-
麻醉、精神药品,若不规范地连续使用,易产生依赖性,若是管理不当,会造成严重的社会危害。为了提升医院麻醉精神药品的管理质量,上海市《医疗机构麻醉药品、第一类精神药品管理规定》沪卫规[2019]008号文件第三章第十三条明确指出:专用账册可以采用医疗机构计算机管理系统自动生成表单。可见,电子信息化的管理已成为当下麻醉精神药品管理发展的必然趋势。目前好多医院仍采取人工管理记录,存在药品批号记录混乱、无法监管追溯、药师工作繁琐、耗时费力、准确性低等弊端[1-3]。为进一步加强麻醉、精神药品的监管与使用,东方肝胆外科医院自2020年起使用自主研发的麻醉、精神药品电子信息化程序。笔者通过比较手工账册与电子化账册的相关数据,展现电子化账册在工作效率、“五专”管理规范化、用药监管、用药安全等方面带来的成效,旨在探索电子化账册的实施对麻醉精神药品管理的意义。
-
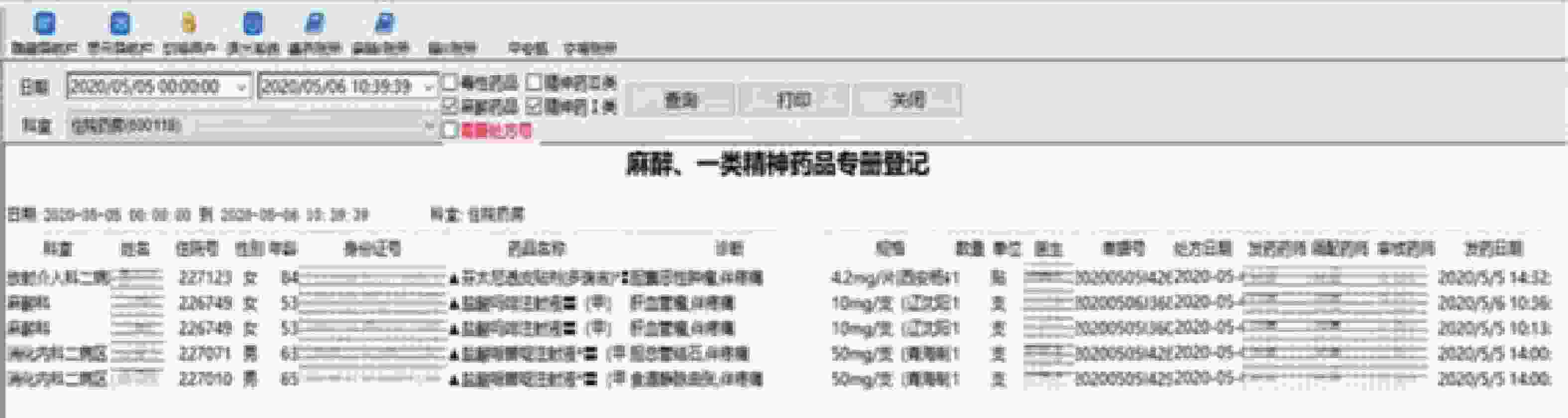
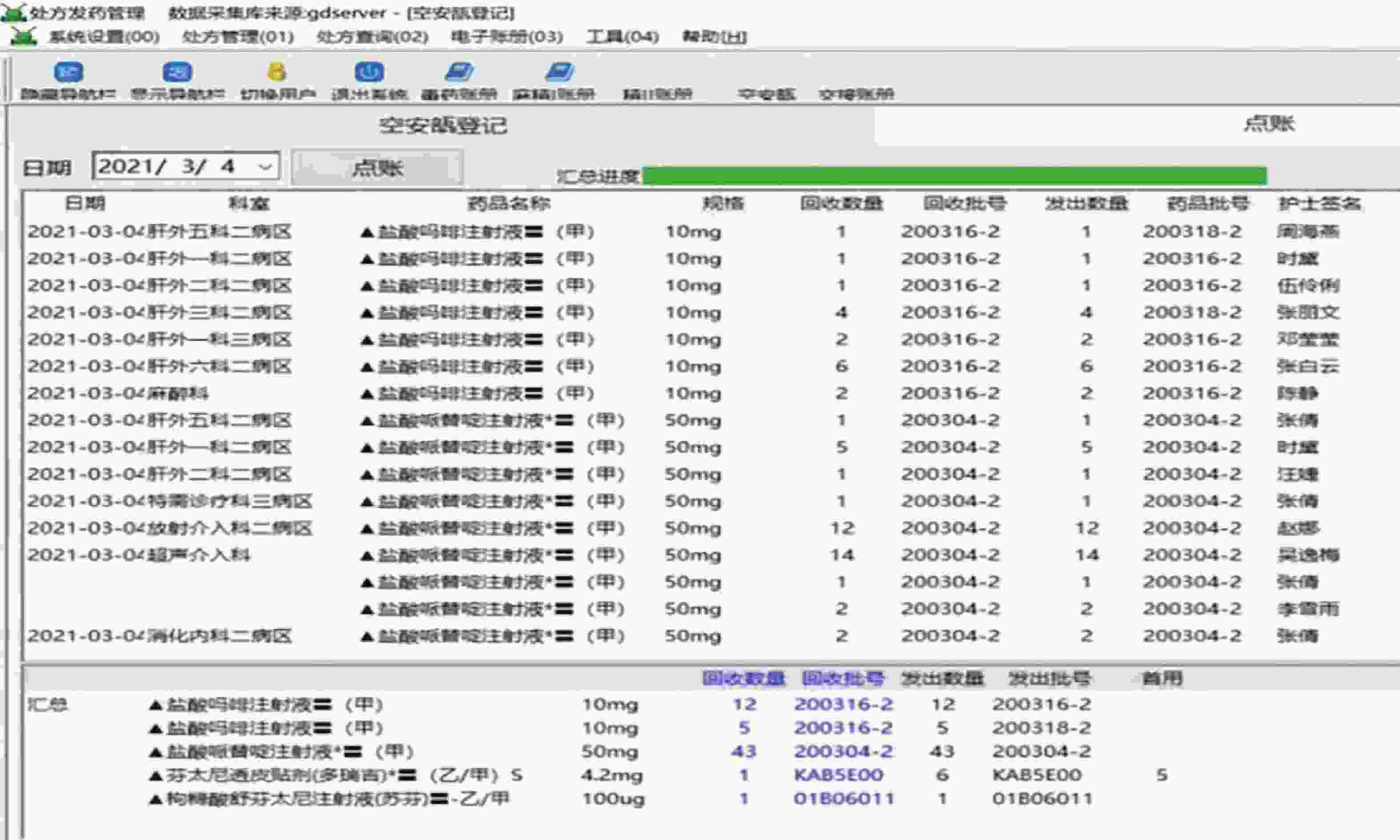
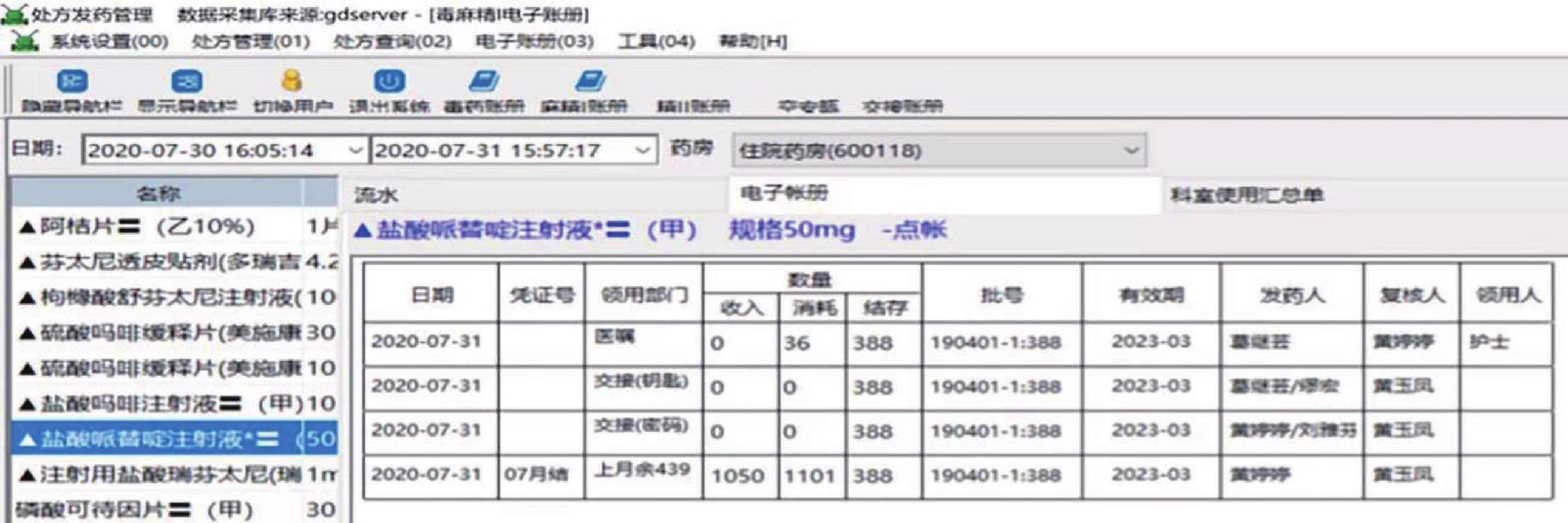
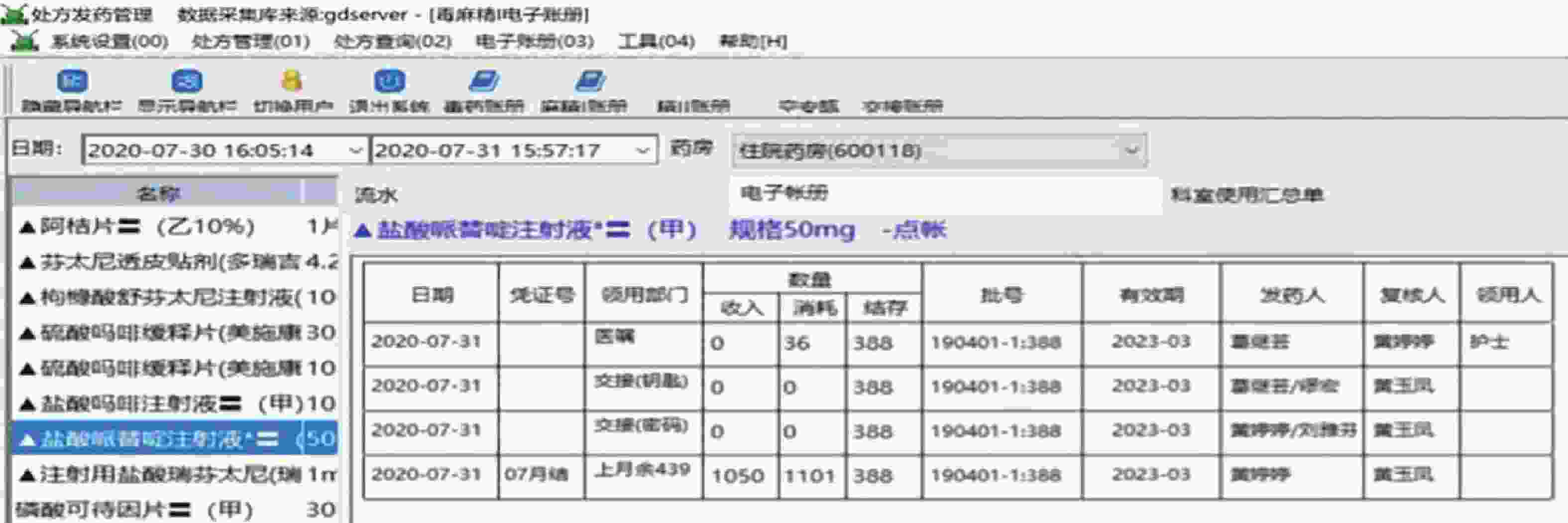
2020年启用由我院自主研发的麻醉精神药品程序,根据工作内容设置做账模块,主要包括8个模块:①日清点记录:打印出的记录单上会显示库存药品的批号、数量及有效期,无需药师进行手写,只需清点库存数量与批号即可。②麻醉药品入库验收专簿:药师利用二维码扫码技术,对药库发来的麻醉药品进行扫描入库操作,随即电脑自动根据药品信息,直接生成《麻醉药品入库验收专簿》,做到实时电子入账,后台记录数据。③电子化专用账册:处方计价时,药师用扫码枪对准所需药品相应的条形码进行扫描出库操作,随即电脑后台记录数据。电脑自动根据当天药品入库、消耗记录,直接生成《麻醉、精神药品专用账册》与《二类精神药品专用账册》做帐单据。并且在电子账册中显示入库、出库、交接、月结等记录,见图1。④电子化专册登记:所有信息无需再转存或导出成二次表格再加工,打印出的内容格式与法规要求一致,同时显示信息与处方信息完全一致。药师只需核对法规规定的14项内容即可(包括第二类精神药品),无需再手抄补足缺项内容,见图2。⑤电子空安瓿、废贴回收记录:计价完毕后,电脑打印二维码,药师将此二维码(包含该患者用药信息)贴于处方背面,随后打开空安瓿、废贴回收界面,将二维码扫入电脑,被认定是该患者的空安瓿、废贴,由于病区备有基数药品,存在先用基数药品的批号、效期与药房库存药品不一致,此时需要药师手工修改回收空安瓿、废贴的批号,以确保回收的批号与患者实际使用的药品批号相一致。另外,为解决人工月结耗时耗力的问题,增加月结统计功能,见图3。⑥加强用药监管:设置医生权限及药品用量限定功能。⑦提高临床用药安全:设置医嘱合理用药审核功能。⑧避免麻醉、精神药品计价程序混乱:建立单独麻醉、精神药品计价界面。
-
收集我院住院药房2019年7月至2019年12月手工账册数据,以及2020年1月至2020年6月电子化账册数据。相关数据包括:每日做账所需时间、每月月结做账所需时间、做账内容正确率统计。麻醉药品专管人员于每日下午16:00~17:30开始做账工作,做账完毕后记录每日做账所需时间。
-
数据采用SPSS 20.0统计软件进行分析,计量资料以(
$\bar x $ ±s)表示,组间比较采用t检验,以P<0.05表示差异具有统计学意义。 -
每日手工账册耗时为(162.8±22.5) min,每日电子化账册耗时为(33.2±7.0) min,两者相比所花时间最大相差159.1 min,明显体现出电子化做账时间快于手工做账时间,具有统计学差异(P<0.05),见表1。
表 1 每日手工账册与电子化账册做账耗时比较
组别 时间 A B C D E F 手工 2019年7—12月 163.5±23.5 154.6±18.7 160.4±22.9 163.5±26.3 168.8±21.1 166.1±20.9 电子 2020年1—6月 32.8±6.9 32.3±6.7 34.6±7.0 35.4±8.1 31.0±5.2 32.8±7.5 t 61.440 P 0.000 注:A-F代表月。手工:A:2019年7月、B:2019年8月、C:2019年9月、D:2019年10月、E:2019年11月、F:2019年12月;电子:A:2020年1月、B:2020年2月、C:2020年3月、D:2020年4月、E:2020年5月、F:2020年6月。 -
月结手工账册耗时为(245.5±7.2) min,月结电子化账册耗时为(46.8±2.5) min,电子化做账时间与手工做账时间最大相差208.4 min,具有显著差异(P<0.001)。
-
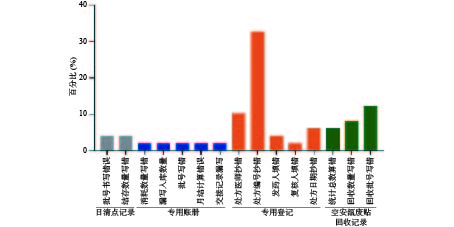
汇总每日手工账册做账错误内容,包括:日清点记录、专用账册、专册登记、空安瓿和废贴回收记录。其中专册登记错误问题占比最高为55.1%,其次空安瓿、废贴回收记录占比26.5%,手工做账正确率为93.34%,
电子化做账正确率为100%。手工做账错误问题分布见图4。
-
每日手工账册内容包括:日清点记录、入库验收专簿、专用账册[4]、专册登记、空安瓿、废贴回收记录、药师交接记录,其中专册登记用时最长,每日平均需要耗时约120 min,最长一次需要花费185.3 min;月末做月结工作还需耗时更多。电子化的实施,显著缩短做账时间,大幅提升药师工作效率。
-
电子化账册中耗时最长且错误率占比最高的是专册登记[5](含14项内容)信息的提取,其正确性与处方信息完全一致,避免人为误差的发生,使电子化账册做账正确率高达100%,促使“五专”管理更规范,药师工作质量有效提升。
-
麻精药品处方中有22项内容需要填写,其中16项信息由电脑自动生成,4项通过敲章签字快速完成,仅剩2项需要医生录入信息,即可快速开具处方,同时支持重复打印功能,若护士或医生将处方遗失,无需重新开具,通过找到历史信息直接打印即可,明显缩短医生开处方的时间。医生通过电脑开具的电子处方,显示的所有信息字体清晰可辨,完全可以避免因人为的笔迹潦草不清,药品名称、规格、用法用量、处方前记填写错误、缺项等[6-7],医生、护士的工作效率得到明显提高。
-
将具备开具麻精药品资格的医师权限进行后台信息维护,无资格医师无法下达医嘱,电脑系统会自动跳出“您无权限开具麻醉、精神药品”。不仅省去药师查找医师权限的时间,还避免人为记忆误差,保证临床用药安全。不仅对医生权限进行信息监管,同时对专管麻精药品的药师,后台也进行数据维护,非麻精小组的药师没有权限进行计价与调配。此外,为了严格控制医生重复开药现象,避免特殊药品流入不法渠道,特地增设2周限量的规则,有效防止患者过度使用或滥用特殊管理药品。
-
条形码技术是迄今为止在自动识别、自动数据采集中应用最普遍、最经济的一种信息标识技术,很多国家基于用药安全,都在不同程度地实施药品条形码化管理[8]。我院的麻醉、精神药品从入库到出库,全部通过扫码操作、电脑记录,可精确追溯到最小包装的去向,同时涉及到的患者用药信息(包括药品生产批号、有效期)、领药时间、领药人等都可追溯,建成独立药品监管与实时追溯体系,确保每一环节都安全规范精细化管理。
-
将麻醉、精神药品的用法用量规则设置在合理用药模块中,药师审方时电脑会直接提示不合理处方医嘱,提升药师审方的准确性,降低不合理处方发生率,从而保证临床合理用药。
-
专管药师登录个人账号,根据电子处方上的病人姓名及药品分类,选择对应“麻精Ⅰ处方”或“精Ⅱ处方”,找到程序中已生成的医嘱信息,此医嘱信息只显示麻醉、精神药品的医嘱,不再显示同一患者的所有医嘱信息(包括麻醉、精神药品、生物制品、特殊级抗菌药物及口服药品的医嘱),避免药师在处理麻醉、精神药品医嘱时需要手工删除非麻醉、精神药品医嘱的操作。
-
上述提及的日清点记录、专用账册等电子账单,通过与医院HIS系统对接,能够提取到有效数据。但对于空安瓿、废贴回收的信息化管理操作,很多医院始终无法找到合理流程,我院经过不断摸索,最终建立现行的空安瓿、废贴回收信息化管理,确保麻精药品管理的每步环节都由信息化监管。操作界面上也涵盖了病区先用基数药品导致发出与回收批号不一致的情况。考虑到每个月还需做空安瓿、废贴的月结处理,牵扯的数据量庞大,每次人工计算都需要反复核算,故在每日回收空安瓿、废贴的界面增加月结功能,有效避免人力耗时耗力的现象。
-
麻醉、精神药品在医院的使用率占比最高,2019年上海市开展麻醉精神药品使用及管理的专项巡查时发现:麻精药品账目不符、药品私售等问题[9]。如何安全、合理、规范地管理麻醉、精神药品,提升“五专”管理质量是迫在眉睫的挑战。目前很多医院对麻醉精神药品的管理参差不齐,有相当一部分医院仍然依赖全手工或半手工半信息化的模式。我院新建的麻醉、精神药品程序无缝对接医院HIS系统,实现数据互通,解决了别家医院无法从电子病历中提取完整且正确信息的难题,且确保提取到的专册登记信息正确率达100%。随着空安瓿、废贴回收的信息化建立,最终实现麻精药品的“请领→入库→医嘱出库→用药”过程的信息化、可追溯的闭环管理。
电子化账册的实施,不仅提高了麻醉、精神药品在实际使用与管理中的安全性,且通过后台数据记载,精准追溯病人用药情况,实现药品批号效期监管,同时支持的数据上传功能,可构建大数据网络平台,为国家后台监管麻精药品提供数据支持。在提高医生、护士、药师工作效率的同时,有助于提高医疗水平和质量。自2020年程序上线以来,电子化账册涉及的信息化内容完全符合国家法规规定,数据准确,揭示了电子化账册对规范化管理麻醉精神药品有着重要作用。
Implementation and exploration of administration of anesthesia and psychotropic drugs by electronic account books
-
摘要:
目的 实施电子化账册,探索其对管理麻醉、精神药品的成效及意义。 方法 分别收集本院住院药房2020年1月至2020年6月实施电子化账册(观察组)、2019年7月至2019年12月手工账册(对照组)的相关数据,对比两组之间的(每日)做账耗时、(月结)做账耗时、做账正确率数据。 结果 药师每日手工做账平均耗时(162.8±22.5) min,每日电子做账平均耗时(33.2±7.0) min;月结手工做账耗时(245.5±7.2) min,月结电子做账耗时(46.8±2.5) min;电子做账包含的日清点记录、专用账册、专册登记、空安瓿、废贴回收记录的正确率高达100%。 结论 电子化账册的实施,在显著提升药师工作效率的同时,加强用药监管,形成全面可追溯体系,保证临床用药安全,使麻醉、精神药品的管理更加高效和规范。 Abstract:Objective To explore the effect and significance of electronic account books on the management of anesthesia and psychotropic drugs. Methods The data of electronic account books from January 2020 to June 2020 in the inpatient pharmacy of the hospital (observation group), and manual account books from July 2019 to December 2019 (control group) were collected respectively. The data of daily accounting time, monthly settlement accounting time and accounting accuracy between the two groups were compared and analyzed. Results The daily average time for pharmacists to manually accounting was (162.8±22.5) min, and the daily average time for pharmacists to make accounts electronically was (33.2±7.0) min. It took (245.5±7.2) min for manual accounting of monthly settlement and (46.8±2.5) min for electronic accounting of monthly settlement. The accuracy rate of daily counting records, special account books, special register and empty ampoule waste paste recovery records included in electronic accounting is up to 100%. Conclusion The implementation of electronic account books not only significantly improved the work efficiency of pharmacists, but also strengthened drug supervision, formed a comprehensive traceability system, which could ensure the safety of clinical medication, and make the management of narcotic psychotropic drugs more efficient and standardized. -
表 1 每日手工账册与电子化账册做账耗时比较
组别 时间 A B C D E F 手工 2019年7—12月 163.5±23.5 154.6±18.7 160.4±22.9 163.5±26.3 168.8±21.1 166.1±20.9 电子 2020年1—6月 32.8±6.9 32.3±6.7 34.6±7.0 35.4±8.1 31.0±5.2 32.8±7.5 t 61.440 P 0.000 注:A-F代表月。手工:A:2019年7月、B:2019年8月、C:2019年9月、D:2019年10月、E:2019年11月、F:2019年12月;电子:A:2020年1月、B:2020年2月、C:2020年3月、D:2020年4月、E:2020年5月、F:2020年6月。 -
-




 下载:
下载: