-
随着人类预期寿命的延长,人口老龄化问题日趋严重,阿尔兹海默症等神经退行性疾病的发病率也大幅上升[1]。学习记忆障碍作为阿尔兹海默症的主要临床表现之一,贯穿阿尔兹海默症疾病发展的全过程,并呈进行性加重,严重降低患者的生活质量,成为亟待解决的公共卫生问题[2]。海龙(Syngnathus)系为海龙科动物刁海龙Solenognathus hardwickii(Gy)、尖海龙Syngnathoides biaculeatus(Bloch)、拟海龙Syngnathus acus Linnaeus的干燥体,具有温肾壮阳、散结消肿的作用[3]。现代研究表明海龙富含多种脂肪酸、氨基酸以及甾体化合物,具有抗衰老、抗骨质疏松、性激素样等药理作用[4]。DHA作为海龙脂肪酸的重要成分之一,具有促进神经元细胞生长发育、抑制神经炎症及氧化应激的作用[5]。目前尚无治疗阿尔兹海默症的特效药物,海龙在改善学习记忆损伤方面的研究亦属空白。本研究拟探讨海龙对D-半乳糖诱导衰老小鼠学习记忆损伤的保护作用,并测定海龙中DHA含量,初步阐明海龙改善学习记忆损伤的作用机制。
-
3月龄雄性ICR小鼠,体重(28±2)g,清洁级,购自昭衍(苏州)新药研究中心有限公司,合格证编号:No.202009910;许可证号:SCXK(苏)2008-0006。动物饲养于海军军医大学药学系实验动物中心,室温控制在(24±0.5) ℃,12 h光照/12 h黑暗,自由饮水、饮食。
-
D-半乳糖、羧甲基纤维素钠(Sigma公司);脂质过氧化物丙二醛(MDA)试剂盒、总超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)试剂盒、BCA蛋白检测试剂盒、蛋白酶磷酸酶抑制剂混合物(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);AKT、p-AKT、FOXO1、SOD2、GAPDH抗体(CST公司);二十二碳六烯酸(DHA,纯度≥98%)购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司。
-
海龙(购自安徽亳州药材市场)经海军军医大学药学系生药学教研室辛海量教授鉴定为刁海龙。精密称取干燥海龙生药,剪碎,以料液比为1:10的80%乙醇浸泡12 h,80%乙醇冷凝回流提取2次,90%乙醇冷凝回流提取1次,每次回流提取2 h,过滤,合并滤液,减压浓缩干燥为浸膏。
-
色谱柱:AcclaimTM120 C18(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm);流动相:乙腈-0.05%磷酸水溶液梯度洗脱;流速:0.6 ml/min;柱温:30 ℃;检测波长:203 nm;进样量:20 μl。
-
精密称定海龙乙醇提取物浸膏,配制成0.04 g/ml(以生药计)乙醇溶液;精密称取DHA对照品,溶解配置成0.5 mg/ml乙醇溶液。供试品溶液及对照品溶液均经0.45 μm微孔滤膜过滤除菌,备用。
-
将24只小鼠随机分为空白组、模型组、海龙低剂量组、海龙高剂量组,每组6只。对照组腹腔注射生理盐水,其余3组小鼠均腹腔注射D-gal(150 mg/kg),每周3次,复制衰老动物模型。海龙低、高剂量组给药剂量为1、2 g/kg(以生药计),空白组、模型组灌胃CMC-Na溶液,每周灌胃给药6 d。给药体积为0.1 ml/10 g,每周称重1次,给药量随体重变化增减,连续造模给药12周。
-
水迷宫实验的前1~4 d为定位航行测试,第5天为空间探索实验。定位航行测试:将各组小鼠从水池4个象限放入水中,记录60 s内小鼠从入水至达平台并停留超过3 s所需时间(即逃避潜伏期),测试4 d,观察各组小鼠逃避潜伏期时间变化。空间探索实验:Morris水迷宫测试第5天,移除平台后,将小鼠从原平台对侧象限放入水中,记录小鼠60 s内的活动轨迹,并分析数据。
-
水迷宫试验结束后处死小鼠,冰上迅速摘取小鼠海马组织。取部分海马组织加入生理盐水匀浆、离心,收集匀浆上清液,BCA法测定蛋白浓度后调整各样本蛋白浓度至一致,严格按照说明书检测小鼠海马组织匀浆上清液中MDA含量及SOD活性。
-
以细胞裂解液制备海马组织匀浆,离心后收集上清液,并以BCA法测定蛋白浓度。海马组织上清液蛋白加热变性后进行十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(PAGE),PVDF膜转印后,室温下5%脱脂牛奶封闭1 h。一抗(1∶1 000)4 ℃孵育过夜,次日TBST洗膜3次,每次10 min。二抗(1∶10 000)室温孵育1 h后,TBST洗膜3次,每次10 min。ECL化学发光法显影,ImageJ软件对目的条带进行分析。
-
实验结果以(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )表示,采用SPSS 21.0软件进行数据分析,选用单因素方差分析法进行组间变量分析,LSD-t法比较组间差异。以 P <0.05表示有显著性差异,以 P <0.01表示有极显著性差异。 -
取对照品溶液,按照“2.2.1”项下方法进样测定。以峰面积为纵坐标、对照品浓度为横坐标进行回归处理,得DHA回归方程:Y=1 085.8X+4.799 9,相关系数r=0.999 9,线性范围0.034~0.41 mg/ml;取供试品液,按照“2.2.1”项下方法进样测定,并计得含量为7.761 3 mg/g(以生药计),见图1。
-
小鼠定位航行实验结果:与空白组相比,模型组小鼠在定位航行实验第4天逃避潜伏期明显延长(P<0.01);与模型组比较,海龙低剂量组、高剂量组小鼠逃避潜伏期均显著缩短(P<0.01),见图2。
空间探索实验结果:与空白组比较,模型组小鼠目标象限游泳时间占比和游泳路程占比显著降低;与模型组比较,海龙高剂量组穿台次数显著增加(P<0.01);海龙低剂量组、海龙高剂量组目标象限游泳时间占比和游泳速度显著提高(P<0.01),见图3。
-
与空白组相比,模型组海马组织MDA含量显著升高,SOD活力显著降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,海龙低剂量组、海龙高剂量组海马组织MDA含量显著降低(P<0.01),SOD活力显著升高(P<0.05, P<0.01),且高剂量组小鼠海马组织氧化损伤程度较低,见图4。
-
与空白组相比,模型组小鼠海马组织p-AKT/AKT比值、FOXO1、SOD2蛋白表达降低;海龙给药组可显著上调D-gal诱导记忆损伤小鼠海马组织中p-AKT、FOXO1、SOD2蛋白表达,激活AKT/FOXO1/SOD2通路(图5A-C),改善学习记忆损伤小鼠海马组织氧化损伤。
-
氧化应激损伤与衰老密切相关。研究发现,氧化应激致机体衰老的主要机制是因过量的ROS导致线粒体损伤、脂质过氧化、抗氧化酶活力降低,进而诱导细胞周期停滞甚至细胞凋亡[6-7];同时自由基也会导致氧化损伤,并且自由基清除酶活力随年龄增长而降低,进一步导致机体氧化损伤加剧[8-9]。海马组织作为负责短时记忆储存转换与空间导航的器官[10],与学习记忆能力密切相关。研究发现[11],过量D-gal可诱导小鼠体内氧化应激加剧,导致海马组织神经元细胞损伤,从而导致动物学习记忆能力降低。本研究发现,经海龙给药干预后,小鼠海马组织MDA含量显著降低,SOD活力显著提高,学习记忆能力显著提高。表明海龙可通过降低海马组织氧化损伤改善D-gal诱导衰老小鼠学习记忆损伤。
PI3K/AKT/FOXO1信号通路是经典的抗氧化通路,能拮抗多种原因引起的氧化应激。AKT信号通过磷酸化活化激活下游mTOR、FOXOs家族蛋白表达[12],从而发挥抗氧化作用。FOXO1作为PI3K/AKT信号通路的重要作用底物,在细胞抗氧化应激反应中发挥重要作用。研究发现,FOXO1激活可以促进其下游抗氧化蛋白SOD2、CAT表达[13]。此外,FOXOs转录因子表达的减少也增加了氧化应激诱导细胞凋亡的易感性[14]。本研究发现,D-gal模型组小鼠海马组织p-AKT/AKT比值、FOXO1、SOD2蛋白表达降低,海龙给药组小鼠海马组织p-AKT/AKT比值、FOXO1、SOD2蛋白表达显著提高。表明海龙可通过激活AKT/FOXO1/ SOD2信号通路改善小鼠海马组织氧化损伤,进而改善D-gal诱导衰老小鼠学习记忆能力。
海龙为海龙科硬骨鱼类,富含多种脂肪酸、氨基酸、甾体类成分。研究发现[15-16],鱼类所含的不饱和脂肪酸类代表成分DHA可促进大脑神经元细胞发育,并通过激活Nrf2/HO-1通路、FOXO3a/SOD通路,促进抗氧化相关蛋白及基因表达,降低活性氧水平,从而减轻神经元细胞氧化及炎症损伤,改善记忆损伤。此外,DHA可通过上调包括小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞在内的神经胶质细胞AKT、Nrf2、HO-1等氧化应激相关蛋白表达,提高抗氧化酶活性从而抑制细胞凋亡,间接防止神经元细胞损伤[17-18]。本研究通过建立海龙HPLC图谱,发现DHA为海龙主要化学成分之一,约占总成分的47%,推测海龙改善小鼠学习记忆损伤作用可能与其富含DHA有关,其作用机制有待进一步研究。
Effect of traditional Chinese medicine Syngnathus on D-galactose-induced learning and memory impairment in aging mice
-
摘要:
目的 研究中药海龙对D-半乳糖诱导衰老小鼠学习记忆损伤的影响及其作用机制。 方法 采用高效液相色谱(HPLC)技术测定海龙中抗学习记忆损伤有效成分二十二碳六烯酸(DHA)含量;腹腔注射D-半乳糖(D-gal)制备衰老小鼠模型,以Morris水迷宫实验及蛋白免疫印迹法等,对小鼠学习记忆能力、海马组织氧化损伤相关生化指标及蛋白表达进行检测,探究海龙对衰老小鼠学习记忆损伤的保护作用及其机制。 结果 HPLC结果显示,海龙中DHA含量为7.761 3 mg/g(以生药计),约占总成分的47%;Morris水迷宫实验结果显示,海龙可减少学习记忆损伤小鼠逃避潜伏期时间,增加小鼠目标象限游泳时间、游泳路程占比、穿台次数,改善小鼠学习记忆损伤;此外,海龙可激活衰老小鼠海马组织AKT/FOXO1/SOD2信号通路,上调氧化应激通路相关蛋白表达,降低衰老小鼠海马组织氧化损伤程度改善小鼠学习记忆损伤。 结论 本研究发现海龙富含二十二碳六烯酸,具有改善D-半乳糖诱导衰老小鼠学习记忆损伤的作用,并初步阐明其作用机制与抗氧化相关,为中药海龙抗学习记忆损伤研究提供了实验依据。 Abstract:Objective To study the effect of traditional Chinese medicine, Syngnathus on learning and memory impairment induced by D-galactose in aging mice and its mechanism of action. Methods HPLC was used to determine the content of DHA, the active ingredient in anti-learning and memory impairment in Syngnathus. The aging mouse model was prepared by intraperitoneal injection of D-galactose (D-gal). Morris water maze test and Western blot were used to detect the ability of learning and memory, biochemical indicators and protein expression related to oxidative damage in the hippocampus, and to explore the protective effect and mechanism of Syngnathus on learning and memory impairment in aging mice. Results HPLC results showed that the DHA content in Syngnathus was 7.761 3 mg/g (calculated as crude drug), accounting for about 47% of the total composition. Morris water maze results showed that Syngnathus could reduce the escape latency of learning and memory-impaired aging mice and increase the target quadrant swimming time, the proportion of swimming distance and the number of times of crossing the platform, and improve the learning and memory impairment of mice. In addition, Syngnathus can activate the AKT/FOXO1/SOD2 signaling pathway in the hippocampus of aging mice with learning and memory impairment, promote the expression of oxidative stress pathway-related proteins, and improve the learning and memory impairment in aging mice by reducing the degree of oxidative damage in the hippocampus of aging mice. Conclusion This study found that Syngnathus is rich in DHA, which has the effect of improving learning and memory impairment induced by D-galactose in aging mice, and preliminarily clarified that its mechanism of action is related to anti-oxidation. Experimental evidence is provided. -
Key words:
- Syngnathus /
- docosahexaenoic acid /
- D-galactose /
- learning and memory impairment /
- hippocampus /
- oxidative damage
-
随着人类预期寿命的延长,人口老龄化问题日趋严重,阿尔兹海默症等神经退行性疾病的发病率也大幅上升[1]。学习记忆障碍作为阿尔兹海默症的主要临床表现之一,贯穿阿尔兹海默症疾病发展的全过程,并呈进行性加重,严重降低患者的生活质量,成为亟待解决的公共卫生问题[2]。海龙(Syngnathus)系为海龙科动物刁海龙Solenognathus hardwickii(Gy)、尖海龙Syngnathoides biaculeatus(Bloch)、拟海龙Syngnathus acus Linnaeus的干燥体,具有温肾壮阳、散结消肿的作用[3]。现代研究表明海龙富含多种脂肪酸、氨基酸以及甾体化合物,具有抗衰老、抗骨质疏松、性激素样等药理作用[4]。DHA作为海龙脂肪酸的重要成分之一,具有促进神经元细胞生长发育、抑制神经炎症及氧化应激的作用[5]。目前尚无治疗阿尔兹海默症的特效药物,海龙在改善学习记忆损伤方面的研究亦属空白。本研究拟探讨海龙对D-半乳糖诱导衰老小鼠学习记忆损伤的保护作用,并测定海龙中DHA含量,初步阐明海龙改善学习记忆损伤的作用机制。
1. 材料
1.1 实验动物
3月龄雄性ICR小鼠,体重(28±2)g,清洁级,购自昭衍(苏州)新药研究中心有限公司,合格证编号:No.202009910;许可证号:SCXK(苏)2008-0006。动物饲养于海军军医大学药学系实验动物中心,室温控制在(24±0.5) ℃,12 h光照/12 h黑暗,自由饮水、饮食。
1.2 试剂与仪器
D-半乳糖、羧甲基纤维素钠(Sigma公司);脂质过氧化物丙二醛(MDA)试剂盒、总超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)试剂盒、BCA蛋白检测试剂盒、蛋白酶磷酸酶抑制剂混合物(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);AKT、p-AKT、FOXO1、SOD2、GAPDH抗体(CST公司);二十二碳六烯酸(DHA,纯度≥98%)购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司。
2. 方法
2.1 海龙提取物制备
海龙(购自安徽亳州药材市场)经海军军医大学药学系生药学教研室辛海量教授鉴定为刁海龙。精密称取干燥海龙生药,剪碎,以料液比为1:10的80%乙醇浸泡12 h,80%乙醇冷凝回流提取2次,90%乙醇冷凝回流提取1次,每次回流提取2 h,过滤,合并滤液,减压浓缩干燥为浸膏。
2.2 海龙中DHA含量测定
2.2.1 色谱条件
色谱柱:AcclaimTM120 C18(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm);流动相:乙腈-0.05%磷酸水溶液梯度洗脱;流速:0.6 ml/min;柱温:30 ℃;检测波长:203 nm;进样量:20 μl。
2.2.2 样品及对照品制备
精密称定海龙乙醇提取物浸膏,配制成0.04 g/ml(以生药计)乙醇溶液;精密称取DHA对照品,溶解配置成0.5 mg/ml乙醇溶液。供试品溶液及对照品溶液均经0.45 μm微孔滤膜过滤除菌,备用。
2.3 动物分组及处理
将24只小鼠随机分为空白组、模型组、海龙低剂量组、海龙高剂量组,每组6只。对照组腹腔注射生理盐水,其余3组小鼠均腹腔注射D-gal(150 mg/kg),每周3次,复制衰老动物模型。海龙低、高剂量组给药剂量为1、2 g/kg(以生药计),空白组、模型组灌胃CMC-Na溶液,每周灌胃给药6 d。给药体积为0.1 ml/10 g,每周称重1次,给药量随体重变化增减,连续造模给药12周。
2.4 Morris水迷宫测试
水迷宫实验的前1~4 d为定位航行测试,第5天为空间探索实验。定位航行测试:将各组小鼠从水池4个象限放入水中,记录60 s内小鼠从入水至达平台并停留超过3 s所需时间(即逃避潜伏期),测试4 d,观察各组小鼠逃避潜伏期时间变化。空间探索实验:Morris水迷宫测试第5天,移除平台后,将小鼠从原平台对侧象限放入水中,记录小鼠60 s内的活动轨迹,并分析数据。
2.5 小鼠海马组织氧化抗氧化指标检测
水迷宫试验结束后处死小鼠,冰上迅速摘取小鼠海马组织。取部分海马组织加入生理盐水匀浆、离心,收集匀浆上清液,BCA法测定蛋白浓度后调整各样本蛋白浓度至一致,严格按照说明书检测小鼠海马组织匀浆上清液中MDA含量及SOD活性。
2.6 蛋白免疫印迹法检测海马组织AKT/FOXO1/SOD相关蛋白表达
以细胞裂解液制备海马组织匀浆,离心后收集上清液,并以BCA法测定蛋白浓度。海马组织上清液蛋白加热变性后进行十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(PAGE),PVDF膜转印后,室温下5%脱脂牛奶封闭1 h。一抗(1∶1 000)4 ℃孵育过夜,次日TBST洗膜3次,每次10 min。二抗(1∶10 000)室温孵育1 h后,TBST洗膜3次,每次10 min。ECL化学发光法显影,ImageJ软件对目的条带进行分析。
2.7 统计学分析
实验结果以(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )表示,采用SPSS 21.0软件进行数据分析,选用单因素方差分析法进行组间变量分析,LSD-t法比较组间差异。以 P <0.05表示有显著性差异,以 P <0.01表示有极显著性差异。3. 结果
3.1 海龙中DHA含量测定结果
取对照品溶液,按照“2.2.1”项下方法进样测定。以峰面积为纵坐标、对照品浓度为横坐标进行回归处理,得DHA回归方程:Y=1 085.8X+4.799 9,相关系数r=0.999 9,线性范围0.034~0.41 mg/ml;取供试品液,按照“2.2.1”项下方法进样测定,并计得含量为7.761 3 mg/g(以生药计),见图1。
3.2 小鼠Morris水迷宫实验结果
小鼠定位航行实验结果:与空白组相比,模型组小鼠在定位航行实验第4天逃避潜伏期明显延长(P<0.01);与模型组比较,海龙低剂量组、高剂量组小鼠逃避潜伏期均显著缩短(P<0.01),见图2。
空间探索实验结果:与空白组比较,模型组小鼠目标象限游泳时间占比和游泳路程占比显著降低;与模型组比较,海龙高剂量组穿台次数显著增加(P<0.01);海龙低剂量组、海龙高剂量组目标象限游泳时间占比和游泳速度显著提高(P<0.01),见图3。
3.3 各组小鼠海马组织MDA含量及SOD活力
与空白组相比,模型组海马组织MDA含量显著升高,SOD活力显著降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,海龙低剂量组、海龙高剂量组海马组织MDA含量显著降低(P<0.01),SOD活力显著升高(P<0.05, P<0.01),且高剂量组小鼠海马组织氧化损伤程度较低,见图4。
3.4 各组小鼠海马组织AKT/FOXO1/SOD蛋白表达
与空白组相比,模型组小鼠海马组织p-AKT/AKT比值、FOXO1、SOD2蛋白表达降低;海龙给药组可显著上调D-gal诱导记忆损伤小鼠海马组织中p-AKT、FOXO1、SOD2蛋白表达,激活AKT/FOXO1/SOD2通路(图5A-C),改善学习记忆损伤小鼠海马组织氧化损伤。
4. 讨论
氧化应激损伤与衰老密切相关。研究发现,氧化应激致机体衰老的主要机制是因过量的ROS导致线粒体损伤、脂质过氧化、抗氧化酶活力降低,进而诱导细胞周期停滞甚至细胞凋亡[6-7];同时自由基也会导致氧化损伤,并且自由基清除酶活力随年龄增长而降低,进一步导致机体氧化损伤加剧[8-9]。海马组织作为负责短时记忆储存转换与空间导航的器官[10],与学习记忆能力密切相关。研究发现[11],过量D-gal可诱导小鼠体内氧化应激加剧,导致海马组织神经元细胞损伤,从而导致动物学习记忆能力降低。本研究发现,经海龙给药干预后,小鼠海马组织MDA含量显著降低,SOD活力显著提高,学习记忆能力显著提高。表明海龙可通过降低海马组织氧化损伤改善D-gal诱导衰老小鼠学习记忆损伤。
PI3K/AKT/FOXO1信号通路是经典的抗氧化通路,能拮抗多种原因引起的氧化应激。AKT信号通过磷酸化活化激活下游mTOR、FOXOs家族蛋白表达[12],从而发挥抗氧化作用。FOXO1作为PI3K/AKT信号通路的重要作用底物,在细胞抗氧化应激反应中发挥重要作用。研究发现,FOXO1激活可以促进其下游抗氧化蛋白SOD2、CAT表达[13]。此外,FOXOs转录因子表达的减少也增加了氧化应激诱导细胞凋亡的易感性[14]。本研究发现,D-gal模型组小鼠海马组织p-AKT/AKT比值、FOXO1、SOD2蛋白表达降低,海龙给药组小鼠海马组织p-AKT/AKT比值、FOXO1、SOD2蛋白表达显著提高。表明海龙可通过激活AKT/FOXO1/ SOD2信号通路改善小鼠海马组织氧化损伤,进而改善D-gal诱导衰老小鼠学习记忆能力。
海龙为海龙科硬骨鱼类,富含多种脂肪酸、氨基酸、甾体类成分。研究发现[15-16],鱼类所含的不饱和脂肪酸类代表成分DHA可促进大脑神经元细胞发育,并通过激活Nrf2/HO-1通路、FOXO3a/SOD通路,促进抗氧化相关蛋白及基因表达,降低活性氧水平,从而减轻神经元细胞氧化及炎症损伤,改善记忆损伤。此外,DHA可通过上调包括小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞在内的神经胶质细胞AKT、Nrf2、HO-1等氧化应激相关蛋白表达,提高抗氧化酶活性从而抑制细胞凋亡,间接防止神经元细胞损伤[17-18]。本研究通过建立海龙HPLC图谱,发现DHA为海龙主要化学成分之一,约占总成分的47%,推测海龙改善小鼠学习记忆损伤作用可能与其富含DHA有关,其作用机制有待进一步研究。
-
-
[1] SHARMA P, SHARMA A, FAYAZ F, et al. , Biological Signatures of Alzheimer's Disease[J]. Curr Top Med Chem,2020,20(9):770-781. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200228095553 [2] WILSON R S, WANG T H, YU L, et al. Cognitive activity and onset age of incident Alzheimer disease dementia[J]. Neurology,2021,97(9):e922-e929. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000012388 [3] 彭维兵, 唐旭利, 李国强, 等. 尖海龙与刁海龙化学成分及药理活性比较研究[J]. 中国海洋药物, 2010, 29(5):10-15. [4] 刘冬, 张红印, 鲍悦, 等. 海龙药理作用研究进展[J]. 吉林中医药, 2015, 35(10):1040-1042. [5] 史筱莉, 徐永健, 牟金婷, 等. 大海马和刁海龙氨基酸与脂肪酸的组成分析与评价[J]. 中国海洋药物, 2017, 36(2):75-83. [6] VATNER S F, ZHANG J, OYDANICH M, et al. Healthful aging mediated by inhibition of oxidative stress[J]. Ageing Res Rev,2020,64:101194. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101194 [7] BRIEGER K, SCHIAVONE S, MILLER F J Jr, et al. Reactive oxygen species: from health to disease[J]. Swiss Med Wkly,2012,142:w13659. [8] LOBO V, PATIL A, PHATAK A, et al. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: impact on human health[J]. Pharmacogn Rev,2010,4(8):118-126. doi: 10.4103/0973-7847.70902 [9] INAL M E, KANBAK G, SUNAL E. Antioxidant enzyme activities and malondialdehyde levels related to aging[J]. Clin Chim Acta,2001,305(1-2):75-80. doi: 10.1016/S0009-8981(00)00422-8 [10] EICHENBAUM H. The role of the Hippocampus in navigation is memory[J]. J Neurophysiol,2017,117(4):1785-1796. doi: 10.1152/jn.00005.2017 [11] PRAJIT R, SRITAWAN N, SUWANNAKOT K, et al. Chrysin protects against memory and hippocampal neurogenesis depletion in D-galactose-induced aging in rats[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(4):E1100. doi: 10.3390/nu12041100 [12] SONG Y S, NARASIMHAN P, KIM G S, et al. The role of Akt signaling in oxidative stress mediates NF-kappaB activation in mild transient focal cerebral ischemia[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2008,28(12):1917-1926. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2008.80 [13] MARTINS R, LITHGOW G J, LINK W. Long live FOXO: unraveling the role of FOXO proteins in aging and longevity[J]. Aging Cell,2016,15(2):196-207. doi: 10.1111/acel.12427 [14] AKASAKI Y, ALVAREZ-GARCIA O, SAITO M, et al. FoxO transcription factors support oxidative stress resistance in human chondrocytes[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol,2014,66(12):3349-3358. doi: 10.1002/art.38868 [15] YAMAGATA K. Dietary docosahexaenoic acid inhibits neurodegeneration and prevents stroke[J]. J Neurosci Res,2021,99(2):561-572. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24728 [16] OGURO A, FUJITA K, ISHIHARA Y, et al. DHA and its metabolites have a protective role against methylmercury-induced neurotoxicity in mouse primary neuron and SH-SY5Y cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2021,22(6):3213. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063213 [17] BECERIR C, KıLıÇ İ, SAHIN Ö, et al. The protective effect of docosahexaenoic acid on the bilirubin neurotoxicity[J]. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem,2013,28(4):801-807. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2012.684053 [18] CHANG C Y, KUAN Y H, LI J R, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid reduces cellular inflammatory response following permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats[J]. J Nutr Biochem,2013,24(12):2127-2137. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.08.004 -





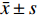
 下载:
下载:

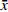
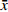

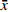

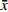
 下载:
下载:


