-
神经炎症是外周血液系统和中枢神经系统中免疫细胞活化和浸润、神经胶质细胞活化和炎性介质产生的过程[1]。脊髓中产生的炎性神经胶质介质调节突触传递,诱导和维持慢性疼痛,并提供神经炎症和慢性疼痛之间的联系[2]。炎症疼痛是一种常见的慢性疾病,以往研究提示,前动力蛋白(prokineticin,PK)系统参与组织损伤和神经损伤后的外周和中枢敏化,其在炎症疼痛中的作用已经被证实[3]。本文针对近年发表的有关PK系统参与炎症疼痛的研究文献,回顾性分析该镇痛靶点所发挥的镇痛机制。
-
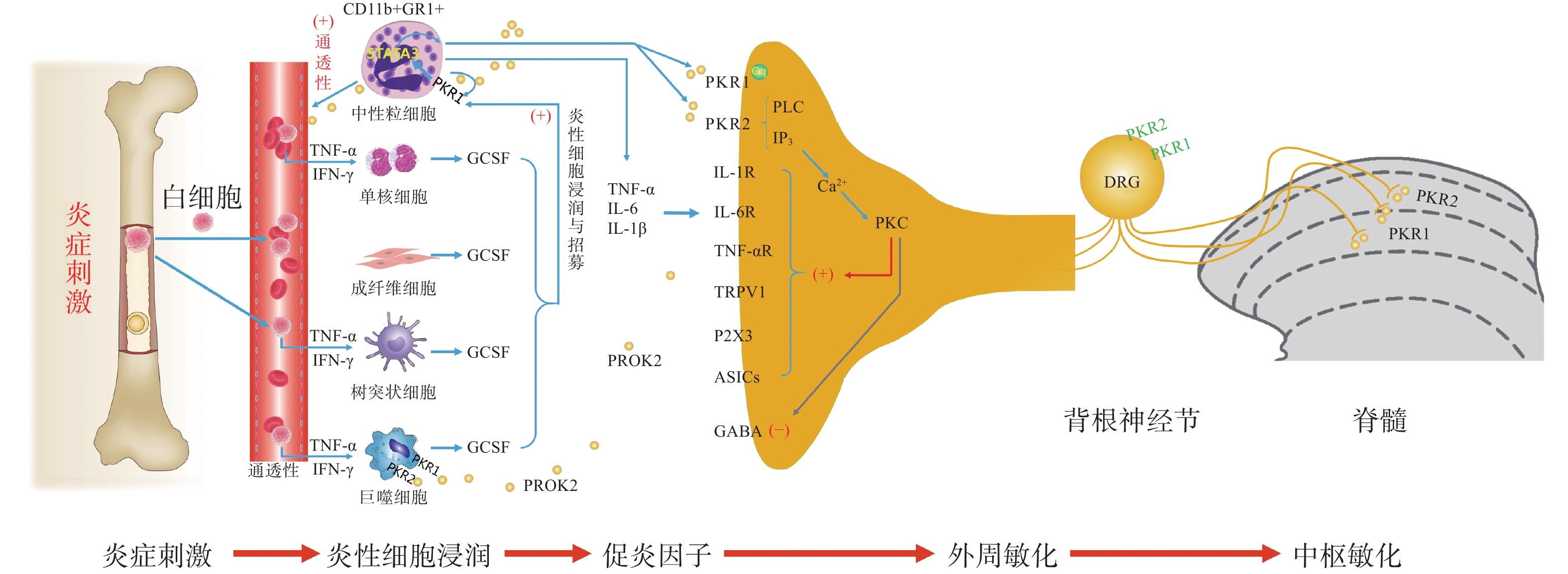
PK信号通路是近年来新发现的介导疼痛发生和维持的重要调节通路,包括两种结构上关联的小分子肽PK1和PK2,以及相应的G蛋白偶联受体PKR1和PKR2[4],PKs及其受体广泛分布在许多人体组织中,例如卵巢、睾丸、肾上腺、胎盘、子宫、大脑、肠道、心脏、骨髓和外周血。虽然PKR1和PKR2在多种组织中共同表达,但PKR1主要表达于外周组织,包括生殖系统[5]的内分泌腺和器官、胃肠道、脾脏、胰腺、肺、心脏和血细胞[6]。PKR2主要在脊髓背角神经元和星形胶质细胞中表达,PKR1主要存在于星形胶质细胞和外周神经元的末端,主要分布于背角的表层(图1)。PK2对这两种受体的亲和力均略高于PK1,而PK1在DRG(背根神经节)和脊髓中不表达,更多地参与血管生成[7],PK1是强有力的血管生成因子,被认为在内分泌腺、心血管、肾脏、肿瘤等血管新生中发挥重要作用。
PKs在神经系统、免疫系统、生殖系统、心血管系统等多部位发挥广泛的生理作用[8],此外PK2可通过降低对化学和机械刺激的疼痛阈值,PKRs的拮抗剂可以用来缓解关节炎炎症和急慢性疼痛[9-10]。PKs通过激活单核细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞上的PKRs,释放炎性细胞因子,触发和维持炎性疼痛(图1),调节免疫炎症反应,而在外周,PK2 /PKR2参与心脏和肾脏新生血管的形成,PKR1的缺失会引起心脏和肾脏的结构和功能变化[11-12]。因此,PKs系统在体内发挥着广泛的生理作用,也是众多疾病的潜在治疗靶点。
-
PK系统在调节与伤害相关的伤害性事件方面起着关键作用,因为它可以调节炎症反应,并同时作用于中枢和外周神经系统。PKRs的激活可以引起痛觉感受,参与痛觉感受器对不同刺激的敏感性。PK系统(PKs和PKRs)是在免疫细胞中参与炎症发生和疼痛传递的重要环节,如PK2参与免疫调节,诱导骨髓细胞分化为单核细胞系和巨噬细胞系,并通过激活单核细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞上的PKRs,释放IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α等炎性细胞因子,触发和维持炎性疼痛,调节免疫炎症反应[13]。
-
PK2在炎症细胞中呈强上调,并在病理状态下维持炎症循环。在纳摩尔范围内,PKs结合并激活受体PKR1和PKR2,使PK2在粒细胞、树突状细胞和巨噬细胞中表达,尤其在局部炎症后表达增加。此外,PK2在免疫细胞和神经胶质细胞中被强烈上调,并在炎症组织中,维持促炎循环。在中性粒细胞依赖性炎症和超痛觉过敏中起关键作用[14]。第一个关于PK的促痛作用的证据来自于对啮齿动物全身注射Bv8/PK2,激活其位于痛觉传入通路的PKRs受体而引起机械和热刺激痛觉过敏[15-16]。在完全弗氏佐剂(CFA)诱导的慢性炎症动物模型中,炎症与浸润炎症组织的粒细胞中PK2的过表达呈高度正相关,而PK2的上调则与炎症相关的痛觉过敏也有关,PKR1拮抗剂PC1能够有效消除CFA引起的痛觉过敏,PC1能明显抑制疼痛、水肿和外渗[17]。PK2在人和动物炎症组织中过表达,主要在浸润的中性粒细胞中作为主要的前感受介质之一,通过激活初级传入神经元上的PKRs受体(图1),增强伤害性信号向中枢神经系统传递。PK2反过来调节血管生成和血管通透性,激活巨噬细胞,并通过PKRs调节毛细血管内皮细胞和白细胞的免疫反应,使得炎症反应循环。
PKR1和PKR2基因的缺失大大降低了炎症诱导的热敏感性和机械敏感性[18-19],但是只有PKR1基因的缺失才会降低PK2的上调,这表明这两种受体虽然都介导疼痛的感受和传递,但只有PKR1参与了炎症过程中Bv8/PK2表达水平的增强。外周局部给予PKRs拮抗剂(PC1或PC7)后疼痛明显减轻,与Bv8/PK2对血管通透性的影响效果一致。在CFA诱导的大鼠或小鼠炎症模型中,在它们健康的爪子中很难检测到的PK2 mRNA,而在炎症皮肤中显著增加,且与浸润细胞(粒细胞和巨噬细胞)相关,并与疼痛和其他炎症在时间上相关。粒细胞释放PK2直接作用于痛觉受器,调节急性炎症性疼痛,进而发挥趋化作用,诱导促炎性巨噬细胞表型,并使Th1(T淋巴细胞1)/Th2(T淋巴细胞2)失衡向Th1倾斜[20-21],抑制Th1介导的免疫反应发挥抗炎作用。
PK2通过激活初级传入神经元上的PKR1和PKR2参与调节痛觉感知(图1),PKRs根据细胞定位可能与G蛋白结合,并激活不同的细胞内信号通路。在单核细胞/巨噬细胞/小胶质细胞谱系中,以及在DRG及脊髓中,PKRs是Gq偶联受体,通过激活磷脂酶C-β (PLC)和形成IP3,促进细胞内Ca2+的动员,诱发蛋白激酶C (PKC) -ε易位到质膜,外周高度表达的PKRs能够对TRPV1(瞬时感受器电位香草素亚型1)和TRPA1 (瞬时感受器电位锚蛋白亚型1)的促进性激活有助于外周敏化[22],尤其是PKR1定位于表达TRPV1和TRPA1的伤害性感觉纤维,在外周DRG水平这些共定位表达,为通过激活PKC-ε的痛觉敏化的协同作用提供了解剖学基础。在大鼠初级感觉神经元中,PK2还通过PKC信号通路增强了门控离子通道电流、抑制GABA激活电流、敏化嘌呤核苷酸P2受体(P2X)[23]。对PK2反应的DRG神经元中50%也表达参与疼痛处理的神经介质,如降钙素基因相关肽(CGRP)和P物质,且在这些神经元暴露于PKs时释放这些神经肽,提示PKs不仅仅参与调节中枢疼痛机制[24]。
-
脊髓PK2主要存在于小鼠脊髓星形胶质细胞中[25],最大密度的PKRs位于背角[26],这表明这些受体可能参与了伤害性信号的中枢传递。非神经元细胞如星形胶质细胞、小胶质细胞等都有PKR1表达,此外,PKR1受体在人和啮齿类单核/巨噬细胞上也比PKR2更为丰富。免疫组化定位显示,PKR1与进入背角和外皮层的伤害感受器末端有关,PKR2存在于沿着浅背角的神经元胞体中,也有可能是投射神经元。PK2诱导脊髓背角和活化的星形胶质细胞中PKRs的激活,有助于中枢敏化和维持慢性痛、神经性疼痛,而且PK2作用于单核细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞上的PKRs,还能诱导炎症因子和致痛因子的释放[27]。在慢些压迫性损伤(CCI)模型中发现,PK2在脊髓星形胶质细胞和初级感觉神经元中表达上调[26]。同时,PK2可抑制下丘脑、导水管周围灰质(PAG)脑区中脑啡肽 (ENK)阳性神经元的动作电位放电,表明PK2能够抑制这类细胞释放阿片样物质。通过配体和受体在神经元和星形胶质细胞中的不同分布,PK2既可以诱导星形胶质细胞激活,发挥星形胶质细胞分泌生长因子的功能,也可以促进脊髓神经元的兴奋性突触传递,增强中枢敏化。PK2小分子拮抗剂改善持续疼痛超敏反应的能力以及在“神经元-神经胶质”和“神经元-免疫细胞”相互作用中分子变化,表明了PK2信号在这种行为中的重要性(图1)。阻断PK受体的药物可能为治疗慢性疼痛状态提供一种新形式[28]。在啮齿动物中注射PK2可激活位于疼痛传递主要部位的PKRs受体诱导对机械和热刺激的痛觉过敏[15]。痛觉过敏的初始阶段是由对伤害感受器的局部作用引起的,痛觉过敏的第二阶段是由于中枢作用引起的[24],表明PKs /PKRs在中枢与周围部位的作用存在差异。在敲除PK2基因的小鼠中进行研究表明,PKs在疼痛感知中具有直接作用,与正常野生型小鼠相比,基因敲除的小鼠对温度和化学刺激的伤害感受降低[18-19]。
损伤部位异常增加的IL-6、IL-1β反过来促进PK2的释放,进一步促进外周免疫细胞的过度激活,加速外周敏化的形成和维持。在DRG和脊髓中,PKR通过Gq激活后增加细胞内钙和诱发蛋白激酶C (PKC) -ε易位到质膜,PK2能够敏化表达TRPV1和TRPA1的痛觉感受器,从外周组织、DRG和脊髓等部位发挥多途径的抑制PK系统的激活而发挥镇痛效应。
综上所述,PKs在疼痛的发生和维持中发挥了重要作用,其在调节与伤害相关的伤害性事件方面起着关键作用,在未来的研究中,有望以PKs信号通路为靶点研究出新的治疗药物。
Prokineticin 2 mediates peripheral and central sensitization of somatic pain
-
摘要: 前动力蛋白2(prokineticin 2,PK2) 是新近发现的一种趋化因子,通过与受体PKR1和PKR2结合,参与机体多种生理功能。PK信号通路是近年来新发现的组织损伤和神经损伤后疼痛发生和维持的重要调节通路,其在调节伤害性事件方面起着关键作用,是众多疾病的潜在治疗靶点。PKRs的激活可以引起痛觉感受,参与痛觉感受器对不同刺激的敏感性。PK系统(PKs和PKRs)是在免疫细胞中参与炎症发生和疼痛传递的重要环节。PK2通过激活初级传入神经元上的PKR1和PKR2参与调节痛觉感知,在大鼠初级感觉神经元中,PK2还通过PKC信号通路增强门控离子通道电流,抑制γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)激活电流,敏化嘌呤核苷酸P2受体(P2X)。本文围绕PK2在躯体疼痛中的研究进展进行述评,以期在未来的研究中,有望找到以PK信号通路为靶点的炎性疼痛治疗的新药。Abstract: Prokineticin 2 (PK2) is a newly discovered chemokine, which participates in various physiological functions of the body by binding to receptors PKR1 and PKR2. PK signaling pathway is a newly discovered important regulatory pathway for the occurrence and maintenance of pain after tissue injury and nerve injury in recent years. It plays a key role in regulating injury-related nociceptive events and is a potential therapeutic target for many diseases. The activation of PKRs can induce pain sensation and participate in the sensitivity of pain receptors to different stimuli. The PK system (PKs and PKRs) is an important link involved in inflammation and pain transmission in immune cells. PK2 is involved in the regulation of pain perception by activating PKR1 and PKR2 on primary sensory neurons. In rat primary sensory neurons, PK2 also enhances gated ion channel current through the PKC signaling pathway, inhibits GABA-activated currents, and sensitizes purine nucleotide P2 receptor (P2X). This paper reviews the research progress of PK2 in physical pain. We hope to find new drugs for the treatment of inflammatory pain that target the PKs signaling pathway in future studies.
-
Key words:
- prokineticin 2 /
- somatalgia /
- PKR1 /
- PKR2 /
- peripheral sensitization /
- central sensitization
-
神经炎症是外周血液系统和中枢神经系统中免疫细胞活化和浸润、神经胶质细胞活化和炎性介质产生的过程[1]。脊髓中产生的炎性神经胶质介质调节突触传递,诱导和维持慢性疼痛,并提供神经炎症和慢性疼痛之间的联系[2]。炎症疼痛是一种常见的慢性疾病,以往研究提示,前动力蛋白(prokineticin,PK)系统参与组织损伤和神经损伤后的外周和中枢敏化,其在炎症疼痛中的作用已经被证实[3]。本文针对近年发表的有关PK系统参与炎症疼痛的研究文献,回顾性分析该镇痛靶点所发挥的镇痛机制。
1. PK系统及其生理功能
PK信号通路是近年来新发现的介导疼痛发生和维持的重要调节通路,包括两种结构上关联的小分子肽PK1和PK2,以及相应的G蛋白偶联受体PKR1和PKR2[4],PKs及其受体广泛分布在许多人体组织中,例如卵巢、睾丸、肾上腺、胎盘、子宫、大脑、肠道、心脏、骨髓和外周血。虽然PKR1和PKR2在多种组织中共同表达,但PKR1主要表达于外周组织,包括生殖系统[5]的内分泌腺和器官、胃肠道、脾脏、胰腺、肺、心脏和血细胞[6]。PKR2主要在脊髓背角神经元和星形胶质细胞中表达,PKR1主要存在于星形胶质细胞和外周神经元的末端,主要分布于背角的表层(图1)。PK2对这两种受体的亲和力均略高于PK1,而PK1在DRG(背根神经节)和脊髓中不表达,更多地参与血管生成[7],PK1是强有力的血管生成因子,被认为在内分泌腺、心血管、肾脏、肿瘤等血管新生中发挥重要作用。
PKs在神经系统、免疫系统、生殖系统、心血管系统等多部位发挥广泛的生理作用[8],此外PK2可通过降低对化学和机械刺激的疼痛阈值,PKRs的拮抗剂可以用来缓解关节炎炎症和急慢性疼痛[9-10]。PKs通过激活单核细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞上的PKRs,释放炎性细胞因子,触发和维持炎性疼痛(图1),调节免疫炎症反应,而在外周,PK2 /PKR2参与心脏和肾脏新生血管的形成,PKR1的缺失会引起心脏和肾脏的结构和功能变化[11-12]。因此,PKs系统在体内发挥着广泛的生理作用,也是众多疾病的潜在治疗靶点。
2. PK系统与躯体痛觉敏化
PK系统在调节与伤害相关的伤害性事件方面起着关键作用,因为它可以调节炎症反应,并同时作用于中枢和外周神经系统。PKRs的激活可以引起痛觉感受,参与痛觉感受器对不同刺激的敏感性。PK系统(PKs和PKRs)是在免疫细胞中参与炎症发生和疼痛传递的重要环节,如PK2参与免疫调节,诱导骨髓细胞分化为单核细胞系和巨噬细胞系,并通过激活单核细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞上的PKRs,释放IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α等炎性细胞因子,触发和维持炎性疼痛,调节免疫炎症反应[13]。
2.1 外周敏化
PK2在炎症细胞中呈强上调,并在病理状态下维持炎症循环。在纳摩尔范围内,PKs结合并激活受体PKR1和PKR2,使PK2在粒细胞、树突状细胞和巨噬细胞中表达,尤其在局部炎症后表达增加。此外,PK2在免疫细胞和神经胶质细胞中被强烈上调,并在炎症组织中,维持促炎循环。在中性粒细胞依赖性炎症和超痛觉过敏中起关键作用[14]。第一个关于PK的促痛作用的证据来自于对啮齿动物全身注射Bv8/PK2,激活其位于痛觉传入通路的PKRs受体而引起机械和热刺激痛觉过敏[15-16]。在完全弗氏佐剂(CFA)诱导的慢性炎症动物模型中,炎症与浸润炎症组织的粒细胞中PK2的过表达呈高度正相关,而PK2的上调则与炎症相关的痛觉过敏也有关,PKR1拮抗剂PC1能够有效消除CFA引起的痛觉过敏,PC1能明显抑制疼痛、水肿和外渗[17]。PK2在人和动物炎症组织中过表达,主要在浸润的中性粒细胞中作为主要的前感受介质之一,通过激活初级传入神经元上的PKRs受体(图1),增强伤害性信号向中枢神经系统传递。PK2反过来调节血管生成和血管通透性,激活巨噬细胞,并通过PKRs调节毛细血管内皮细胞和白细胞的免疫反应,使得炎症反应循环。
PKR1和PKR2基因的缺失大大降低了炎症诱导的热敏感性和机械敏感性[18-19],但是只有PKR1基因的缺失才会降低PK2的上调,这表明这两种受体虽然都介导疼痛的感受和传递,但只有PKR1参与了炎症过程中Bv8/PK2表达水平的增强。外周局部给予PKRs拮抗剂(PC1或PC7)后疼痛明显减轻,与Bv8/PK2对血管通透性的影响效果一致。在CFA诱导的大鼠或小鼠炎症模型中,在它们健康的爪子中很难检测到的PK2 mRNA,而在炎症皮肤中显著增加,且与浸润细胞(粒细胞和巨噬细胞)相关,并与疼痛和其他炎症在时间上相关。粒细胞释放PK2直接作用于痛觉受器,调节急性炎症性疼痛,进而发挥趋化作用,诱导促炎性巨噬细胞表型,并使Th1(T淋巴细胞1)/Th2(T淋巴细胞2)失衡向Th1倾斜[20-21],抑制Th1介导的免疫反应发挥抗炎作用。
PK2通过激活初级传入神经元上的PKR1和PKR2参与调节痛觉感知(图1),PKRs根据细胞定位可能与G蛋白结合,并激活不同的细胞内信号通路。在单核细胞/巨噬细胞/小胶质细胞谱系中,以及在DRG及脊髓中,PKRs是Gq偶联受体,通过激活磷脂酶C-β (PLC)和形成IP3,促进细胞内Ca2+的动员,诱发蛋白激酶C (PKC) -ε易位到质膜,外周高度表达的PKRs能够对TRPV1(瞬时感受器电位香草素亚型1)和TRPA1 (瞬时感受器电位锚蛋白亚型1)的促进性激活有助于外周敏化[22],尤其是PKR1定位于表达TRPV1和TRPA1的伤害性感觉纤维,在外周DRG水平这些共定位表达,为通过激活PKC-ε的痛觉敏化的协同作用提供了解剖学基础。在大鼠初级感觉神经元中,PK2还通过PKC信号通路增强了门控离子通道电流、抑制GABA激活电流、敏化嘌呤核苷酸P2受体(P2X)[23]。对PK2反应的DRG神经元中50%也表达参与疼痛处理的神经介质,如降钙素基因相关肽(CGRP)和P物质,且在这些神经元暴露于PKs时释放这些神经肽,提示PKs不仅仅参与调节中枢疼痛机制[24]。
2.2 中枢敏化
脊髓PK2主要存在于小鼠脊髓星形胶质细胞中[25],最大密度的PKRs位于背角[26],这表明这些受体可能参与了伤害性信号的中枢传递。非神经元细胞如星形胶质细胞、小胶质细胞等都有PKR1表达,此外,PKR1受体在人和啮齿类单核/巨噬细胞上也比PKR2更为丰富。免疫组化定位显示,PKR1与进入背角和外皮层的伤害感受器末端有关,PKR2存在于沿着浅背角的神经元胞体中,也有可能是投射神经元。PK2诱导脊髓背角和活化的星形胶质细胞中PKRs的激活,有助于中枢敏化和维持慢性痛、神经性疼痛,而且PK2作用于单核细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞上的PKRs,还能诱导炎症因子和致痛因子的释放[27]。在慢些压迫性损伤(CCI)模型中发现,PK2在脊髓星形胶质细胞和初级感觉神经元中表达上调[26]。同时,PK2可抑制下丘脑、导水管周围灰质(PAG)脑区中脑啡肽 (ENK)阳性神经元的动作电位放电,表明PK2能够抑制这类细胞释放阿片样物质。通过配体和受体在神经元和星形胶质细胞中的不同分布,PK2既可以诱导星形胶质细胞激活,发挥星形胶质细胞分泌生长因子的功能,也可以促进脊髓神经元的兴奋性突触传递,增强中枢敏化。PK2小分子拮抗剂改善持续疼痛超敏反应的能力以及在“神经元-神经胶质”和“神经元-免疫细胞”相互作用中分子变化,表明了PK2信号在这种行为中的重要性(图1)。阻断PK受体的药物可能为治疗慢性疼痛状态提供一种新形式[28]。在啮齿动物中注射PK2可激活位于疼痛传递主要部位的PKRs受体诱导对机械和热刺激的痛觉过敏[15]。痛觉过敏的初始阶段是由对伤害感受器的局部作用引起的,痛觉过敏的第二阶段是由于中枢作用引起的[24],表明PKs /PKRs在中枢与周围部位的作用存在差异。在敲除PK2基因的小鼠中进行研究表明,PKs在疼痛感知中具有直接作用,与正常野生型小鼠相比,基因敲除的小鼠对温度和化学刺激的伤害感受降低[18-19]。
损伤部位异常增加的IL-6、IL-1β反过来促进PK2的释放,进一步促进外周免疫细胞的过度激活,加速外周敏化的形成和维持。在DRG和脊髓中,PKR通过Gq激活后增加细胞内钙和诱发蛋白激酶C (PKC) -ε易位到质膜,PK2能够敏化表达TRPV1和TRPA1的痛觉感受器,从外周组织、DRG和脊髓等部位发挥多途径的抑制PK系统的激活而发挥镇痛效应。
综上所述,PKs在疼痛的发生和维持中发挥了重要作用,其在调节与伤害相关的伤害性事件方面起着关键作用,在未来的研究中,有望以PKs信号通路为靶点研究出新的治疗药物。
-
[1] VISWANATH O, URITS I, BURNS J, et al. Central neuropathic mechanisms in pain signaling pathways: current evidence and recommendations[J]. Adv Ther,2020,37(5):1946-1959. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01334-w [2] GILHUS N E, DEUSCHL G. Neuroinflammation-a common thread in neurological disorders[J]. Nat Rev Neurol,2019,15(8):429-430. doi: 10.1038/s41582-019-0227-8 [3] FRANCHI S, SACERDOTE P, PANERAI A. The prokineticin system: an interface between neural inflammation and pain[J]. Neurol Sci,2017,38(Suppl 1):27-30. [4] LATTANZI R, MAFTEI D, NEGRI L, et al. PK2β ligand, a splice variant of prokineticin 2, is able to modulate and drive signaling through PKR1 receptor[J]. Neuropeptides,2018,71:32-42. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2018.06.005 [5] LIU Y N, YANG Z, KONG D B, et al. Metformin ameliorates testicular damage in male mice with streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes through the PK2/PKR pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev,2019,2019:5681701. [6] BASSI I, LUZZANI F, MARELLI F, et al. Knocking-down of the Prokineticin receptor 2 affects reveals its complex role in the regulation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal axis in the zebrafish model[J]. Sci Rep,2020,10(1):7632. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64077-2 [7] REN P, ZHANG H P, QIU F, et al. Prokineticin 2 regulates the electrical activity of rat suprachiasmatic nuclei neurons[J]. PLoS One,2011,6(6):e20263. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020263 [8] ZHAO Y G, WU J Y, WANG X Y, et al. Prokineticins and their G protein-coupled receptors in health and disease[J]. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci,2019,161:149-179. [9] ITO H, NODA K, YOSHIDA K, et al. Prokineticin 2 antagonist, PKRA7 suppresses arthritis in mice with collagen-induced arthritis[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord,2016,17:387. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-1243-0 [10] NEGRI L, LATTANZI R. Bv8/PK2 and prokineticin receptors: a druggable pronociceptive system[J]. Curr Opin Pharmacol,2012,12(1):62-66. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2011.10.023 [11] BOULBERDAA M, URAYAMA K, NEBIGIL C G. Prokineticin receptor 1 (PKR1) signalling in cardiovascular and kidney functions[J]. Cardiovasc Res,2011,92(2):191-198. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr228 [12] DORMISHIAN M, TURKERI G, URAYAMA K, et al. Prokineticin receptor-1 is a new regulator of endothelial insulin uptake and capillary formation to control insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular and kidney functions[J]. J Am Heart Assoc,2013,2(5):e000411. [13] NEGRI L, MAFTEI D. Targeting the prokineticin system to control chronic pain and inflammation[J]. Curr Med Chem,2018,25(32):3883-3894. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170713102514 [14] VELLANI V, COLUCCI M, LATTANZI R, et al. Sensitization of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 by the prokineticin receptor agonist Bv8[J]. J Neurosci,2006,26(19):5109-5116. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3870-05.2006 [15] NEGRI L, LATTANZI R, GIANNINI E, et al. Nociceptive sensitization by the secretory protein Bv8[J]. Br J Pharmacol,2002,137(8):1147-1154. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704995 [16] MOLLAY C, WECHSELBERGER C, MIGNOGNA G, et al. Bv8, a small protein from frog skin and its homologue from snake venom induce hyperalgesia in rats[J]. Eur J Pharmacol,1999,374(2):189-196. doi: 10.1016/S0014-2999(99)00229-0 [17] BALBONI G, LAZZARI I, TRAPELLA C, et al. Triazine compounds as antagonists at Bv8-prokineticin receptors[J]. J Med Chem,2008,51(23):7635-7639. doi: 10.1021/jm800854e [18] NEGRI L, LATTANZI R, GIANNINI E, et al. Impaired nociception and inflammatory pain sensation in mice lacking the prokineticin receptor PKR1: focus on interaction between PKR1 and the capsaicin receptor TRPV1 in pain behavior[J]. J Neurosci,2006,26(25):6716-6727. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5403-05.2006 [19] HU W P, ZHANG C K, LI J D, et al. Impaired pain sensation in mice lacking prokineticin 2[J]. Mol Pain,2006,2:35. [20] MARTUCCI C, FRANCHI S, GIANNINI E, et al. Bv8, the amphibian homologue of the mammalian prokineticins, induces a proinflammatory phenotype of mouse macrophages[J]. Br J Pharmacol,2006,147(2):225-234. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706467 [21] FRANCHI S, GIANNINI E, LATTUADA D, et al. The prokineticin receptor agonist Bv8 decreases IL-10 and IL-4 production in mice splenocytes by activating prokineticin receptor-1[J]. BMC Immunol,2008,9:60. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-9-60 [22] MAFTEI D, VELLANI V, ARTICO M, et al. Abnormal pain sensation in mice lacking the prokineticin receptor PKR2: interaction of PKR2 with transient receptor potential TRPV1 and TRPA1[J]. Neuroscience,2020,427:16-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.12.003 [23] REN C X, QIU C Y, GAN X, et al. Prokineticin 2 facilitates mechanical allodynia induced by α, β-methylene ATP in rats[J]. Eur J Pharmacol,2015,767:24-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.09.047 [24] DE FELICE M, MELCHIORRI P, OSSIPOV M H, et al. Mechanisms of Bv8-induced biphasic hyperalgesia: increased excitatory transmitter release and expression[J]. Neurosci Lett,2012,521(1):40-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.05.055 [25] NEAL M, LUO J, HARISCHANDRA D S, et al. Prokineticin-2 promotes chemotaxis and alternative A2 reactivity of astrocytes[J]. Glia,2018,66(10):2137-2157. doi: 10.1002/glia.23467 [26] MAFTEI D, MARCONI V, FLORENZANO F, et al. Controlling the activation of the Bv8/prokineticin system reduces neuroinflammation and abolishes thermal and tactile hyperalgesia in neuropathic animals[J]. Br J Pharmacol,2014,171(21):4850-4865. doi: 10.1111/bph.12793 [27] LATTANZI R, MAFTEI D, MARCONI V, et al. Prokineticin 2 upregulation in the peripheral nervous system has a major role in triggering and maintaining neuropathic pain in the chronic constriction injury model[J]. Biomed Res Int,2015,2015:301292. [28] GUIDA F, LATTANZI R, BOCCELLA S, et al. PC1, a non-peptide PKR1-preferring antagonist, reduces pain behavior and spinal neuronal sensitization in neuropathic mice[J]. Pharmacol Res,2015,91:36-46. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2014.11.004 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李贞,陈伟琴,刘维薇. 中药协同抗真菌药物抗念珠菌的研究进展. 现代药物与临床. 2022(12): 2891-2896 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:


