-
信使 RNA(mRNA)是蛋白质合成中从基因到核糖体的遗传信息的瞬时载体[1],相对于 DNA 治疗, 有更多优势,例如,无整合到宿主基因组中而导致插入突变的风险、比DNA更能获得持久预测蛋白表达动力学蛋白表达,且体外合成 mRNA 相对容易等。然而,由于mRNA不稳定性,其需要一个递送载体保护,免受核酸酶降解的同时还要使其被细胞吞噬,核酸胞内释放并翻译成蛋白。目前已上市的mRNA疫苗,大多采用的是脂质纳米粒(LNPs)载体[2-4]。LNP有4个重要组成部分:结构性脂质、胆固醇、阳离子脂质(或可电离脂质体)和隐形脂质。其中,阳离子脂质或可电离脂质是将带负电的mRNA能够装载到LNP必不可少的组成部分。Lipo8000是新型的阳离子脂质体转染试剂,转染效率和Lipo3000基本一致,适用于将DNA和RNA转染入真核细胞,对多种细胞具有高转染效率,常作为脂质纳米粒载核酸药物研究的对照试剂 [5-6]。DLin-MC3-DMA被认为是最有效的阳离子脂质体之一,具有“低毒高效”的优势[7],2018年全球首个上市的siRNA产品Onpattro就是采用DLin-MC3-DMA作为载体[8]。DLin-MC3-DMA在酸性条件下呈正电性,而生理pH条件(pH值为7.4)下呈电中性,现已成为制备肝脏靶向siRNA/LNP系统的“标准”脂质材料。但其递送mRNA的能力尚未见到报道。本研究以DLin-MC3-DMA作为阳离子脂质构建脂质纳米粒,并以Lipo8000为对照对其体外递送mRNA的能力进行考察,为后续肿瘤基因治疗研究提供参考。
-
小鼠前列腺癌 RM-1 细胞(中国科学院典型培养物保藏委员会细胞库)。
MalvernZS90 激光粒径电位测试仪(Malvern公司,英国);JEM-2010型透射电镜(JEOL公司,日本);激光共聚焦显微镜 (Olympus公司,日本);SartoriusBS11os精密电子天平(德国赛多利斯集团);超净工作台(淀山湖净化设备仪器厂);MSHPRO磁力搅拌器(大龙兴创实验仪器有限公司);5804R 低温高速离心机(Eppendorf,美国);DMIL 荧光显微镜(Leica 公司,德国);CellmeterMini 全自动细胞计数仪(Nexcelom,美国);旋转蒸发仪(常州英峪予华仪器有限公司);超声波细胞粉碎机(宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司);真空冷冻干燥机(上海精密实验设备有限公司);琼脂糖凝胶电泳仪(北京六一仪器厂);二氧化碳培养箱(Thermo Fisher,美国);MULTISKAN MK3酶标仪(Thermo公司,美国)。
1640培养基、DMEM培养基、胎牛血清、双抗、胰酶(Gibco公司,美国);PBS(上海源培生物科技有限公司);CCK-8试剂盒、DAPI水溶性封片液(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);Lipo8000™ 转染试剂(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);DLin-MC3-DMA(艾伟拓医药科技有限公司);DEPC(艾伟拓医药科技有限公司);β-谷甾醇(上海麦克林生化科技有限公司);PEG2K-DMG(艾伟拓医药科技有限公司);二氯甲烷(上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司);4% 多聚甲醛(武汉塞维尔生物科技有限公司);EGFP-mRNA(吉玛基因);琼脂糖(上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司);TBE(5×)(南京江苑生物科技有限公司);Gel-red(Biosharp)。
RM-1细胞培养于含10 % 胎牛血清、青霉素 100 U/ml 及链霉素 100 μg/ml 的 1640完全培养基,在 37 ℃、5 % CO2 孵箱中培养,待细胞生长至 80% 融合时用于实验。
-
称取DLin-MC3-DMA、DEPC、β-谷甾醇、PEG2K-DMG(摩尔比为50∶10∶38.5∶1.5)分别为12.5 μl(约10 mg)、2.5 mg、4.6 mg、1.3 mg,加入2 ml二氯甲烷,室温搅拌8 h。旋蒸蒸干有机溶剂后纯水重悬,超声乳化,每超声10 s,间隔5 s,重复3次,得DLin-MC3-DMA 脂质纳米粒(DLin-LNP)。将脂质纳米粒溶液在−80 ℃ 冰箱中预冻,放入冷冻干燥机中,制成 DLin 冻干粉。DLin冻干粉置于−20 ℃环境中储存。待使用时,取适量 DLin-LNP冻干粉溶解稀释,按比例加入适量模型药EGFP-mRNA,室温孵育30 min,制备成载mRNA脂质纳米粒DLin@mRNA。
-
取适量制备的DLin@mRNA,用纯水稀释制成1 mg/ml的溶液,使用MalvernZS90 激光粒径电位测试仪检测粒径及Zeta电位,使用透射电镜观察纳米粒的形态及大小并拍照记录。
-
取新制备的DLin空白载体(DLin-Blank)和DLin@mRNA 纳米粒重悬于纯水中,配置浓度为1 mg/ml的脂质纳米粒溶液,静置20 d,用粒径电位测试仪检测其粒径和Zeta电位的变化情况。
-
采用琼脂糖电泳实验考察DLin-LNP对mRNA的包载能力。取 1 μg EGFP-mRNA,按照DLin-LNP/mRNA质量比为0、0.5、1、2、4、6、8、10 的比例,将各组EGFP-mRNA 和DLin 按比例加入到2 ml的EP管中,涡旋混匀,孵育30 min后可在预制的凝胶板上上样。在电压为100 kV的条件下进行电泳,40 min后取出电泳板,置于紫外光条件下观察显影并拍照记录。
-
采用 EGFP-mRNA 为模型药,以RM-1为模型细胞,以 4×105 个/ml的密度铺48孔板,每孔加入250 μl含FBS的DMEM培养基,在培养箱中培养24 h。以质量比(载体/mRNA)为2、4、6、8分别配置 Lipo8000@mRNA 和 DLin@mRNA,每组复3孔, PBS组为对照组。室温孵育30 min后可加入孔板中。每孔加入 DMEM空白培养基 250 μl,加入样品溶液,培养4 h。吸除原培养液,换上含FBS的DMEM培养基。继续培养,20 h后荧光显微镜下观察mRNA的表达情况。
-
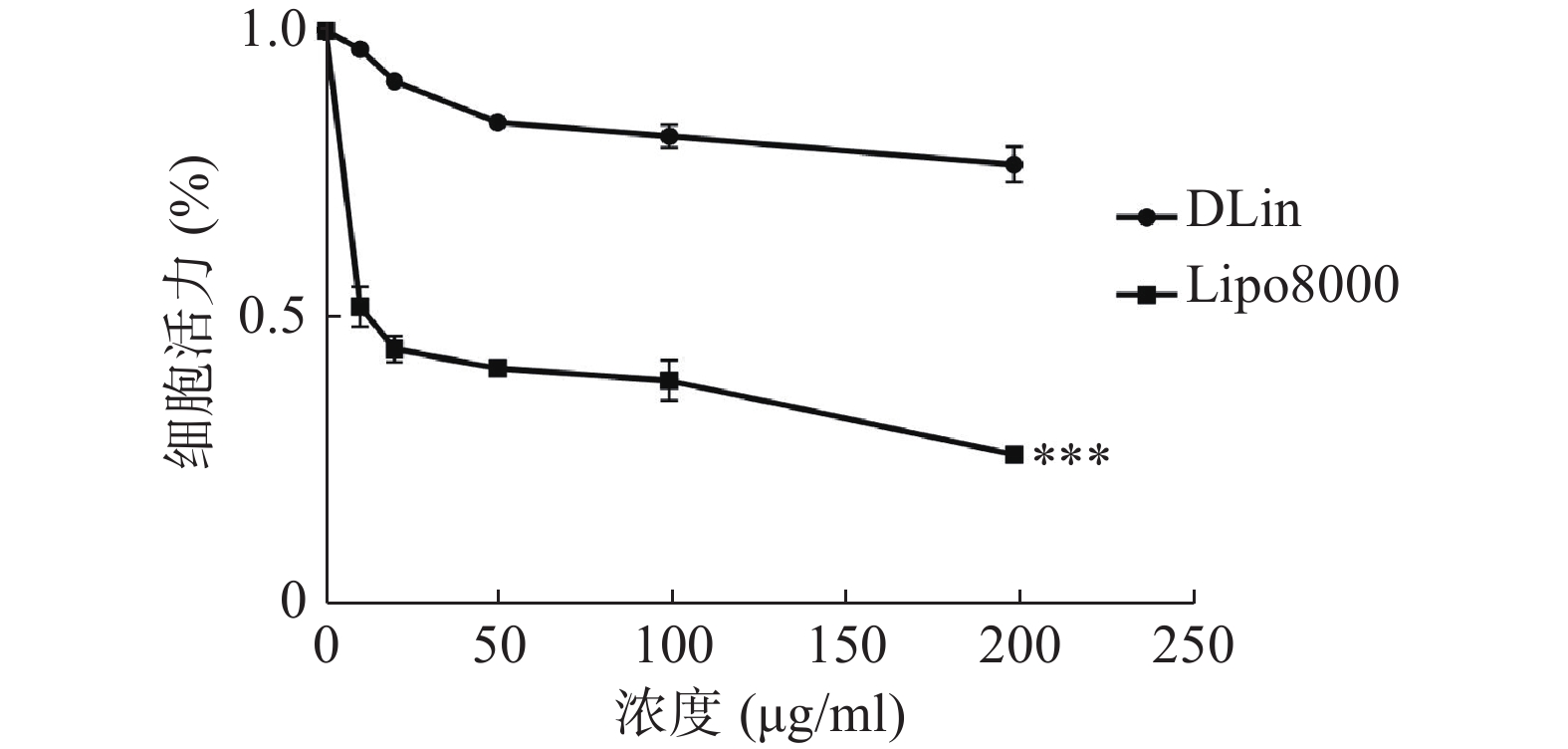
为了考察DLin-Blank载体本身的安全性,采用CCK-8法考察对RM-1细胞的细胞毒性作用,具体方法如下:以4×105 个/ml铺于96孔板,培养箱中培养24 h。分别加入不同浓度的Lipo8000-Blank、DLin-Blank,使终质量浓度分别为0、10、20、50、100、200 μg/ml,每组重复6孔,同时设置无细胞的孔为空白孔,PBS组为对照组,于细胞培养箱中孵育24 h。孵育结束后,吸除培养基,每孔加入10 μl CCK-8溶液,并用1640空白培养基补至100 μl,置于培养箱孵育2 h。使用酶标仪检测每孔450 nm波长处的吸光度。
计算每孔的细胞活力公式如下:
细胞活力=[(A加药−A空白 )/(A对照−A空白)]×100 %
-
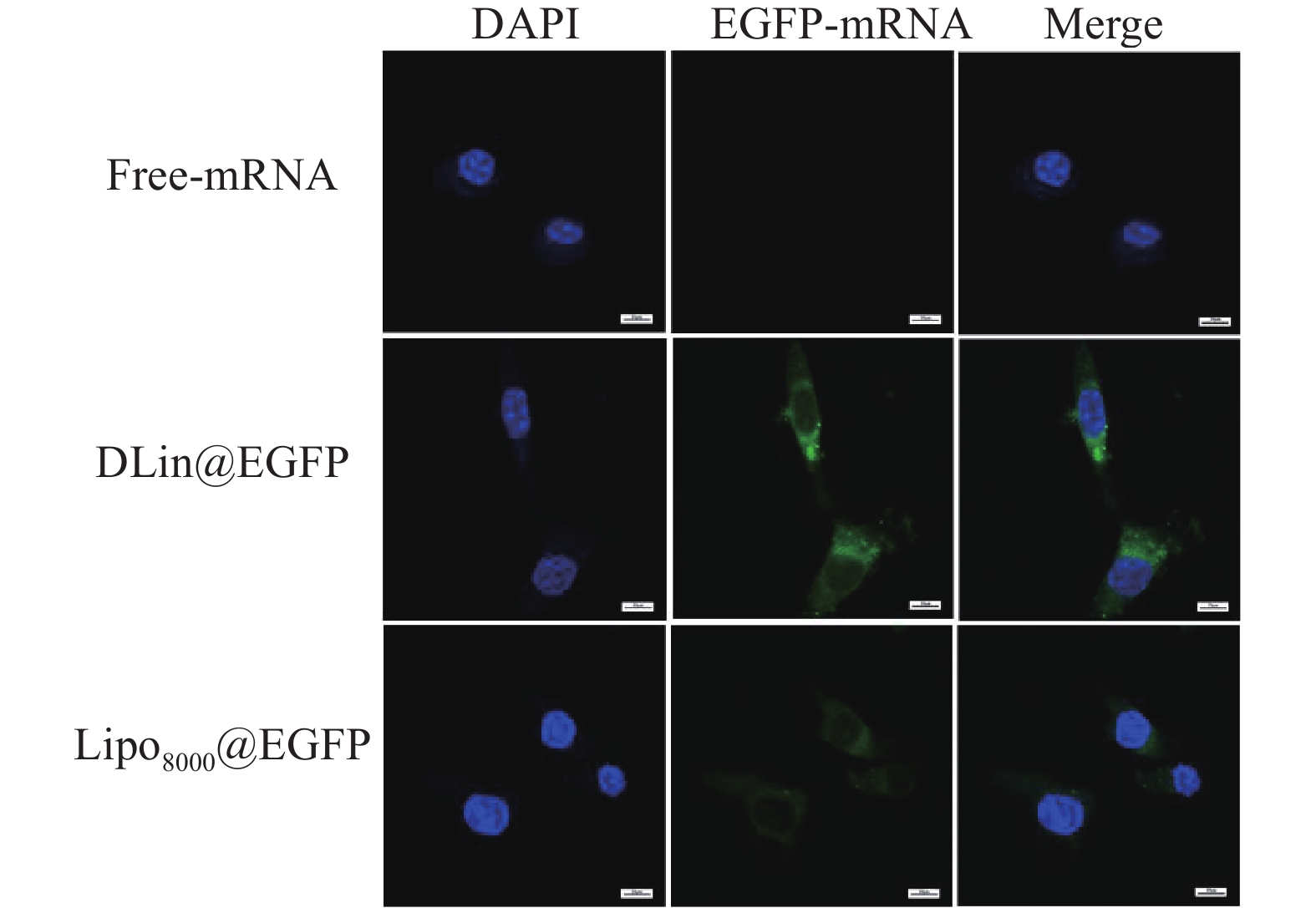
采用RM-1细胞为模型,以 4×105 个/ml密度铺24孔板,每孔500 μl。将其放于 37 ℃、5 % CO2 的孵箱中培养24 h。弃去旧培养液,PBS 洗2次,分别加入含游离EGFP-mRNA、Lipo8000@mRNA、DLin@mRNA 的纳米粒溶液(Lipo8000组和DLin组的脂质体/mRNA分别为2和6),补充无血清培养基,使 EGFP-mRNA终含量为 1 μg/孔,在孵箱中培养 24 h。吸去培养液,PBS 洗 1 次,用预冷的4 %多聚甲醛溶液固定30 min,PBS洗2次。取8 μl含有DAPI的封片液滴于载玻片上,将盖玻片含有细胞的一面贴于含有封片液的载玻片上,玻片两侧用指甲油固定。利用激光扫描共聚焦显微镜观察脂质纳米粒在RM-1细胞内的分布情况,并拍照记录。
-
实验数据采用软件GraphPad Prism 7进行分析。正态分布数据以(
$\bar{{x}}\pm \mathrm{s}$ ) 表示,组间比较使用ANOVA分析法,以P<0.05和P<0.01为差别有显著性和极显著性。 -
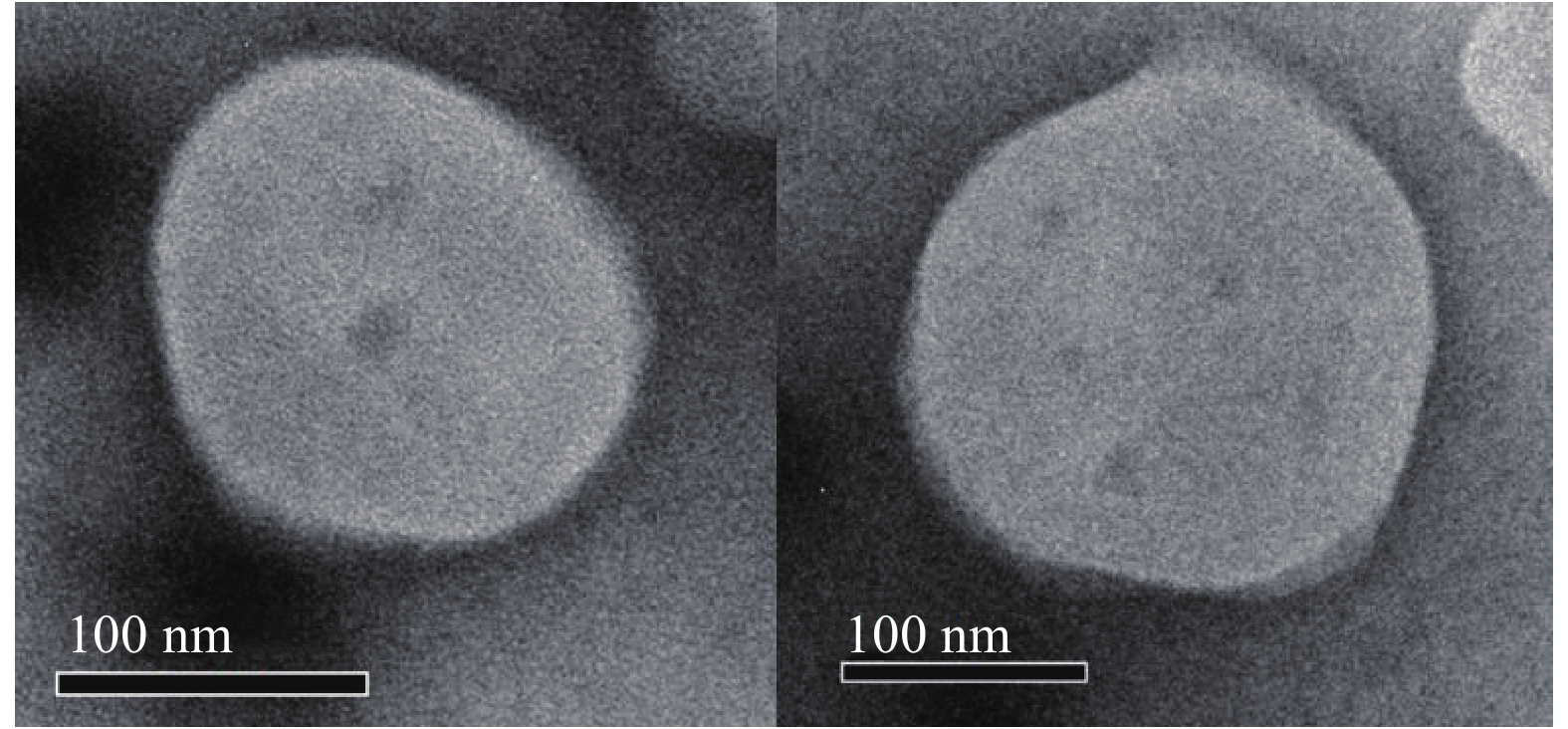
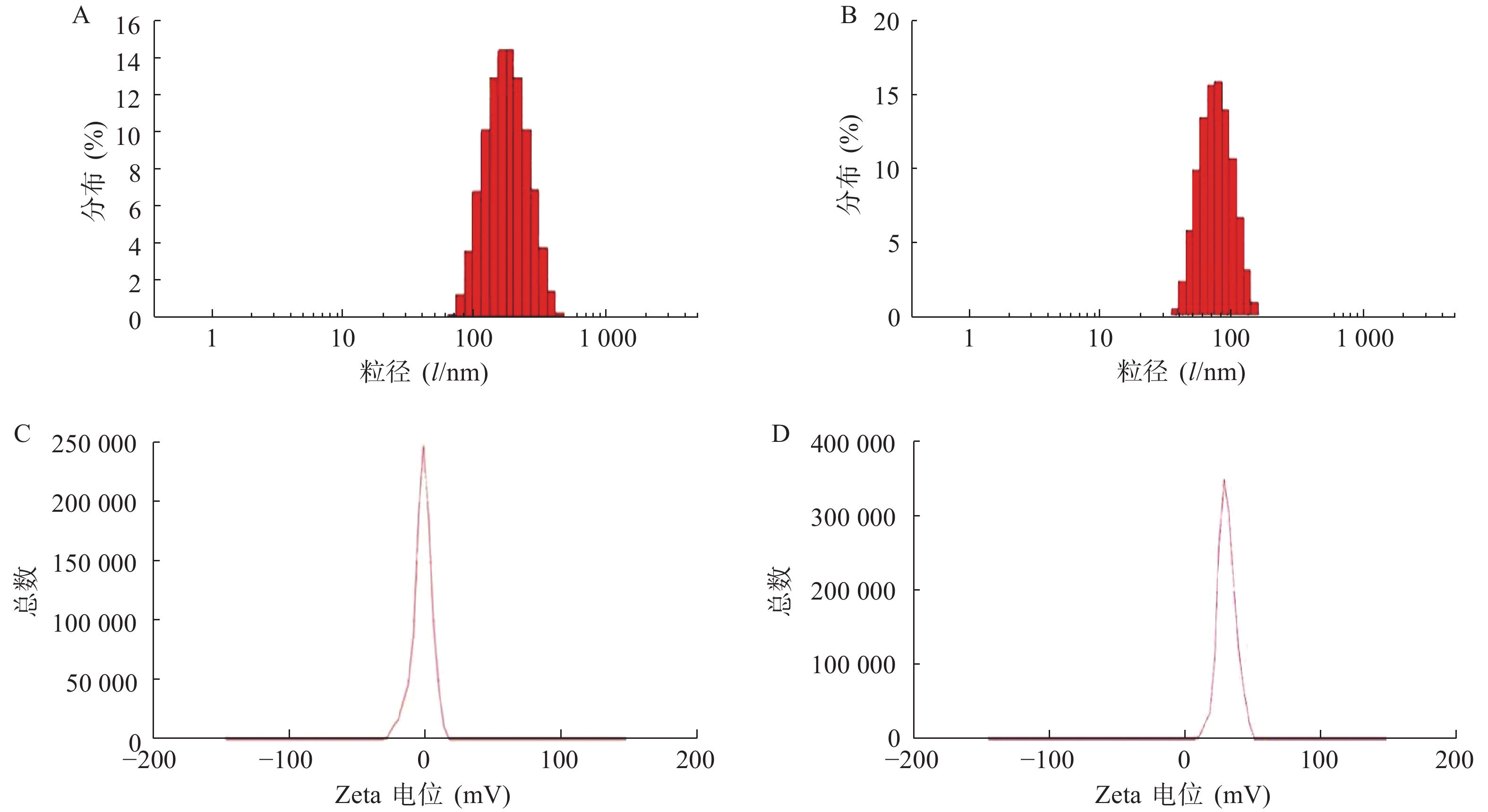
使用激光粒度仪检测DLin-Blank和DLin@mRNA的平均粒径分别为(151.10±2.10) nm(图1A)和(164.75±1.85) nm(图1B),显示载mRNA后的脂质纳米粒平均粒径略有增大。DLin-Blank和DLin@mRNA的Zeta电位结果分别为(23.70±0.50) mV(图1C)和(2.6±0.2) mV(图1D)。使用透射电镜观察脂质纳米粒的形态,DLin-Blank和DLin@mRNA 纳米粒均为类球形(图2),纳米粒载药前后形态无明显变化,粒径在150 nm 左右,大小与粒度仪检测结果一致。
-
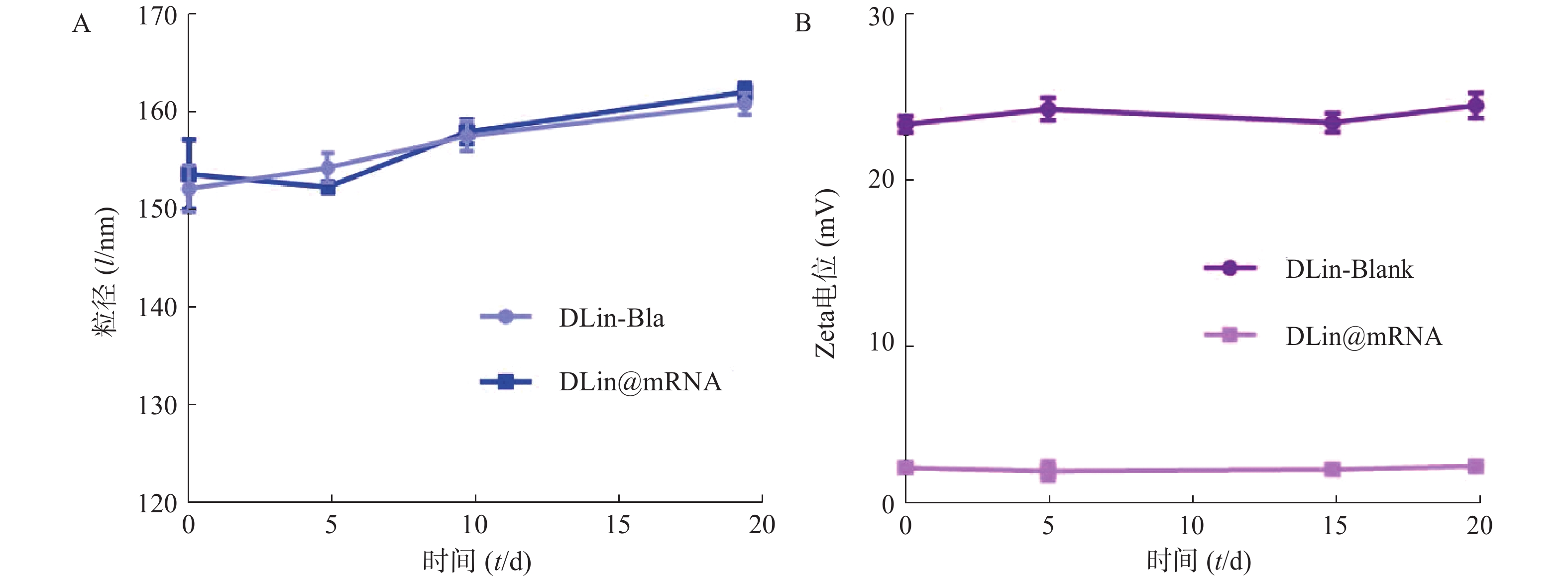
为了评价各纳米粒的稳定性,进行了稳定性考察,结果如图3所示。实验期间,各纳米粒粒径和电位保持基本稳定,证明其具有较好的稳定性。
-
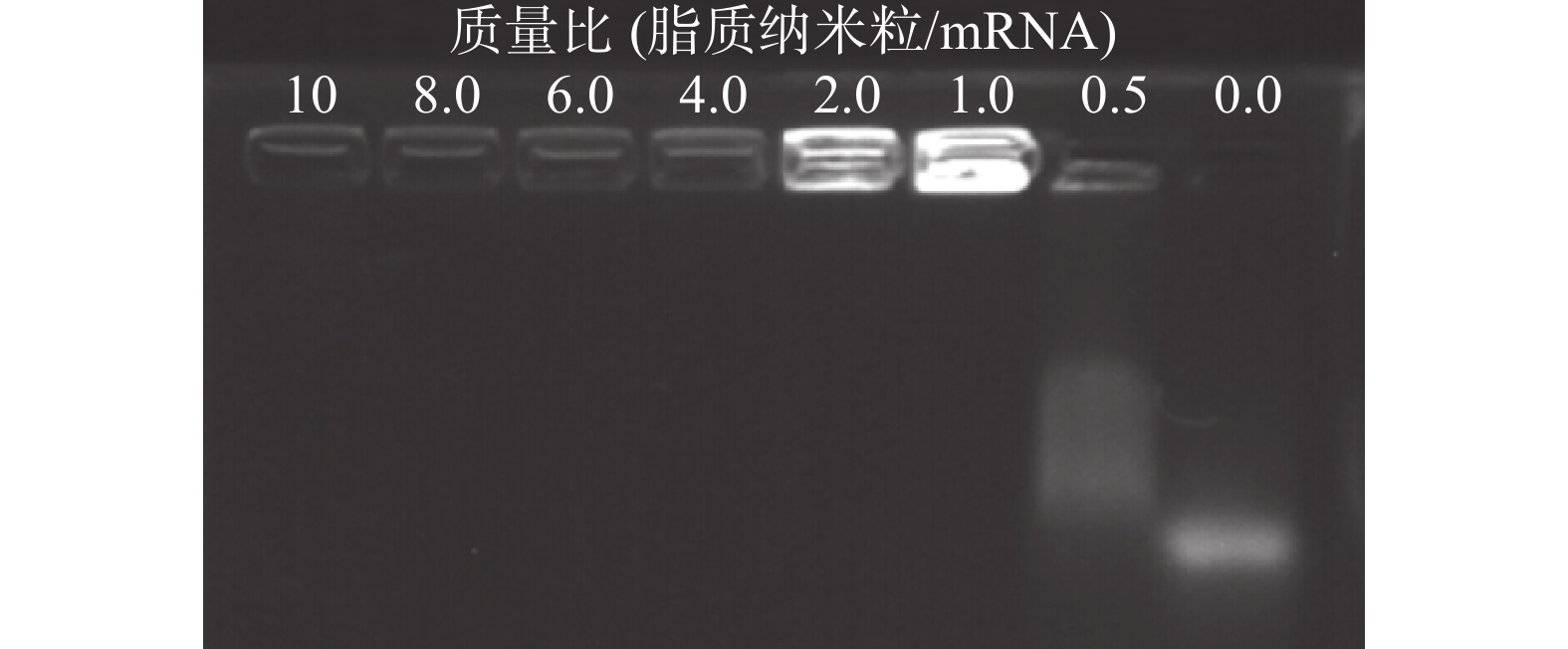
脂质纳米粒的包载作用保护mRNA 免受酶解,是基因能够有效转染的关键。将DLin-LNP与mRNA以不同的质量比共同孵育结合,进行琼脂糖电泳实验。紫外光线下的显影结果显示,当质量比为 >1 时,脂质纳米粒可以通过静电作用将mRNA完全包裹,阻止mRNA在电泳板上的迁移 (图4)。
-
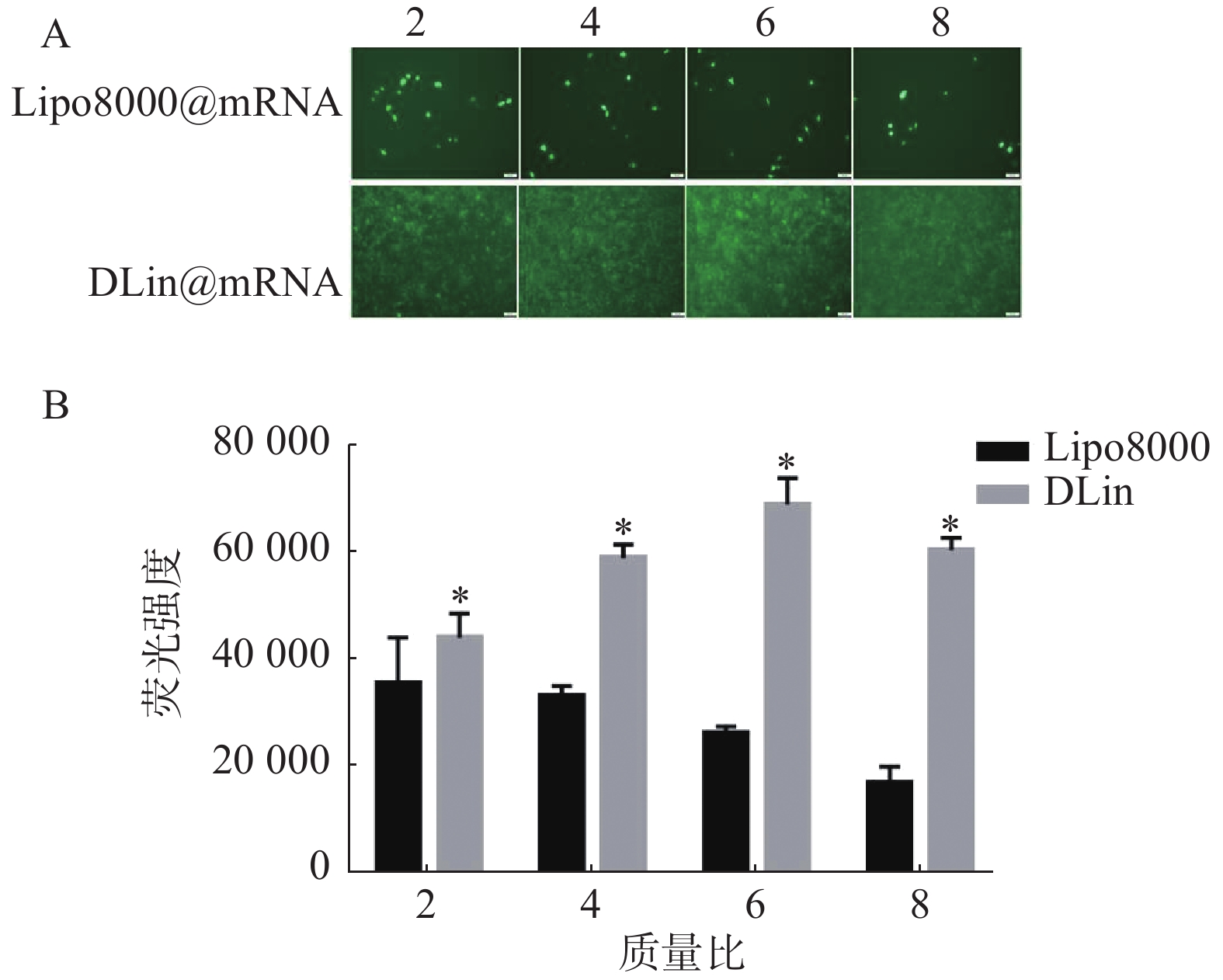
以质量比(脂质体/mRNA)分别为2、4、6、8的Lipo8000@mRNA和DLin@mRNA 考察RM-1细胞中的转染情况,同时设置PBS组为对照组,每组复3孔。用荧光显微镜下观察细胞转染后的荧光强度,拍照记录,并使用Image J统计各组荧光强度。结果如图5所示,DLin纳米粒在质量比为6时转染效果最好,DLin组在各质量比时的荧光强度均较Lipo8000组的更强,显示出更佳的转染效果。
-
使用CCK-8法检测细胞活力,结果如图6所示,DLin-Blank的毒性远低于Lipo8000-Blank,当浓度达到100 μg/ml时Lipo8000-Blank组的RM-1细胞存活率降到50 %以下。DLin-Blank 组的细胞存活率在所检测浓度范围内均保持在80 %以上。DLin-LNP较Lipo8000-LNP具有更低的细胞毒性。
-
制备DLin@mRNA和Lipo8000@mRNA分别与RM-1细胞共同孵育3 h,并以PBS作为对照,使用激光共聚焦显微镜观察RM-1细胞对纳米粒的分布情况。结果显示,在细胞质部分可观察到绿色荧光蛋白(EGFP-mRNA),说明纳米粒被肿瘤细胞摄取后主要分布在胞质内,且DLin@EGFP组的荧光强度略高于Lipo8000@EGFP组,与转染实验中的结果保持基本一致 (图7)。
-
LNP 作为目前 mRNA 主流的递送载体之一,目前已常用于肿瘤治疗和疫苗[9-10]。DLin-MC3-DMA是新型阳离子脂质,为了探究DLin-MC3-DMA包载mRNA的效果,本研究以DLin-MC3-DMA作为纳米粒的重要组成制备了DLin@mRNA,并以此为基础进行了体外研究。结果显示,阳离子脂质所制备的LNP形成了正电位效果,对带负电mRNA的装载具有较好的包载效果。DLin-LNP的纳米粒为类球形,粒径为(151.10±2.10) nm,空载电位为(23.7±0.5) mV,载药前后形态无明显变化。DLin@mRNA 溶液在20 d内仍具有较好的溶液稳定性,可有效装载mRNA并保护其不受分解。此外,DLin较市售Lipo8000具有更高的转染效率且细胞毒性更低,显示出良好的优势。
LNP的均匀性和核酸负载效率影响最终药效的两个重要的因素。LNP的制备取决于脂质成分发生分子间相互作用而自组装。脂质体的多样性、核酸的独特性以及两者混合的时间特性均会对纳米粒最终的特性造成影响。LNP制备方法很多,脂质体挤出法、纳米沉淀法、微流控等都是常见的制备方法,其中微流控技术备受研究者的喜爱,但鉴于微流控通量小,在中试生产中可能受到限制[11]。因此,在载药纳米材料不断发展的同时,对于如何生产稳定、载量高、载药效果好的LNP的制备工艺,还需要进一步深入研究[12]。
综上所述,本实验成功构建了DLin@mRNA纳米粒,并进行了载药比例、膜包覆条件及相关体外特性的考察,该仿生纳米体系具有成为安全、 高效的体内靶向给药递送系统的潜力。后期我们将开展体外细胞学评价及体内的靶向性、药效学评价,并进一步探索其抗肿瘤作用的机制。
Construction and in vitro evaluation of an LNP system for mRNA delivery
-
摘要:
目的 构建脂质纳米粒DLin-LNP,以EGFP-mRNA为模型药,考察DLin-LNP对于mRNA的体外递送能力。 方法 采用薄膜水化法制备DLin-LNP, 并进一步制备 DLin@mRNA,对纳米粒进行表征,使用激光扫描共聚焦显微镜观察脂质纳米粒胞内的分布情况,以RM-1细胞为模型考察胞内转染情况。 结果 成功制备了脂质纳米粒DLin-LNP,其粒径为(151.1±2.1) nm,空载电位为(23.7±0.5) mV。DLin-LNP在RM-1细胞中转染mRNA效率较高,其毒性远低于市售脂质体Lipo8000,且 DLin-LNP脂质纳米粒稳定性好。 结论 DLin-LNP具有高转染效率和安全性,且稳定性好,可作为mRNA递送载体,为后续脂质纳米粒肿瘤治疗中的应用提供依据。 -
关键词:
- 脂质纳米粒 /
- DLin-MC3-DMA /
- 信使核糖核酸 /
- 药物递送
Abstract:Objective To construct lipid nanoparticles DLin-LNP for mRNA delivery. Methods DLin-LNP was prepared by thin film hydration method, and DLin-LNP/mRNA was further constructed by using EGFP-mRNA as model drug. The particle size, zeta potential, and appearance morphology were measured. Furthermore, the intracellular distribution and transfection of DLin-LNP/mRNA in RM-1 cells was investigated by laser scanning confocal microscope. Results DLin-LNP was successfully prepared. The average particle size was about (151.1±2.1) nm, the no-load potential was (23.7±0.5) mV. The cytotoxicity of DLin-LNP was far lower than that of the commercially available liposomal Lipo8000. The results of transfection experiment indicated that DLin-LNP has high transfection efficiency for mRNA delivery with low cytotoxicity and good stability. Conclusion DLin-LNP could become a potential mRNA vector for gene therapy. -
Key words:
- LNP /
- DLin-MC3-DMA /
- mRNA /
- drug delivery
-
-
[1] 吕建军, 段大鑫, 蒋帅, 等. 体外转录信使RNA免疫疗法的研究进展[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2016, 32(1):129-132. doi: 10.13423/j.cnki.cjcmi.007640 [2] NDEUPEN S, QIN Z, JACOBSEN S, et al. The mRNA-LNP platform’s lipid nanoparticle component used in preclinical vaccine studies is highly inflammatory[J]. J Immunol,2021,206(1_Supplement):30.01. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.206.Supp.30.01 [3] YANG B, JEANG J, YANG A, et al. DNA vaccine for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Hum Vaccin Immunother,2014,10(11):3153-3164. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.980686 [4] KON E, ELIA U, PEER D. Principles for designing an optimal mRNA lipid nanoparticle vaccine[J]. Curr Opin Biotechnol,2022,73:329-336. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2021.09.016 [5] ZOU Y, ZHEN Y H, ZHAO Y N, et al. pH-sensitive, tail-modified, ester-linked ionizable cationic lipids for gene delivery[J]. Biomater Adv,2022,139:212984. doi: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2022.212984 [6] XUE C, HU S Y, GAO Z H, et al. Programmably tiling rigidified DNA brick on gold nanoparticle as multi-functional shell for cancer-targeted delivery of siRNAs[J]. Nat Commun,2021,12(1):2928. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23250-5 [7] ERMILOVA I, SWENSON J. DOPC versus DOPE as a helper lipid for gene-therapies: molecular dynamics simulations with DLin-MC3-DMA[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys,2020,22(48):28256-28268. doi: 10.1039/D0CP05111J [8] AKINC A, MAIER M A, MANOHARAN M, et al. The Onpattro story and the clinical translation of nanomedicines containing nucleic acid-based drugs[J]. Nat Nanotechnol,2019,14(12):1084-1087. doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0591-y [9] 张琳, 陈会英, 赵轶男, 等. 阳离子脂质体的环境响应性评价[C]//中国化学会第30届学术年会摘要集-第三十八分会: 纳米生物效应与纳米药物化学. 大连, 2016: 199. [10] KIAIE S H, MAJIDI ZOLBANIN N, AHMADI A, et al. Recent advances in mRNA-LNP therapeutics: immunological and pharmacological aspects[J]. J Nanobiotechnology,2022,20(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01478-7 [11] MAEKI M, UNO S, NIWA A, et al. Microfluidic technologies and devices for lipid nanoparticle-based RNA delivery[J]. J Control Release,2022,344:80-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.02.017 [12] CUI L L, PEREIRA S, SONZINI S, et al. Development of a high-throughput platform for screening lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery[J]. Nanoscale,2022,14(4):1480-1491. doi: 10.1039/D1NR06858J -





 下载:
下载: