-
舒肝宁注射液是在中国传统医学经典方剂——张仲景《伤寒杂病论》“茵陈蒿汤”基础上进一步研发的纯中药注射剂,由茵陈、栀子、黄芩、板蓝根和灵芝等五味中药材的提取物组合而成,在临床上主要用于治疗急慢性病毒性肝炎、药物性肝炎、胆汁淤积性肝炎等肝脏疾病[1-2]。舒肝宁注射液所含中药种类繁多,化学成分复杂,其改善肝炎的有效成分及相应的作用机制尚不清楚,因此,研究舒肝宁注射液的有效活性成分、作用靶点及其抗炎保肝的作用机制具有重要的科学意义。
中药复方活性成分不明是中药复方药效物质基础研究的瓶颈之一,网络药理学通过将化学成分映射到疾病基因网络中来寻找潜在的生物活性成分,为筛选中药活性成分提供了一种方法。同时以中药成分、靶点和疾病等数据相关信息为基础,构建生物网络,通过网络分析阐释中药的作用机制,对中药复方在临床应用具有重要的意义。
本研究通过检索TCMSP数据库以及相关文献收集舒肝宁注射液的活性成分信息,并在此基础上利用药物靶点分析平台STITCH预测舒肝宁注射液可能的作用靶点,采用Cytoscape构建舒肝宁注射液抗肝炎作用的“活性成分-作用靶点”网络,对这些靶点进行蛋白-蛋白相互作用分析,利用DAVID数据库进行基因功能和信号通路分析,探讨舒肝宁注射液抗炎保肝作用可能的作用机制。
-
通过检索中药系统药理学数据库和分析平台(TCMSP)以及相关文献,分别收集舒肝宁注射液中茵陈、栀子、黄芩、板蓝根和灵芝的主要的化学成分,建立舒肝宁注射液化学成分数据库。在此基础上,考察化学成分生物利用度(OB>30%)、药物相似性(DL>0.18)[3]、化合物含量以及相关生物功能,通过文献筛选舒肝宁注射液中有效的活性成分。
-
主要通过化合物与蛋白互作数据库(STITCH)进行分析,将活性成分输入,选择“人类”物种进行搜索。将搜索得到靶点结果以TSV格式进行保存,筛选结合得分大于0.7的靶点。以“hepatitis”作为疾病关键词,搜寻GeneCards数据库与OMIM数据库中与肝炎相关的靶点。将舒肝宁注射液活性成分作用靶点与肝炎相关疾病靶点取交集,靶点名称以靶点基因名称为准,用于后续靶点网络的构建、蛋白相互作用网络构建、基因功能和信号通路分析等工作。
-
根据舒肝宁注射液中主要有效成分作用的肝炎相关靶点,建立活性成分-肝炎作用靶点之间的相互对应关系。将活性成分和肝炎靶点作为网络中的节点,两者之间的相互作用作为网络中的连接,导入Cytoscape 3.8.2软件中构建舒肝宁注射液“活性成分-作用靶点”网络。并应用内置工具分析有效成分及靶点的网络拓扑参数,包括连接度、介度、及紧密度等,并根据网络拓扑学参数判断核心靶点及发挥药效的主要活性成分。
-
蛋白质相互作用数据库(String)是一种包含已知和预测的蛋白质−蛋白质相互作用的数据库, 其中收集了大量的蛋白质相互作用关系。将舒肝宁注射液与肝炎相关的靶点导入String数据库,获取蛋白间的相互作用关系,将结果保存成TSV格式,保留文件中节点1、节点2和结合得分信息,导入Cytoscape 3.8.2软件中绘制相互作用网络,并对网络进行分析,保存结果。使用Cytoscape 3.8.2软件设置节点大小和颜色反映度(Degree)值的大小,边的粗细用于反映结合得分的大小,获得舒肝宁注射液作用靶点蛋白-蛋白相互作用网络图。
-
生物学信息注释数据库(DAVID)为基因和蛋白提供系统综合的生物功能注释信息,可以对差异基因进行功能和通路富集分析。将舒肝宁注射液作用与肝炎相关的蛋白靶点导入DAVID数据库,选择标识符为标准的基因名称,列表类型设置为基因列表,限定物种为人,对舒肝宁注射液作用靶点进行KEGG通路分析,阈值设置为P<0.01保存结果,并按照涉及的靶点数目多少进行排序,筛选排名靠前的信号通路,采用GraphPad Prism 5.0软件绘图。GO富集分析是指在某一功能层次上统计蛋白或者基因的数目组成的一个有向无环图,包括生物过程(BP)、分子功能(MF)和细胞组分(CC)3个分支。使用Cytoscape 3.8.2软件中的插件对舒肝宁注射液中活性成分作用靶点进行GO分析,阈值设置为P<0.05,筛选靠前的条目,采用GraphPad Prism 5.0软件绘图。
-
通过搜索中药系统药理学数据库和分析平台TCMSP,从茵陈、栀子、黄芩、板蓝根和灵芝中分别收集到53、98、87、169、242个主要的化学成分。对收集到的化学成分,以生物利用度>30%、药物相似性>0.18以及相关文献参考作为筛选标准,获得30个活性成分,黄芩10个、栀子8个、板蓝根7个、茵陈3个、灵芝2个。黄芩含有刺槐黄素、黄芩素、β-谷甾醇、黄连碱、千层纸素A、谷甾醇、黄芩黄酮I、豆甾醇、角鲨烯、汉黄芩素;栀子含有异欧前胡素、β-谷甾醇、藏红花酸、欧前胡素、山奈酚、槲皮素、豆甾醇、角鲨烯;板蓝根含有刺槐黄素、β-谷甾醇、半齿泽兰素、高车前素、甜橙黄酮、谷甾醇、豆甾醇;茵陈含有谷甾醇、芫花素和槲皮素;灵芝含有β-谷甾醇、过氧麦角甾醇。删除重复活性成分后,共得到活性成分20个。
-
通过STITCH软件进行分析,预测舒肝宁注射液中20个活性成分的靶点,预测得到87个蛋白靶点。再通过GeneCards和OMIM数据库中与肝炎有关的基因进行比对,取交集得到83个与肝炎相关的靶点。其中肝炎相关性得分大于10分并且经文献证实的基因有15个,分别为:肿瘤蛋白P53(TP53)、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)、白细胞介素-10(IL-10)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)、载脂蛋白E(APOE )、ATP 结合盒亚家族B成员11(ABCB11)、半胱氨酸蛋白酶-8(CASP8)、溶质载体有机阴离子转运蛋白家族成员1B1(SLCO1B1)、细胞色素 P450 2D6(CYP2D6)、UDP-葡萄糖醛酸转移酶 1A7(UGT1A7)、细胞色素 P450 3A4(CYP3A4)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶8(MAPK8)、UDP-葡萄糖醛酸转移酶 1A3(UGT1A3)、细胞色素 P450 1A2(CYP1A2)、血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)。
-
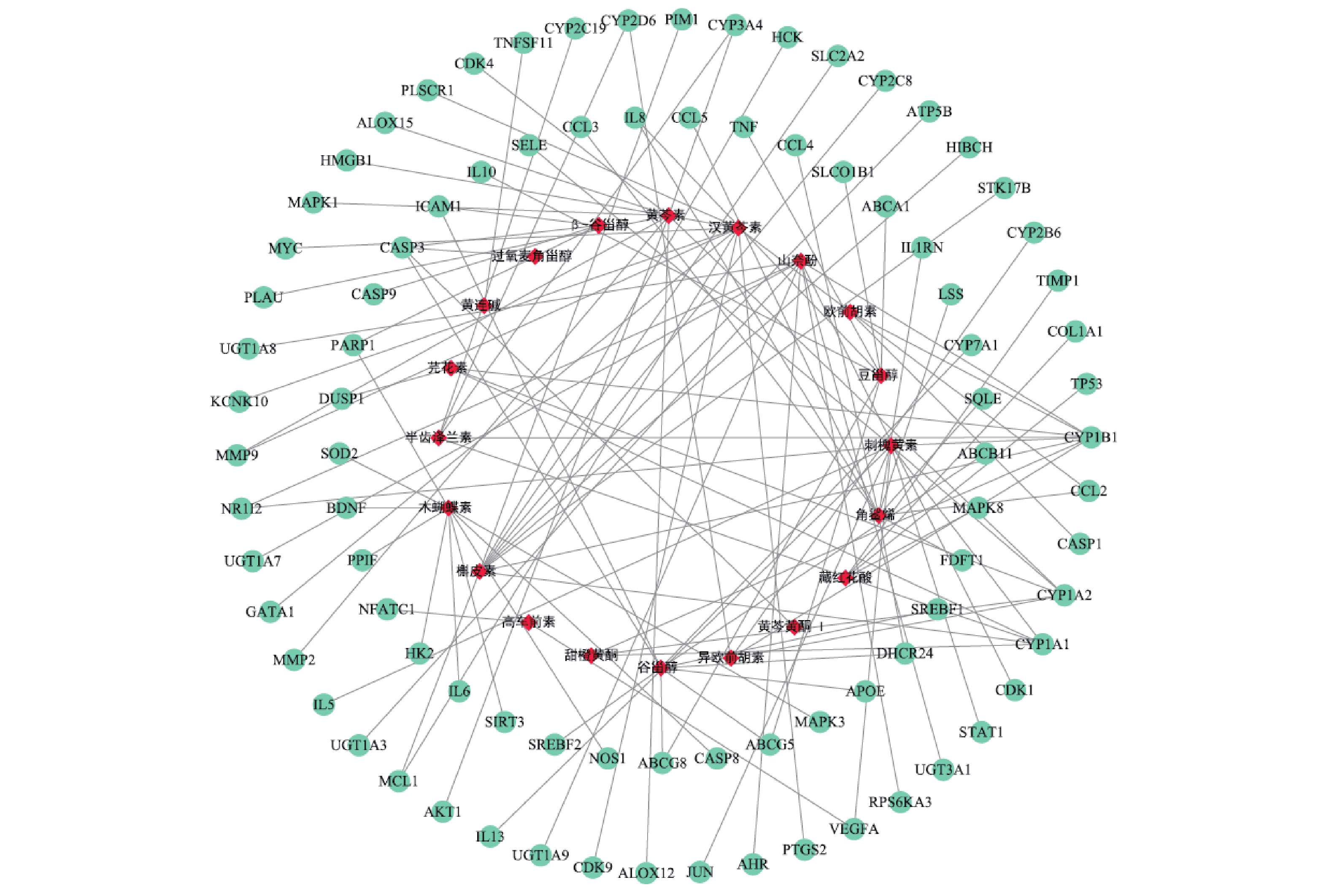
使用Cytoscape构建“活性成分-肝炎作用靶点”网络见图1。网络分析结果显示,度值排名靠前的活性成分有 :刺槐黄素、谷甾醇、黄芩素、木蝴蝶素、汉黄芩素、槲皮素、山奈酚、角鲨烯,度值都为10。提示以上活性成分为舒肝宁注射液抗肝炎的主要活性成分。度值排名靠前的肝炎靶点有:CYP1B1、CYP1A2、CYP1A1、CASP3,度值分别为8、5、5、4;EGFA、NR1I2、ICAM1、PARP1 、CYP2D6、CYP3A4,度值都为2。图中可以看到刺槐黄素、甜橙黄酮、黄芩素、芫花素、异欧前胡素可共同作用于靶点CYP1A2;β-谷甾醇、谷甾醇、黄芩黄酮 I可共同作用于靶点CASP3;刺槐黄素、高车前素、可同时作用于靶点VEGFA,汉黄芩素、槲皮素可共同作用于MCL1,而豆甾醇可同时作用于ABCA1、ABCG8、ABCG5、SLCO1B1、TNF、IL-8、IL-10。同一靶点可对应不同的活性成分,不同靶点也可以对应相同的活性成分,充分体现了舒肝宁注射液多成分、多靶点的作用特点。
-
将蛋白靶点导入STRING 数据库获取蛋白间的相互作用关系,构建的蛋白质相互关系网络详见图2。网络分析结果显示度值排名靠前的靶点有:TNF、TP53、IL-6、AKT1、CASP3、JUN、VEGFA、MAPK3、CXCL8、IL-10,度值分别为33、32、31、23、23、23、22、22、20、19。度值大的靶点提示在网络调控中起着关键作用,度值大的靶点很可能是舒肝宁注射液治疗肝炎的关键靶点。
-
GO富集分析的结果详见图3~图5。其中BP (图3)分析中排名靠前的生物过程依次为细胞过程、生物过程的调控、对化学刺激的反应、对应激的反应、细胞代谢过程调控、生物质量调控、基础代谢过程调控、大分子代谢过程的调控、细胞对刺激的反应、信号处理。CC分析(图4)中排名靠前的细胞组分依次为细胞质、膜结合细胞器、细胞质部分、细胞器部分、细胞内细胞器部分、不溶性组分、细胞器腔、膜封闭腔、细胞器膜、细胞内细胞器腔。 MF分析(图5)中排名靠前的分子功能依次为蛋白结合、催化活性、过度金属离子结合、核苷酸结合、转移酶活性、受体结合、腺苷酸结合、嘌呤核苷结合、核苷结合、嘌呤核苷酸结合。
-
KEGG通路分析结果如图6所示,排名靠前的是TNF (15个靶点) 、IL-17(14个靶点)、MAPK(14个靶点)等信号通路。
-
舒肝宁注射液是茵陈、栀子、黄芩、板蓝根和灵芝等五味中药材的提取物组合而成的一种纯中药注射剂,在临床上被广泛用于治疗急慢性病毒性肝炎、药物性肝炎、胆汁淤积性肝炎、肝硬化和肝功能衰竭等肝脏疾病。研究发现舒肝宁注射液对于肝炎患者治疗效果显著,且不良反应较少,安全有效性高[4],但其抗肝炎保肝的作用机制尚不清楚。
本研究中,通过检索TCMSP获得舒肝宁注射液中的活性成分,根据ADME值对活性成分进行筛选,绘制“活性成分-靶点”网络图,并经过网络分析获得度值排名靠前的活性成分,作为可能为舒肝宁注射中发挥抗炎作用的主要活性成分,结果显示其主要有刺槐黄素、谷甾醇、黄芩素、木蝴蝶素、汉黄芩素、槲皮素、山奈酚、角鲨烯。研究发现,黄芩中的黄芩素、汉黄芩素和千层纸素A可以分别作用NF-κB信号通路的不同阶段发挥抗炎作用[5];栀子中的异欧前胡素,可以通过下调肝纤维化指标,抑制炎症因子的释放,改善肝纤维化的进程[6];山奈酚具有良好的抗炎镇痛作用[7]并且可以通过抑制CHOP分子改善内质网应激诱导的肝细胞损伤[8];槲皮素能通过调控PI3K/AKT/NF-κB信号通路来改善非酒精性脂肪性肝炎大鼠肝组织脂肪变性程度,减轻肝脏炎症[9];板蓝根中的豆甾醇能明显抑制LPS诱导的环氧合酶-2、诱导型一氧化氮合酶mRNA和蛋白水平的提高,抑制前列腺素E2和一氧化氮的释放从而实现其抗炎作用[10];茵陈中的芫花素具一定的清除自由基、抗炎、抑制肿瘤的作用[11]。舒肝宁注射液可能通过以上活性成分发挥其抗肝炎保肝作用。
本研究发现,舒肝宁注射液活性成分作用于83个肝炎靶点,成分靶点网络显示了舒肝宁注射液多成分、多靶点的抗炎保肝作用特点(图1)。蛋白作用网络显示了舒肝宁注射液靶蛋白间存在着相互关系(图2)。靶点的GO分析结果表明,舒肝宁注射液抗炎保肝作用涉及细胞、生物过程的调控、对化学刺激的反应、对应激的反应等过程的调控,涉及细胞质、膜结合细胞器、细胞内细胞器等细胞组分,以及蛋白结合、催化活性、过度金属离子结合、核苷酸结合、转移酶活性等分子功能,是一个复杂的过程(图3~图5)。靶点KEGG通路分析结果显示,舒肝宁注射液抗炎保肝的的靶点主要涉及TNF、IL-17、MAPK等信号通路(图6)。
舒肝宁注射液作用的肝炎靶点中, PPI 网络分析结果和“活性成分-靶点”网络分析结果中度值排名前十、肝炎相关性得分大于10分并且有文献证实的基因共有8个分别为:CYP1A2、CYP2D6、CYP3A4、IL-10、IL-6、TNF、TP53、VEGFA,提示以上靶点可能为舒肝宁注射液抗肝炎的主要靶点。TP53是一个抑癌基因,编码的蛋白质对各种细胞应激作出反应,以调节靶基因的表达,从而诱导细胞周期停滞、凋亡、衰老、DNA修复或代谢变化。TP53突变与乙型肝炎相关的肝细胞癌密切相关[12]。也有研究发现TP53突变与肝细胞癌的免疫微环境失调有关,会导致肝细胞癌免疫应答下调[13]。IL-10编码的蛋白质是一种细胞因子,主要由单核细胞产生,少部分由淋巴细胞产生。该细胞因子在免疫调节和炎症中具有多效作用,被认为在乙型肝炎病毒感染的免疫学中起重要作用[14]。IL-6编码的细胞因子在炎症和B细胞成熟中起作用。该蛋白质主要在急性和慢性炎症的部位产生,在那里它被分泌到血清中,并通过IL-6受体α诱导转录炎症反应,其中包括经典的NF-κB信号通路,通过控制一系列生长因子和细胞因子的表达在肝脏炎症反应中起着至关重要的作用[15]。CYP1A2、CYP3A4 和CYP2D6基因编码的蛋白质属于细胞色素P450超家族酶的成员,可催化药物代谢、合成胆固醇、类固醇和其他脂类的许多反应。这类蛋白质定位于内质网,可代谢多达25%的常用处方药。有研究发现自身免疫性肝炎患者中,CYP2D6可作为LKM-1的主要靶自身抗原,在肝细胞质膜上异常表达,引发自身免疫性反应[16]。CYP1A2 则被发现其基因多态性在吸烟者和 HBsAg血清阴性个体中是与肝细胞癌易感性相关的[17]。VEGFA是PDGF/VEGF生长因子家族的成员,它编码一种肝素结合蛋白,以二硫键连接的同源二聚体形式存在。丙型肝炎病毒感染的主要并发症是诱发肝纤维化。有文献报道VEGFA的mRNA和蛋白质表达水平与丙型肝炎病毒相关肝纤维化进展之间相关,并且丙型肝炎病毒患者的VEGFA在mRNA和蛋白质的表达明显高于对照组,而且晚期肝纤维化阶段的患者表现出最高的VEGFA mRNA和蛋白质水平[18]。舒肝宁注射液的活性成分可能通过对以上靶点相互作用,实现其抗肝炎保肝的作用机制。
舒肝宁注射液筛选得到的肝炎靶点所富集的通路中,肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)通路参与多种生物过程的调节,包括细胞增殖、分化、凋亡、脂质代谢和凝血过程。研究显示TNF通路相关基因的变异与乙型肝炎病毒的清除有关[19],TNF-α/JNK信号通路也与孟鲁司特改善刀豆素A诱导的小鼠自身免疫性肝炎的作用相关[20]。IL-17介导的信号通路与自身免疫性肝病的治疗相关,通过影响组织微环境可促进肝脏炎症和自身免疫[21]。女性失代偿性急性乙型肝炎患者中,IFN-γ和IL-4下调的伴有增强的肝IL-17阳性细胞增多可以加速破坏性免疫,以增强病毒清除。靶向涉及IL-17的通路的治疗可预防肝移植或失代偿性急性乙型肝炎患者的死亡[22]。MAPK8、MAPK3编码的蛋白质是 MAP 激酶家族的成员,MAP激酶,也称为细胞外信号调节激酶,在信号级联反应中起作用,该级联调节响应各种细胞外信号的各种细胞过程,例如增殖、分化和细胞周期进程。有文献研究了宿主遗传因素在乙肝疫苗抗乙型肝炎病毒感染长期免疫中的作用,发现MAPK8的变异影响了宿主anti-HBs的峰值水平[23]。并且有研究发现micro RNA-155通过MAPK信号通路,通过靶向SOCS1,调节酒精性肝炎大鼠的肝星状细胞的增殖、凋亡和细胞周期进展[24]。舒肝宁注射液活性成分可能作用于以上靶点及信号通路实现其抗炎保肝作用。
综上所述,网络药理学分析显示舒肝宁注射液的20种活性成分作用于83个蛋白靶点,其中刺槐黄素、谷甾醇、黄芩素、木蝴蝶素、汉黄芩素、槲皮素、山奈酚、角鲨烯为舒肝宁注射液治疗肝炎的主要活性成分,CYP1A2、CYP2D6、CYP3A4、IL-10、IL-6、TNF、TP53、VEGFA为舒肝宁注射液治疗肝炎的主要靶点,舒肝宁注射液可能通过以上活性成分和蛋白靶点相互作用,实现其抗肝癌作用,并通过TNF、IL-17、MAPK等信号通路改善肝炎患者症状。本研究表明舒肝宁注射液作用机制涉及多种过程、分子和通路,体现了舒肝宁注射液多成分-多靶点-多途径的作用特点。本研究为舒肝宁注射液抗炎保肝作用分子机制的进一步研究提供了思路和方法。
Study on the mechanism of anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective effects of Shuganning injection based on network pharmacology
-
摘要:
目的 构建舒肝宁注射液活性成分-作用靶点和蛋白相互作用网络,探讨舒肝宁注射液抗炎保肝作用机制。 方法 通过TCMSP数据库获取舒肝宁注射液中茵陈、栀子、黄芩、板蓝根和灵芝的主要活性成分;利用GeneCard和OMIM数据库筛选舒肝宁注射液活性成分对应靶点中与肝炎相关靶点;采用Cytoscape构建活性成分-作用靶点网络;应用String数据库和Cytoscape软件绘制蛋白相互作用网络;通过DAVID数据库对靶点进行GO及KEGG通路分析。 结果 筛选得到舒肝宁注射液活性成分20个,共83个作用靶点。GO分析表明,舒肝宁注射液主要影响细胞过程和生物过程的调控,以及对化学刺激和应激的反应等作用。KEGG通路分析显示,舒肝宁注射液抗炎保肝作用的靶点主要涉及TNF、IL-17、MAPK等信号通路。 结论 舒肝宁注射液的抗炎保肝作用具有多成分、多靶点、多通路的特点,可能通过调节TNF、IL-17、MAPK等通路发挥作用。 Abstract:Objective To explore the anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective mechanism of Shuganning injection through establishing the active ingredients-targets network and protein interactions network. Methods The main active ingredients of Artemisiae scopariae, Fructus gardenia, Radix scutellariae, Radix isatidis and Ganoderma in Shuganning injection were obtained by TCMSP; GeneCards and OMIM were used to screen the hepatitis-related targets among the corresponding targets of the active ingredient of Shuganning injection; The Cytoscape software was used to construct the active ingredient-targets network of Shuganning injection. The protein interactions network was constructed using the String database and Cytoscape software. The GO and KEGG pathways involved in the targets were analyzed by DAVID database. Results The results showed that 20 active ingredients and 83 targets of Shuganning injection were involved. GO analysis showed that Shuganning injection mainly affected the regulation of cellular processes and biological processes, as well as the response to chemical stimulation and stress. KEGG pathway analysis showed that the targets of the anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective effect of Shuganning injection mainly involved in signaling pathways such as TNF, IL-17, and MAPK. Conclusion The anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective effect of Shuganning injection have the characteristics of multiple components, multiple targets and multiple pathways, which may play a role by regulating pathways such as TNF、IL-17 and MAPK . -
舒肝宁注射液是在中国传统医学经典方剂——张仲景《伤寒杂病论》“茵陈蒿汤”基础上进一步研发的纯中药注射剂,由茵陈、栀子、黄芩、板蓝根和灵芝等五味中药材的提取物组合而成,在临床上主要用于治疗急慢性病毒性肝炎、药物性肝炎、胆汁淤积性肝炎等肝脏疾病[1-2]。舒肝宁注射液所含中药种类繁多,化学成分复杂,其改善肝炎的有效成分及相应的作用机制尚不清楚,因此,研究舒肝宁注射液的有效活性成分、作用靶点及其抗炎保肝的作用机制具有重要的科学意义。
中药复方活性成分不明是中药复方药效物质基础研究的瓶颈之一,网络药理学通过将化学成分映射到疾病基因网络中来寻找潜在的生物活性成分,为筛选中药活性成分提供了一种方法。同时以中药成分、靶点和疾病等数据相关信息为基础,构建生物网络,通过网络分析阐释中药的作用机制,对中药复方在临床应用具有重要的意义。
本研究通过检索TCMSP数据库以及相关文献收集舒肝宁注射液的活性成分信息,并在此基础上利用药物靶点分析平台STITCH预测舒肝宁注射液可能的作用靶点,采用Cytoscape构建舒肝宁注射液抗肝炎作用的“活性成分-作用靶点”网络,对这些靶点进行蛋白-蛋白相互作用分析,利用DAVID数据库进行基因功能和信号通路分析,探讨舒肝宁注射液抗炎保肝作用可能的作用机制。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 舒肝宁注射液中活性成分的筛选
通过检索中药系统药理学数据库和分析平台(TCMSP)以及相关文献,分别收集舒肝宁注射液中茵陈、栀子、黄芩、板蓝根和灵芝的主要的化学成分,建立舒肝宁注射液化学成分数据库。在此基础上,考察化学成分生物利用度(OB>30%)、药物相似性(DL>0.18)[3]、化合物含量以及相关生物功能,通过文献筛选舒肝宁注射液中有效的活性成分。
1.2 活性成分潜在作用靶点的预测及筛选
主要通过化合物与蛋白互作数据库(STITCH)进行分析,将活性成分输入,选择“人类”物种进行搜索。将搜索得到靶点结果以TSV格式进行保存,筛选结合得分大于0.7的靶点。以“hepatitis”作为疾病关键词,搜寻GeneCards数据库与OMIM数据库中与肝炎相关的靶点。将舒肝宁注射液活性成分作用靶点与肝炎相关疾病靶点取交集,靶点名称以靶点基因名称为准,用于后续靶点网络的构建、蛋白相互作用网络构建、基因功能和信号通路分析等工作。
1.3 舒肝宁注射液“活性成分-作用靶点”网络的构建
根据舒肝宁注射液中主要有效成分作用的肝炎相关靶点,建立活性成分-肝炎作用靶点之间的相互对应关系。将活性成分和肝炎靶点作为网络中的节点,两者之间的相互作用作为网络中的连接,导入Cytoscape 3.8.2软件中构建舒肝宁注射液“活性成分-作用靶点”网络。并应用内置工具分析有效成分及靶点的网络拓扑参数,包括连接度、介度、及紧密度等,并根据网络拓扑学参数判断核心靶点及发挥药效的主要活性成分。
1.4 蛋白质相互关系网络的构建
蛋白质相互作用数据库(String)是一种包含已知和预测的蛋白质−蛋白质相互作用的数据库, 其中收集了大量的蛋白质相互作用关系。将舒肝宁注射液与肝炎相关的靶点导入String数据库,获取蛋白间的相互作用关系,将结果保存成TSV格式,保留文件中节点1、节点2和结合得分信息,导入Cytoscape 3.8.2软件中绘制相互作用网络,并对网络进行分析,保存结果。使用Cytoscape 3.8.2软件设置节点大小和颜色反映度(Degree)值的大小,边的粗细用于反映结合得分的大小,获得舒肝宁注射液作用靶点蛋白-蛋白相互作用网络图。
1.5 基因功能和信号通路分析
生物学信息注释数据库(DAVID)为基因和蛋白提供系统综合的生物功能注释信息,可以对差异基因进行功能和通路富集分析。将舒肝宁注射液作用与肝炎相关的蛋白靶点导入DAVID数据库,选择标识符为标准的基因名称,列表类型设置为基因列表,限定物种为人,对舒肝宁注射液作用靶点进行KEGG通路分析,阈值设置为P<0.01保存结果,并按照涉及的靶点数目多少进行排序,筛选排名靠前的信号通路,采用GraphPad Prism 5.0软件绘图。GO富集分析是指在某一功能层次上统计蛋白或者基因的数目组成的一个有向无环图,包括生物过程(BP)、分子功能(MF)和细胞组分(CC)3个分支。使用Cytoscape 3.8.2软件中的插件对舒肝宁注射液中活性成分作用靶点进行GO分析,阈值设置为P<0.05,筛选靠前的条目,采用GraphPad Prism 5.0软件绘图。
2. 结果
2.1 舒肝宁注射液中活性成分的筛选
通过搜索中药系统药理学数据库和分析平台TCMSP,从茵陈、栀子、黄芩、板蓝根和灵芝中分别收集到53、98、87、169、242个主要的化学成分。对收集到的化学成分,以生物利用度>30%、药物相似性>0.18以及相关文献参考作为筛选标准,获得30个活性成分,黄芩10个、栀子8个、板蓝根7个、茵陈3个、灵芝2个。黄芩含有刺槐黄素、黄芩素、β-谷甾醇、黄连碱、千层纸素A、谷甾醇、黄芩黄酮I、豆甾醇、角鲨烯、汉黄芩素;栀子含有异欧前胡素、β-谷甾醇、藏红花酸、欧前胡素、山奈酚、槲皮素、豆甾醇、角鲨烯;板蓝根含有刺槐黄素、β-谷甾醇、半齿泽兰素、高车前素、甜橙黄酮、谷甾醇、豆甾醇;茵陈含有谷甾醇、芫花素和槲皮素;灵芝含有β-谷甾醇、过氧麦角甾醇。删除重复活性成分后,共得到活性成分20个。
2.2 潜在靶点的预测及筛选
通过STITCH软件进行分析,预测舒肝宁注射液中20个活性成分的靶点,预测得到87个蛋白靶点。再通过GeneCards和OMIM数据库中与肝炎有关的基因进行比对,取交集得到83个与肝炎相关的靶点。其中肝炎相关性得分大于10分并且经文献证实的基因有15个,分别为:肿瘤蛋白P53(TP53)、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)、白细胞介素-10(IL-10)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)、载脂蛋白E(APOE )、ATP 结合盒亚家族B成员11(ABCB11)、半胱氨酸蛋白酶-8(CASP8)、溶质载体有机阴离子转运蛋白家族成员1B1(SLCO1B1)、细胞色素 P450 2D6(CYP2D6)、UDP-葡萄糖醛酸转移酶 1A7(UGT1A7)、细胞色素 P450 3A4(CYP3A4)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶8(MAPK8)、UDP-葡萄糖醛酸转移酶 1A3(UGT1A3)、细胞色素 P450 1A2(CYP1A2)、血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)。
2.3 舒肝宁注射液“活性成分-作用靶点”网络的构建
使用Cytoscape构建“活性成分-肝炎作用靶点”网络见图1。网络分析结果显示,度值排名靠前的活性成分有 :刺槐黄素、谷甾醇、黄芩素、木蝴蝶素、汉黄芩素、槲皮素、山奈酚、角鲨烯,度值都为10。提示以上活性成分为舒肝宁注射液抗肝炎的主要活性成分。度值排名靠前的肝炎靶点有:CYP1B1、CYP1A2、CYP1A1、CASP3,度值分别为8、5、5、4;EGFA、NR1I2、ICAM1、PARP1 、CYP2D6、CYP3A4,度值都为2。图中可以看到刺槐黄素、甜橙黄酮、黄芩素、芫花素、异欧前胡素可共同作用于靶点CYP1A2;β-谷甾醇、谷甾醇、黄芩黄酮 I可共同作用于靶点CASP3;刺槐黄素、高车前素、可同时作用于靶点VEGFA,汉黄芩素、槲皮素可共同作用于MCL1,而豆甾醇可同时作用于ABCA1、ABCG8、ABCG5、SLCO1B1、TNF、IL-8、IL-10。同一靶点可对应不同的活性成分,不同靶点也可以对应相同的活性成分,充分体现了舒肝宁注射液多成分、多靶点的作用特点。
2.4 蛋白质相互关系网络的构建
将蛋白靶点导入STRING 数据库获取蛋白间的相互作用关系,构建的蛋白质相互关系网络详见图2。网络分析结果显示度值排名靠前的靶点有:TNF、TP53、IL-6、AKT1、CASP3、JUN、VEGFA、MAPK3、CXCL8、IL-10,度值分别为33、32、31、23、23、23、22、22、20、19。度值大的靶点提示在网络调控中起着关键作用,度值大的靶点很可能是舒肝宁注射液治疗肝炎的关键靶点。
2.5 基因功能分析
GO富集分析的结果详见图3~图5。其中BP (图3)分析中排名靠前的生物过程依次为细胞过程、生物过程的调控、对化学刺激的反应、对应激的反应、细胞代谢过程调控、生物质量调控、基础代谢过程调控、大分子代谢过程的调控、细胞对刺激的反应、信号处理。CC分析(图4)中排名靠前的细胞组分依次为细胞质、膜结合细胞器、细胞质部分、细胞器部分、细胞内细胞器部分、不溶性组分、细胞器腔、膜封闭腔、细胞器膜、细胞内细胞器腔。 MF分析(图5)中排名靠前的分子功能依次为蛋白结合、催化活性、过度金属离子结合、核苷酸结合、转移酶活性、受体结合、腺苷酸结合、嘌呤核苷结合、核苷结合、嘌呤核苷酸结合。
2.6 信号通路分析
KEGG通路分析结果如图6所示,排名靠前的是TNF (15个靶点) 、IL-17(14个靶点)、MAPK(14个靶点)等信号通路。
3. 讨论
舒肝宁注射液是茵陈、栀子、黄芩、板蓝根和灵芝等五味中药材的提取物组合而成的一种纯中药注射剂,在临床上被广泛用于治疗急慢性病毒性肝炎、药物性肝炎、胆汁淤积性肝炎、肝硬化和肝功能衰竭等肝脏疾病。研究发现舒肝宁注射液对于肝炎患者治疗效果显著,且不良反应较少,安全有效性高[4],但其抗肝炎保肝的作用机制尚不清楚。
本研究中,通过检索TCMSP获得舒肝宁注射液中的活性成分,根据ADME值对活性成分进行筛选,绘制“活性成分-靶点”网络图,并经过网络分析获得度值排名靠前的活性成分,作为可能为舒肝宁注射中发挥抗炎作用的主要活性成分,结果显示其主要有刺槐黄素、谷甾醇、黄芩素、木蝴蝶素、汉黄芩素、槲皮素、山奈酚、角鲨烯。研究发现,黄芩中的黄芩素、汉黄芩素和千层纸素A可以分别作用NF-κB信号通路的不同阶段发挥抗炎作用[5];栀子中的异欧前胡素,可以通过下调肝纤维化指标,抑制炎症因子的释放,改善肝纤维化的进程[6];山奈酚具有良好的抗炎镇痛作用[7]并且可以通过抑制CHOP分子改善内质网应激诱导的肝细胞损伤[8];槲皮素能通过调控PI3K/AKT/NF-κB信号通路来改善非酒精性脂肪性肝炎大鼠肝组织脂肪变性程度,减轻肝脏炎症[9];板蓝根中的豆甾醇能明显抑制LPS诱导的环氧合酶-2、诱导型一氧化氮合酶mRNA和蛋白水平的提高,抑制前列腺素E2和一氧化氮的释放从而实现其抗炎作用[10];茵陈中的芫花素具一定的清除自由基、抗炎、抑制肿瘤的作用[11]。舒肝宁注射液可能通过以上活性成分发挥其抗肝炎保肝作用。
本研究发现,舒肝宁注射液活性成分作用于83个肝炎靶点,成分靶点网络显示了舒肝宁注射液多成分、多靶点的抗炎保肝作用特点(图1)。蛋白作用网络显示了舒肝宁注射液靶蛋白间存在着相互关系(图2)。靶点的GO分析结果表明,舒肝宁注射液抗炎保肝作用涉及细胞、生物过程的调控、对化学刺激的反应、对应激的反应等过程的调控,涉及细胞质、膜结合细胞器、细胞内细胞器等细胞组分,以及蛋白结合、催化活性、过度金属离子结合、核苷酸结合、转移酶活性等分子功能,是一个复杂的过程(图3~图5)。靶点KEGG通路分析结果显示,舒肝宁注射液抗炎保肝的的靶点主要涉及TNF、IL-17、MAPK等信号通路(图6)。
舒肝宁注射液作用的肝炎靶点中, PPI 网络分析结果和“活性成分-靶点”网络分析结果中度值排名前十、肝炎相关性得分大于10分并且有文献证实的基因共有8个分别为:CYP1A2、CYP2D6、CYP3A4、IL-10、IL-6、TNF、TP53、VEGFA,提示以上靶点可能为舒肝宁注射液抗肝炎的主要靶点。TP53是一个抑癌基因,编码的蛋白质对各种细胞应激作出反应,以调节靶基因的表达,从而诱导细胞周期停滞、凋亡、衰老、DNA修复或代谢变化。TP53突变与乙型肝炎相关的肝细胞癌密切相关[12]。也有研究发现TP53突变与肝细胞癌的免疫微环境失调有关,会导致肝细胞癌免疫应答下调[13]。IL-10编码的蛋白质是一种细胞因子,主要由单核细胞产生,少部分由淋巴细胞产生。该细胞因子在免疫调节和炎症中具有多效作用,被认为在乙型肝炎病毒感染的免疫学中起重要作用[14]。IL-6编码的细胞因子在炎症和B细胞成熟中起作用。该蛋白质主要在急性和慢性炎症的部位产生,在那里它被分泌到血清中,并通过IL-6受体α诱导转录炎症反应,其中包括经典的NF-κB信号通路,通过控制一系列生长因子和细胞因子的表达在肝脏炎症反应中起着至关重要的作用[15]。CYP1A2、CYP3A4 和CYP2D6基因编码的蛋白质属于细胞色素P450超家族酶的成员,可催化药物代谢、合成胆固醇、类固醇和其他脂类的许多反应。这类蛋白质定位于内质网,可代谢多达25%的常用处方药。有研究发现自身免疫性肝炎患者中,CYP2D6可作为LKM-1的主要靶自身抗原,在肝细胞质膜上异常表达,引发自身免疫性反应[16]。CYP1A2 则被发现其基因多态性在吸烟者和 HBsAg血清阴性个体中是与肝细胞癌易感性相关的[17]。VEGFA是PDGF/VEGF生长因子家族的成员,它编码一种肝素结合蛋白,以二硫键连接的同源二聚体形式存在。丙型肝炎病毒感染的主要并发症是诱发肝纤维化。有文献报道VEGFA的mRNA和蛋白质表达水平与丙型肝炎病毒相关肝纤维化进展之间相关,并且丙型肝炎病毒患者的VEGFA在mRNA和蛋白质的表达明显高于对照组,而且晚期肝纤维化阶段的患者表现出最高的VEGFA mRNA和蛋白质水平[18]。舒肝宁注射液的活性成分可能通过对以上靶点相互作用,实现其抗肝炎保肝的作用机制。
舒肝宁注射液筛选得到的肝炎靶点所富集的通路中,肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)通路参与多种生物过程的调节,包括细胞增殖、分化、凋亡、脂质代谢和凝血过程。研究显示TNF通路相关基因的变异与乙型肝炎病毒的清除有关[19],TNF-α/JNK信号通路也与孟鲁司特改善刀豆素A诱导的小鼠自身免疫性肝炎的作用相关[20]。IL-17介导的信号通路与自身免疫性肝病的治疗相关,通过影响组织微环境可促进肝脏炎症和自身免疫[21]。女性失代偿性急性乙型肝炎患者中,IFN-γ和IL-4下调的伴有增强的肝IL-17阳性细胞增多可以加速破坏性免疫,以增强病毒清除。靶向涉及IL-17的通路的治疗可预防肝移植或失代偿性急性乙型肝炎患者的死亡[22]。MAPK8、MAPK3编码的蛋白质是 MAP 激酶家族的成员,MAP激酶,也称为细胞外信号调节激酶,在信号级联反应中起作用,该级联调节响应各种细胞外信号的各种细胞过程,例如增殖、分化和细胞周期进程。有文献研究了宿主遗传因素在乙肝疫苗抗乙型肝炎病毒感染长期免疫中的作用,发现MAPK8的变异影响了宿主anti-HBs的峰值水平[23]。并且有研究发现micro RNA-155通过MAPK信号通路,通过靶向SOCS1,调节酒精性肝炎大鼠的肝星状细胞的增殖、凋亡和细胞周期进展[24]。舒肝宁注射液活性成分可能作用于以上靶点及信号通路实现其抗炎保肝作用。
综上所述,网络药理学分析显示舒肝宁注射液的20种活性成分作用于83个蛋白靶点,其中刺槐黄素、谷甾醇、黄芩素、木蝴蝶素、汉黄芩素、槲皮素、山奈酚、角鲨烯为舒肝宁注射液治疗肝炎的主要活性成分,CYP1A2、CYP2D6、CYP3A4、IL-10、IL-6、TNF、TP53、VEGFA为舒肝宁注射液治疗肝炎的主要靶点,舒肝宁注射液可能通过以上活性成分和蛋白靶点相互作用,实现其抗肝癌作用,并通过TNF、IL-17、MAPK等信号通路改善肝炎患者症状。本研究表明舒肝宁注射液作用机制涉及多种过程、分子和通路,体现了舒肝宁注射液多成分-多靶点-多途径的作用特点。本研究为舒肝宁注射液抗炎保肝作用分子机制的进一步研究提供了思路和方法。
-
-
[1] 陈明泉, 李谦, 张琼华, 等. 舒肝宁注射液治疗急慢性病毒性肝炎的临床疗效观察[J]. 肝脏, 2007, 12(3):194-196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2007.03.014 [2] 张瑾. 舒肝宁注射液对顺铂中毒小鼠肝脏损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国药房, 2016, 27(7):920-922. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2016.07.17 [3] 汝锦龙. 中药系统药理学数据库和分析平台的构建和应用[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2015. [4] 王艳春, 王建强. 舒肝宁注射液临床应用研究进展[J]. 中国药物警戒, 2020, 17(8):543-548. doi: 10.19803/j.1672-8629.2020.08.20 [5] 刘媛媛, 刘陶, 吴玉梅, 等. 基于雌激素受体调节Nrf2-ARE通路的黄芩中抗氧化成分的筛选[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2019, 35(6):822-827. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2019.06.017 [6] 朱悦. 异欧前胡素激活LXRα/β介导HMGB1-NLRP3炎症信号通路改善肝纤维化进程的研究[D]. 延吉: 延边大学, 2021. [7] 陈丹. 山奈酚的抗炎镇痛作用及其机制研究[D]. 南京: 南京中医药大学, 2021. [8] 郭媛媛, 任锋, 张向颖, 等. 山奈酚对内质网应激诱导的肝细胞损伤的保护及机制[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2014, 22(35):5400-5407. [9] 刘鸣昊, 张丽慧, 马庆亮, 等. 槲皮素对非酒精性脂肪性肝炎大鼠的影响[J]. 中成药, 2019, 41(8):1820-1825. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2019.08.014 [10] PANDITH H, ZHANG X B, THONGPRADITCHOTE S, et al. Effect of Siam weed extract and its bioactive component scutellarein tetramethyl ether on anti-inflammatory activity through NF-κB pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol,2013,147(2):434-441. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.03.033 [11] 樊江波, 黄琳红. 益母草活性成分芫花素对小鼠凝血及抗炎作用的研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 40(1):158-161. [12] GAO Q, ZHU H W, DONG L Q, et al. Integrated proteogenomic characterization of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell,2019,179(5):1240. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.038 [13] LONG J Y, WANG A Q, BAI Y, et al. Development and validation of a TP53-associated immune prognostic model for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. EBioMedicine,2019,42:363-374. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.022 [14] TOK Y T, ŞENER A G, GÖKMEN A A, et al. Investigation of regulatory T cells and secreted immunomodulatory cytokine IL-10 levels in patients with hepatitis B[J]. Mikrobiyol Bul,2020,54(2):266-278. doi: 10.5578/mb.69340 [15] HE G B, KARIN M. NF-κB and STAT3 - key players in liver inflammation and cancer[J]. Cell Res,2011,21(1):159-168. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.183 [16] MIZUTANI T, SHINODA M, TANAKA Y, et al. Autoantibodies against CYP2D6 and other drug-metabolizing enzymes in autoimmune hepatitis type 2[J]. Drug Metab Rev,2005,37(1):235-252. doi: 10.1081/DMR-200028798 [17] CHEN X P, WANG H J, XIE W M, et al. Association of CYP1A2 genetic polymorphisms with hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility: a case-control study in a high-risk region of China[J]. Pharmacogenet Genomics,2006,16(3):219-227. doi: 10.1097/01.fpc.0000194424.20393.c6 [18] SALUM G M, BADER EL DIN N G, IBRAHIM M K, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in hepatitis C virus-induced liver fibrosis: a potential biomarker[J]. J Interferon Cytokine Res,2017,37(7):310-316. doi: 10.1089/jir.2016.0127 [19] DU T, GUO X H, ZHU X L, et al. Association of TNF-alpha promoter polymorphisms with the outcomes of hepatitis B virus infection in Chinese Han population[J]. J Viral Hepat,2006,13(9):618-624. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2006.00731.x [20] EL-KASHEF D H, ABDELRAHMAN R S. Montelukast ameliorates Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis in mice via inhibiting TNF-α/JNK signaling pathway[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol,2020,393:114931. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.114931 [21] ZHANG H Y, BERNUZZI F, LLEO A, et al. Therapeutic potential of IL-17-mediated signaling pathway in autoimmune liver diseases[J]. Mediators Inflamm,2015,2015:436450. [22] CHANG M L, YEH C T, CHIEN R N, et al. Overt acute hepatitis B deteriorates in females: destructive immunity with an exaggerated interleukin-17 pathway[J]. Front Immunol,2021,12:631976. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.631976 [23] HENNIG B J, FIELDING K, BROXHOLME J, et al. Host genetic factors and vaccine-induced immunity to hepatitis B virus infection[J]. PLoS One,2008,3(3):e1898. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001898 [24] OFFICE F E. Retraction: microRNA-155 modulates hepatic stellate cell proliferation, apoptosis, and cell cycle progression in rats with alcoholic hepatitis via the MAPK signaling pathway through targeting SOCS1[J]. Front Pharmacol,2022,12:840009. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.840009 -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:


