-
STAT3是一种重要的转录因子,参与众多细胞因子和生长因子受体的信号转导,在细胞生长和细胞凋亡等多种细胞过程中发挥着关键作用[1-2]。STAT3的活化可以通过刺激白介素-6受体(IL-6R)、Janus酪氨酸激酶、BCR-ABL和SRC家族激酶等来启动[3]。STAT3经磷酸化活化后形成同源和异源二聚体,并易位至细胞核,发挥转录激活因子的作用[4-6]。目前,越来越多的证据显示,多种恶性肿瘤存在STAT3的过度激活,包括前列腺癌、肺癌、乳腺癌、皮肤癌和宫颈癌等,抑制STAT3的磷酸化成为一种很有前景的治疗策略。此外,STAT3还与肝损伤、纤维化、风湿性关节炎、心肌缺血等疾病有关[7]。尽管一些STAT3抑制剂正在进行临床试验,但迄今为止尚未批准STAT3抑制剂用于癌症的治疗。因此,仍然迫切需要发现潜在的STAT3抑制剂[8]。
SPR是一种光学生物传感技术,该技术利用光学测量的折射率变化,分析样品与固定在SPR传感器上的分子的结合情况。因其无需标记样品,具有高灵敏度,能实时检测生物分子间的相互作用而被广泛运用于医疗检测、药物筛选、环境监测和食品检测等领域[9]。
本课题采用SPR技术从中药单体中筛选能与STAT3特异性结合的小分子化合物,通过蛋白免疫印迹技术和双荧光素酶报告基因考察小分子对STAT3的抑制作用,采用分子对接技术拟合化合物与STAT3的结合模式,明确其可能的作用位点,从而为STAT3抑制剂的发现提供理论指导和实践经验。
-
DMSO(美国Sigma公司);EDC/NHS(GE公司);胰酶(美国Gibco公司);DMEM培养基(美国Corning公司);胎牛血清(美国Gibco公司);细胞裂解液、PMSF、30%丙烯酰胺溶液、1.5 mol/L Tris(pH=8.8)、1.0 mol/L Tris(pH=6.8)、10%SDS、TEMED、BCA试剂盒、双荧光素酶报告基因检测试剂盒(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);硝酸纤维素膜(德国Sartorius Stedim公司);转染试剂(美国Life Technology公司)
-
Biacore T2000(GE医疗生命科学公司);电子天平(上海天平仪器厂);电泳仪(美国Bio-Rad公司);制冰机(德国Eppendorf公司);−80℃低温冰箱(美国Thermo公司);CO2细胞培养箱(美国Thermo公司);离心管(美国Corning公司);低温高速台式离心机(美国Thermo公司);移液枪(德国Eppendorf公司);超纯水仪(美国Millipore公司);多功能酶标仪(美国Thermo公司)。
-
HeLa细胞(购自上海碧云天生物科技有限公司,由本实验室冻存、培养);HeLa-STAT3-Luc细胞(由本实验室构建、培养、冻存)。
-
(1)STAT3预富集
将STAT3纯化蛋白用去离子水溶解并配成1 g/L的蛋白母液,用4种不同pH的醋酸盐缓冲液(pH4.0、pH4.5、pH5.0、pH5.5)稀释蛋白母液至50 mg/L,进样,于Biacore预富集系统检测不同pH条件下蛋白STAT3的响应值,确定最佳蛋白偶联条件。
(2) STAT3偶联
在预富集实验中所得最佳pH条件下,将STAT3稀释至50 mg/L,通过EDC/NHS活化CM5芯片表面羧基,然后通过羧基氨基缩合反应将STAT3键合到CM5芯片上,乙醇胺封闭未结合的羧基,从而实现STAT3偶联到CM5芯片上的目的。
(3)亲和力分子
将中药小分子单体化合物用DMSO溶解,然后用PBS稀释成32 μmol/L (DMSO终浓度为5%)的样品后进样,流动相为5%DMSO的PBS溶液,通过Biacore系统分析其流过STAT3蛋白表面的响应值,筛选出对STAT3响应值较高(高于阳性对照或与其相当)的单体化合物作为候选化合物。
(4)动力学分析
将候选化合物浓度以二倍比进行梯度稀释,浓度范围为0.0625~64 μmol/L(DMSO终浓度均为5%),通过Biacore系统分析获得结合响应值,根据响应值与候选化合物浓度之间的量效关系绘制动力学曲线,根据曲线拟合情况判断候选化合物与STAT3的结合特异性,从而找到能与STAT3蛋白特异性结合的小分子单体。
-
HeLa细胞以5×105个/孔接种于6孔板,于37 ℃、5%CO2细胞培养箱中培养过夜。次日,加入不同浓度的化合物,作用24 h后,加入100 μl Western及IP细胞裂解液(含1 mmol/L PMSF),冰上裂解25 min,收集蛋白于1.5 ml离心管,12 000 r/min,4 ℃离心10 min,吸取上清液,使用BCA蛋白定量试剂盒进行总蛋白定量。蛋白样品中加入5×蛋白上样缓冲液,煮沸5 min,进行SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳。电泳结束后,在250 mA恒流电下将蛋白从凝胶转移到NC膜上,5%脱脂牛奶封闭,进行一抗(p-STAT3/STAT3)、二抗孵育,结束后在红外双色激光成像系统(Odyssey)上扫膜检测700和800通道激发的荧光信号,观察各泳道中蛋白表达情况。
-
HeLa-STAT3-Luc细胞计数后按1×105个/孔接种于24孔板,置于37 ℃、5%CO2细胞培养箱中培养24 h,加入不同浓度化合物孵育4 h,然后加入IL-6(100 ng/ml)和IL-6R(100 ng/ml)共同刺激24 h,弃上清液,每孔加入120 μl细胞裂解液,离心后取5 μl上清液转移至新的384孔板,每孔加入25 μl荧光素酶1液,使用多功能酶标仪检测荧光值,然后加入25 μl荧光素酶2液,再次测荧光值,定内参。
-
分子对接以Protein Preparation Wizard模块处理蛋白,选择STAT3蛋白与小分子抑制剂的晶体复合物6NUQ,依次去水、加氢,以LigPrep模块处理配体,力场优化均采用OPLS2005模式,其余参数均使用默认;以Grid模块建立蛋白对接坐标,范德华力半径设置为1.0;采用精确对接模式(XP)的方法进行对接,对接结果用PyMol软件作图。
-
数据以(x±s)表示,采用统计学软件SPSS19.0对数据进行单因素方差分析,进行组间差异比较。P<0.05认为差异具有统计学意义。
-
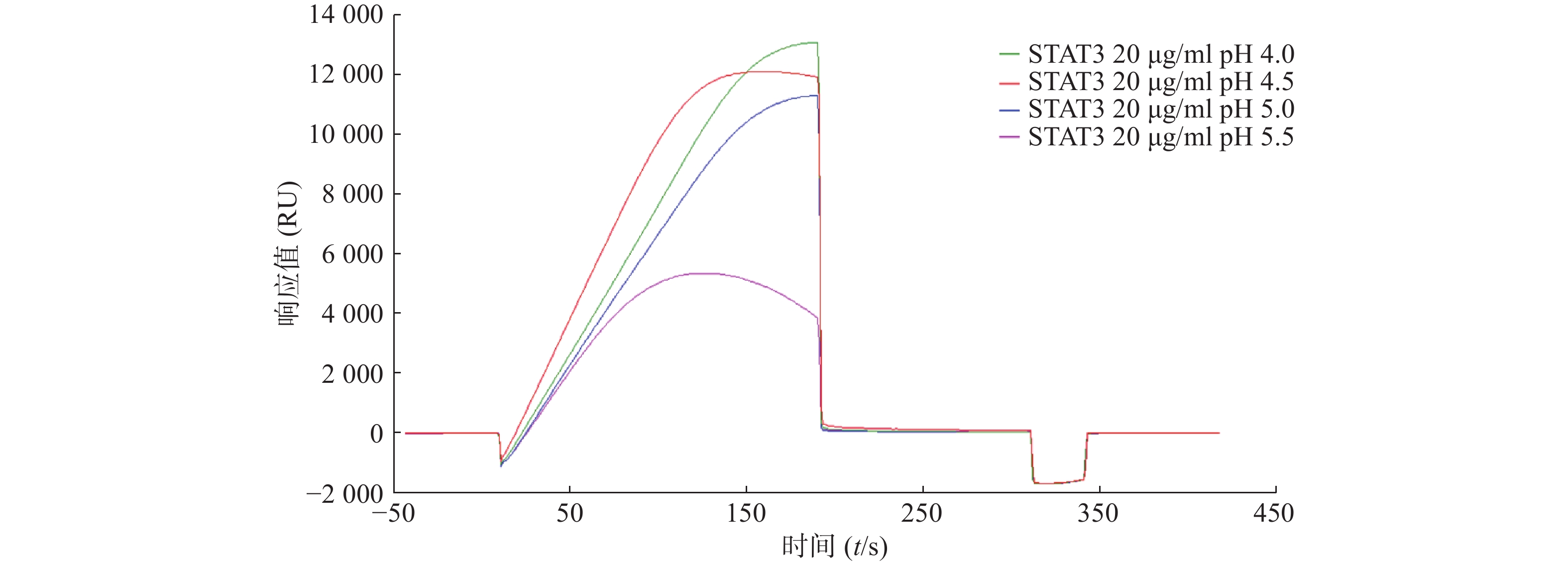
为了研究STAT3蛋白的最佳偶联条件,采用不同pH的醋酸盐缓冲液稀释蛋白,进行预富集分析,结果显示STAT3在pH4.0的条件下响应值最高(图1)。因此,后续实验选择pH4.0的缓冲液进行偶联。
-
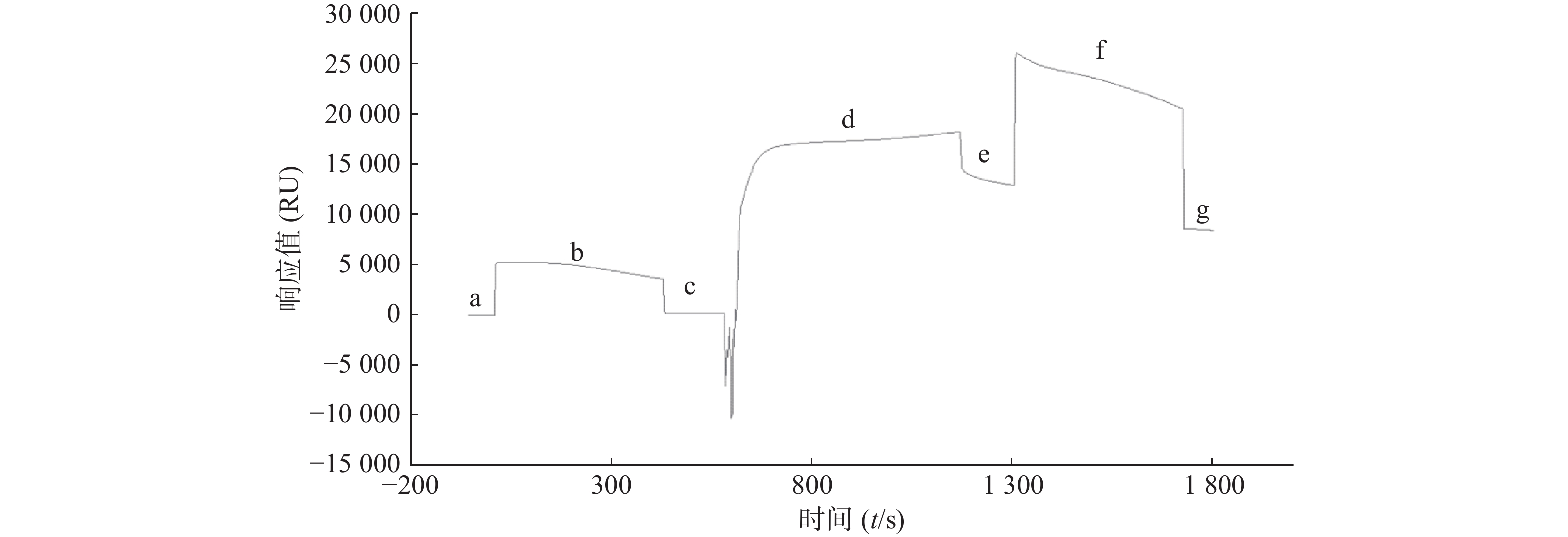
取市售的STAT3蛋白用pH4.0醋酸盐缓冲液稀释至50 mg/L,通过Biacore系统的内置程序偶联到CM5芯片上,结果显示STAT3偶联量为8 000 RU,达到预计偶联水平(图2)。
-
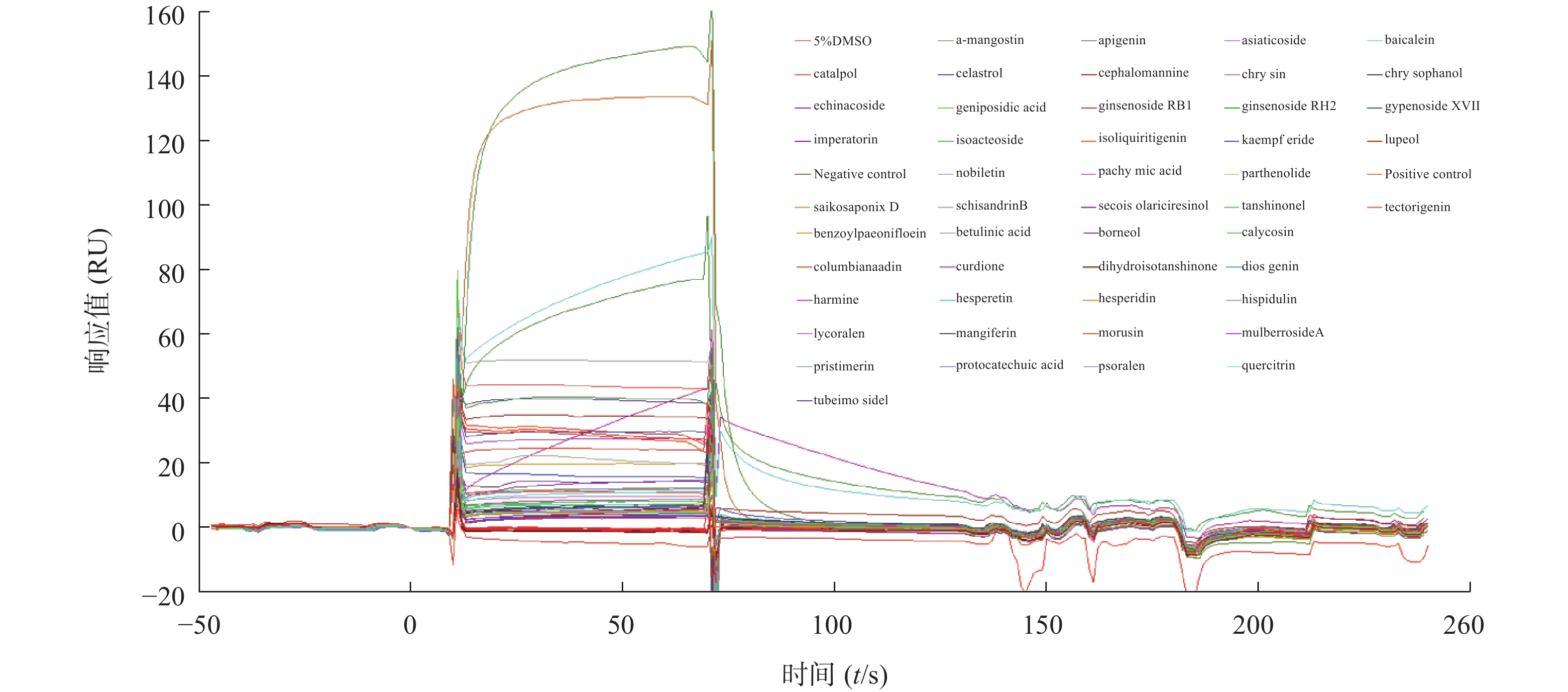
为了筛选能够结合STAT3蛋白的小分子化合物,我们将50种中药单体统一稀释到32 μmol/L,利用Biacore系统检测结合情况,通过响应值观察小分子与STAT3蛋白的结合强度。结果发现,不同小分子化合物与STAT3蛋白的结合存在差异(图3),我们以阳性对照(C188-9)为标准,筛选响应值不低于阳性对照响应值的化合物,得到了梓醇(catalpol)、黄芩素(baicalein)、芹黄素(apigenin)、槲皮素(quercitrin)、人参皂苷(ginsenoside)、京尼平苷酸(geniposidic acid)、桑辛素(morusin)等10多种小分子作为候选化合物,接着进行动力学分析以确定它们与STAT3蛋白的结合特异性。
-
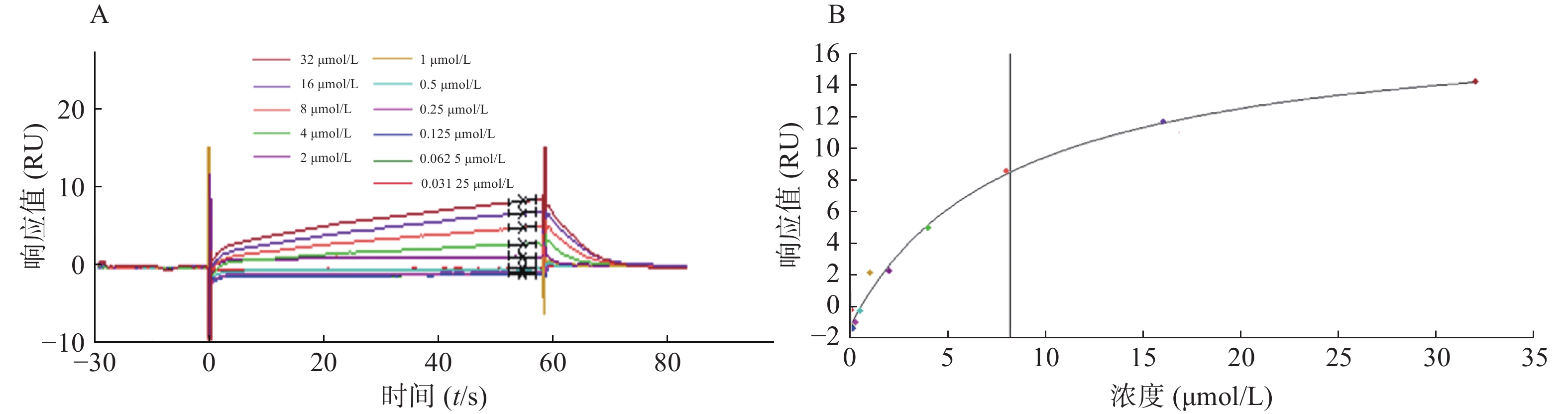
为了验证候选化合物与STAT3蛋白的结合是否为特异性结合,我们将候选化合物进行梯度稀释,通过Biacore系统分析获得结合响应值,绘制动力学结合曲线。对10多种化合物均进行动力学分析,发现只有芹黄素与STAT3的结合具有特异性。芹黄素与STAT3的结合响应值随着药物浓度的增大而升高,当浓度增大到一定值时响应值呈水平趋势不再变化,说明高浓度芹黄素同STAT3的结合存在饱和现象,即芹黄素与STAT3的结合为特异性结合(图4)。因此,选择芹黄素作为可能的STAT3抑制剂进行生物学验证。
-
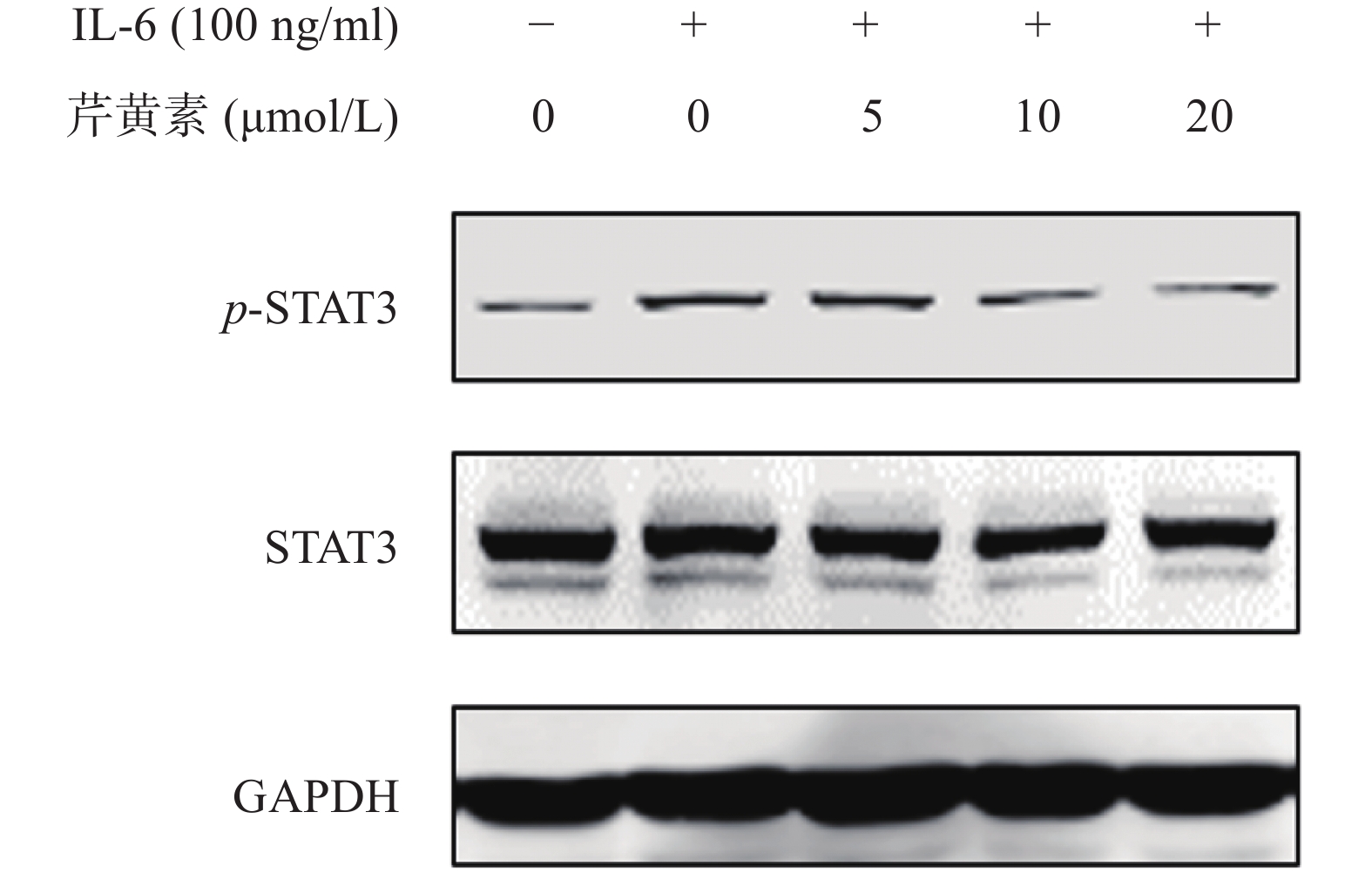
动力学分析结果证实芹黄素可以特异性结合STAT3,为了确证芹黄素对STAT3磷酸化的抑制作用,我们利用IL-6诱导活化STAT3,通过Western-blot检测芹黄素对STAT3磷酸化的抑制作用。结果发现,IL-6可以显著刺激HeLa细胞STAT3的活化,而芹黄素能剂量依赖地抑制IL-6诱导的STAT3磷酸化,表明芹黄素可能是STAT3的抑制剂(图5)。
-
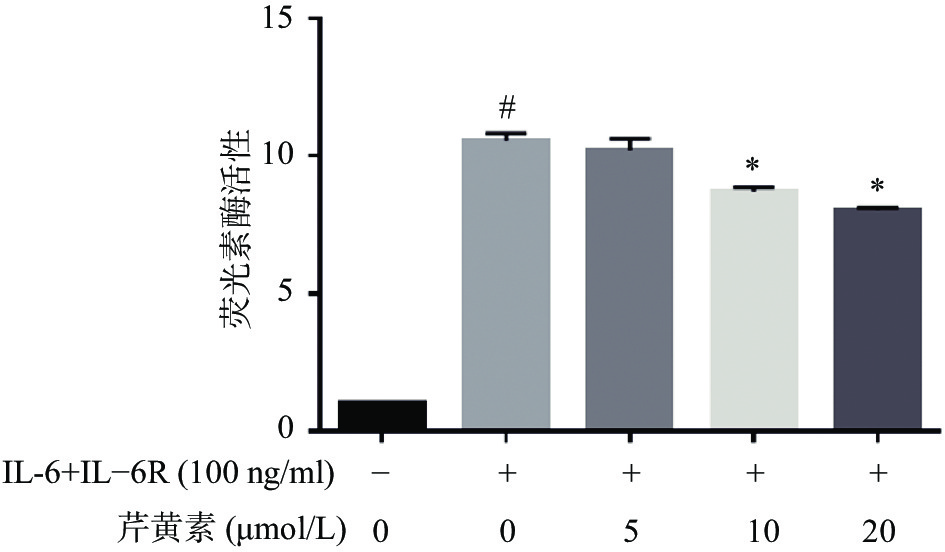
为了进一步确证芹黄素对STAT3的抑制作用,我们采用双荧光素酶报告基因系统研究芹黄素对STAT3转录活性的影响。结果显示,IL-6刺激可以显著促进STAT3的转录活性,10μmol/L、20 μmol/L芹黄素能够抑制IL-6诱导的STAT3转录活性的增加(图6)。以上结果表明芹黄素能够抑制STAT3的转录活性,进一步证实芹黄素是STAT3的小分子抑制剂。
-
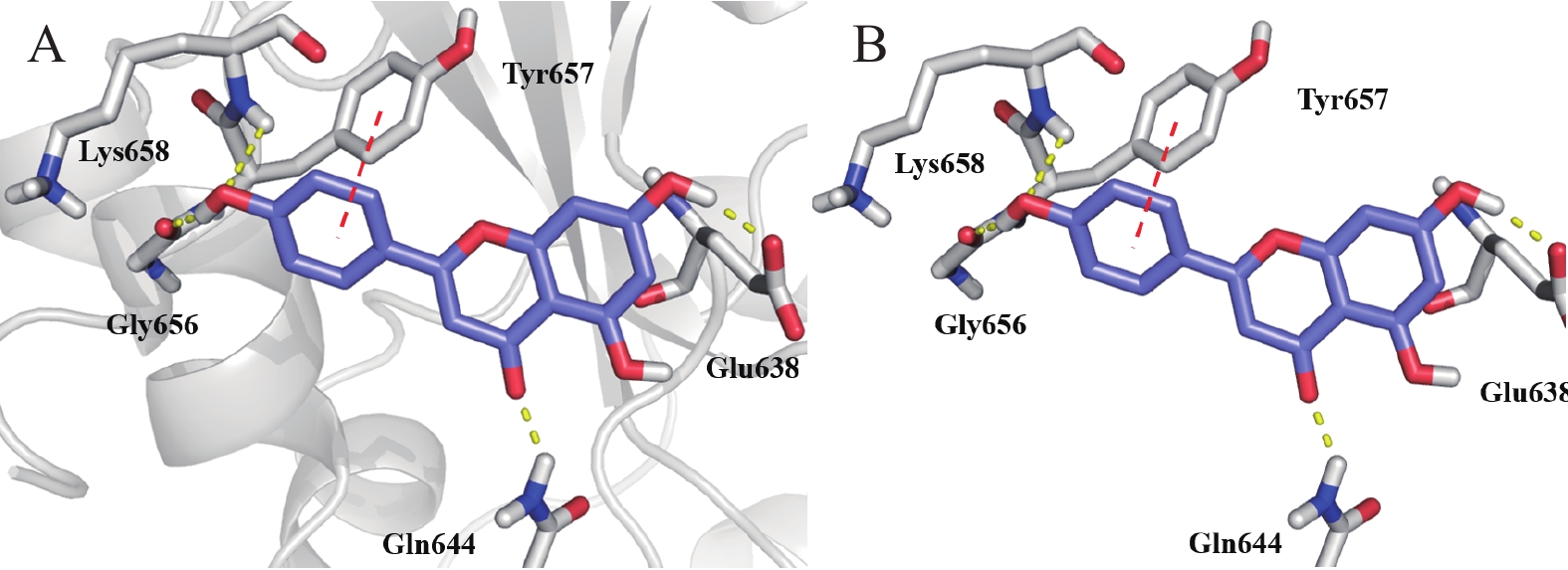
为了明确STAT3与芹黄素的相互作用情况,我们采用分子对接技术分析STAT3与芹黄素的结合位点。结果显示,芹黄素结合于STAT3蛋白的SH2结构域,占据了STAT3磷酸络氨酸的结合口袋。与关键残基Glu638、Gln644、Gly656、Lys658形成氢键相互作用,与Tyr657残基形成π-π相互作用(图7)。
-
STAT3在肿瘤中的持续激活和过度表达与肿瘤细胞的多种恶性生物学特征密切相关。STAT3的活化受多种细胞因子、生长因子,生长因子受体,非受体蛋白酪氨酸激酶等多重信号分子的调控,目前已成为肿瘤治疗领域的研究热点之一[10]。 STAT3存在6个结构域,包括氨基末端结构域(NTD)、卷曲螺旋结构域(CCD)、DNA结合结构域(DBD)、接头结构域、Src同源结构域(SH2)和羧基末端反式激活(TAD)结构域。目前,对STAT3的直接抑制作用可以通过破坏SH2、DBD或NTD结构域来阻止功能性STAT3二聚体的形成。STAT3的直接抑制剂主要分为三类:肽,小分子抑制剂和寡核苷酸。间接抑制剂则通过靶向STAT3信号通路阻断上游信号通路(如IL-6和JAK通路)间接抑制STAT3[11-12]。目前,STAT3抑制剂的研发已成为肿瘤治疗领域的研究热点之一。
芹黄素是一种天然黄酮类化合物,具有抗炎、抗氧化和抗癌作用 [13],其在多种癌症中(如乳腺癌、肺癌、肝癌、前列腺癌等)表现出对细胞的生长抑制与促凋亡作用。芹黄素不仅能够通过内源性与外源性凋亡途径促进细胞凋亡,也能通过降低基质金属蛋白酶-2,-9的表达抑制肿瘤细胞侵袭[14]。但是,芹黄素与STAT3的关系尚未研究,其对STAT3的抑制作用也没有报道。
本研究利用表面等离子体共振技术,从50个中药单体中筛选出能与STAT3特异性结合的小分子化合物芹黄素,然后运用Western-blot、双荧光素酶报告基因实验证实了芹黄素对STAT3的抑制作用。采用分子对接技术分析STAT3与芹黄素的结合位点,结果揭示芹黄素主要通过结合STAT3的SH2结构域抑制其磷酸化。本研究为芹黄素抗癌作用提供了理论基础,同时,也为发现STAT3及其他药物靶点的小分子抑制剂提供了研究经验。
Screening small molecular inhibitors of STAT3 based on surface plasmon resonance technology
-
摘要:
目的 基于表面等离子体共振(SPR)技术,筛选能与信号转导和转录激活因子3(STAT3)特异性结合并抑制其活性的小分子化合物。 方法 使用基于SPR技术的Biacore T200生物分子互作分析系统,在最优pH富集条件下将纯化蛋白STAT3偶联到SPR系统的CM5芯片上,从50个中药单体中筛选出能够与STAT3结合且响应值较高的化合物,并对其结合特异性进行确认,然后运用生物学相关实验确证筛选所得化合物对STAT3的抑制作用,最后采用分子对接技术拟合化合物与STAT3的结合模式,明确其可能的作用位点。 结果 初步筛选获得10多个高响应的候选分子,通过动力学测定发现其中仅有1个分子芹黄素显示特异性结合。Western-blot实验结果表明,芹黄素能够剂量依赖地抑制STAT3的磷酸化;双荧光素酶报告基因结果显示,芹黄素能够剂量依赖地抑制IL-6诱导的STAT3的转录活性。分子对接结果表明,芹黄素与STAT3蛋白的SH2结构域结合,与关键残基Glu638、Gln644、Gly656、Lys658形成氢键相互作用,与Tyr657残基形成π-π相互作用。 结论 基于SPR技术筛选,发现芹黄素是STAT3的抑制剂。 -
关键词:
- 表面等离子体共振技术 /
- 信号转导和转录激活因子3 /
- 小分子抑制剂 /
- 芹黄素
Abstract:Objective To find small molecules binding specifically to signal transducer and activator of transcription3 (STAT3) based on surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technology and confirm their inhibitory activities to STAT3. Methods The biomolecular interaction analysis T200 system based on SPR technology was used to couple the purified protein STAT3 to CM5 chip under the optimal pH conditions. The compounds with high binding response value were screened out from 50 candidate compounds derived from traditional Chinese medicines and the binding specificity was then confirmed. Biological experiments were performed to confirm the inhibitory effects of the screened compounds on STAT3. The binding pattern of STAT3 and the compound was fitted by molecular docking technique. Results More than 10 candidate molecules exhibited binding activities to STAT3 and kinetics assays revealed that only one candidate molecule, apigenin, showed specific binding. Western-blot analysis exhibited that apigenin inhibited the phosphorylation of STAT3 dose-dependently. Luciferase reporter gene assays demonstrated that apigenin also inhibited IL-6-induced STAT3 transcriptional activity in a dose-dependent manner. Molecular docking results showed that apigenin binds to the SH2 domain of STAT3, and interacts with key residues Glu638, Gln644, Gly656 and Lys658 by hydrogen bonds and with Tyr657 through π-π interactions. Conclusion Apigenin was a direct inhibitor of STAT3. -
Key words:
- surface plasmon resonance /
- STAT3 /
- small molecular inhibitors /
- apigenin
-
STAT3是一种重要的转录因子,参与众多细胞因子和生长因子受体的信号转导,在细胞生长和细胞凋亡等多种细胞过程中发挥着关键作用[1-2]。STAT3的活化可以通过刺激白介素-6受体(IL-6R)、Janus酪氨酸激酶、BCR-ABL和SRC家族激酶等来启动[3]。STAT3经磷酸化活化后形成同源和异源二聚体,并易位至细胞核,发挥转录激活因子的作用[4-6]。目前,越来越多的证据显示,多种恶性肿瘤存在STAT3的过度激活,包括前列腺癌、肺癌、乳腺癌、皮肤癌和宫颈癌等,抑制STAT3的磷酸化成为一种很有前景的治疗策略。此外,STAT3还与肝损伤、纤维化、风湿性关节炎、心肌缺血等疾病有关[7]。尽管一些STAT3抑制剂正在进行临床试验,但迄今为止尚未批准STAT3抑制剂用于癌症的治疗。因此,仍然迫切需要发现潜在的STAT3抑制剂[8]。
SPR是一种光学生物传感技术,该技术利用光学测量的折射率变化,分析样品与固定在SPR传感器上的分子的结合情况。因其无需标记样品,具有高灵敏度,能实时检测生物分子间的相互作用而被广泛运用于医疗检测、药物筛选、环境监测和食品检测等领域[9]。
本课题采用SPR技术从中药单体中筛选能与STAT3特异性结合的小分子化合物,通过蛋白免疫印迹技术和双荧光素酶报告基因考察小分子对STAT3的抑制作用,采用分子对接技术拟合化合物与STAT3的结合模式,明确其可能的作用位点,从而为STAT3抑制剂的发现提供理论指导和实践经验。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
1.1.1 实验试剂
DMSO(美国Sigma公司);EDC/NHS(GE公司);胰酶(美国Gibco公司);DMEM培养基(美国Corning公司);胎牛血清(美国Gibco公司);细胞裂解液、PMSF、30%丙烯酰胺溶液、1.5 mol/L Tris(pH=8.8)、1.0 mol/L Tris(pH=6.8)、10%SDS、TEMED、BCA试剂盒、双荧光素酶报告基因检测试剂盒(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);硝酸纤维素膜(德国Sartorius Stedim公司);转染试剂(美国Life Technology公司)
1.1.2 实验仪器
Biacore T2000(GE医疗生命科学公司);电子天平(上海天平仪器厂);电泳仪(美国Bio-Rad公司);制冰机(德国Eppendorf公司);−80℃低温冰箱(美国Thermo公司);CO2细胞培养箱(美国Thermo公司);离心管(美国Corning公司);低温高速台式离心机(美国Thermo公司);移液枪(德国Eppendorf公司);超纯水仪(美国Millipore公司);多功能酶标仪(美国Thermo公司)。
1.1.3 实验细胞
HeLa细胞(购自上海碧云天生物科技有限公司,由本实验室冻存、培养);HeLa-STAT3-Luc细胞(由本实验室构建、培养、冻存)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 Biacore鉴定STAT3特异性结合小分子
(1)STAT3预富集
将STAT3纯化蛋白用去离子水溶解并配成1 g/L的蛋白母液,用4种不同pH的醋酸盐缓冲液(pH4.0、pH4.5、pH5.0、pH5.5)稀释蛋白母液至50 mg/L,进样,于Biacore预富集系统检测不同pH条件下蛋白STAT3的响应值,确定最佳蛋白偶联条件。
(2) STAT3偶联
在预富集实验中所得最佳pH条件下,将STAT3稀释至50 mg/L,通过EDC/NHS活化CM5芯片表面羧基,然后通过羧基氨基缩合反应将STAT3键合到CM5芯片上,乙醇胺封闭未结合的羧基,从而实现STAT3偶联到CM5芯片上的目的。
(3)亲和力分子
将中药小分子单体化合物用DMSO溶解,然后用PBS稀释成32 μmol/L (DMSO终浓度为5%)的样品后进样,流动相为5%DMSO的PBS溶液,通过Biacore系统分析其流过STAT3蛋白表面的响应值,筛选出对STAT3响应值较高(高于阳性对照或与其相当)的单体化合物作为候选化合物。
(4)动力学分析
将候选化合物浓度以二倍比进行梯度稀释,浓度范围为0.0625~64 μmol/L(DMSO终浓度均为5%),通过Biacore系统分析获得结合响应值,根据响应值与候选化合物浓度之间的量效关系绘制动力学曲线,根据曲线拟合情况判断候选化合物与STAT3的结合特异性,从而找到能与STAT3蛋白特异性结合的小分子单体。
1.2.2 蛋白免疫印迹(Western-blot)检测化合物对STAT3磷酸化的抑制情况
HeLa细胞以5×105个/孔接种于6孔板,于37 ℃、5%CO2细胞培养箱中培养过夜。次日,加入不同浓度的化合物,作用24 h后,加入100 μl Western及IP细胞裂解液(含1 mmol/L PMSF),冰上裂解25 min,收集蛋白于1.5 ml离心管,12 000 r/min,4 ℃离心10 min,吸取上清液,使用BCA蛋白定量试剂盒进行总蛋白定量。蛋白样品中加入5×蛋白上样缓冲液,煮沸5 min,进行SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳。电泳结束后,在250 mA恒流电下将蛋白从凝胶转移到NC膜上,5%脱脂牛奶封闭,进行一抗(p-STAT3/STAT3)、二抗孵育,结束后在红外双色激光成像系统(Odyssey)上扫膜检测700和800通道激发的荧光信号,观察各泳道中蛋白表达情况。
1.3 双荧光素酶报告基因鉴定化合物抑制STAT3磷酸化的作用
HeLa-STAT3-Luc细胞计数后按1×105个/孔接种于24孔板,置于37 ℃、5%CO2细胞培养箱中培养24 h,加入不同浓度化合物孵育4 h,然后加入IL-6(100 ng/ml)和IL-6R(100 ng/ml)共同刺激24 h,弃上清液,每孔加入120 μl细胞裂解液,离心后取5 μl上清液转移至新的384孔板,每孔加入25 μl荧光素酶1液,使用多功能酶标仪检测荧光值,然后加入25 μl荧光素酶2液,再次测荧光值,定内参。
1.4 分子对接技术
分子对接以Protein Preparation Wizard模块处理蛋白,选择STAT3蛋白与小分子抑制剂的晶体复合物6NUQ,依次去水、加氢,以LigPrep模块处理配体,力场优化均采用OPLS2005模式,其余参数均使用默认;以Grid模块建立蛋白对接坐标,范德华力半径设置为1.0;采用精确对接模式(XP)的方法进行对接,对接结果用PyMol软件作图。
1.5 统计学分析
数据以(x±s)表示,采用统计学软件SPSS19.0对数据进行单因素方差分析,进行组间差异比较。P<0.05认为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 实验结果
2.1 Biacore系统预富集STAT3蛋白
为了研究STAT3蛋白的最佳偶联条件,采用不同pH的醋酸盐缓冲液稀释蛋白,进行预富集分析,结果显示STAT3在pH4.0的条件下响应值最高(图1)。因此,后续实验选择pH4.0的缓冲液进行偶联。
2.2 Biacore系统偶联STAT3蛋白
取市售的STAT3蛋白用pH4.0醋酸盐缓冲液稀释至50 mg/L,通过Biacore系统的内置程序偶联到CM5芯片上,结果显示STAT3偶联量为8 000 RU,达到预计偶联水平(图2)。
2.3 筛选中药单体小分子化合物
为了筛选能够结合STAT3蛋白的小分子化合物,我们将50种中药单体统一稀释到32 μmol/L,利用Biacore系统检测结合情况,通过响应值观察小分子与STAT3蛋白的结合强度。结果发现,不同小分子化合物与STAT3蛋白的结合存在差异(图3),我们以阳性对照(C188-9)为标准,筛选响应值不低于阳性对照响应值的化合物,得到了梓醇(catalpol)、黄芩素(baicalein)、芹黄素(apigenin)、槲皮素(quercitrin)、人参皂苷(ginsenoside)、京尼平苷酸(geniposidic acid)、桑辛素(morusin)等10多种小分子作为候选化合物,接着进行动力学分析以确定它们与STAT3蛋白的结合特异性。
2.4 候选化合物的动力学分析
为了验证候选化合物与STAT3蛋白的结合是否为特异性结合,我们将候选化合物进行梯度稀释,通过Biacore系统分析获得结合响应值,绘制动力学结合曲线。对10多种化合物均进行动力学分析,发现只有芹黄素与STAT3的结合具有特异性。芹黄素与STAT3的结合响应值随着药物浓度的增大而升高,当浓度增大到一定值时响应值呈水平趋势不再变化,说明高浓度芹黄素同STAT3的结合存在饱和现象,即芹黄素与STAT3的结合为特异性结合(图4)。因此,选择芹黄素作为可能的STAT3抑制剂进行生物学验证。
2.5 Western-blot检测结果
动力学分析结果证实芹黄素可以特异性结合STAT3,为了确证芹黄素对STAT3磷酸化的抑制作用,我们利用IL-6诱导活化STAT3,通过Western-blot检测芹黄素对STAT3磷酸化的抑制作用。结果发现,IL-6可以显著刺激HeLa细胞STAT3的活化,而芹黄素能剂量依赖地抑制IL-6诱导的STAT3磷酸化,表明芹黄素可能是STAT3的抑制剂(图5)。
2.6 双荧光素酶报告基因检测结果
为了进一步确证芹黄素对STAT3的抑制作用,我们采用双荧光素酶报告基因系统研究芹黄素对STAT3转录活性的影响。结果显示,IL-6刺激可以显著促进STAT3的转录活性,10μmol/L、20 μmol/L芹黄素能够抑制IL-6诱导的STAT3转录活性的增加(图6)。以上结果表明芹黄素能够抑制STAT3的转录活性,进一步证实芹黄素是STAT3的小分子抑制剂。
2.7 分子对接结果
为了明确STAT3与芹黄素的相互作用情况,我们采用分子对接技术分析STAT3与芹黄素的结合位点。结果显示,芹黄素结合于STAT3蛋白的SH2结构域,占据了STAT3磷酸络氨酸的结合口袋。与关键残基Glu638、Gln644、Gly656、Lys658形成氢键相互作用,与Tyr657残基形成π-π相互作用(图7)。
3. 讨论
STAT3在肿瘤中的持续激活和过度表达与肿瘤细胞的多种恶性生物学特征密切相关。STAT3的活化受多种细胞因子、生长因子,生长因子受体,非受体蛋白酪氨酸激酶等多重信号分子的调控,目前已成为肿瘤治疗领域的研究热点之一[10]。 STAT3存在6个结构域,包括氨基末端结构域(NTD)、卷曲螺旋结构域(CCD)、DNA结合结构域(DBD)、接头结构域、Src同源结构域(SH2)和羧基末端反式激活(TAD)结构域。目前,对STAT3的直接抑制作用可以通过破坏SH2、DBD或NTD结构域来阻止功能性STAT3二聚体的形成。STAT3的直接抑制剂主要分为三类:肽,小分子抑制剂和寡核苷酸。间接抑制剂则通过靶向STAT3信号通路阻断上游信号通路(如IL-6和JAK通路)间接抑制STAT3[11-12]。目前,STAT3抑制剂的研发已成为肿瘤治疗领域的研究热点之一。
芹黄素是一种天然黄酮类化合物,具有抗炎、抗氧化和抗癌作用 [13],其在多种癌症中(如乳腺癌、肺癌、肝癌、前列腺癌等)表现出对细胞的生长抑制与促凋亡作用。芹黄素不仅能够通过内源性与外源性凋亡途径促进细胞凋亡,也能通过降低基质金属蛋白酶-2,-9的表达抑制肿瘤细胞侵袭[14]。但是,芹黄素与STAT3的关系尚未研究,其对STAT3的抑制作用也没有报道。
本研究利用表面等离子体共振技术,从50个中药单体中筛选出能与STAT3特异性结合的小分子化合物芹黄素,然后运用Western-blot、双荧光素酶报告基因实验证实了芹黄素对STAT3的抑制作用。采用分子对接技术分析STAT3与芹黄素的结合位点,结果揭示芹黄素主要通过结合STAT3的SH2结构域抑制其磷酸化。本研究为芹黄素抗癌作用提供了理论基础,同时,也为发现STAT3及其他药物靶点的小分子抑制剂提供了研究经验。
-
-
[1] AKIRA S, NISHIO Y, INOUE M, et al. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway[J]. Cell,1994,77(1):63-71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90235-6 [2] YUAN Z L, GUAN Y J, WANG L, et al. Central role of the threonine residue within the p+1 loop of receptor tyrosine kinase in STAT3 constitutive phosphorylation in metastatic cancer cells[J]. Mol Cell Biol,2004,24(21):9390-9400. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.21.9390-9400.2004 [3] SRIVASTAVA J, DIGIOVANNI J. Non-canonical Stat3 signaling in cancer[J]. Mol Carcinog,2016,55(12):1889-1898. doi: 10.1002/mc.22438 [4] TKACH M, ROSEMBLIT C, RIVAS M A, et al. p42/p44 MAPK-mediated Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation is required for progestin-induced full activation of Stat3 and breast cancer growth[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer,2013,20(2):197-212. doi: 10.1530/ERC-12-0194 [5] SILVA C M. Role of STATs as downstream signal transducers in Src family kinase-mediated tumorigenesis[J]. Oncogene,2004,23(48):8017-8023. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208159 [6] LIM C P, CAO X M. Structure, function, and regulation of STAT proteins[J]. Mol Biosyst,2006,2(11):536-550. doi: 10.1039/b606246f [7] 岳晓虹, 叶霁青, 孙丽萍. 信号转导与转录激活因子的生物学功能及相关疾病[J]. 中国药科大学学报, 2016, 47(4):404-411. doi: 10.11665/j.issn.1000-5048.20160404 [8] XU L, QIU S, YANG L, et al. Aminocyanopyridines as anti-lung cancer agents by inhibiting the STAT3 pathway[J]. Mol Carcinog,2019,58(8):1512-1525. doi: 10.1002/mc.23038 [9] PILIARIK M, VAISOCHEROVÁ H, HOMOLA J. Surface plasmon resonance biosensing[J]. Methods Mol Biol Clifton N J,2009,503:65-88. [10] 陈越, 季鸣, 陈晓光. STAT3与肿瘤关系的研究进展[J]. 药学学报, 2017, 52(9):1351-1358. [11] ZOU S, TONG Q, LIU B, et al. Targeting STAT3 in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Mol Cancer,2020,19(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01258-7 [12] CHAI E Z, SHANMUGAM M K, ARFUSO F, et al. Targeting transcription factor STAT3 for cancer prevention and therapy[J]. Pharmacol Ther,2016,162:86-97. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.10.004 [13] SHUKLA S, GUPTA S. Apigenin: a promising molecule for cancer prevention[J]. Pharm Res,2010,27(6):962-978. doi: 10.1007/s11095-010-0089-7 [14] IMRAN M, ASLAM GONDAL T, ATIF M, et al. Apigenin as an anticancer agent[J]. Phytother Res,2020,34(8):1812-1828. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6647 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 赵珊,张文青,张欣悦,阎星旭,钱文秀,李遇伯. 基于药物靶标识别中药活性成分的研究方法及应用. 药物评价研究. 2023(07): 1578-1586 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(2)
-





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:


