-
艰难梭菌的感染率近年来有所提高[1],其孢子很难根除,并且很容易通过医护人员传播,是医院、养老院和一些健康护理机构出现腹泻感染的原因之一[2]。目前针对艰难梭菌的可用治疗方法都有一些缺点,例如成本过高、耐药性的发展和选择性问题。 虽然轻度至中度的艰难梭菌病例目前可以通过可用的治疗方法进行控制,但对严重的病例可能需要使用单一常规药物或联合疗法进行长期抑制治疗,如果不成功,则要采用非常规和(或)侵入性的手段,如粪便移植和结肠切除术[3]。因此,临床上对药物研发需求越来越大,寻求一种更有效的替代疗法迫在眉睫[1]。
含有喹啉的杂芳族化合物具有多种生物和药理活性,例如,抗疟疾[4]、抗结核病[5]、抗炎[6]、抗癌[7]、抗高血压[8]以及抗菌[9-11]。Musiol 等[12]曾报道 8-羟基喹啉衍生物的抗真菌活性。此外,8-羟基喹啉衍生物显示出对神经退行性疾病如阿尔茨海默病良好活性[13]。最近,研究发现8-羟基喹啉衍生物具有抗金黄色葡萄球菌的潜在作用[14]。我们的小组最近通过药物数据库筛选发现,溴氧喹啉(5,7-二溴喹啉-8-酚)对艰难梭菌具有强效抗菌活性。基于此有前景的化合物,我们进行了一系列8-羟基喹啉类似物的设计、合成和抗艰难梭菌活性研究。
-
化学原料均为市售分析纯;Bruker AM-400 (400 MHz) 核磁共振仪,TMS 作为内标,化学位移与偶合常数分别用 ppm 和 Hz 表示 ;Agilent 6538 UHD Accurate-Mass Q-TOF LC/MS高分辨质谱(HRMS)仪。
-
4-溴-2-甲氧基苯胺通过 Skraup 合成[16] ,在 H2SO4、3-硝基苯磺酸钠和甘油中回流,得到中间体 1(见图2)。随后,甲基保护基被脱除,再在DIPEA存在下用MOMCl保护,得到化合物 2。此外,化合物 1 还经 Suzuki 反应与芳基硼酸偶联反应得到中间体 3a-j 。 化合物2与苯乙烯偶联,得到化合物 4a,然后使用 1 mol/L 的盐酸脱保护,得到化合物 5a。其中,化合物 3a-g 和 3i-j使用 HBr (48%) 在回流下脱保护,以较高的收率得到化合物 6a-g 和 6i-j,化合物 3h 用 BBr3 处理得到化合物 6h。
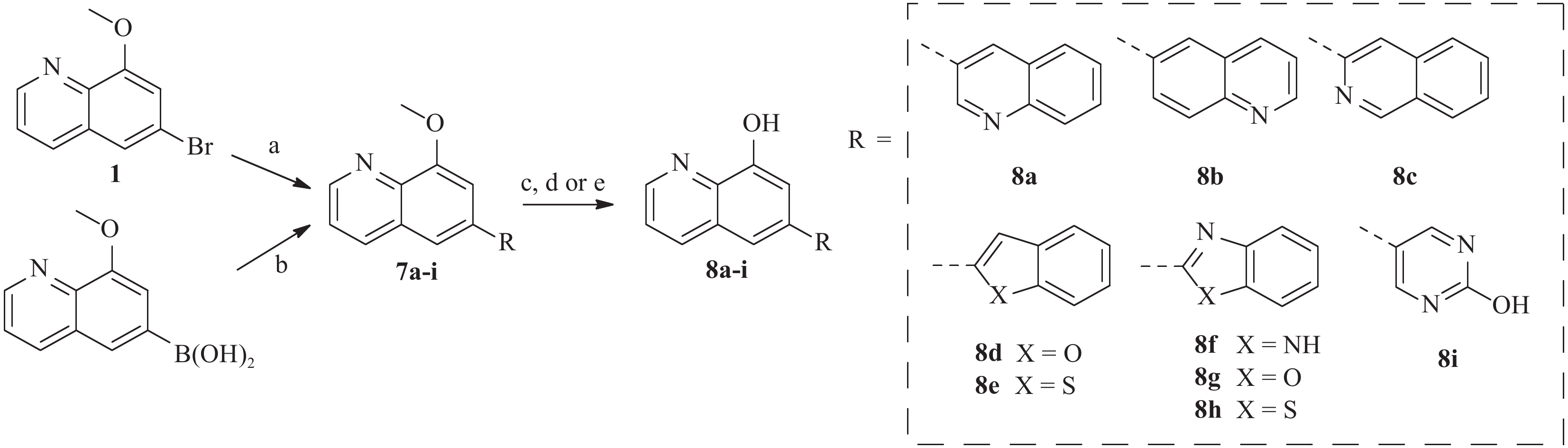
为了进一步研究8-羟基喹啉衍生物的构效关系,我们还设计并合成了)一系列6位杂环取代的化合物, 如图3 所示。首先,中间体1或相应的硼酸与市售芳基硼酸或卤代物通过Suzuki反应偶联得到7a-i,然后在氢溴酸(48%)中回流脱甲基以高收率得到化合物8a-i。
-
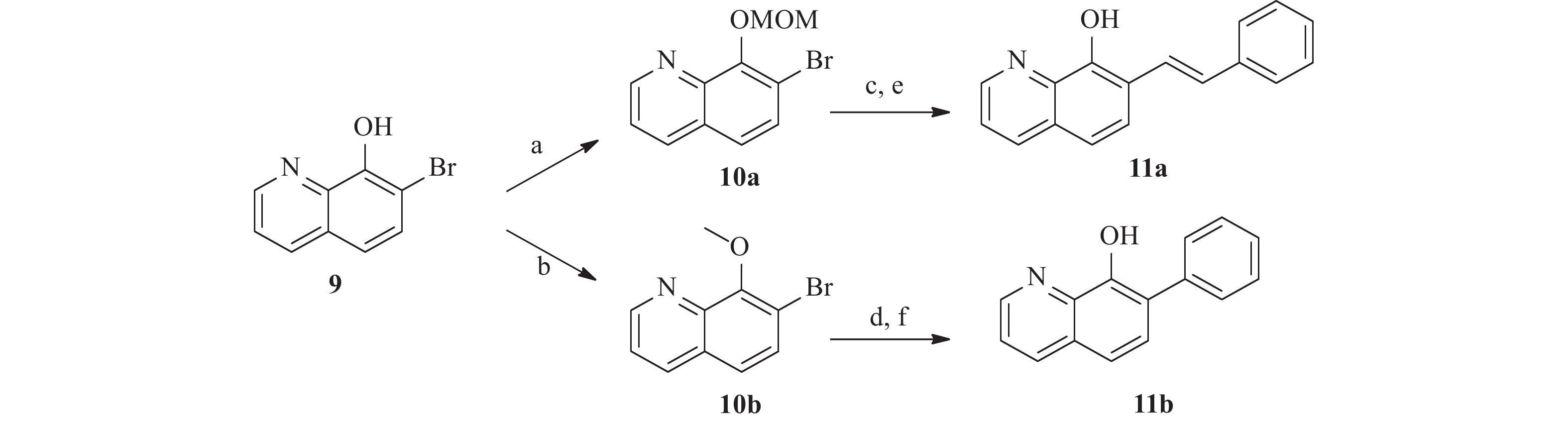
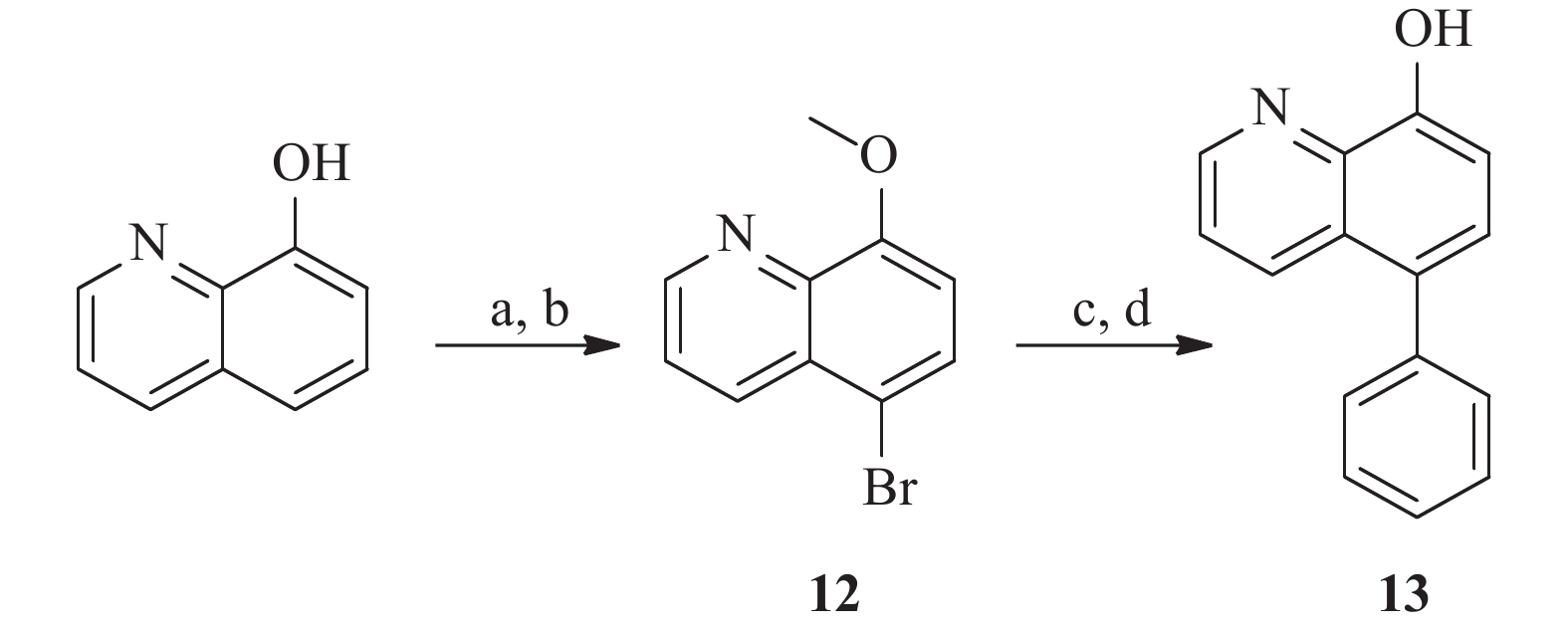
为了研究5和7位的构效关系,我们还设计合成了一系列在5和7位具有不同取代基的化合物。 如图4 所示,市售的 7-溴-8-羟基喹啉(9)经MOM和甲基保护,分别得到中间体10a和10b。 随后,这些中间体与苯乙烯和苯硼酸偶联,分别得到中间体11a 和11b。 最后,化合物 17a 和 17b 分别经 1 mol/L盐酸水溶液和氢溴酸水溶液(48%)脱保护,得到所需的 8-羟基喹啉类似物18a 和18b。 此外, 5 位取代化合物的合成如图5 所示。首先,将市售的8-羟基喹啉在碳酸钾存在下与碘甲烷反应,随后在甲醇中与溴素在室温下反应得到中间体12[17]。随后,化合物12按照与前述相同的方法合成13。
-
所有目标化合物及部分中间体均针对两种菌株 BAA1875 和 R20291 的艰难梭菌进行了活性测试。基于生物活性(见表1),SAR总结如下:①8位的游离羟基对艰难梭菌的抑制活性起着非常重要的作用,其甲基化会大幅降低活性(化合物1和3c分别对BAA-1875为大于256 μg/ml)。② 6 位的取代对于活性很重要,体积大的基团(例如萘基)对活性有利(萘基 6f > 苯基 6a )。此外,对于 6 位萘取代的化合物,2-萘基优于1-萘基(6f vs 6h),且带有 OH 或 OCH3 取代基的萘环也会降低活性(5b-c, 6i-j)。③对于6位杂环取代的类似物,引入杂原子后会导致活性整体下降,且六六并环( 8a-c )的活性显著好于五六并环( 8d-h )。 ④对于7位的替换,大基团对活性不利。溴原子是最佳取代,随着取代基大小的增加,活性略有下降(9>11b>11a)。 ⑤5 位苯环取代依旧可以保持活性(13)。
表 1 针对两种菌株BAA1875和R20291的抗艰难梭菌活性 (MIC, µg/ml)
化合物 BAA 1875a R20291a 化合物 BAA 1875a R20291a 1 >256 >256 8a 4 2 3c >256 >256 8b 8 8 5a 4 2 8c 8 4 5b 32 32 8d >256 >256 5c 8 8 8e >256 >256 6a 1 4 8f 32 32 6b 1 4 8g 64 32 6c >256 >256 8h 64 16 6d >256 >256 8i 32 32 6e 8 8 9 0.5 0.25 6f 0.5 0.25 11a 4 4 6g 2 2 11b 2 1 6h 8 4 13 0.5 0.25 6i 16 8 万古霉素 0.25 0.125 6j 16 16 注:a.化合物起始浓度256 µg/ml -
进一步测试了部分8-羟基喹啉衍生物针对艰难梭菌R20291的最小杀菌浓度(MBC)(表2),所测试化合物的最小杀菌浓度(MBC)和MIC相当,表明这些化合物能够有效地杀死艰难梭菌,具有更强的抑菌作用。在这些化合物中,化合物 6f 表现出良好的活性,这使其成为可进一步开发的良好先导化合物。
表 2 部分8-羟基喹啉衍生物的MIC和MBC测试结果(µg/ml)
化合物 R20291 MIC MBC 5a 3.2 3.2 6e 6.4 6.4 6f 0.1 0.2 6h 3.2 3.2 9 0.1 0.2 11a 3.2 3.2 13 0.4 0.4 -
基于重要的抗艰难梭菌骨架8-羟基喹啉,我们设计并合成了一系列8-羟基喹啉衍生物,所有目标化合物均经过了核磁和质谱确证结构,纯度均高于95%。 针对艰难梭菌菌株BAA1875和R20291的抑菌试验显示,多个化合物具有强效的抑菌作用,且MIC 与MBC 非常接近,表明这些化合物还具有强效的杀菌作用。这使它们成为可进一步开发的良好先导化合物,后续的结构优化工作尚在进行之中。
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives as potential clostridium difficile antibiotics
-
摘要:
目的 艰难梭菌感染(CDI)目前治疗措施主要包括抗生素疗法、粪菌移植疗法等,其治疗后存在较高的复发率,需寻求一种更有效的替代疗法。 方法 本研究基于有前景的8-羟基喹啉骨架,设计、合成了一系列8-羟基喹啉衍生物。 结果 针对艰难梭菌的活性测试表明,多数分子对艰难梭菌具有良好的抑菌作用,其中化合物 6 f 显示出较强的杀伤艰难梭菌活性。 结论 本研究发现了新型具有抗艰难梭菌的8-羟基喹啉衍生物,可作为良好的先导化合物进一步研发。 Abstract:Objective To find a more effective alternative therapy for antibiotic therapy and fecal microbiota transplantation in current primary treatment of clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) because of the high recurrence rate. Methods A series of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives were designed and synthesized based on 8-hydroxyquinoline scarffold. Results The activity test against C. difficile showed that most of the molecules exhibited good antibacterial activity against C. difficile, and compound 6 f showed attractive anti-C. difficile activity. Conclusion A new type of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives with anti-clostridium difficile was found, which could be used as good lead compounds for further development. -
艰难梭菌的感染率近年来有所提高[1],其孢子很难根除,并且很容易通过医护人员传播,是医院、养老院和一些健康护理机构出现腹泻感染的原因之一[2]。目前针对艰难梭菌的可用治疗方法都有一些缺点,例如成本过高、耐药性的发展和选择性问题。 虽然轻度至中度的艰难梭菌病例目前可以通过可用的治疗方法进行控制,但对严重的病例可能需要使用单一常规药物或联合疗法进行长期抑制治疗,如果不成功,则要采用非常规和(或)侵入性的手段,如粪便移植和结肠切除术[3]。因此,临床上对药物研发需求越来越大,寻求一种更有效的替代疗法迫在眉睫[1]。
含有喹啉的杂芳族化合物具有多种生物和药理活性,例如,抗疟疾[4]、抗结核病[5]、抗炎[6]、抗癌[7]、抗高血压[8]以及抗菌[9-11]。Musiol 等[12]曾报道 8-羟基喹啉衍生物的抗真菌活性。此外,8-羟基喹啉衍生物显示出对神经退行性疾病如阿尔茨海默病良好活性[13]。最近,研究发现8-羟基喹啉衍生物具有抗金黄色葡萄球菌的潜在作用[14]。我们的小组最近通过药物数据库筛选发现,溴氧喹啉(5,7-二溴喹啉-8-酚)对艰难梭菌具有强效抗菌活性。基于此有前景的化合物,我们进行了一系列8-羟基喹啉类似物的设计、合成和抗艰难梭菌活性研究。
1. 目标化合物的设计
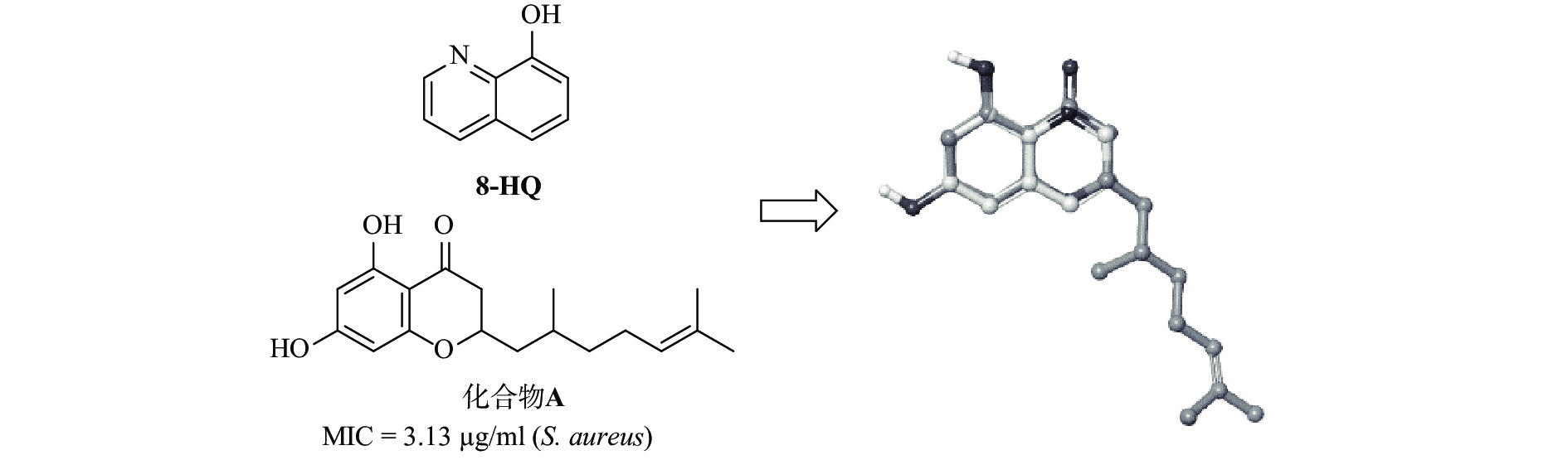
早期研究发现,黄酮化合物 A(图1)具有良好的抗菌活性,对金黄色葡萄球菌的最小抑菌浓度(MIC)为 3.13 μg/ml [15],而从8-羟基喹啉与化合物A的叠合图(图1)可见,8-羟基喹啉骨架具有与黄酮类化合物相似的药效基团。为了探索取代基的功能并研究详细的 SAR,我们设计并合成了一系列在8-羟基喹啉5、 6和7 位具有芳香取代基的化合物。
2. 材料和方法
2.1 试剂和仪器
化学原料均为市售分析纯;Bruker AM-400 (400 MHz) 核磁共振仪,TMS 作为内标,化学位移与偶合常数分别用 ppm 和 Hz 表示 ;Agilent 6538 UHD Accurate-Mass Q-TOF LC/MS高分辨质谱(HRMS)仪。
2.2 6-位取代目标化合物的合成
4-溴-2-甲氧基苯胺通过 Skraup 合成[16] ,在 H2SO4、3-硝基苯磺酸钠和甘油中回流,得到中间体 1(见图2)。随后,甲基保护基被脱除,再在DIPEA存在下用MOMCl保护,得到化合物 2。此外,化合物 1 还经 Suzuki 反应与芳基硼酸偶联反应得到中间体 3a-j 。 化合物2与苯乙烯偶联,得到化合物 4a,然后使用 1 mol/L 的盐酸脱保护,得到化合物 5a。其中,化合物 3a-g 和 3i-j使用 HBr (48%) 在回流下脱保护,以较高的收率得到化合物 6a-g 和 6i-j,化合物 3h 用 BBr3 处理得到化合物 6h。
为了进一步研究8-羟基喹啉衍生物的构效关系,我们还设计并合成了)一系列6位杂环取代的化合物, 如图3 所示。首先,中间体1或相应的硼酸与市售芳基硼酸或卤代物通过Suzuki反应偶联得到7a-i,然后在氢溴酸(48%)中回流脱甲基以高收率得到化合物8a-i。
2.3 5-位和7-位取代目标化合物的合成
为了研究5和7位的构效关系,我们还设计合成了一系列在5和7位具有不同取代基的化合物。 如图4 所示,市售的 7-溴-8-羟基喹啉(9)经MOM和甲基保护,分别得到中间体10a和10b。 随后,这些中间体与苯乙烯和苯硼酸偶联,分别得到中间体11a 和11b。 最后,化合物 17a 和 17b 分别经 1 mol/L盐酸水溶液和氢溴酸水溶液(48%)脱保护,得到所需的 8-羟基喹啉类似物18a 和18b。 此外, 5 位取代化合物的合成如图5 所示。首先,将市售的8-羟基喹啉在碳酸钾存在下与碘甲烷反应,随后在甲醇中与溴素在室温下反应得到中间体12[17]。随后,化合物12按照与前述相同的方法合成13。
3. 结果
3.1 8-羟基喹啉衍生物的抗艰难梭菌活性评价
所有目标化合物及部分中间体均针对两种菌株 BAA1875 和 R20291 的艰难梭菌进行了活性测试。基于生物活性(见表1),SAR总结如下:①8位的游离羟基对艰难梭菌的抑制活性起着非常重要的作用,其甲基化会大幅降低活性(化合物1和3c分别对BAA-1875为大于256 μg/ml)。② 6 位的取代对于活性很重要,体积大的基团(例如萘基)对活性有利(萘基 6f > 苯基 6a )。此外,对于 6 位萘取代的化合物,2-萘基优于1-萘基(6f vs 6h),且带有 OH 或 OCH3 取代基的萘环也会降低活性(5b-c, 6i-j)。③对于6位杂环取代的类似物,引入杂原子后会导致活性整体下降,且六六并环( 8a-c )的活性显著好于五六并环( 8d-h )。 ④对于7位的替换,大基团对活性不利。溴原子是最佳取代,随着取代基大小的增加,活性略有下降(9>11b>11a)。 ⑤5 位苯环取代依旧可以保持活性(13)。
表 1 针对两种菌株BAA1875和R20291的抗艰难梭菌活性 (MIC, µg/ml)化合物 BAA 1875a R20291a 化合物 BAA 1875a R20291a 1 >256 >256 8a 4 2 3c >256 >256 8b 8 8 5a 4 2 8c 8 4 5b 32 32 8d >256 >256 5c 8 8 8e >256 >256 6a 1 4 8f 32 32 6b 1 4 8g 64 32 6c >256 >256 8h 64 16 6d >256 >256 8i 32 32 6e 8 8 9 0.5 0.25 6f 0.5 0.25 11a 4 4 6g 2 2 11b 2 1 6h 8 4 13 0.5 0.25 6i 16 8 万古霉素 0.25 0.125 6j 16 16 注:a.化合物起始浓度256 µg/ml 3.2 部分8-羟基喹啉衍生物的MIC和MBC测试结果
进一步测试了部分8-羟基喹啉衍生物针对艰难梭菌R20291的最小杀菌浓度(MBC)(表2),所测试化合物的最小杀菌浓度(MBC)和MIC相当,表明这些化合物能够有效地杀死艰难梭菌,具有更强的抑菌作用。在这些化合物中,化合物 6f 表现出良好的活性,这使其成为可进一步开发的良好先导化合物。
表 2 部分8-羟基喹啉衍生物的MIC和MBC测试结果(µg/ml)化合物 R20291 MIC MBC 5a 3.2 3.2 6e 6.4 6.4 6f 0.1 0.2 6h 3.2 3.2 9 0.1 0.2 11a 3.2 3.2 13 0.4 0.4 4. 讨论
基于重要的抗艰难梭菌骨架8-羟基喹啉,我们设计并合成了一系列8-羟基喹啉衍生物,所有目标化合物均经过了核磁和质谱确证结构,纯度均高于95%。 针对艰难梭菌菌株BAA1875和R20291的抑菌试验显示,多个化合物具有强效的抑菌作用,且MIC 与MBC 非常接近,表明这些化合物还具有强效的杀菌作用。这使它们成为可进一步开发的良好先导化合物,后续的结构优化工作尚在进行之中。
-
表 1 针对两种菌株BAA1875和R20291的抗艰难梭菌活性 (MIC, µg/ml)
化合物 BAA 1875a R20291a 化合物 BAA 1875a R20291a 1 >256 >256 8a 4 2 3c >256 >256 8b 8 8 5a 4 2 8c 8 4 5b 32 32 8d >256 >256 5c 8 8 8e >256 >256 6a 1 4 8f 32 32 6b 1 4 8g 64 32 6c >256 >256 8h 64 16 6d >256 >256 8i 32 32 6e 8 8 9 0.5 0.25 6f 0.5 0.25 11a 4 4 6g 2 2 11b 2 1 6h 8 4 13 0.5 0.25 6i 16 8 万古霉素 0.25 0.125 6j 16 16 注:a.化合物起始浓度256 µg/ml 表 2 部分8-羟基喹啉衍生物的MIC和MBC测试结果(µg/ml)
化合物 R20291 MIC MBC 5a 3.2 3.2 6e 6.4 6.4 6f 0.1 0.2 6h 3.2 3.2 9 0.1 0.2 11a 3.2 3.2 13 0.4 0.4 -
[1] TAGLIALEGNA A. Helping C. difficile to thrive[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2023, 21(2):65. [2] CHEN J, LI Y, WANG S, et al. Targeting Clostridioides difficile: new uses for old drugs[J]. Drug Discov Today, 2022, 27(7):1862-1873. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2022.03.021 [3] LIM S C, KNIGHT D R, RILEY T V. Clostridium difficile and one health[J]. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2020, 26(7):857-863. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.10.023 [4] LILIENKAMPF A, MAO J, WAN B, et al. Structure-activity relationships for a series of quinoline-based compounds active against replicating and nonreplicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J]. J Med Chem, 2009, 52(7): 2109-2118. [5] SILVA J, BATTS D H, FEKETY R, et al. Treatment of Clostridium difficile colitis and diarrhea with vancomycin[J]. Am J Med, 1981, 71(5):815-822. [6] NASVELD P, KITCHENER S. Treatment of acute vivax malaria with tafenoquine[J]. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg, 2005, 99(1):2-5. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2004.01.013 [7] LEATHAM P A, BIRD H A, WRIGHT V, et al. A double blind study of antrafenine, naproxen and placebo in osteoarthrosis[J]. Eur J Rheumatol Inflamm, 1983, 6(2):209-211. [8] LAM K H, GAMBARI R, YUEN M C W, et al. The preparation of 2, 6-disubstituted pyridinyl phosphine oxides as novel anti-cancer agents[J]. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2009, 19(8):2266-2269. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.02.091 [9] MAHAMOUD A, CHEVALIER J, DAVIN-REGLI A, et al. Quinoline derivatives as promising inhibitors of antibiotic efflux pump in multidrug resistant Enterobacter aerogenes isolates[J]. Curr Drug Targets, 2006, 7(7):843-847. doi: 10.2174/138945006777709557 [10] MUSIOL R, TABAK D, NIEDBALA H, et al. Investigating biological activity spectrum for novel quinoline analogues 2: Hydroxyquinolinecarboxamides with photosynthesis-inhibiting activity[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2008, 16(8):4490-4499. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.02.065 [11] PALIT P, PAIRA P, HAZRA A, et al. Phase transfer catalyzed synthesis of bis-quinolines: Antileishmanial activity in experimental visceral leishmaniasis and in vitro antibacterial evaluation[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2009, 44(2):845-853. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2008.04.014 [12] MUSIOL R, JAMPILEK J, KRALOVA K, et al. Investigating biological activity spectrum for novel quinoline analogues[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2007, 15(3):1280-1288. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2006.11.020 [13] BARNHAM K J, GAUTIER E C, KOK G B, et al. 8-hydroxy quinoline derivatives. WO2004007461 A1[P]. 2004. [14] LAM K H, GAMBARI R, LEE K K H, et al. Preparation of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives as potential antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2014, 24(1):367-370. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.10.072 [15] FENG L, MADDOX M M, ALAM M Z, et al. Synthesis, structure-activity relationship studies, and antibacterial evaluation of 4-chromanones and chalcones, as well as olympicin A and derivatives[J]. J Med Chem, 2014, 57(20):8398-8420. doi: 10.1021/jm500853v [16] ZHANG L, MEGGERS E. An extremely stable and orthogonal DNA base pair with a simplified three-carbon backbone[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2005, 127(1):74-75. doi: 10.1021/ja043904j [17] KOHO K T. Preparation of carbostyryl derivatives as phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors for treatment of heart failure, hypertension, Crohn’s disease, etc. JP2009040711[P]. 2009. -





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:


