-
血红铆钉菇[Chroogomphus rutilus (Schaeff.) O.Ƙ. Mill.],属担子菌亚门伞菌目铆钉菇科铆钉菇属[1]。菌体铆钉状且菌肉为酒红色,故名血红铆钉菇。分布于中国北方及西南多省,以及日本、欧洲及北美多国,主要生于松林中地上的杂草丛林之间,是一种与油松、樟子松、马尾松、赤松共生的外生菌根真菌,群生、散生或单生,营养价值极高,深受人们喜爱[2]。研究表明,血红铆钉菇富含蛋白质、多糖、黄酮、香豆素及甾醇[3-8]等多种活性物质,具有极高的食用和药用价值。随着人民生活水平的提高和科学技术的不断进步,糖化学及其活性研究正在经历着飞速的发展,越来越多的动物多糖、植物多糖、真菌多糖被开发利用。多糖作为食用菌重要的活性成分,具有抗肿瘤、抗氧化、抗疲劳、免疫调节、神经保护、降血糖、降血脂[9-13]等诸多药理作用。目前,各类真菌多糖的免疫调节作用研究已广泛开展[14-23]。然而,迄今关于血红铆钉菇多糖开发的研究较少,对其免疫调节作用的研究报道亦少,本文探讨血红铆钉菇多糖对小鼠巨噬细胞RAW264.7的细胞毒性、免疫调节因子释放、NF-κB信号通路激活等一系列的免疫调节作用,以期为血红铆钉菇进一步的开发利用提供依据。
-
RAW264.7细胞购自中国科学院上海细胞库,储藏于牡丹江医学院医药研究中心−80 ℃冰箱中,经复苏后,置于含10% FBS的DMEM培养基中培养。
-
血红铆钉菇经25%乙醇沉淀后,通过DEAE-52纤维柱洗脱出多糖组分CRPS25-Ⅱ,实验室自制。
-
κZ-II匀浆仪(Servicebio);κZ-II酶标仪(Rayto);D3024R台式高速冷冻型微量离心机、D1008E台式高速冷冻离心机(DRAGONLAB);Stepone plus荧光定量PCR仪(ABI);SW-CJ-1FD超净工作台(苏净安泰);NanoDrop2000超微量分光光度计(Thermo);G0203-150G化学发光仪(CLINX);FBZ2001-up-p标准试剂型纯水仪(青岛富勒姆科技有限公司)。
-
RNA提取液(批号:G3013)、引物、RIPA裂解液(批号:G2002)、PMSF(100mM,批号:G2008)、磷酸化蛋白酶抑制剂(批号:G2007)、β-肌动蛋白(批号:GB12001)、GAPDH(批号:GB12002)、Histone H3(批号:GB11026)、HRP标记山羊抗兔(批号:GB23303)、HRP标记驴抗山羊(批号:GB23404)、HRP标记山羊抗小鼠(批号:GB23301)、HRP标记山羊抗大鼠(批号:GB23302)、转移缓冲液(批号:G2017)、电泳缓冲液(批号:G2018)、TBS缓冲液(批号:G0001-2L)均购自Servicebio公司;三氯甲烷、异丙醇、无水乙醇(国药集团化学试剂有限公司)。
-
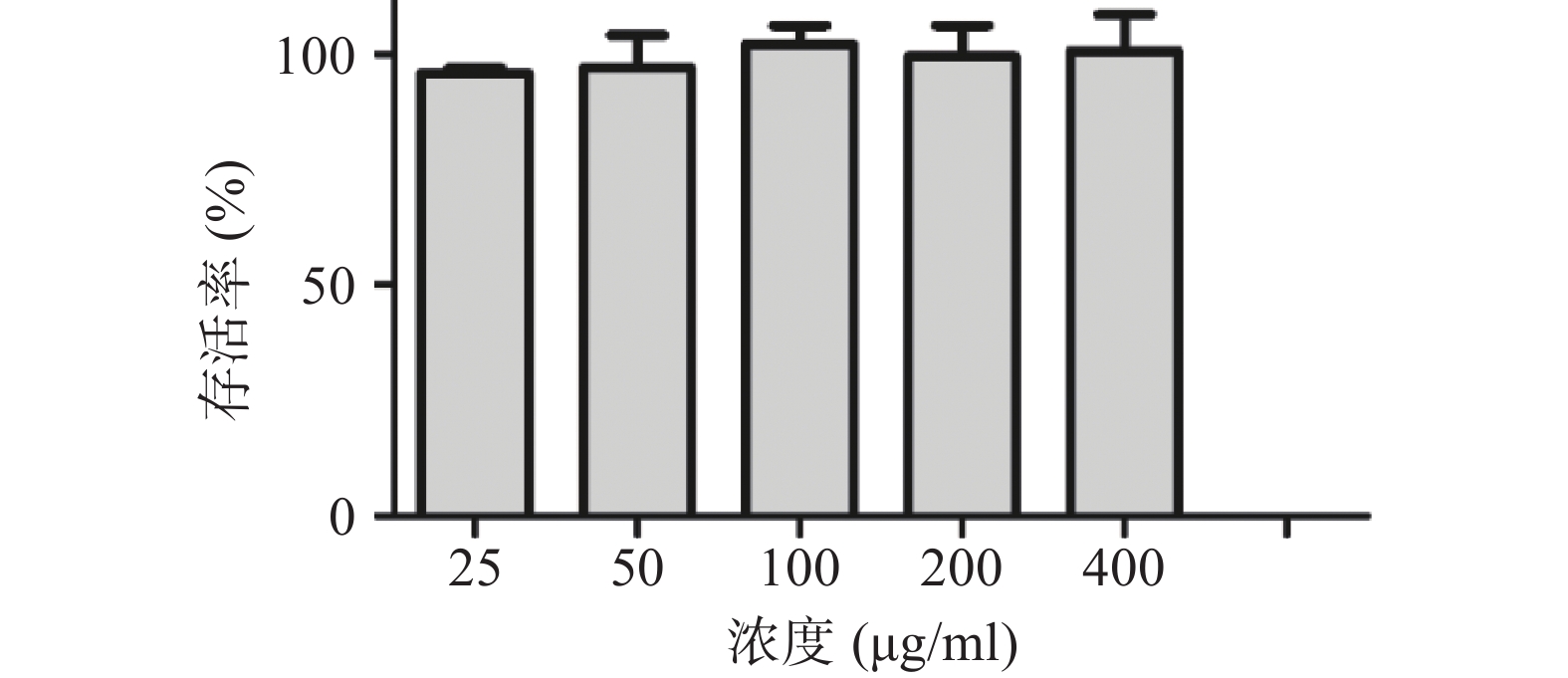
收集对数期RAW264.7细胞,制成单细胞悬液,RAW264.7细胞以1×106个细胞/孔接种于96孔板中,随后,置于恒温培养箱(37 ℃,5% CO2)中培养24 h(边缘孔用无菌PBS填充),培养完成后去除原有培养基,加入浓度梯度分别为25、50、100、200、400 μg/ml的血红铆钉菇多糖溶液(各设置6个复孔)于恒温箱中培养12 h。弃去孔内原有培养液,每孔加入配制好的MTT溶液20 μl,连续培养4 h后,弃去原有MTT溶液。每孔加入150 μl DMSO,于恒温箱中孵育10 min后,用锡纸包裹避光,操作轻盈防震,使结晶物充分溶解。孵育完成后,置于490 nm处测定吸光度(A)值。计算细胞增殖活力:细胞增殖活力=[(试验组OD均值-对照组OD均值)/ 对照组OD均值]×100%。实验表明血红铆钉菇多糖CRPS25-Ⅱ在25~400 μg/ml的范围内无明显的细胞毒性,见图1。
-
收集对数期RAW264.7细胞,制成单细胞悬液,随后以每孔1×106个细胞接种于六孔培养板中,加入1 ml的DMEM完全培养基,并于恒温培养箱(37 ℃,5% CO2)中培养24 h。设置不同浓度梯度的血色铆钉菇多糖溶液1、20、40、80、160 μg/ml及空白对照组,于恒温培养箱中孵育12 h。弃去原培养基,PBS清洗2次,加入1 ml的Trizol试剂(冰上操作)。12000 r/min离心10 min取上清。加入250 μl三氯甲烷,颠倒离心管15 s,充分混匀,静置3 min。4 ℃下12000 r/min离心10 min。将上清转移到一新的离心管中,加入0.8倍体积的异丙醇,颠倒混匀。−20 ℃放置15 min,4 ℃下12 000 r/min离心10 min,管底的白色沉淀即为RNA。吸除液体,加入75%乙醇1.5 ml洗涤沉淀。4 ℃下12 000 r/min离心5 min。将液体吸除干净,将离心管置于超净台上吹3 min。加入15 μl无RNA酶的水溶解RNA。55 ℃孵育5 min。使用Nanodrop 2000检测RNA浓度及纯度:仪器空白调零后取2.5 μl待测RNA溶液于检测基座上,放下样品臂,开始吸光值检测。将浓度过高的RNA进行适当比例的稀释,使其终浓度为100~500 ng/μl。
-
取一PCR管,加入含10 μl RNA的溶液。加入0.5 μl Oligo (dT)18底物和0.5 μl随机六聚体引物。用无核糖核酸酶的去离子水补足至15 μl。于PCR仪上65 ℃保温5 min,迅速置冰上冷却。依次加入4 μl×5反应缓冲液,1 μl RT酶混合物,用移液器抽吸混匀。于PCR仪上42 ℃保温60 min,结束后70 ℃保温5 min灭活反转录酶。
-
①取0.2 ml PCR管,配制如下反应体系,每个反转录产物配制3管:2×荧光定量PCR试剂10 μl;2.5 μmol/L基因引物2 μl;反转录产物2 μl;双蒸水6 μl。
②PCR扩增:预变性95 ℃,10 min;循环(40次)95 ℃,15 s→60 ℃,60 s;熔解曲线60 ℃→95 ℃,每15 s升温0.3 ℃
-
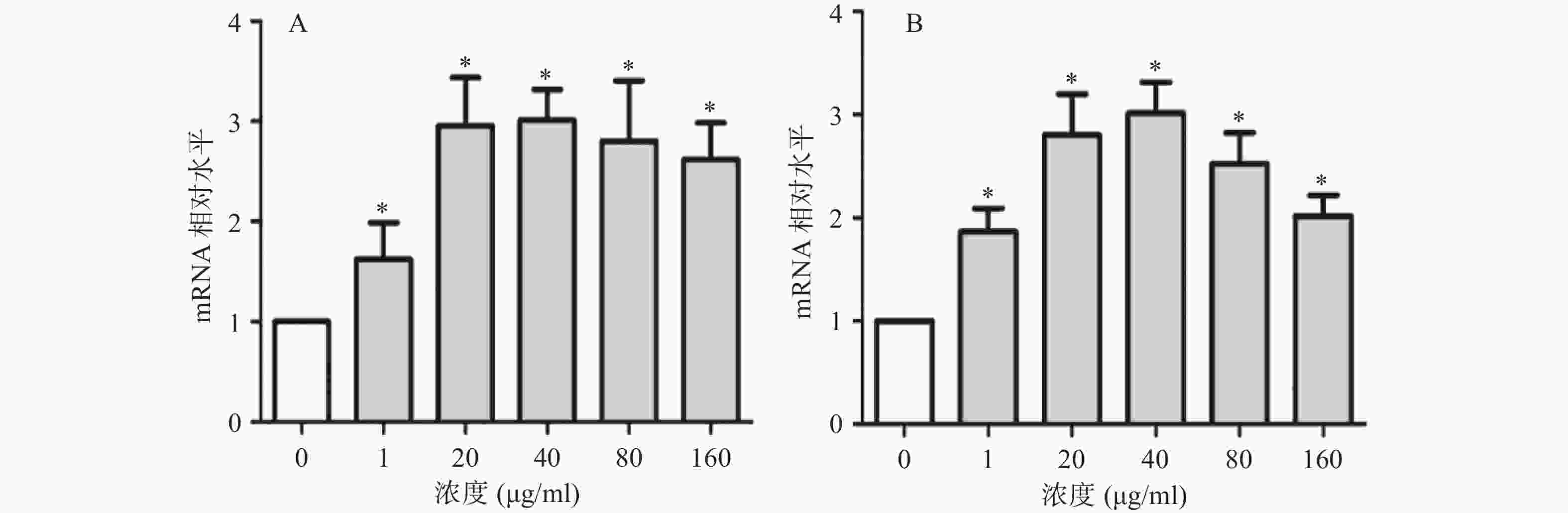
使用SPSS 25.0统计软件进行单因素方差分析和t检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。结果表明,血红铆钉菇多糖CRPS25-Ⅱ在1~160 μg/ml范围内对细胞炎症因子IL-6和TNF-α的mRNA表达均有促进作用,其中在40 μg/ml时达到峰值,80~160 μg/ml呈逐渐减弱的趋势,见图2。
-
收集对数期RAW264.7细胞,制成单细胞悬液,随后以每孔1×106个细胞接种于六孔培养板中,加入1 ml的DMEM完全培养基,并于恒温培养箱(37 ℃,5% CO2)中培养24 h。设置不同浓度梯度的血色铆钉菇多糖溶液1、20、40、80、160 μg/ml及空白对照组,于恒温培养箱中孵育12 h,用PBS冲洗细胞2~3次,最后一次清洗完成,倒掉PBS,用移液器尽量吸干残留液体;加入适当体积的RIPA裂解液(使用前数分钟内加入蛋白酶抑制剂)于培养板/培养瓶内3~5 min。期间反复晃动培养板/瓶,使试剂与细胞充分接触;用细胞刮刀将细胞刮下,转移到1.5 ml离心管中;冰上裂解30 min,期间用移液器反复吹打,确保细胞完全裂解。12000 r/min,4 ℃,离心10 min,收集上清,即为总蛋白溶液.
-
将蛋白溶液按照4∶1的比例加入5×还原型蛋白上样缓冲液,沸水浴变性15 min,置于−20 ℃冰箱保存备用。
-
清洗玻璃板;制胶与上样,放入制胶器,插入斜插板将玻璃板固定,检查底部是否对齐,避免漏胶;将分离胶灌到适当的高度,将纯水缓慢均匀加入到分离胶上层,直至加满。大约30 min后待分离胶凝固即可倒去分离胶上层水并用吸水纸将剩余水吸干;配制5%的浓缩胶,加入四甲基乙二胺后立即混合均匀,灌胶,开始电泳;电泳至溴酚蓝里最底部大约1 cm即可终止电泳,进行转膜。将转印完的膜放入装有TBST的孵育槽中,快速涮洗一次,然后加上脱脂牛奶,放置脱色摇床上,室温下封闭30 min;按照抗体说明书,进行一抗稀释,配制好后,倒掉孵育槽中的封闭液,加入配制好的一抗,4 ℃孵育摇床过夜;回收一抗,用TBST快速涮洗膜3次,然后加入TBST,放置脱色摇床上快速洗脱,每次5 min,洗3次;将二抗用TBST按照1∶5000的比例进行稀释,然后加入孵育槽中,放置摇床上慢摇,室温下孵育30 min;用TBST快速涮洗膜3次,然后再加入TBST,放置脱色摇床上快速洗脱,每次5 min,洗3次。
-
在暗室中将ECL A液和ECL B液两种试剂在离心管中等体积混合,在曝光匣上贴双层PE手套或者其他透明薄膜,将聚偏二氟乙烯膜的蛋白面朝上放在曝光匣两层薄膜之间,加入混合好的ECL溶液充分反应,1~2 min后,去尽残液,盖上层薄膜开始压胶片。压完的胶片用显影、定影试剂进行显影和定影。
-
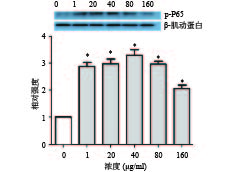
胶片扫描存档,PhotoShop整理去色,Alpha软件处理系统分析目标带的光密度值,使用SPSS 25.0统计软件进行单因素方差分析和t检验,P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。结果表明,血红铆钉菇多糖CRPS25-Ⅱ在1~160 μg/ml范围内对细胞p-P65蛋白的表达有促进作用,其中在40 μg/ml时达到峰值,80~160 μg/ml呈逐渐减弱的趋势,见图3。
-
本文对血红铆钉菇多糖进行了研究,在实验室通过水提醇沉的方法制备出血红铆钉菇多糖,通过DEAE纤维素-52柱层析精制得到CRPS25-Ⅱ,而后将CRPS25-Ⅱ溶液按1~800 μg/ml浓度分别加入细胞悬液中,按照6、12、24 h进行培养,考察多糖浓度和孵育时间对巨噬细胞RAW264.7的影响,最终发现1~400 μg/ml浓度范围孵育12 h细胞生长状态良好,适于实验研究。
人体的免疫系统调控着机体健康的平衡与稳定,巨噬细胞是人体天然免疫防线的重要一员,参与机体的非特异性防卫(先天性免疫)和特异性防卫(细胞免疫)。巨噬细胞可以呈递抗原、分泌细胞因子等生物活性物质,从而调控机体微环境,达到抗炎、抗肿瘤的作用,细胞因子通过调节细胞分化、生长和凋亡控制整个机体的动态平衡。
本实验是以小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞为靶细胞,研究CRPS25-Ⅱ体外的免疫调节活性,探讨CRPS25-Ⅱ在体内发挥免疫调节活性的作用机制。通过MTT法检测了CRPS25-Ⅱ对巨噬细胞RAW264.7的细胞毒性,数据表明多糖浓度在25~400 μg/ml范围内CRPS25-Ⅱ不具有细胞毒性,说明该药物应用于临床的安全性较高,具备深入研究的意义。通过RT-PCR法证实CRPS25-Ⅱ可显著促进腹腔巨噬细胞释放IL-6和TNF-α等细胞因子,通过增强细胞因子的活性,达到抗炎、抗肿瘤的目的。研究表明多糖浓度在1~160 μg/ml的范围内,CRPS25-Ⅱ对IL-6和TNF-α释放具有显著促进作用,其中1~40 μg/ml浓度范围呈上升趋势,40~160 μg/ml范围内随着CRPS25-Ⅱ的浓度的增加对IL-6和TNF-α释放的促进作用逐渐减弱。Western blot试验显示,CRPS25-Ⅱ作用于RAW264.7细胞12 h后,1~160 μg/ml浓度范围内血红铆钉菇多糖均可显著诱导RAW264.7细胞中p-P65蛋白的表达,从而激活NF-κB信号通路,达到免疫调节的作用。其中1~40 μg/ml浓度范围对p-P65蛋白分泌的促进作用呈上升趋势,40~160 μg/ml范围内随着CRPS25-Ⅱ的浓度的增加p-P65蛋白的促进作用逐渐减弱。
综上所述,血红铆钉菇多糖具有显著的免疫调节活性,作为一种新型的免疫调节剂,具有较为广阔的开发前景,后续工作可进行更加系统深入的研究。
Immunoregulatory effect of polysaccharides derived from chroogomphus rutilus on macrophage cell line RAW264.7
-
摘要:
目的 研究血红铆钉菇多糖对RAW264.7小鼠单核巨噬细胞的免疫调节作用。 方法 将小鼠的巨噬细胞进行复苏培养,制备细胞悬液,设置空白对照组以及不同质量浓度的血红铆钉菇多糖(CRPS25-Ⅱ)组(1、20、40、80和160 μg/ml)。采用MTT法测定血红铆钉多糖对小鼠巨噬细胞RAW264.7的细胞毒性;采用RT-PCR法检测血红铆钉菇多糖对小鼠巨噬细胞RAW264.7分泌免疫调节因子IL-6和TNF-α的影响;采用Western-blot法检测血红铆钉菇多糖对小鼠巨噬细胞RAW264.7的NF-κB信号通路中p-P65蛋白表达的影响。 结果 实验证明血红铆钉菇多糖在1~160 μg/ml的范围内没有明显的细胞毒性,CRPS25-Ⅱ质量浓度在1~160 μg/ml可提高细胞因子的分泌量,从而促进细胞因子IL-6和TNF-α的mRNA表达;CRPS25-Ⅱ可促进p-P65蛋白的磷酸化,激活NF-κB信号通路从而促进细胞的免疫调节作用,1~160 μg/ml浓度范围内均可促进p-P65蛋白的增加,1~40 μg/ml呈上升趋势,40~160 μg/ml促进作用逐渐减弱。 结论 血红铆钉菇多糖对小鼠巨噬细胞无毒性,且可以促进炎症因子IL-6和TNF-α的分泌以及激活NF-κB信号通路,从而起到免疫调节作用。 Abstract:Objective To study the immunomodulatory effect of polysaccharides (CRPS25-Ⅱ) derived from Chroogomphus rutilus on mouse mononuclear macrophages, RAW264.7 cells. Methods RAW264.7 cells were resuspended and cultured, cell suspension was prepared. The blank control group and CRPS25-Ⅱ groups with different mass concentrations (1, 20, 40, 80 and 160 μg/ml) were set up. MTT assay was used to determine the cytotoxicity of CRPS25-Ⅱ on RAW264.7 cells. RT-PCR was used to detect the effects of CRPS25-Ⅱ on the secretion of immune regulatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α from RAW264.7 cells. Western blot was used to detect the effects of CRPS25-Ⅱ on the expression of p-P65 protein in NF-κB pathway of RAW264.7 cells. Results The results showed that CRPS25-Ⅱ (1−160 μg/ml) had no obvious cytotoxicity. CRPS25-Ⅱ (1−160 μg/ml) increased the secretion of cytokines, and thus promoted the mRNA expression of IL-6 and TNF-α. CRPS25-Ⅱ increased the phosphorylation of p-P65 protein and activated the NF-κB signaling pathway, and thus promoted the immune regulation of cells. CRPS25-Ⅱ (1−160 μg/ml) could increase the p-P65 protein, and the promoting effects of CRPS25-Ⅱshowed an upward trend in the concentration range of 1−40 μg/ml and gradually weakened in the concentration range of 40−160 μg/ml. Conclusion Polysaccharides derived from chroogomphus rutilus had no cytotoxicity to mouse macrophages, and could promote the secretion of inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α and activate the NF-κB signaling pathway, thus playing an immunomodulatory role. -
Key words:
- CRPS25-Ⅱ /
- RAW264.7 cells /
- immune regulation
-
[1] 戴玉成. 中国药用真菌图志[M]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学出版社, 2013 [2] 栾庆书. 血红铆钉菇研究现状及开发利用[J]. 食用菌, 2002, 24(2):2-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8357.2002.02.001 [3] 岳峥嵘, 赵博, 张国财, 等. 血红铆钉菇多糖超声微波联合提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技, 2020, 41(22):165-171. [4] 李贞卓, 包海鹰. 血红铆钉菇化学成分和药理活性研究概述[J]. 菌物研究, 2015, 13(3):181-186. [5] 王贺, 宋文刚, 任婷, 等. 血红铆钉菇多糖分离纯化及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 北华大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 20(1):64-67. [6] 张海悦, 杨雪, 李震, 等. 血红铆钉菇黄酮体外抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2016, 37(19):109-113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.19.026 [7] MARTÍN M P, SIQUIER J L, SALOM J C, et al. Barcoding sequences clearly separate Chroogomphus mediterraneus (Gomphidiaceae, Boletales) from C. rutilus, and allied species[J]. Mycoscience,2016,57(6):384-392. doi: 10.1016/j.myc.2016.06.004 [8] LUO J, ZHOU W, CAO S, et al. Chemical constituents of Chroogomphus rutilus (schaeff.) o. k. mill[J]. Biochem Syst Ecol,2015,61:203-207. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2015.06.013 [9] SONG S, YANG H, SU C P, et al. Ultrasonic-microwave assisted synthesis of stable reduced graphene oxide modified melamine foam with superhydrophobicity and high oil adsorption capacities[J]. Chem Eng J,2016,306:504-511. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.086 [10] 李志锐, 韩淑琴. 超声-微波协同萃取玛卡多糖工艺研究[J]. 农产品加工, 2017(3):22-23, 27. [11] GAO C J, WANG Z Y, SU T T, et al. Optimisation of exopolysaccharide production by Gomphidius rutilus and its antioxidant activities in vitro[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2012,87(3):2299-2305. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.10.064 [12] 唐超, 王清吉, 葛蔚, 等. 血红铆钉菇多糖对小鼠S180肉瘤的抑制作用[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(6):2966-2967. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.06.076 [13] WANG C, ZHANG J, WANG F, et al. Extraction of crude polysaccharides from Gomphidius rutilus and their antioxidant activities in vitro[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2013,94(1):479-486. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.01.034 [14] 李燕华, 李仲昆, 李丛元, 夏洪颖. 车前草粗多糖对人巨噬细胞免疫功能的调节作用及其机制研究[J/OL]. 中药材, 2020(11): 2795-2798. [15] 王晶, 史琪, 随晶晶, 等. 鳞柄小奥德蘑多糖对巨噬细胞免疫功能的调节作用[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2020, 32(5):845-850, 892. [16] 孙林浩, 程安怡, 黄小红, 等. 黄芪多糖对大黄鱼头肾巨噬细胞的免疫调节作用[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2020, 39(1):27-34. [17] 刘肖肖, 汪雯翰, 冯婷, 等. 金针菇子实体多糖FVPB1对小鼠T细胞和巨噬细胞的免疫调节作用[J]. 食用菌学报, 2019, 26(4):123-130. [18] 季瑞雪, 鹿保鑫, 王新茹, 等. 野生亚侧耳多糖的提取和对巨噬细胞RAW264.7的免疫调节作用研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2020, 41(4):271-276. [19] 木尼萨·迪力夏提. 阿里红多糖对RAW264.7巨噬细胞免疫调节作用机制的初步研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学, 2019. [20] 热西代姆·阿卜力孜, 李敏, 胡君萍. 锁阳多糖对巨噬细胞RAW264.7的免疫调节作用的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2018, 9(21):5694-5698. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.21.027 [21] 张丽娟, 王珍, 廖尚高. 太子参多糖对RAW 264.7巨噬细胞免疫调节作用的初步研究[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 2018, 37(4):14-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9690.2018.04.003 [22] 吴静, 胡居吾, 熊伟, 等. 樟树果实多糖对巨噬细胞RAW264.7的免疫调节作用[J]. 现代食品科技, 2018, 34(9):12-18, 309. [23] 热孜亚木·吾甫尔, 李月红, 海力茜·陶尔大洪. 恰麻古多糖对巨噬细胞RAW264.7体外免疫调节作用初探[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2018, 30(1):15-20. -




 下载:
下载: