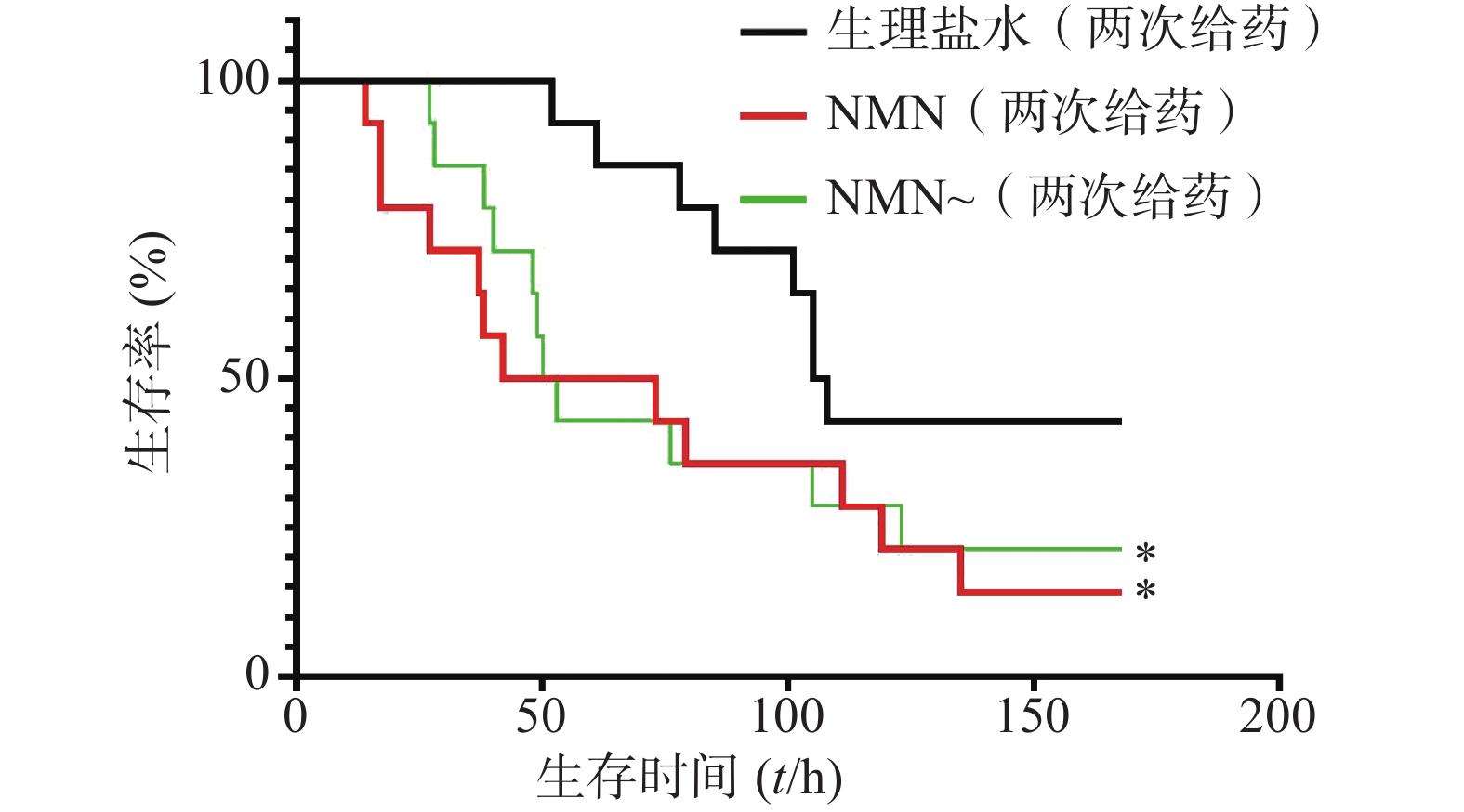
如图5所示,2次重复实验结果均表明,LPS造模后0.5 h和12 h,给予2次NMN(每次300 mg/kg)治疗组小鼠其首次出现死亡的时间早于生理盐水组;之后,NMN治疗组小鼠死亡速度明显快于对照组,且观察末期NMN治疗组小鼠存活率不及对照组一半,2次重复实验的生存曲线间均具有统计学差异(P=0.0404;P=0.0038)。因此,该结果表明,LPS造模后2次NMN给药明显增加小鼠内毒素休克死亡率。
-
不同厂家生产的NMN因药物纯度、杂质成分不同等,可能导致治疗效果有差别。为排除非药物分子本身因素如厂家生产工艺因素,进一步明确上述NMN治疗内毒素休克的作用,接着引入另一厂家生产的NMN(以下均简称NMN~),并同时测试比较两家NMN产品治疗内毒素休克的效果。
实验首先对LPS造模后0.5 h和12 h的2次给予NMN(每次300 mg/kg)增加内毒素休克死亡率的作用进行了验证。如图6所示,NMN给药组和NMN~给药组这2组小鼠首次出现死亡的时间和观察末期小鼠存活数都接近,整个观察期小鼠死亡趋势非常相似,与生理盐水对照组相比,两组都明显加重内毒素休克小鼠的死亡率,与对照组的生存曲线间均有统计学差异(P=0.0499;P=0.0260)。3组中位生存时间分别是:NMN给药组57.5 h、NMN~给药组51.5 h、生理盐水组106.5 h。此外,该结果与上述单个NMN产品连续2次给药效果类似(图5)。因此,两家NMN产品效果基本相同,也进一步证明了LPS造模后0.5 h和12 h的2次给予NMN(每次300 mg/kg)确实可加重内毒素休克病情,加速小鼠的死亡。
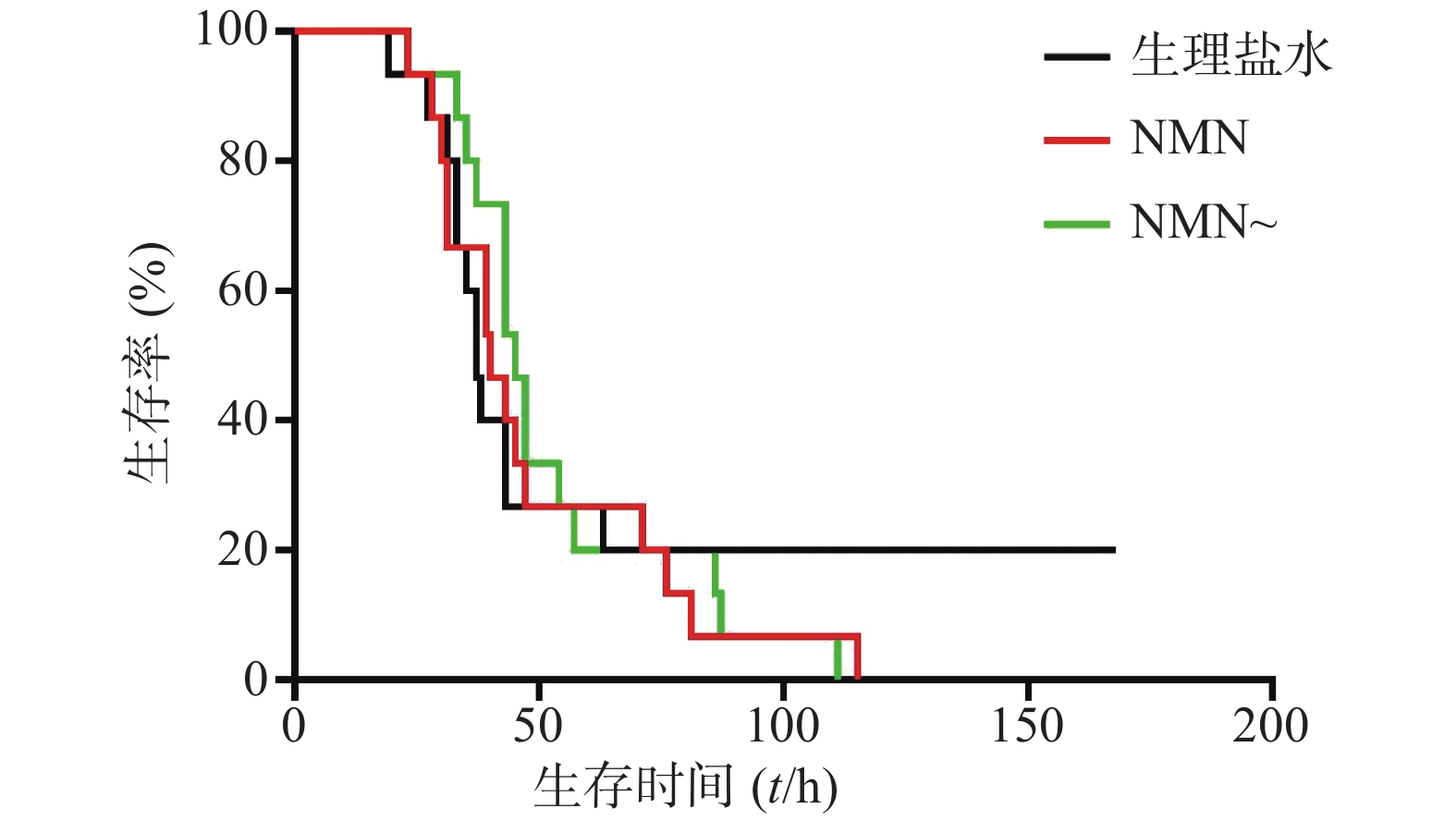
最后,实验又考察了两家NMN产品预防给药效果,即在LPS造模前0.5 h进行NMN或NMN~给药。如图7所示,NMN组、NMN~组、生理盐水组3组小鼠首次出现死亡的时间及之后每组小鼠死亡的速度都相近,直至每组均剩20%小鼠存活(第71小时)。之后,生理盐水组小鼠不再死亡,而NMN组、NMN~组小鼠陆续死亡殆尽。3组中位生存时间分别是:NMN给药组40 h、NMN~给药组45 h、生理盐水组37 h。可见,两家NMN产品作用相似,对LPS所致的内毒素休克无治疗效果,且与生理盐水组比较时均有加重内毒素休克死亡率的趋势,但是均无统计学意义(P=0.6447;P=0.9725)。该结果与上述NMN单次预防给药的实验结果相一致(图3和图4)。
-
目前NMN是保健品领域的开发热点,以抗衰老以及各类疾病治疗作用为目的,在国内外已有不少人开始服用NMN[14]。但是NMN对内毒素休克的作用尚未知,对患有这种疾病的患者能否服用NMN亦不清楚。
根据现有的研究报道,NMN在小鼠疾病模型其腹腔注射给药的有效剂量为10~600 mg/kg[2, 4]。本实验中,我们测试了不同NMN剂量尤其是300 mg/kg时对小鼠内毒素休克的治疗效果,结果显示,小鼠在LPS造模后0.5 h或造模前0.5 h单次给予不同剂量NMN均无明显改善生存率的作用,不具有治疗效果;甚至在LPS造模后两次NMN给药明显增加小鼠内毒素休克死亡率。为排除厂家生产工艺等因素,我们又同时用两个厂家生产的NMN产品进行实验,以重复上述结果,最终再次证明LPS造模后两次给予NMN确实可加速小鼠的死亡,增加死亡率。
因此,本次实验结果表明,NMN在某些疾病尚未证明其安全性的情况下,应谨慎推广,尤其是内毒素休克的患者,应慎用甚至是禁用NMN治疗。
Effect of nicotinamide mononucleotide on mortality of mice with endotoxic shock
-
摘要:
目的 探究烟酰胺单核苷酸(NMN)对脂多糖(LPS)诱导的内毒素休克小鼠死亡率的影响。 方法 将10周龄C57BL/6J雄性小鼠随机分组,均腹腔注射LPS(10 mg/kg)造模。NMN腹腔注射给药,分为3种方式:①造模后0.5 h给药,剂量为10、30、100、300 mg/kg;②造模前0.5 h给药,剂量为30、100、300、600 mg/kg;③造模后0.5 h和12 h两次给药,每次300 mg/kg。观察记录每组小鼠的死亡情况,并绘制生存曲线。 结果 与溶剂对照组相比,造模后0.5 h或造模前0.5 h给予不同剂量NMN,均不能改善小鼠死亡率或延缓死亡时间;造模后0.5 h和12 h两次给予NMN会加速小鼠死亡,增加小鼠死亡率。两个厂家的NMN产品效果类似。 结论 NMN对LPS诱导的内毒素休克小鼠不具有治疗作用,小鼠内毒素休克发生后进行NMN多次给药会增加死亡率。 Abstract:Objective To study the effect of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) on the mortality of the lipopoly-saccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxic shock mouse model. Methods 10-week-old C57BL/6J male mice were randomly divided into groups, and were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with LPS (10 mg/kg) to induce endotoxic shock models. NMN was i.p. injected in three ways: (1) 0.5 h after modeling, doses of 10, 30, 100 and 300 mg/kg; (2) 0.5 h before modeling, doses of 30, 100, 300 and 600 mg/kg; or (3) 0.5 and 12 h after modeling, dose of 300 mg/kg each time. The death times of each group were recorded, and the survival curves were drawn. Results Compared with the solvent control group, NMN at different doses given 0.5 h after or before modeling didn’t improve the survival rate or delay the death time of endotoxic shock mice; But when given at 0.5 and 12 h 300 mg/kg after modeling, NMN accelerated the death of mice and increased the mortality of mice. NMN products by two manufacturers showed similar effects. Conclusion NMN has no therapeutic effect on LPS-induced endotoxic shock, and repeated administration of NMN after endotoxic shock will increase the mortality. -
Key words:
- nicotinamide mononucleotide /
- lipopolysaccharide /
- endotoxic shock /
- mortality
-
放线菌以其能产生结构新颖且有良好生物活性的先导化合物而备受关注[1],一直被认为是天然药物的重要生产者,其主要结构类型包括聚酮、生物碱、多肽和萜烯类化合物等,同时涵盖了多种多样的生物活性如抗菌、抗寄生虫、免疫调节、抗炎、抗癌等[2-4],这突显了放线菌具有不可预估的药物开发潜力。
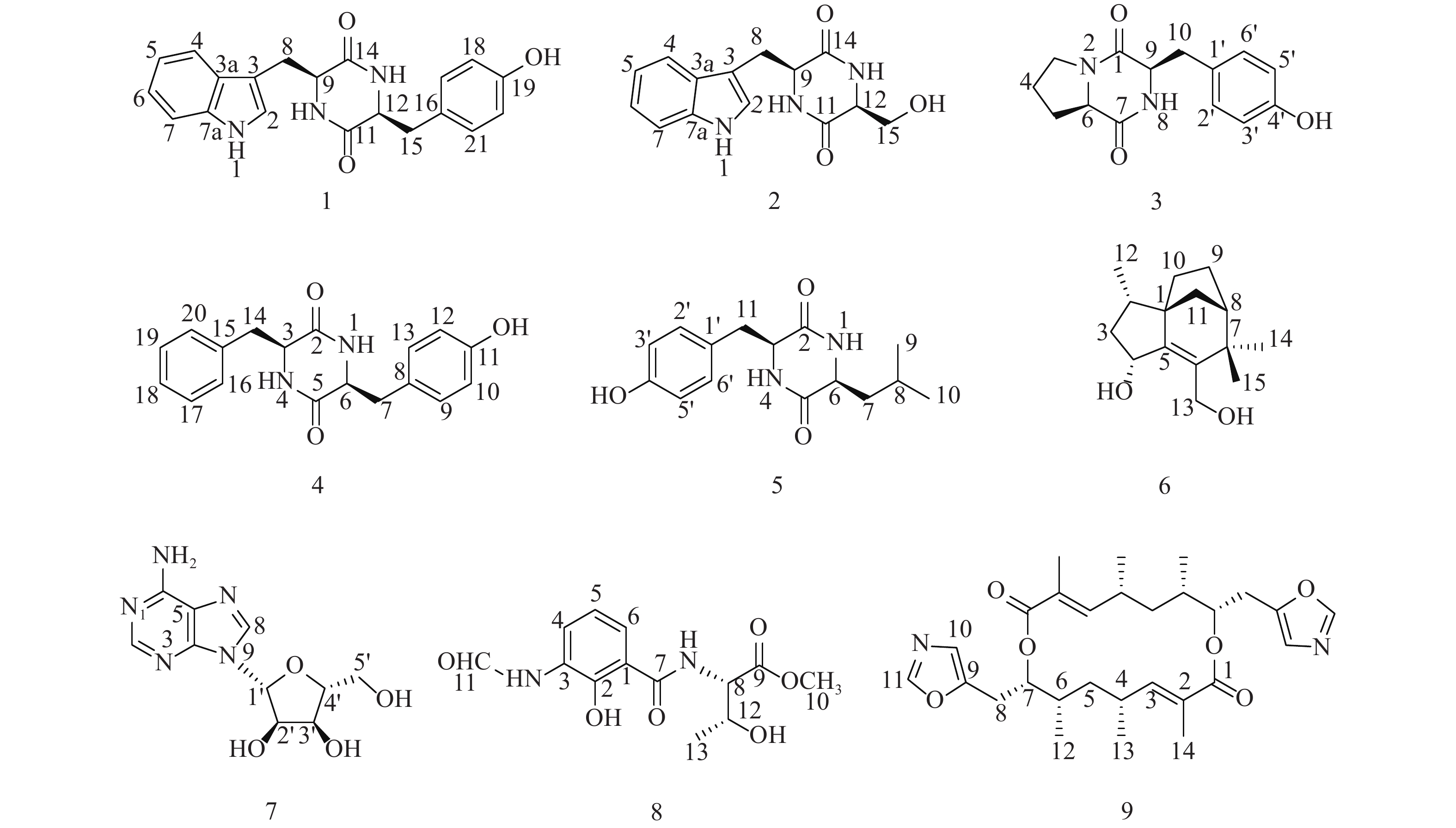
随着研究的深入,陆地和普通环境中的资源日趋枯竭,很多微生物及其次生代谢产物被重复开发和提取分离,发现新活性分子的几率愈来愈低,开发创新药物的难度越来越大[5-6];而极地极端的生态环境造就的微生物具有产生更为特别的化学骨架和活性次生代谢产物的能力,是新型药源分子的重要来源。本文以采自北极楚克奇海域海绵共附生放线菌Streptomyces sp. LHW11-07为研究对象,从其发酵浸膏中分离鉴定了9个单体化合物1~9(图1),其中化合物1和2为该属内首次分离得到。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 实验仪器与试剂
AMX-600型核磁共振仪(德国Bruker公司);Xevo G2-XS Q-TOF液质联用仪、1525/2996, 2998型高效液相色谱仪(美国Waters公司);半制备型HPLC色谱柱(Atlantis Prep T3,美国Waters公司;YMC C18,日本YMC公司);中压柱色谱仪(法国Interchim公司);恒温振荡培养箱(上海一恒科学仪器有限公司);N-1000型旋转蒸发仪(上海爱郎仪器有限公司);反相ODS硅胶和Sephadex LH-20柱色谱填料(Pharmacia公司);正相硅胶(200-300目)和TLC薄层板(烟台江友硅胶开发有限公司);分析级试剂(上海化学试剂公司);色谱级试剂(德国Merck公司);氘代试剂(美国剑桥同位素实验室公司)。
1.2 菌株的来源及鉴定
菌株分离于北极海域来源的海绵样本,经16S rRNA基因序列鉴定为Streptomyces sp.,编号为LHW11-07,菌种保存于上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院药学部海洋药物研究中心。
1.3 菌株的大发酵
培养基为ISP2:葡萄糖(4 g/L)、酵母提取物(4 g/L)、麦芽糖提取物(10 g/L)以及海盐(25 g/L),加水溶解后调节pH为7.2~7.4,分装后高压灭菌20 min (121 ℃),冷却备用。
挑取Streptomyces sp. LHW11-07单菌落至1级种子培养基里(100 ml ISP2培养基至250 ml三角瓶),置于30 ℃,220 r/min的恒温摇床培养3 d,得1级种子液;将1级种子液按5%接种量接到2级种子培养基里(150 ml ISP2培养基至500 ml三角瓶),置于30 ℃,220 r/min的恒温摇床培养3 d,得2级种子液;将2级种子液按5%接种量接到大发酵培养基里(700 ml ISP2培养基至2 L三角瓶),置于30 ℃,220 r/min的恒温摇床培养7 d,共得到发酵液50 L。
1.4 发酵产物的提取与分离
菌株培养7 d后,用等体积的乙酸乙酯萃取3次,合并乙酸乙酯提取液,减压浓缩得粗浸膏9.8 g。粗浸膏先经凝胶柱分离,二氯甲烷:甲醇(1∶1)的混合溶剂进行洗脱,得到组份Fr.1~Fr.7。
组份Fr.4经正相中压柱色谱分离(二氯甲烷:甲醇100:0~0:100),得到组份Fr.4a~Fr.4j。组份Fr.4d再经反相中压柱色谱分离(10%~100%乙腈水),得到组份Fr.4d1~Fr.4d8,Fr.4d2和Fr.4d3用反相半制备HPLC纯化(35%甲醇水,YMC C18),分别得到化合物1 (12 mg, tR=26 min)和2 (47.6 mg, tR=30 min);Fr.4d6用反相半制备HPLC纯化(49%甲醇水,YMC C18),得到化合物3 (8.4 mg, tR=23 min)和4 (2.0 mg, tR=30 min);组份Fr.4g再经凝胶柱纯化,洗脱剂为正己烷:二氯甲烷:甲醇(4∶5∶1),得到组份Fr.4g1~Fr.4g11,其中Fr.4g3用反相半制备HPLC纯化(25%乙腈水,YMC C18),得到化合物5 (1.2 mg, tR=18 min)。
组份Fr.7经反相中压柱色谱分离(10%~100%乙腈水),得到组份Fr.7A~Fr.7D。组份Fr.7A用反相半制备HPLC纯化(20%乙腈水,YMC C18),得到化合物6 (18 mg, tR=19 min)和7 (3.4 mg, tR=25 min);组份Fr.7B经正相中压柱分离(石油醚:丙酮100:0~0:100),得到组份Fr.7B1~Fr.7B9,Fr.7B4用反相半制备HPLC纯化(88%乙腈水,Atlantis Prep T3),得到化合物8 (12 mg, tR=23 min)和9 (8.4 mg, tR=26 min)。
2. 结构鉴定
化合物1:淡黄色固体,ESI-MS显示准分子离子峰m/z 372 [M+Na]+。1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO)显示在低场区有吲哚环的特征信号δH 7.00 (1H, s, H-2),7.49 (1H, d, J=8.0 Hz, H-4),7.02 (1H, t, J=7.6 Hz, H-5),7.05 (1H, t, J=7.6 Hz, H-6),7.32 (1H, d, J=8.0 Hz, H-7);4个活泼氢质子信号δH 10.89 (1H, d, J=2.6 Hz, NH-1),7.83 (1H, d, J=3.0 Hz, NH-10),7.62 (1H, d, J=3.0 Hz, NH-13),9.20 (1H, s, OH-19);4个芳香质子信号δH 6.53 (2H, d, J=8.4 Hz, H-17, H-21),6.59 (2H, d, J=8.4 Hz, H-18, H-20),提示分子中有1个对位二取代的苯环;在高场区有两组亚甲基质子信号δH 2.80 (1H, dd, J=14.5, 4.5 Hz, H-8),2.43 (1H, ov, H-8),δH 1.83 (1H, dd, J=13.4, 6.9 Hz, H-15),2.47 (1H, ov, H-15),两个次甲基质子信号δH 4.01 (1H, m, H-9),3.95 (1H, m, H-12)。13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO)结合DEPT谱表明其有20个碳信号,2个酮羰基碳δC 166.7,166.2,14个芳香碳,2个亚甲基碳δC 30.0,40.0和2个次甲基碳δC 55.9,55.2。对其碳信号进行归属:δC 118.7 (C-2)、108.9 (C-3)、127.5 (C-3a)、118.4 (C-4)、120.8 (C-5)、124.3 (C-6)、111.3 (C-7)、136.0 (C-7a)、30.0 (C-8)、55.9 (C-9)、166.7 (C-11)、55.2 (C-12)、166.2 (C-14)、40.1 (C-15)、126.4 (C-16)、130.7 (C-17, C-21)、114.9 (C-18, C-20)、156.0 (C-19)。以上数据与文献[7]对比基本一致,故确定为cyclo-(L-Tyr-L-Trp)。
化合物2:淡黄色固体,ESI-MS显示准分子离子峰m/z 274 [M+H]+。1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO)发现其与化合物1一样有吲哚环的特征信号δH 7.09 (1H, s, H-2),7.52 (1H, d, J = 7.9 Hz, H-4),6.99 (1H, t, J = 7.8 Hz, H-5),7.02 (1H, t, J = 7.8 Hz, H-6),7.30 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-7);3个活泼氨基质子信号δH 10.87 (1H, s, NH-1),δH 8.30 (1H, m, NH-10),7.85 (1H, d, J = 2.9 Hz, NH-13);两组亚甲基质子信号δH 3.21 (1H, m, H-8),3.13 (1H, m, H-8),δH 3.65 (1H, m, H-15),3.05 (1H, m, H-15),两个次甲基质子信号δH 4.87 (1H, m, H-9),4.00 (1H, m, H-12)。13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO)结合DEPT谱表明其有14个碳信号,2个酮羰基碳δC 167.2,165.7,8个芳香碳,2个亚甲基碳δC 63.0,30.3和2个次甲基碳δC 57.3,55.5。对其碳信号进行归属:δC 127.6 (C-2)、111.2 (C-3)、136.0 (C-3a)、118.6 (C-4)、120.8 (C-5)、124.0 (C-6)、118.3 (C-7)、109.0 (C-7a)、30.3 (C-8)、57.3 (C-9)、167.2 (C-11)、55.5 (C-12)、165.7 (C-14)、63.0 (C-15)。以上数据与文献[8]对比基本一致,故确定为cyclo-(L-Trp-L-Ser)。
化合物3:白色固体,ESI-MS显示准分子离子峰m/z 261 [M+H]+。1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO)提示有2个活泼氢质子信号δH 7.87 (1H, s, NH-8),9.22 (1H, s, OH-4’);1组对位二取代的苯环芳香质子信号δH 7.04 (2H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, H-2’, H-6’),6.63 (2H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, H-3’, H-5’);2个次甲基质子信号δH 4.24 (1H, t, J = 8.2 Hz, H-6),4.03 (1H, dd, J = 9.9, 2.9 Hz, H-9);4组亚甲基质子信号δH 3.42 (1H, m, H-3),3.24 (1H, m, H-3),1.73 (2H, m, H2-4),2.00 (1H, m, H-5),1.41 (1H, m, H-5),2.93 (2H, m, H2-10)。13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO)结合DEPT谱表明其有14个碳信号,2个酮羰基碳δC 168.9,165.1,6个芳香碳,2个次甲基碳δC 58.4,56.0以及4个亚甲基碳δC 44.6,34.7,27.8,21.9。对其碳信号进行归属:δC 165.1 (C-1)、44.6 (C-3)、21.9 (C-4)、27.8 (C-5)、58.4 (C-6)、168.9 (C-7)、56.0 (C-9)、34.7 (C-10)、127.0 (C-1’)、130.8 (C-2’, C-6’)、114.8 (C-3’, C-5’)、155.9 (C-4’)。以上数据与文献[9]对比基本一致,故确定为cyclo-(D-Tyr-D-Pro)。
化合物4:白色固体,ESI-MS显示准分子离子峰m/z 311 [M+H]+。1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO)显示3个活泼氢质子信号δH 9.30 (1H, s, OH-11),7.84 (2H, t, J = 2.9 Hz, NH-1, NH-4);9个芳香区质子信号:4个归为1组对位二取代苯环δH 6.85 (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz, H-9, H-13),6.65 (2H, t, J = 8.5 Hz, H-10, H-12),5个归为1组单取代苯环δH 7.20 (1H, t, J = 7.6 Hz, H-18),7.04 (2H, d, J = 6.9 Hz, H-16, H-20),7.28 (2H, t, J = 7.6 Hz, H-17, H-19);2组亚甲基质子信号δH 2.58 (1H, dd, J = 13.6, 5.0 Hz, H-7),2.20 (1H, d, J = 6.5 Hz, H-7),2.19 (2H, dd, J = 13.6, 6.5 Hz, H2-14),2个次甲基质子信号δH 3.95 (1H, m, H-3),3.90 (1H, m, H-6)。13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO)结合DEPT谱显示其有18个碳信号,2个酮羰基碳δC 166.2,166.2,12个芳香碳,2个亚甲基碳δC 40.1,38.5和2个次甲基碳δC 55.7,55.4。对其碳信号进行归属:δC 166.2 (C-2)、55.7 (C-3)、166.3 (C-5)、55.4 (C-6)、40.1 (C-7)、126.5 (C-8)、130.8 (C-9, C-13)、115.0 (C-10, C-12)、156.1 (C-11)、38.5 (C-14)、136.7 (C-15)、129.7 (C-16, C-20)、128.2 (C-17, C-19)、126.4 (C-18)。以上数据与文献[10]对比基本一致,故确定为cyclo-(L-Tyr-L-Phe)。
化合物5:白色固体,ESI-MS显示准分子离子峰m/z 277 [M+H]+。1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO)显示3个活泼氢质子信号δH 9.22 (1H, s, OH-4’),8.02 (2H, dd, J = 5.6, 2.5 Hz, NH-1, NH-4);4个芳香质子信号δH 6.90 (2H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, H-2’, H-6’),6.64 (2H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, H-3’, H-5’),提示分子中有1个对位二取代苯环;3个次甲基质子信号δH 4.06 (1H, q, J = 3.3 Hz, H-3),3.44 (1H, m, H-6),1.43 (1H, ov, H-8),2个亚甲基质子信号δH 1.43 (1H, m, H-7),1.23 (1H, m, H-7),2.69 (1H, q, J = 13.6, 4.8 Hz, H-11),3.01 (1H, q, J = 13.7, 3.7 Hz, H-11)以及2个末端甲基质子信号δH 0.63 (6H, ov, H3-9, H3-10)。13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO)结合DEPT谱显示其有15个碳信号,2个酮羰基碳δC 166.2,167.4,6个芳香碳,2个亚甲基碳δC 43.7,37.7,3个次甲基碳δC 55.7,52.3,21.4以及2个甲基碳δC 22.9,22.8。对其碳信号进行归属:δC 166.2 (C-2)、55.7 (C-3)、167.4 (C-5)、52.3 (C-6)、43.7 (C-7)、21.4 (C-8)、22.9 (C-9)、22.8 (C-10)、37.7 (C-11)、125.8 (C-1’)、131.2 (C-2’, C-6’)、114.8 (C-3’, C-5’)、156.4 (C-4’)。以上数据与文献[11]对比基本一致,故确定为cyclo-(L-Tyr-L-Leu)。
化合物6:白色固体,ESI-MS显示准分子离子峰m/z 259 [M+Na]+。1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO)显示有2个活泼氢质子信号δH 5.05 (1H, d, J = 4.5 Hz, OH-4)和4.39 (1H, q, J = 4.0 Hz, OH-13),3个甲基质子信号δH 0.88 (3H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H3-12),0.98 (3H, s, H3-14)和δH 1.05 (3H, s, H3-15),5对亚甲基质子信号δH 2.14 (1H, m, H-3),1.23 (1H, m, H-3),1.74 (1H, m, H-9),1.60 (1H, m, H-9),1.44 (3H, m, H2-10, H-11),1.32 (1H, d, J = 10.4 Hz, H-11),3.95 (2H, m, H2-13),3个次甲基质子信号δH 1.68 (1H, m, H-2),4.57 (1H, m, H-4),1.77(1H, m, H-8)。13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO)结合DEPT谱共显示有15个碳信号,包括4个季碳δC 52.1,150.1,136.7,39.8;3个次甲基碳δC 35.2,69.8,46.4;5个亚甲基碳δC 42.4,23.8,28.7,36.4,57.1以及3个甲基碳δC 13.7,29.1,24.4。对其碳信号进行归属:δC 52.1 (C-1)、35.2 (C-2)、42.4 (C-3)、68.9 (C-4)、150.1 (C-5)、136.7 (C-6)、39.8 (C-7)、46.4 (C-8)、23.8 (C-9)、28.7 (C-10)、36.4 (C-11)、13.7 (C-12)、57.1 (C-13)、29.1 (C-14)、24.4 (C-15)。以上数据与文献[12]对比基本一致,故确定为albaflavenol B。
化合物7:白色结晶固体,ESI-MS显示准分子离子峰m/z 268 [M+H]+。1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO)可看出其有13个氢信号,包括5个活泼氢质子信号δH 3.56 (2H, m, NH2),5.49 (1H, s, OH-5’),5.36 (1H, t, J = 4.9 Hz, OH-2’)和5.23 (1H, s, OH-3’),4个连氧次甲基质子信号δH 4.56 (1H, s, H-2’),4.14 (1H, s, H-3’),3.96 (1H, m, H-4’)和5.90 (1H, d, J = 5.8 Hz, H-1’),1组亚甲基信号δH 3.66 (2H, m, H2-5’)以及2个低场区的烯氢质子信号δH 8.37 (1H, s, H-8)和8.21 (1H, s, H-2)。13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO)显示其共有10个碳信号,结合DEPT谱可推测有3个芳香季碳δC 149.9,119.8,154.3,2个连氮的芳香次甲基碳δC 151.7,138.6,4个次甲基碳δC 87.8,73.5,70.5,85.7,1个亚甲基碳δC 61.5。对其碳信号进行归属:δC 151.7 (C-2)、149.9 (C-4)、119.8 (C-5)、154.3 (C-6)、138.6 (C-8)、87.8 (C-1’)、73.5 (C-2’)、70.5 (C-3’)、85.7 (C-4’)、61.5 (C-5’)。以上数据与文献[13]对比基本吻合,故确定为β-adenosine。
化合物8:绿色无定型固体,ESI-MS显示准分子离子峰m/z 297 [M+H]+。1H-NMR (600 MHz, MeOD)显示有12个氢信号,包括1个活泼氢质子信号δH 8.37 (1H, s, H-11),1个甲氧基质子信号δH 3.79 (3H, s),1个甲基质子信号δH 1.25 (3H, d, J = 6.4 Hz, H3-13),3个低场区的芳香氢质子信号δH 8.31 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-4),6.92 (1H, t, J = 8.0 Hz, H-5)和7.65 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-6),以及2个次甲基质子信号δH 4.74 (1H, d, J = 3.2 Hz, H-8)和4.40 (1H, m, H-12),后与文献[14]对比发现其有4个活泼氢质子信号没有显示出来,而根据相关化学位移可确定其是同一个已知化合物。13C-NMR (150 MHz, MeOD)显示有13个碳信号,结合DEPT谱可推测有6个芳香碳δC 123.4,119.4,126.2,128.2,152.5,115.6,2个羰基碳δC 171.8,172.4,而δC 162.1为醛基碳,2个次甲基碳δC 59.4,68.4,1个甲基碳δC 20.5,以及1个甲氧基碳δC 52.9。对其碳信号进行归属:δC 115.6 (C-1)、152.5 (C-2)、128.2 (C-3)、126.2 (C-4)、119.4 (C-5)、123.4 (C-6)、171.8 (C-7)、59.4 (C-8)、172.4 (C-9)、52.9 (C-10)、162.1 (C-11)、68.4 (C-12)、20.5 (C-13)。以上数据与文献[14]对比基本吻合,故确定为N-formylantimyic acid methyl ester。
化合物9:白色粉末状固体,ESI-MS显示准分子离子峰m/z 499 [M+H]+。1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO)显示有19个氢信号:δH 8.20 (1H, s, H-11),6.82 (1H, s, H-10),6.32 (1H, dd, J = 10.5, 1.3 Hz, H-3),5.01 (1H, m, H-7),2.99 (1H, dd, J = 2.5, 15.8 Hz, H-8),2.80 (1H, dd, J = 10.3, 15.6 Hz, H-8),2.58 (1H, m, H-4),1.66 (1H, m, H-5),1.65 (3H, s, 2-Me),1.27 (1H, m, H-6),1.25 (1H, m, H-5),1.06 (3H, d, J = 6.5 Hz, 4-Me)和0.95 (3H, d, J = 5.9 Hz, 6-Me)。而13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO)结合DEPT谱显示只有14个碳信号:δC 166.0 (C-1),126.8 (C-2),147.4 (C-3),30.7 (C-4),37.6 (C-5),35.1 (C-6),74.5 (C-7),24.0 (C-8),149.4 (C-9),122.9 (C-10),151.3 (C-11),12.7 (2-Me),21.1 (4-Me)和16.2 (6-Me),说明这个化合物可能是一个具有对称结构的二聚体,通过与文献[15]中化合物conglobatin A对比后发现两者波谱数据完全吻合,故最终确定为conglobatin A。
3. 讨论
自上世纪发现青霉素以来,微生物中活性次生代谢产物一直是药物先导化合物的重要来源之一,据统计1940年—2019年间,科学家从微生物中开发出293种治疗不同疾病的临床药物[16]。但随着研究的深入,很多微生物及其次生代谢产物存在被重复开发和提取分离的问题,加之多重耐药性的产生,迫使人们需要开拓新的制造药物的微生物来源[5-6],而其中极地微生物资源是珍贵而特殊的。来自极地海洋等特殊生态环境的生物往往具有比陆地生物更为丰富的代谢途径和功能基因簇,增加了产生结构新颖且功能独特的次生代谢物的可能性。极地生物以微生物和一些能适应极端条件的海洋生物为主,然而与已报道的大量极地微生物相比,鲜有微生物活性天然产物相关研究报道,因此,极地微生物极具研究价值[17-18]。
笔者以一株采自北极海域海绵共附生放线菌Streptomyces sp. LHW11-07为研究对象,从其发酵浸膏中分离得到9个单体化合物1~9,包括环二肽化合物1~5,倍半萜化合物6,核苷类化合物7,以及两个其他结构类型化合物8和9,其中化合物1和2是首次分离于Streptomyces放线菌,而这些化合物的生物活性还有待进一步探究;本研究进一步丰富了该属放线菌的化学多样性,同时,为高值化开发利用极地微生物这一国家战略资源提供了物质基础和理论依据。
据文献报道,化合物1对所测试的病原性细菌和真菌均具有一定的对抗作用[19],化合物2测试了4种肿瘤细胞均无明显的细胞毒性[20],化合物3对海胆Strongylocentrotus intermedius胚胎具有细胞毒活性[9],化合物5具有抗炎活性并对H1N1和RSV病毒有一定的杀伤作用[21],化合物7作为一种内源性嘌呤核苷,具有降低血压、抑制血小板聚焦、舒张血管、减慢心律等生理活性[22],而化合物9可抑制癌细胞株的增殖,在体外对Trypanosoma brucei brucei GUTat 3.1表现出抗锥虫体活性等[23]。
-
[1] YOSHINO J, BAUR J A, IMAI S I. NAD+ intermediates: the biology and therapeutic potential of NMN and NR[J]. Cell Metab,2018,27(3):513-528. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.11.002 [2] HONG W Q, MO F, ZHANG Z Q, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide: a promising molecule for therapy of diverse diseases by targeting NAD+ metabolism[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol,2020,8:246. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00246 [3] YOU Y N, GAO Y, WANG H, et al. Subacute toxicity study of nicotinamide mononucleotide via oral administration[J]. Front Pharmacol,2020,11:604404. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.604404 [4] MILLS K F, YOSHIDA S, STEIN L R, et al. Long-term administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates age-associated physiological decline in mice[J]. Cell Metab,2016,24(6):795-806. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.013 [5] SIMS C A, GUAN Y X, MUKHERJEE S, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide preserves mitochondrial function and increases survival in hemorrhagic shock[J]. JCI Insight,2018,3(17):120182. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.120182 [6] MÉNDEZ-LARA K A, LETELIER N, FARRE N, et al. Nicotinamide prevents apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein oxidation, inflammation and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice[J]. Antioxidants,2020,9(11):1162. doi: 10.3390/antiox9111162 [7] MEHMEL M, JOVANOVIĆ N, SPITZ U. Nicotinamide riboside-the current state of research and therapeutic uses[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(6):1616. doi: 10.3390/nu12061616 [8] KISS T, NYÚL-TÓTH Á, BALASUBRAMANIAN P, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation promotes neurovascular rejuvenation in aged mice: transcriptional footprint of SIRT1 activation, mitochondrial protection, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects[J]. Geroscience,2020,42(2):527-546. doi: 10.1007/s11357-020-00165-5 [9] HONG G L, ZHENG D, ZHANG L L, et al. Administration of nicotinamide riboside prevents oxidative stress and organ injury in Sepsis[J]. Free Radic Biol Med,2018,123:125-137. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.05.073 [10] 盛杰, 张福琴, 魏萍, 等. 抗菌药物诱导内毒素释放及抗内毒素药物研究进展[J]. 医药导报, 2004, 23(4):252-253. [11] 金泓, 赖旭东, 关信民, 等. 血必净注射液在脓毒血症治疗中的疗效观察[J]. 中医临床研究, 2017, 9(36):71-73. [12] 王洪亮, 章志丹, 黄伟. 拯救脓毒症运动: 脓毒症与感染性休克治疗国际指南(2016)的解读与展望[J]. 中华重症医学电子杂志, 2017, 3(1):26-32. [13] 张含飞, 张金龙, 王振华. 抗内毒素药物的研究进展[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2008, 29(1):57-60. [14] IRIE J, INAGAKI E, FUJITA M, et al. Effect of oral administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide on clinical parameters and nicotinamide metabolite levels in healthy Japanese men[J]. Endocr J,2020,67(2):153-160. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ19-0313 -





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载: