-
1965年,Rosenberg 发现了顺铂的抗肿瘤活性,1978年,引入临床研究之后,顺铂开始广泛应用于肿瘤治疗[1]。对于睾丸癌,顺铂有超过95%的治愈率,对于其他肿瘤,如卵巢癌、膀胱癌、头颈部癌和肺癌等也有一定疗效。继顺铂之后,卡铂、奥沙利铂、奈达铂、洛铂、庚铂等几种经典铂类化合物先后被研发出来,尽管铂类已成为临床上治疗肿瘤的一线化疗药物,但是,其严重的耐药性极大的限制了它的临床应用,因此,研究者们不断探索铂类药物的耐药机制,期望研发出低毒高效的新型铂类抗肿瘤药物。
-
铂类药物的作用靶点是DNA,当铂进入细胞后能够和肿瘤细胞的DNA结合,形成Pt-DNA加合物,影响DNA的转录和复制等功能,最终导致肿瘤细胞死亡。铂类药物抗肿瘤过程可分为4个阶段,包括细胞摄取药物、药物的水化/活化、DNA铂化、细胞内处理。
不同铂类药物的作用机制会有一定的差异,但它们主要的作用靶点都是DNA。以顺铂为例,顺铂可通过被动扩散、铜特异性转运蛋白(CTR)等机制跨膜转运进入细胞。顺铂在氯离子浓度高的血液中不进行水化,而当顺铂穿过细胞膜进入肿瘤细胞后,由于细胞内氯离子浓度显著降低,顺铂两个氯离子迅速发生解离,并与水结合生成带正电的水合铂。而细胞核内的DNA 带负电,由于正负相吸的静电作用,带正电的水合物会定向移动到细胞核,与DNA中鸟嘌呤核苷酸N-7位形成加合物。Pt-DNA加合物的形成阻止了DNA的转录和复制,激活一系列信号传导途径,使DNA的合成受阻,最终导致肿瘤细胞死亡[2]。
-
铂类药物耐药机制包括以下几个方面:细胞内的铂积累减少、细胞内的铂失活、DNA的损伤修复能力增强、肿瘤细胞凋亡抑制作用增强等。
-
铂类抗肿瘤药物在细胞内的积累是产生抗肿瘤作用的必要条件,无论是铂的内流减少或者外排增加都会造成铂类药物在细胞内积累量的减少,这是铂类药物耐药的一种重要机制。铂类药物的摄取主要包括被动扩散和主动转运,当跨膜转运相关蛋白表达异常时,会造成肿瘤细胞摄取铂量的锐减,引起肿瘤细胞耐药性的发生。
研究发现与铂类药物跨膜转运相关的蛋白有多种,主要包括铜转运蛋白CTR1、铜输出蛋白ATP7A和ATP7B以及铜伴侣蛋白Atox1。铜转运蛋白CTR1能够介导铂类药物的跨膜运输,促进细胞对铂类药物的摄取,是铂类药物进入细胞的一条重要途径。Buß等[3]发现铜转运蛋白CTR1以及阳离子转运蛋白OCT2与奥沙利铂以及顺铂的跨膜运输和耐药性密切相关。CTR1也是卡铂摄取的一个关键蛋白,Konishi等[4]发现在含卡铂治疗方案中CTR1高表达的患者治疗效果明显优于CTR1低表达的患者。研究表明铜输出蛋白ATP7A和ATP7B可能通过以下3种途径影响铂类药物的摄取:与铂类药物的结合或螯合;促进铂类药物的外流;维持细胞内铜稳态[5-6]。Bravo-Cuellar A等[7]研究证明己酮可可碱能够下调ATP7A和ATP7B的表达,增强顺铂耐药的宫颈癌细胞对顺铂的敏感性。铜伴侣蛋白Atox1能够介导铂类药物的摄取和外排,与铂类药物耐药密切相关,Atox1能与进入细胞内的铂类药物结合,可能打破细胞内铜稳态而引起细胞功能的紊乱。Atox1缺失会导致CTR1的表达下调,减弱细胞对顺铂的摄取能力,降低细胞内铂类药物的积累,另外Atox1可以和顺铂结合并转移至ATP7A/B外排蛋白,Atox1过表达会使顺铂被ATP7A/B排出细胞外[8]。无论是铂类药物的摄取减少还是排出增多,最终都会导致肿瘤细胞中铂类药物的积累量减少。
-
谷胱甘肽(GSH)、金属硫蛋白(MT)、蛋氨酸等还原性物质能够与进入细胞内的铂类药物紧密结合形成加合物,加合物停在细胞质中而不能到达DNA,无法杀灭肿瘤细胞,也是铂类药物耐药的重要原因。
谷胱甘肽是一种在细胞内大量存在且有抗氧化作用的细胞内硫醇,能够与进入细胞内的铂类药物共价结合形成Pt-GSH复合物,从而导致进入细胞内的铂的失活,不能发挥抗肿瘤作用。Zhang等[9]研究表明,近红外光照射诱导的轻度热疗能够增强谷胱甘肽的消耗进而减少铂的失活,以提高铂类药物的疗效。Zhang等[10]首次制备了卡铂-月桂酸纳米颗粒,能够降低细胞内谷胱甘肽水平,并提高卡铂与DNA的结合效率。Daubeuf等[11]研究发现γ-谷氨酰转移酶(γ-GGT)能够通过增加细胞内谷胱甘肽的水平,引起细胞内卡铂的失活增多,导致细胞耐药性增加。另外针对GGT作用靶点,Wang等[12]合成了一种基于γ-谷氨酰转移酶抑制剂的四价铂前药的纳米制剂,能够有效抑制 GGT 的表达,降低谷胱甘肽的水平并提高活性氧的含量,通过打破氧化还原平衡来克服谷胱甘肽介导的铂类药物耐药。金属硫蛋白是细胞内一种含半胱氨酸的小分子蛋白质,因其和重金属有高度的亲和性,能够参与重金属的解毒和维持细胞内环境的稳定,也能够和进入细胞中的铂类药物结合使其失活。Gansukh等[13]研究发现和铂类药物耐药相关的金属硫蛋白主要存在于细胞核中,一个金属硫蛋白分子能和10个铂分子共价结合,同时铂类药物能够促使大量的金属硫蛋白生成。Borchert等[14]研究发现恶性胸膜间皮瘤MSTO-211H 细胞在顺铂给药期间金属硫蛋白表达水平显著增加,但在敲低金属硫蛋白基因表达后,细胞的凋亡明显增加,表明抑制金属硫蛋白的表达能改善铂类药物耐药。
-
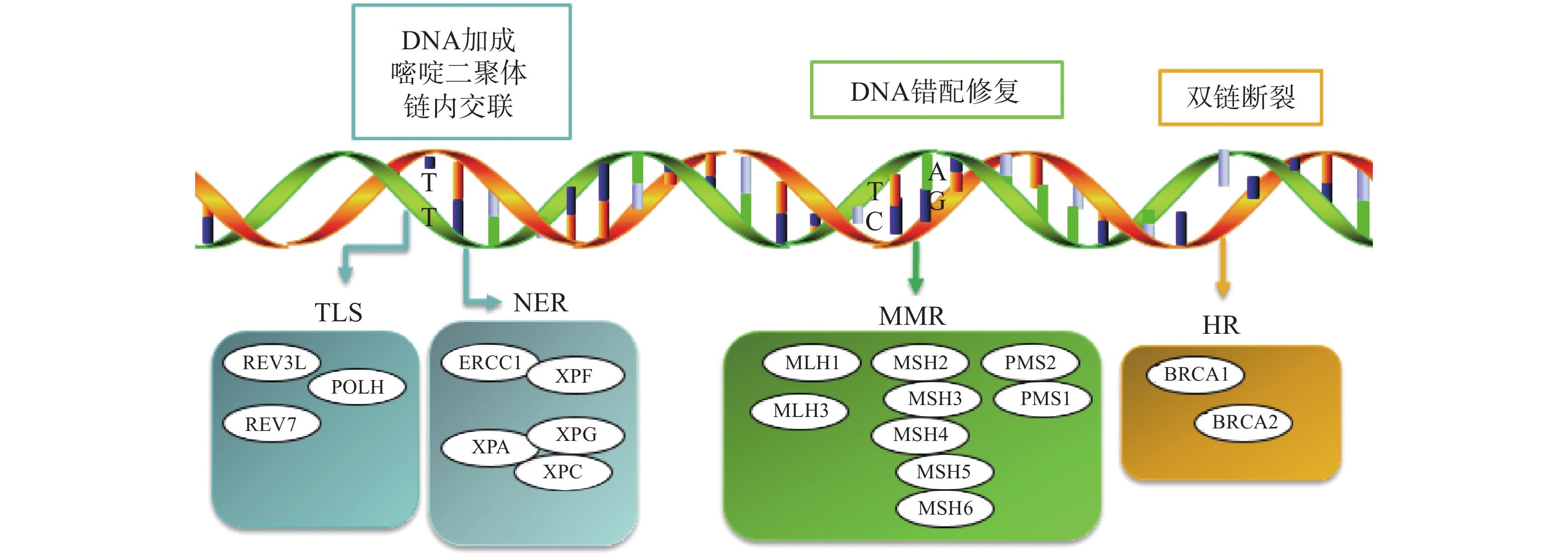
铂类药物能够与DNA结合形成复合物,影响其转录和复制等功能,造成DNA损伤,导致肿瘤细胞死亡。如果当损伤DNA的功能及时得到修复时,会引起细胞耐药。目前与铂类耐药相关的损伤修复途径主要包括核苷酸切除修复(NER)、错配修复(MMR)、DNA的同源重组修复(HR)、跨损伤合成(TLS)等,其修复途径如图1所示。
-
核苷酸切除修复(NER)是DNA损伤修复中的主要形式,修复包括3个工序即DNA损伤识别、从 3 '和 5 '位对损伤处切除、修复切除部分DNA的合成[15]。DNA切除修复交叉互补基因 1(ERCC1)是NER过程中重要参与者,ERCC1 可以识别和修复铂类药物引起的损伤,它可以有效、及时清除受损的核苷酸,使肿瘤细胞本身避开铂类药物的作用而产生耐药性。一项关于ERCC1 表达与卵巢癌铂类药物化疗敏感性的Meta分析[16]表明,与ERCC1高表达的卵巢癌患者相比,ERCC1低表达的卵巢癌患者对铂类药物更敏感。He等[17]研究证明组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂通过调节miR-149抑制了 ERCC1 表达,ERCC1高表达的非小细胞肺癌对顺铂敏感。核苷酸切除修复蛋白(XPA-XPG) 是NER 通路的关键调节因子,XPA、XPC 和XPE是 DNA 损伤识别基因,活跃于 DNA 修复的早期阶段,XPB 和 XPD在 DNA 解旋以及转录修复中发挥重要作用,XPF、XPG是NER 通路中两种核苷酸内切酶,对于修复铂类药物造成的 DNA 损伤至关重要[18-20]。Wada等[21]研究表明通过下调XPA表达显著增加了宫颈癌细胞对顺铂的敏感性。Li等[22]制备了一种靶向XPF的自组装脂质体纳米颗粒,能够通过下调 XPF 的表达,提高人肺癌耐药细胞对顺铂的敏感性。ERCC1 和 XPF 可以形成 ERCC1-XPF 复合物,该复合物在 NER 后期作为核酸酶起作用。Ciniero等[23]通过合成靶向 ERCC1 和 XPF 之间的蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用抑制剂来增强铂类药物敏感性。另外Liu等[24]研究发现端粒调控蛋白(RIF1)能够通过调解NER蛋白的表达来增加顺铂对卵巢上皮癌(EOC)的敏感性。随着对核苷酸切除修复相关基因的深入研究,它们与铂类药物耐药的关系也会进一步明确。
-
DNA错配修复(MMR)是细胞复制后的一种保护机制,在纠正 DNA复制过程中产生的碱基错配起着重要作用。已报道的人类MMR基因有hMLH1、hMLH3、hMSH2、hMSH3、hMSH4、hMSH5、hMSH6、hPMS1 和hPMS2。MMR蛋白能够识别Pt-DNA加合物,但是不能成功修复铂类药物对DNA造成的损伤[25]。铂类药物作用细胞后,如果MMR系统功能健全,能够识别铂类药物DNA的损伤,并活化p53、p73、c-ABL等细胞周期调控因子,导致细胞周期阻滞进而引起细胞凋亡[26]。但MMR 基因的突变或表达的下调可引起MMR功能的缺失,肿瘤细胞将忽略铂类药物导致的DNA损伤而继续进行DNA复制,最终不能引起细胞死亡,肿瘤细胞产生耐药性[27]。研究表明存在这些基因缺陷的肿瘤细胞更容易发生铂类药物耐药,而MMR基因正常表达的肿瘤细胞对铂类药物更敏感,肿瘤的治疗效果更好[28]。
-
Pt-DNA加合物会造成DNA双链发生断裂,而同源重组修复(HR)是此类损伤修复的一种重要途径,也是引起肿瘤细胞耐药的另一种机制。BRCA1和BRCA2基因是HR系统的最重要的两种基因,这两种基因经常在家族性乳腺癌和卵巢癌中发生基因突变[29]。最近一项关于BRCA突变的晚期乳腺癌疗效III期临床试验表明,卡铂对BRCA1/2缺陷的乳腺癌患者有较好的疗效[30]。另外有研究表明BRCA1/2缺陷的卵巢癌细胞对铂类药物的治疗更为敏感,BRCA1/2缺陷会导致同源重组失败,DNA断裂的双链不能被修复,如果修复这种缺陷并使之恢复正常的 HR作用,肿瘤细胞会逐渐对铂类药物产生耐药性[31]。
-
跨损伤合成(TLS)是指细胞能够忽略一些未修复的DNA损伤而继续进行DNA复制的过程,由一组特殊的TLS DNA聚合酶执行。目前研究报道哺乳动物细胞中主要存在POLH、POLI、POLK、REV1、REV3、REV7六种特殊的TLS DNA聚合酶,不同类型的TLS DNA聚合酶作用底物不同,分别参与不同类型的DNA损伤的跨损伤合成[32]。铂类抗肿瘤药物对肿瘤细胞的耐药性或敏感性与TLS DNA聚合酶的表达有一定的关系,当其表达受到抑制时能够增加肿瘤细胞对铂类药物的敏感性,而当其过表达时可能会引起铂类药物耐药[33-34]。Kong等[35]研究表明,REV3L 的缺失可上调经顺铂处理的 H1299 肺癌细胞中 p53的表达,并增加癌细胞对顺铂的敏感性。Vassel等[36]研究发现REV7 缺失会导致肿瘤细胞对顺铂的敏感性增强,并在高度耐药的 NSCLC 小鼠模型中显著改善化疗反应。另外一项研究表明,POLH表达缺失使肿瘤细胞对顺铂治疗更敏感,而在高表达的POLH肿瘤细胞中耐药性更强,同时研究发现POLH的丧失导致DNA损伤反应增强[37]。这些研究都说明了TLS可能引起铂类药物耐药。
-
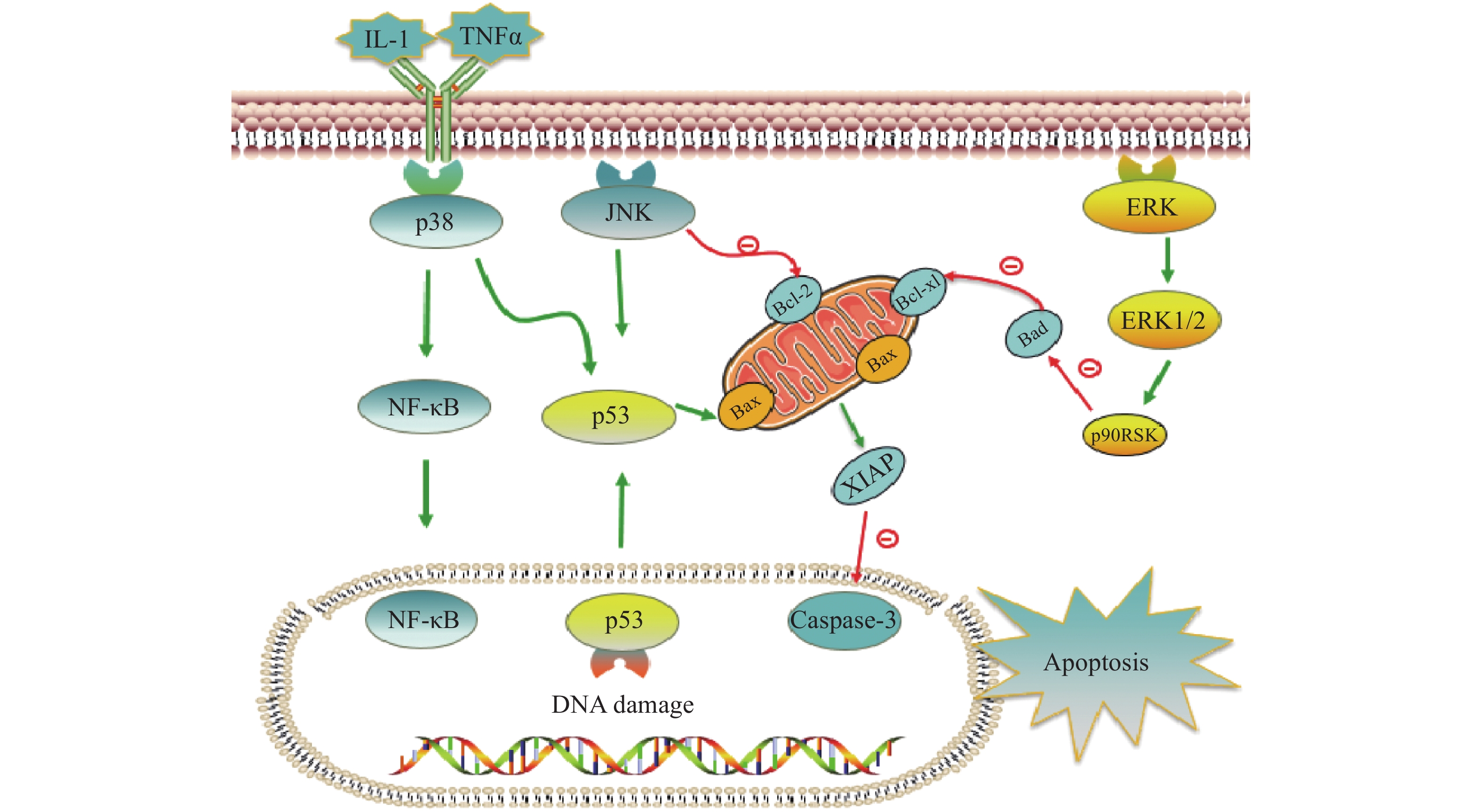
铂类抗肿瘤药物能否最终引起肿瘤细胞的死亡,是其发挥抗肿瘤作用的关键。当肿瘤细胞凋亡受到抑制时,铂类药物在常规浓度下不足以引起细胞发生凋亡,肿瘤细胞发生耐药。与铂类药物相关的细胞凋亡蛋白主要有肿瘤抑制蛋白p53,抗凋亡蛋白XIAP和Bcl-2家族蛋白以及丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)细胞内信号通路蛋白等,见图2。
在DNA 损伤介导的信号通路中p53蛋白具有极其重要的地位,它能够介导细胞周期阻滞或促进肿瘤细胞凋亡。野生型p53是人体重要的一种抑癌基因,因此当p53基因表达出现异常时,细胞凋亡功能也会受到抑制或丧失,可能会导致肿瘤的产生。铂类抗肿瘤药物作用机制是通过DNA损伤介导肿瘤细胞的死亡,而当p53蛋白表达缺失时常常会引起肿瘤细胞对铂类药物耐药。Liu等[38]制备了一种新型的顺铂纳米制剂,通过上调p53蛋白的表达,促进了非小细胞肺癌细胞的凋亡,有效克服了顺铂的耐药性。研究证明睾丸癌中p53基因很少发生突变[39],睾丸癌对铂类药物更敏感,因此临床上对睾丸癌的治疗主要以铂类药物的化疗为主,并显示了很好的治疗效果。
X-连锁凋亡抑制蛋白(XIAP)是人类细胞凋亡抑制蛋白(IAP)家族中的一种,在不同类型的肿瘤细胞中均过度表达,能够与半胱天冬酶 (caspase激酶)结合,从而抑制它们的活化,来阻止细胞凋亡。在铂类抗肿瘤药物的研究中,XIAP也是其细胞凋亡通路上的重要参与者。有研究报道,多种 microRNA可以下调XIAP的表达,提高卵巢癌细胞对顺铂的敏感性[40-42]。Hua等[43]研究表明直肠癌细胞中XIAP的上调是对奥沙利铂获得性耐药的原因,而miR-122 能够抑制XIAP 的表达,逆转了结直肠癌细胞中的奥沙利铂耐药性。
Bcl-2家族也是和细胞凋亡密切相关的蛋白,包括抑制凋亡的Bcl-2、Bcl-xL以及促凋亡的Bax,而它们的异常表达可能会引起肿瘤细胞耐药性的发生。Qi等[44]研究发现载有顺铂的纳米制剂能够显著上调Bax,同时下调Bcl-2的表达水平,逆转非小细胞肺癌耐药。Alam发现在顺铂抗性口腔鳞状细胞癌中,Fra-2 的敲低和其他药物的联用降低Bcl-xL的表达并诱导细胞死亡,证明抑制Bcl-xL蛋白或阻断其上游通路可逆转顺铂耐药[45]。
目前与铂类药物耐药相关的丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)细胞内信号通路主要包括c-Jun氨基末端激酶(JNK)、p38和细胞外调节蛋白激酶(ERK)三种亚型,在细胞增殖、凋亡、分化等中发挥重要作用[46]。其中JNK被激活后能够参与细胞增殖、分化和凋亡,研究结果显示JNK 的激活既能促进肿瘤细胞的凋亡,也可能促进肿瘤细胞的存活[47]。Lin等[48]设计并合成了一种新型水溶性二价铂配合物Diplatin,其抗肿瘤活性优于顺铂和卡铂,能够抑制顺铂耐药肿瘤细胞的生长,作用机制的研究结果表明Diplatin能够通过 JNK 激活来上调 p53 表达诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡。p38 在自身免疫中发挥重要作用,能被IL-1 和 TNFα等细胞因子激活,进而激活NFkB 和 p53等通路来发挥抗肿瘤作用, Al-Khayal等[49]报道一种新型铂配位络合物,能够通过 ROS 介导的细胞凋亡和激活 p38 MAPK 途径来抑制结直肠癌细胞的生长。ERK 信号通路在几乎所有细胞功能中都起着至关重要的作用,包括细胞生长、凋亡、自噬和衰老。目前也有多项研究报道了通过激活ERK信号通路来逆转铂类药物耐药, Carmi等[50]的研究发现黄酮类化合物能够通过恢复ERK1/2的磷酸化,激活ERK信号通路,增强卵巢癌细胞对铂类药物的敏感性。
-
铂类药物首先要进入肿瘤细胞才能发挥抗肿瘤作用,因此肿瘤细胞对铂类药物的摄取效果也是影响铂类药物耐药的重要因素。通过调节铂类药物跨膜转运相关蛋白的表达,减少药物的外排和增加药物的摄入,来增加肿瘤细胞对铂类药物的摄取,是目前应对铂类药物耐药的一种策略。同时在铂类药物的研发过程中发现四价铂前药脂溶性好,更容易被肿瘤细胞摄取,极大地改善肿瘤细胞对铂类药物的摄取,同时通过化学修饰,对四价铂配合物的轴向位置引入具有协同作用的药效基团、靶向分子或功能性药物传递系统等,可提高抗肿瘤效果[51]。另外研究证实通过纳米粒、脂质体和胶束等药物载体增加细胞内铂的浓度也可逆转铂类的耐药。Liu等[38]用铂纳米簇介入非小细胞肺癌,结果显示细胞核内药物浓度增加,铂纳米簇降低了p53蛋白的表达,抑制了肺癌细胞的生长与增殖。Ravaioli[52]研究显示铂类脂质体lipoplatin能够延长顺铂在体内的半衰期,增加细胞内顺铂含量,对非小细胞肺癌有良好的治疗效果,该药已进入三期临床试验。此外,顺铂磷酸钙植入体通过改变水介质的离子组成进而提高铂类药物对植入体的吸附,从而增加动物体内顺铂的释放,达到提高顺铂在动物肿瘤部位浓度的目的[53]。
-
谷胱甘肽、金属硫蛋白、蛋氨酸等能够与进入肿瘤细胞的铂类药物发生结合,增加铂的失活。针对铂类药物的失活,目前的主要策略包括增加肿瘤细胞内谷胱甘肽的消耗或降低谷胱甘肽的产生,以及降低金属硫蛋白的表达,进而减少铂类药物的失活。比如运用药剂学手段将铂类配合物和谷胱甘肽消耗剂-醌甲基化物结合,研制出负载四价铂的PEG-b-PBEMA胶束。通过提高细胞摄取铂的效率和降低细胞内谷胱甘肽水平,减少铂的失活,来逆转肿瘤细胞的顺铂耐药性[54]。
-
铂类抗肿瘤药物能引起DNA损伤,而当DNA损伤修复功能增强时,肿瘤细胞对铂类药物易产生耐药。目前主要是通过抑制与DNA损伤修复相关蛋白的表达,来抑制DNA损伤修复作用,改善铂类药物的耐药。PolyADPribose聚合酶(PARP)是一种DNA损伤的修复酶,新型的抗肿瘤药物PARP抑制剂奥拉帕利、尼拉帕利、氟唑帕利与帕米帕利在国内已获准上市,PARP是细胞凋亡核心成员半胱天冬酶的切割底物,其抑制剂通过抑制DNA损伤修复,能与铂类药物联用发挥协同作用,增强药物的抗肿瘤活性[55-56]。
-
铂类药物造成DNA损伤以及引起DNA功能紊乱,能够激活相关的凋亡通路,导致肿瘤细胞的死亡,目前研究表明铂类药物的凋亡通路主要和肿瘤抑制蛋白p53,抗凋亡蛋白XIAP和Bcl-2家族蛋白、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶细胞内信号通路蛋白以及蛋白酶体相关。通过抑制或者促进铂类药物凋亡通路中相关蛋白的表达以增加铂类药物的抗肿瘤活性是克服铂类耐药的重要策略[38, 43, 48]。
Research progress and coping strategy of the drug resistant mechanism of platinum anti-tumor drugs
-
摘要: 铂类抗肿瘤药物是目前临床应用最广泛的一线化疗药物,疗效显著。但临床使用过程中出现的非小细胞肺癌、乳腺癌、卵巢癌等铂类药物耐药问题,严重影响了铂类药物的疗效,也极大限制了铂类药物的使用。铂类药物耐药是由多种因素引起的,目前关于铂类药物的耐药机制主要有以下几个方面:减少细胞内铂的积累、促进细胞内铂的失活、DNA的损伤修复能力增强、肿瘤细胞凋亡抑制作用增强等。本文就铂类抗肿瘤药物的耐药机制和应对策略做一综述,为铂类抗肿瘤药物的研发提供思路,为克服临床铂类药物耐药问题提供参考。Abstract: Platinum anti-tumor drugs are currently the most widely used first-line chemotherapeutic drugs in clinical practice, and their curative effects are remarkable. However, the problems of platinum drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer and others seriously limit effectiveness and clinical application of platinum drugs. The occurrence of platinum drug resistance is caused by many factors. At present, the resistance mechanism of platinum drugs mainly includes the following aspects: decreasing the accumulation of platinum in cells, increasing the inactivation of platinum in cells, repairing DNA damage and tumor cell apoptosis inactivation. This article reviews the drug resistance mechanism and coping strategy of platinum anti-tumor drugs, providing ideas for the development of platinum anti-tumor drugs and references for overcoming clinical platinum drug resistance.
-
Key words:
- platinum drugs /
- anti-tumor drugs /
- drug resistance mechanism
-
[1] MUGGIA F M, BONETTI A, HOESCHELE J D, et al. Platinum antitumor complexes: 50 years since barnett rosenberg's discovery[J]. J Clin Oncol,2015,33(35):4219-4226. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.60.7481 [2] DILRUBA S, KALAYDA G V. Platinum-based drugs: past, present and future[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol,2016,77(6):1103-1124. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-2976-z [3] BUß I, HAMACHER A, SARIN N, et al. Relevance of copper transporter 1 and organic cation transporters 1-3 for oxaliplatin uptake and drug resistance in colorectal cancer cells[J]. Metallomics,2018,10(3):414-425. doi: 10.1039/C7MT00334J [4] KONISHI M, IMAI A, FUJII M, et al. Correlation of expression levels of copper transporter 1 and thymidylate synthase with treatment outcomes in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with S-1/carboplatin doublet chemotherapy[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev,2018,19(2):435-441. [5] PETRUZZELLI R, POLISHCHUK R S. Activity and trafficking of copper-transporting ATPases in tumor development and defense against platinum-based drugs[J]. Cells,2019,8(9):1080. doi: 10.3390/cells8091080 [6] LUKANOVIĆ D, HERZOG M, KOBAL B, et al. The contribution of copper efflux transporters ATP7A and ATP7B to chemoresistance and personalized medicine in ovarian cancer[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother,2020,129:110401. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110401 [7] BRAVO-CUELLAR A, ORTIZ-LAZARENO P C, SIERRA-DÍAZ E, et al. Pentoxifylline sensitizes cisplatin-resistant human cervical cancer cells to cisplatin treatment: involvement of mitochondrial and NF-kappa B pathways[J]. Front Oncol,2020,10:592706. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.592706 [8] ARNESANO F, NATILE G. Interference between copper transport systems and platinum drugs[J]. Semin Cancer Biol,2021,76:173-188. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.05.023 [9] ZHANG J M, ZHAO B C, CHEN S Z, et al. Correction to near-infrared light irradiation induced mild hyperthermia enhances glutathione depletion and DNA interstrand cross-link formation for efficient chemotherapy[J]. ACS Nano,2020,14(11):16159-16160. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c09203 [10] LIANG S, HAN L Q, MU W W, et al. Carboplatin-loaded SMNDs to reduce GSH-mediated platinum resistance for prostate cancer therapy[J]. J Mater Chem B,2018,6(43):7004-7014. doi: 10.1039/C8TB01721B [11] DAUBEUF S, BALIN, LEROY P, et al. Different mechanisms for gamma-glutamyltransferase-dependent resistance to carboplatin and cisplatin[J]. Biochem Pharmacol,2003,66(4):595-604. doi: 10.1016/S0006-2952(03)00343-5 [12] WANG L N, LIU Z J, HE S M, et al. Fighting against drug-resistant tumors by the inhibition of γ-glutamyl transferase with supramolecular platinum prodrug nano-assemblies[J]. J Mater Chem B,2021,9(22):4587-4595. doi: 10.1039/D1TB00149C [13] GANSUKH T, DONIZY P, HALON A, et al. In vitro analysis of the relationships between metallothionein expression and cisplatin sensitivity of non-small cellular lung cancer cells[J]. Anticancer Res,2013,33(12):5255-5260. [14] BORCHERT S, SUCKRAU P M, WALTER R F H, et al. Impact of metallothionein-knockdown on cisplatin resistance in malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. Sci Rep,2020,10(1):18677. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75807-x [15] SUGASAWA K. Molecular mechanisms of DNA damage recognition for mammalian nucleotide excision repair[J]. DNA Repair (Amst),2016,44:110-117. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.05.015 [16] ZHANG C J, GAO S, HOU J W. ERCC1 expression and platinum chemosensitivity in patients with ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. Int J Biol Markers,2020,35(4):12-19. doi: 10.1177/1724600820963396 [17] HE Y W, CHEN D Y, YI Y M, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor sensitizes ERCC1-high non-small-cell lung cancer cells to cisplatin via regulating miR-149[J]. Mol Ther Oncolytics,2020,17:448-459. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.05.001 [18] BOULIKAS T. Xeroderma pigmentosum and molecular cloning of DNA repair genes[J]. Anticancer Res,1996,16(2):693-708. [19] PRADHAN S, DAS P, MATTAPARTHI V S K. Characterizing the binding interactions between DNA-binding proteins, XPA and XPE: a molecular dynamics approach[J]. ACS Omega,2018,3(11):15442-15454. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b01793 [20] PAJUELO-LOZANO N, BARGIELA-IPARRAGUIRRE J, DOMINGUEZ G, et al. XPA, XPC, and XPD modulate sensitivity in gastric cisplatin resistance cancer cells[J]. Front Pharmacol,2018,9:1197. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01197 [21] WADA T, FUKUDA T, SHIMOMURA M, et al. XPA expression is a predictive marker of the effectiveness of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced uterine cervical cancer[J]. Oncol Lett,2018,15(3):3766-3771. [22] LI C, LI T Z, HUANG L F, et al. Self-assembled lipid nanoparticles for ratiometric codelivery of cisplatin and siRNA targeting XPF to combat drug resistance in lung cancer[J]. Chem Asian J,2019,14(9):1570-1576. doi: 10.1002/asia.201900005 [23] CINIERO G, ELMENOUFY A H, GENTILE F, et al. Enhancing the activity of platinum-based drugs by improved inhibitors of ERCC1-XPF-mediated DNA repair[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol,2021,87(2):259-267. doi: 10.1007/s00280-020-04213-x [24] LIU Y B, MEI Y, TIAN Z W, et al. Downregulation of RIF1 enhances sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) by regulating nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem,2018,46(5):1971-1984. doi: 10.1159/000489418 [25] MOGGS J G, SZYMKOWSKI D E, YAMADA M, et al. Differential human nucleotide excision repair of paired and mispaired cisplatin-DNA adducts[J]. Nucleic Acids Res,1997,25(3):480-491. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.3.480 [26] BELLACOSA A. Functional interactions and signaling properties of mammalian DNA mismatch repair proteins[J]. Cell Death Differ,2001,8(11):1076-1092. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400948 [27] SAWANT A, KOTHANDAPANI A, ZHITKOVICH A, et al. Role of mismatch repair proteins in the processing of cisplatin interstrand cross-links[J]. DNA Repair (Amst),2015,35:126-136. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.10.003 [28] ZHAO C C, LI S S, ZHAO M H, et al. Prognostic values of DNA mismatch repair genes in ovarian cancer patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet,2018,297(1):153-159. doi: 10.1007/s00404-017-4563-x [29] ENDRIS V, STENZINGER A, PFARR N, et al. NGS-based BRCA1/2 mutation testing of high-grade serous ovarian cancer tissue: results and conclusions of the first international round robin trial[J]. Virchows Arch,2016,468(6):697-705. doi: 10.1007/s00428-016-1919-8 [30] DIÉRAS V, HAN H S, KAUFMAN B, et al. Veliparib with carboplatin and paclitaxel in BRCA-mutated advanced breast cancer (BROCADE3): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol,2020,21(10):1269-1282. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30447-2 [31] ŠKAPA P. BRCA1 and BRCA2 - pathologists starting kit[J]. Cesk Patol,2016,52(4):193-196. [32] O'GRADY S, FINN S P, CUFFE S, et al. The role of DNA repair pathways in cisplatin resistant lung cancer[J]. Cancer Treat Rev,2014,40(10):1161-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.10.003 [33] OUZON-SHUBEITA H, BAKER M, KOAG M C, et al. Structural basis for the bypass of the major oxaliplatin-DNA adducts by human DNA polymerase Η[J]. Biochem J,2019,476(4):747-758. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20180848 [34] LI X Q, REN J, CHEN P, et al. Co-inhibition of Pol η and ATR sensitizes cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells to cisplatin by impeding DNA damage repair[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin,2018,39(8):1359-1372. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.187 [35] KONG L H, MURATA M M, DIGMAN M A. Absence of REV3L promotes p53-regulated cancer cell metabolism in cisplatin-treated lung carcinoma cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2018,496(1):199-204. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.026 [36] VASSEL F M, BIAN K, WALKER G C, et al. Rev7 loss alters cisplatin response and increases drug efficacy in chemotherapy-resistant lung cancer[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2020,117(46):28922-28924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2016067117 [37] ZHANG J, SUN W Q, REN C, et al. A PolH transcript with a short 3'UTR enhances PolH expression and mediates cisplatin resistance[J]. Cancer Res,2019,79(14):3714-3724. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3928 [38] LIU Y Q, HU F J, ZHAO L. Effect of nano-platinum on proliferation and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells via P53 pathway[J]. J Nanosci Nanotechnol,2021,21(2):903-908. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2021.18629 [39] PENG H Q, HOGG D, MALKIN D, et al. Mutations of the p53 gene do not occur in testis cancer[J]. Cancer Res,1993,53(15):3574-3578. [40] LI X D, CHEN W, ZENG W S, et al. microRNA-137 promotes apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells via the regulation of XIAP[J]. Br J Cancer,2017,116(1):66-76. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.379 [41] LI X D, CHEN W, JIN Y H, et al. miR-142-5p enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells by targeting multiple anti-apoptotic genes[J]. Biochem Pharmacol,2019,161:98-112. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.01.009 [42] CHEN W, ZENG W S, LI X D, et al. microRNA-509-3p increases the sensitivity of epithelial ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis[J]. Pharmacogenomics,2016,17(3):187-197. doi: 10.2217/pgs.15.166 [43] HUA Y Q, ZHU Y D, ZHANG J J, et al. miR-122 targets X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein to sensitize oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin-mediated cytotoxicity[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem,2018,51(5):2148-2159. doi: 10.1159/000495832 [44] QI Y X, YANG W P, LIU S, et al. Cisplatin loaded multiwalled carbon nanotubes reverse drug resistance in NSCLC by inhibiting EMT[J]. Cancer Cell Int,2021,21(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01771-9 [45] ALAM M, MISHRA R. Bcl-xL expression and regulation in the progression, recurrence, and cisplatin resistance of oral cancer[J]. Life Sci,2021,280:119705. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119705 [46] GARCÍA-CANO J, ROCHE O, CIMAS F J, et al. p38MAPK and chemotherapy: we always need to hear both sides of the story[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol,2016,4:69. [47] WU Q H, WU W D, JACEVIC V, et al. Selective inhibitors for JNK signalling: a potential targeted therapy in cancer[J]. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem,2020,35(1):574-583. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1720013 [48] LIN X X, JIA Y L, DONG X W, et al. Diplatin, a novel and low-toxicity anti-lung cancer platinum complex, activation of cell death in tumors via a ROS/JNK/p53-dependent pathway, and a low rate of acquired treatment resistance[J]. Front Pharmacol,2019,10:982. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00982 [49] AL-KHAYAL K, VAALI-MOHAMMED M A, ELWATIDY M, et al. Correction to: a novel coordination complex of platinum (PT) induces cell death in colorectal cancer by altering redox balance and modulating MAPK pathway[J]. BMC Cancer,2020,20(1):834. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07245-x [50] KOREN CARMI Y, MAHMOUD H, KHAMAISI H, et al. Flavonoids restore platinum drug sensitivity to ovarian carcinoma cells in a phospho-ERK1/2-dependent fashion[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2020,21(18):E6533. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186533 [51] DAN G. Multi-action Pt(IV) anticancer agents; do we understand how they work? J Inorg Biochem,2019,191:77-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2018.11.008 [52] RAVAIOLI A, PAPI M, PASQUINI E, et al. Lipoplatin monotherapy: a phase II trial of second-line treatment of metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Chemother,2009,21(1):86-90. doi: 10.1179/joc.2009.21.1.86 [53] ZOU Y, WU Q P, TANSEY W, et al. Effectiveness of water soluble poly(L-glutamic acid)-camptothecin conjugate against resistant human lung cancer xenografted in nude mice[J]. Int J Oncol,2001,18(2):331-336. [54] HAN Y, YIN W, LI J J, et al. Intracellular glutathione-depleting polymeric micelles for cisplatin prodrug delivery to overcome cisplatin resistance of cancers[J]. J Control Release,2018,273:30-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.01.019 [55] ZHAO Y, ZHANG L X, JIANG T, et al. The ups and downs of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitors in cancer therapy-current progress and future direction[J]. Eur J Med Chem,2020,203:112570. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112570 [56] LI H F, WANG C M, LAN L X, et al. PARP1 inhibitor combined with oxaliplatin efficiently suppresses oxaliplatin resistance in gastric cancer-derived organoids via homologous recombination and the base excision repair pathway[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol,2021,9:719192. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.719192 -





 下载:
下载: