-
随着当代社会老龄化发展与生活方式的改变,2型糖尿病(T2DM)和骨质疏松(OP)的发病率均呈增长趋势,是常见的两大慢性疾病,严重影响患者的生活质量和预期寿命[1]。大量临床研究表明2型糖尿病患者的骨折风险明显增加,而且T2DM患者病程越长,骨质疏松的风险越高,糖尿病患者若血糖控制不佳,长期处于高血糖状态会引起骨代谢紊乱,最终导致糖尿病性骨质疏松(DOP),是糖尿病患者常见的严重并发症之一[2-3]。DOP主要表现为骨密度(BMD)低、骨脆性增加、骨质量下降和骨折风险增加等,但它的发病机制目前尚不明确,可能与高血糖、氧化应激、晚期糖基化产物及微血管病变等有关[4-5]。虽然在临床中糖尿病和骨质疏松常被认为是两个相互独立的疾病,但它们之间存在着相互关系,笔者通过分析、探讨1例糖尿病伴骨质疏松患者的药物治疗方案,以期为临床积极防治DOP提供治疗参考。
-
患者,女性,77岁,身高155 cm,体重55 kg,BMI 22.89 kg/m2。患者于20多年前无明显诱因出现易饥、多食,多饮、多尿、多汗、消瘦,心慌、手抖等症状,未予重视,后出现头晕、视物旋转,至当地医院就诊,诊断“2型糖尿病”,口服降糖药治疗,具体不详,血糖得到控制。2010年患者因血糖控制不佳改为精蛋白锌重组人胰岛素降糖治疗,并根据血糖变化调整用量,血糖维持在餐后12~13 mmol/L。但患者2年前开始出现四肢肢端麻木,呈持续性症状;并于1年前出现腰部酸痛,伴左下肢放射痛,右侧偶有累及。外院MRI检查示:腰椎退行性改变,腰骶椎间盘膨出,部分椎体压缩,骨质疏松;未予以重视,近半个月来加重,行走困难。遂于2020年10月20日入长海医院内分泌科就诊,入院后完善相关检验检查,X线片检查示:胸腰段椎体多发陈旧性压缩骨折改变,骨密度:T=−4.0;糖化血红蛋白:11.0%;尿常规检查(2020-10-21):尿葡萄糖(++++);尿蛋白质(+);总胆红素35.00 μmol/L;直接胆红素16.00 μmol/L; 天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶89U/L;γ-谷氨酰基转移酶250 U/L,肌酐:76 μmol/L。既往史:自诉腰椎有外伤后压缩骨折病史,具体不详;心脏偶有不适,5年前曾于外院诊断为“冠心病”,自服麝香救心丸后可缓解;病史:自述患有“慢性胃炎”8年;20年前曾因“胆囊结石、胆囊炎”于外院行胆囊切除术。初始诊断:①2型糖尿病;②骨质疏松;③腰椎管病理性骨折,腰椎管狭窄;④冠状动脉粥样硬化心脏病;⑤慢性胃炎;⑥胆囊切除术后。
-
患者入院后,给予精蛋白锌重组人胰岛素降血糖治疗,血糖依旧偏高,调整胰岛素剂量,同时加用口服降糖药阿卡波糖片50 mg,tid和二甲双胍片0.425 g,bid,血糖控制良好;患者骨质疏松严重,胸腰椎多发压缩性改变,考虑患者目前骨质情况较差,手术风险较大,建议先行保守治疗,佩戴支具,药物治疗,使用唑来磷酸盐注射液5 mg,ivgtt抗骨质疏松治疗,并给予阿法骨化醇软胶囊0.25 μg po bid及氨基酸钙片600 mg po bid补钙;腺苷钴胺注射液(福欣康林)3 mg ivgtt qd,前列地尔注射液10 μg ivgtt qd,改善血管病变;使用奥美拉唑肠溶胶囊20 mg po bid 护胃;使用注射用还原型谷胱甘肽1.2 g ivgtt qd,进行保肝等辅助治疗。经过12 d治疗,患者血糖控制良好,腰痛较前有缓解,予以出院。
-
本病例患者是一位老年女性,BMD评分为−4.0,糖尿病病史20余年,既往有骨折病史,提示严重骨质疏松,具有骨折高危风险,使用唑来膦酸盐注射液静脉滴注治疗符合患者的用药需求。临床药师对唑来膦酸盐(密固达)进行重点监护:①使用前评估肾功能情况,不推荐严重肾功能不全患者使用(肌酐清除率<35 ml/min),避免加重肾功能损害,对于有肾功能损害,应谨慎同时使用其他对肾功能有害的药物;②因唑来膦酸能快速对骨转换起效,可导致低血钙,所以使用期间需要监测血钙,对于低血钙患者,在使用唑来膦酸时,需要补充足量的钙剂和维生素D;③使用时不能与其他钙剂或其他二价离子注射剂同时使用,必须通过单独的输液管恒量恒速输注,滴注时间不得少于15 min;④关注可能发生的不良反应,常见的比如发热、肌痛、流感样症状、关节痛、头痛等,绝大多数出现于用药后3d内,所以密切关注患者注射该药3d内的反应;为避免发生以上这些一过性不良反应,短时间服用对乙酰氨基酚或布洛芬,可降低用药后症状的发生率。该患者肾功能正常,根据常规剂量使用,通过药学监护,该患者未发生药物不良反应。
-
骨质疏松治疗常使用BMD评分和骨折作为骨质疏松风险的指标,研究表明BMD评分为−1.6 的T2DM老年女性与BMD评分为−2.5的非糖尿病女性的髋部骨折风险相同。研究显示,骨形成与骨微环境均会受到糖尿病的影响而发生整体改变[6]。T2DM 患者骨密度下降的发生率高达50% ~ 75%,骨折发生率也随之增高[7-8],而且T2DM患者病程越长,骨质疏松风险越高。T2DM患者普遍存在胰岛素抵抗,随病程发展,长期高血糖状态会造成其骨骼肌、脂肪组织的葡萄糖利用减少,改变骨骼结构,并使骨细胞内大量氨基酸堆积,引发钙盐沉积,最终导致骨钙素合成减少,而造成骨质疏松[9]。且长期血糖异常升高也可导致维生素D代谢异常,对人体骨代谢过程产生影响[10];另外,2型糖尿病的多饮、多食、多尿及体重减轻和糖尿病肾病会增加钙质从尿液排出,导致低钙血症[11];此外,有研究表明,老年女性DOP骨折的发病率较男性显著升高,这可能与随着年龄增长,炎症因子和氧化应激产物生成增加,以及内源性雌激素减少等有关[12]。本病例患者是糖尿病伴骨质疏松患者,并同时存在多个骨质疏松高危险因素,比如:高龄、女性患者、既往骨折史等,所以需要更加关注该患者的治疗效果,加强对其血糖的控制,并且合理使用抗骨质疏松药物,及时补充钙剂,减缓病情的进展,从而降低致残率和致死率。
-
目前临床抗骨质疏松的治疗手段从病理机制上主要是抗骨吸收治疗和促合成治疗。双磷酸盐为防治骨质疏松症的一线用药,是焦磷酸盐的类似物,通过与骨骼中羟磷灰石结晶结合,可特异性结合到骨转换活跃的骨表面,抑制破骨细胞的成熟及其功能、促进破骨细胞凋亡,从而抑制骨吸收、减少骨丢失、使骨量增加,来降低发生骨折的风险[13]。阿仑膦酸钠和唑来磷酸盐为目前临床最常用的双磷酸盐,其中阿仑膦酸钠是用于预防和治疗骨质疏松的口服药物,唑来磷酸盐为第三代双磷酸盐类药物,适用于治疗因骨质疏松而产生的骨痛、骨密度下降等情况,尤其是适用于女性绝经后骨质疏松的静脉用药物。Schwartz等[14]通过对双磷酸盐在糖尿病中的抗骨折功效研究发现糖尿病妇女接受唑来膦酸每年一次的骨折风险试验(HORIZO N-PFT),对比试验组和安慰剂治疗组,非椎骨骨折的相对风险是0.52(95%CI 0.33~0.80),形态学椎体骨折的相对风险为0.34(95%Cl 0.18~0.67),结果表明双磷酸盐对于 BMD T评分<−2.5 的糖尿病患者的非脊椎骨折的治疗可以实现明确的降低骨折风险。另有研究表明[15-16],注射唑来膦酸治疗骨质疏松症患者比口服阿仑膦酸盐更有效地增加髋和腰椎部位的BMD,且唑来膦酸给药间隔是每年一次,能使患者顺应性提升,对于提高治疗效果具有重要意义。
-
该患者存在严重的骨质疏松,需要结合患者自身病理特征选择合适的钙剂和维生素D产品,市面上的钙剂种类很多,含钙量及吸收度均不一样。氨基酸钙是一种螯合钙,具有适中的结合常数,结构稳定,通过氨基酸运载系统而被吸收,在血液中形成一种缓冲的流动钙,在需要钙的地方能缓慢的释放钙离子,有效的保证了生物利用度。维生素 D3在体内需经肝脏25ɑ羟化酶活化后,再经肾脏1ɑ 羟化酶活化才能发挥作用,阿法骨化醇为已经体外 1ɑ羟基酶活化的 1ɑ-(OH)-D3,进入体内后,需经肝脏代谢,转化为活性维生素 D3。考虑到该患者肝功能异常状态下可能会影响阿法骨化醇在体内的吸收,从而影响患者血钙水平及体内活性维生素D的水平。因此,临床药师建议将阿法骨化醇改为骨化三醇更符合患者的用药需求,因为骨化三醇是活性维生素D,其主要成分为 1,25-(OH)2-D3,在体内可直接发挥药理作用,促进钙的吸收和利用,但在补钙期间,注意定期监测血钙水平,临床医生采纳药师建议进行用药方案优化。
-
该患者是一位糖尿病伴有骨质疏松的患者,其糖尿病病史较长,且长期血糖控制不佳,糖尿病性骨质疏松可能性大。患者联合使用长效胰岛素和口服降糖药控制血糖,通过多次胰岛素剂量调整,患者餐后2 h血糖控制在7.0 mmol/L左右;患者使用唑来膦酸抗骨质疏松,唑来膦酸每年静脉滴注一次,其起效时间需要2~3个月,使用期间适当补钙和维生素D有利于促进骨矿化,但需要注意定期监测血钙、骨密度等;另外,该患者是绝经后的老年女性,由于雌激素分泌减少,骨折的发病率也显著增加,建议定期检测雌激素水平。该患者在内分泌科进行药物治疗后,病情得到改善,予以出院,考虑患者需长期治疗糖尿病及骨质疏松,嘱其定期到医院随访。
随着糖尿病患者数量的不断增加,DOP的防治逐渐引起关注,但DOP的发病机制复杂,由于其发病隐匿,临床中容易被忽视,不仅降低患者生活质量,也给社会和患者带来经济负担,因此在糖尿病早期加强综合管理有助于预防骨质疏松,这在慢病管理中需要予以重视[17]。目前人们对DOP的认识尚有限,有待更深入的探讨DOP的发病机制,对未来积极防治糖尿病性骨折等提供理论基础。当前对DOP的治疗以有效的降血糖药物联合抗骨质疏松药物进行治疗,对于糖尿病病程较长的患者需要加强对血糖的控制,虽然骨质疏松是不可逆的,但是骨质疏松的进程可以通过药物来延缓。除了合理使用药物外,还应加强患者的饮食控制,这对于糖尿病患者来说也是尤为重要的,但不可忽视的是骨质疏松需要补充足够的钙,所以在食物选择上应多摄入富含钙元素的水果和蔬菜,比如虾皮、紫菜、豆制品等,适当的光照有利于钙的吸收[18]。DOP当前的治疗方式较单一,更多基因分子水平的治疗和诊断方法亟待发现[19]。
Pharmaceutical care of a patient with type 2 diabetes and osteoporosis
-
摘要:
目的 探讨糖尿病合并骨质疏松患者的疾病特点及药学监护要点,为临床合理有效用药提供参考。 方法 临床药师通过参与1例2型糖尿病伴骨质疏松患者的用药分析,结合患者疾病特点及病理特征,并提出药学建议,协助治疗方案的优化。 结果 治疗方案重整及药学监护后,患者的治疗效果得到明显改善。 结论 糖尿病性骨质疏松发病机制复杂,当前的治疗以降血糖联合抗骨质疏松药物为主,通过慢病用药管理、药学监护,可以促进合理用药。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the disease characteristics and key factors of pharmaceutical care in patients with diabetes and osteoporosis, and provide references for clinical rational and effective medication. Methods Clinical pharmacist participated in the drug analysis of a patient with type 2 diabetes and osteoporosis. The pharmaceutical recommendations were proposed to assist physicians in optimizing the treatment plan, combined with the patient’s disease characteristics and pathological characteristics. Results After the reorganization of the treatment plan and pharmaceutical care, the patient's treatment effect had been significantly improved. Conclusion The pathogenesis of diabetic osteoporosis is complex. The current treatment is based on hypoglycemic combined with anti-osteoporosis drugs. Through chronic disease drug management and pharmaceutical monitoring, rational drug use could be promoted. -
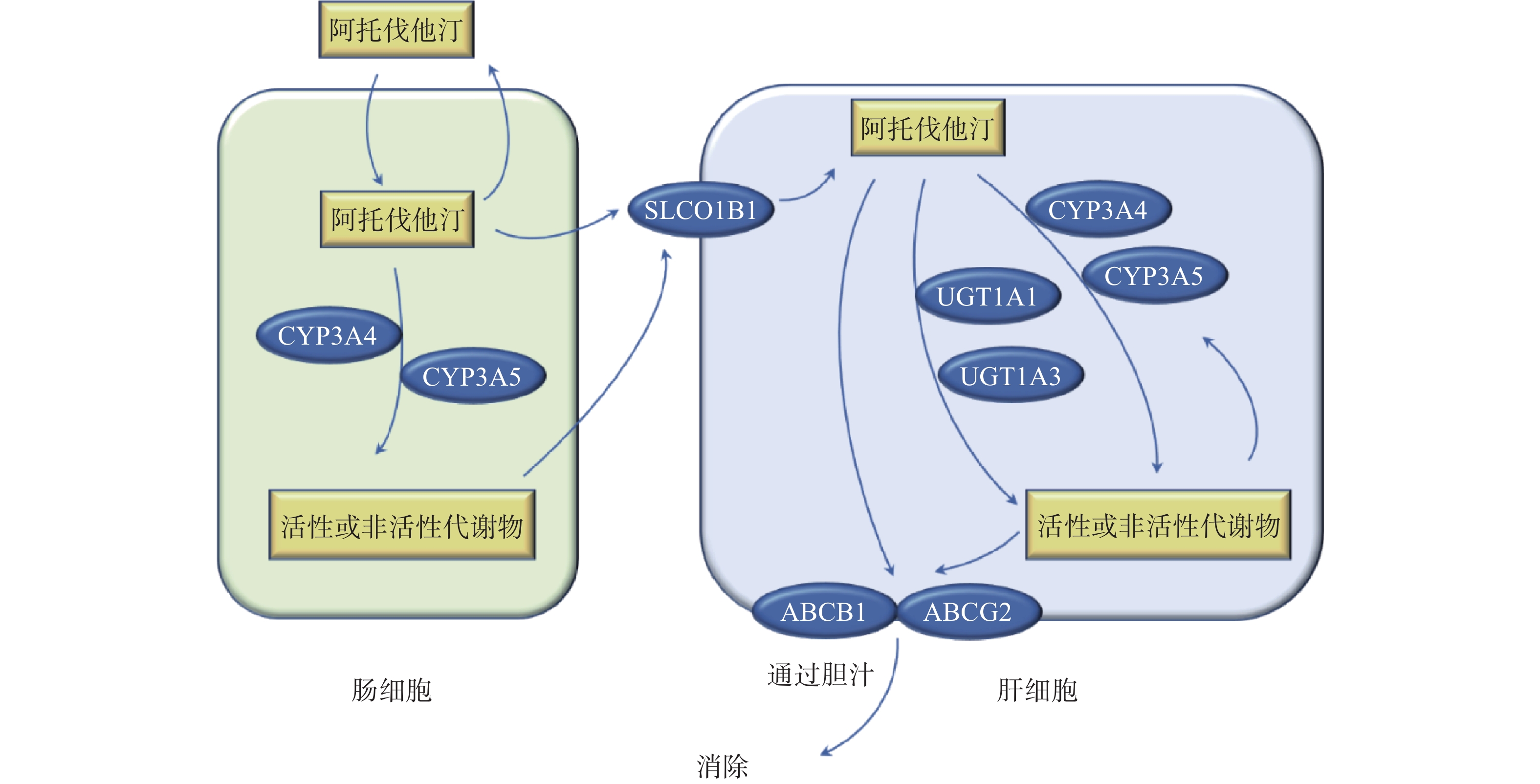
他汀类药物抑制胆固醇合成途径的限速酶3-羟基-3-甲基戊二酸单酰辅酶A还原酶(HMG-CoA还原酶)的活性,抑制胆固醇的生成,上调肝细胞表面的LDL受体以加快LDL的分解代谢。阿托伐他汀以活性酸形式给药,通过被动扩散或OATP1B1转运进入肝细胞,主要由CYP3A4在肝脏和肠壁代谢阿托伐他汀,少量由CYP2C9、CYP2C19、CYP3A5和UGT1A1代谢。阿托伐他汀酸由CYP3A代谢产生邻、对位羟基活性代谢产物,在体内它们与各自的非活性内酯形式处于平衡状态。ABCB1(编码p-gp)和ABCG2(编码BCRP)介导阿托伐他汀及其代谢物从肝脏排入胆汁后消除(图1)[1]。
1. 药物代谢酶及其基因多态性
1.1 CYP3A4
大多数CYP3A代谢发生在肝细胞内,部分发生在小肠内。CYP3A的活性存在较大的个体间差异,显著影响阿托伐他汀的体内代谢。阿托伐他汀和阿托伐他汀内酯主要由CYP3A4同工酶代谢,CYP3A4的活性在不同个体之间可能存在10倍的差异,这可能是由于编码酶的基因多态性所致[2]。
CYP3A4*1G/*1G基因型患者的阿托伐他汀AUC0-∞比野生型和*1/*1G基因型低36%和25%。阿托伐他汀和2-羟基阿托伐他汀的tmax和(CL/Fm)在CYP3A4*1G/*1G基因型和野生型之间存在显著性差异[3]。
经阿托伐他汀治疗后,CYP3A4启动子变异(rs2740574)与野生型等位基因相比显示出更低的LDL-C水平和更好的疗效[2]。CYP3A4*1G(20230G>A)多态性对血清TC下降具有剂量依赖性(P<0.01)。携带CYP3A4*1G增加了阿托伐他汀的降脂效果,对辛伐他汀降脂治疗没有显著影响[4]。CYP3A4*22(rs35599367)会导致CYP3A4酶含量和活性显著降低,CYP3A4*22携带者的阿托伐他汀、辛伐他汀或洛伐他汀的剂量仅为野生型的20%~60%[5]。携带CYP3A4*1B(290A>G)G等位基因可降低辛伐他汀和阿托伐他汀的血药浓度,特别是女性和具有ABCB1 3435T变异等位基因的患者[6]。CYP3A4 A290G变异等位基因与阿托伐他汀治疗后较高的LDL-C水平显著相关,而非同义多态性M445T变异与治疗后较低的LDL-C水平显著相关[7]。此外,携带CYP3A4 A290G变异等位基因比野生型等位基因型的患者具有更高的HDL水平(P<0.001),可能与体内CYP3A4活性降低相关,导致阿托伐他汀活性增加[8]。临床上可减少CYP3A4*22携带者的药物剂量,CYP3A4*1B突变对他汀类药物降脂作用影响尚无定论。
1.2 CYP3A5
CYP3A4和CYP3A5约占CYP450的30%,CYP3A4和CYP3A5均在肝脏和肠道中表达,其中CYP3A5主要在肝外组织中表达。CYP3A5基因与CYP3A家族其他成员一起位于7q22.1染色体上,由9个外显子组成,编码502个氨基酸。
Kivistö等[9]研究发现洛伐他汀、辛伐他汀和阿托伐他汀对CYP3A5表达者(CYP3A5*1)的疗效显著低于非表达者(CYP3A5*3)。携带CYP3A5*1等位基因的受试者1年内的平均血清TC水平和LDL-C水平分别比CYP3A5*3纯合等位基因的受试者高23%(P=0.0014)和24%(P=0.036)。在服用不依赖于CYP3A5代谢的氟伐他汀、普伐他汀的23名受试者中,未发现降血脂与CYP3A5多态性的关联。因此,CYP3A5*3突变可导致CYP3A5酶的表达降低,提高了他汀类药物的降脂疗效。
1.3 CYP2D6
在192例由阿托伐他汀治疗缺血性卒中的中国患者中,Chen等[10]发现CYP2D6 rs1065852显著影响ΔLDL(P<0.001),ΔLDL/LDL (P<0.001),Δ(LDL/HDL)(P<0.001),Δ(LDL/HDL)/(LDL/HDL)(P<0.001)水平。阿托伐他汀对CYP2D6 rs1065852 G等位基因携带者具有较好的降脂效果。
1.4 UGTs
阿托伐他汀由UGT1A1和UGT1A3介导的葡萄糖醛酸化转化为相应的内酯形式,UGT1A3是内酯化的主要酶。
Sung等[11]研究表明UGT1A3*2携带者内酯的生成量显著增加。UGT1A3*2/*2组阿托伐他汀内酯和2-羟基阿托伐他汀内酯的AUC分别比UGT1A3*1/*1组高72%和160%。UGT1A3*2携带者的TC和LDL-C降低百分比分别比非携带者低29%和18%。UGT1A3*2多态性与阿托伐他汀内酯化增加相关,可能影响其降脂作用。低表达等位基因UGT1A1*28(TA)7的携带者较正常活性等位基因(TA)6携带者的阿托伐他汀内酯水平更低(P<0.05)[12]。
2. 药物转运体及其基因多态性
阿托伐他汀易于口服吸收,其吸收取决于转运蛋白的活性,包括摄取性转运体(如有机阴离子转运多肽OATPs)和外排性转运体(乳腺癌耐药蛋白BCRP和P-gp)。阿托伐他汀通过OATP1B1摄取进入肝细胞,通过ABC转运体家族成员(BCRP、P-gp)排泄到胆汁。
2.1 OATP1B1
有机阴离子转运多肽1B1(OATP1B1)表达于人肝细胞的窦状膜上,负责他汀类药物的肝脏摄取,SLCO1B1基因编码。SLCO1B1的SNP影响他汀类药物的体内分布和效能,目前研究最多的两个SNPs为SLCO1B1 521T>C(rs4149056)和388A>G(rs2306283)。
在携带SLCO1B1和ABCG2野生型等位基因的中国和日本受试者的瑞舒伐他汀、阿托伐他汀和辛伐他汀的AUC比白种人更高,其中,阿托伐他汀AUC0-∞分别比白种人高53%和69%[13]。SLCO1B1 c.521CC基因型患者的阿托伐他汀AUC0-48比TT基因型高144%(P<0.001),比TC基因型高61%(P=0.049)[14]。521C等位基因携带者的阿托伐他汀和2-羟基阿托伐他汀的平均Cmax、AUC0-24h和AUC0-∞显著高于521TT基因型组,平均CL值较521TT基因型受试者低,521C等位基因受试者的阿托伐他汀肌毒性风险增加[15]。SLCO1B1 521T>C在阿托伐他汀的临床试验中均可增高AUC,388A>G多态性对疗效影响不显著。
一项体外研究表明[16],SLCO1B1 521T>C下调质膜上OATP1B1的表达以减少阿托伐他汀转运进肝细胞。SLCO1B1 521T>C通过降低肝脏对阿托伐他汀的摄取使药物对HMG-COA还原酶的抑制作用减弱,同时血药浓度升高。SLCO1B1 521C(rs4149056)与辛伐他汀、阿托伐他汀、洛伐他汀和普伐他汀的降脂作用减弱有关[17]。然而,Prado等[18]研究表明,阿托伐他汀对智利高胆固醇血症受试者的降脂作用与SLCO1B1 rs4149056和rs2306283多态性无关(P>0.05),但388A>G rs2306283与阿托伐他汀治疗后更高的HDL-C相关(P=0.02)。现有的研究支持 SLCO1B1 521T>C基因多态性可增加阿托伐他汀的血药浓度,携带突变基因型的患者应适量减少用药剂量。
2.2 乳腺癌耐药蛋白
乳腺癌耐药蛋白(BCRP)由ABCG2基因编码,BCRP在肝脏、小肠、胆管等多种正常组织和癌细胞中均有表达。
ABCG2 c.421C>A在非洲人群中突变频率较低,但在白种人中突变频率为10%~14%,在日本或中国受试者中突变频率高达35%[19]。ABCG2 c.421C>A显著影响阿托伐他汀和瑞舒伐他汀的药动学,ABCG2在抑制这类他汀药物肠道吸收方面起到重要作用。c.421AA基因型携带者的瑞舒伐他汀AUC0-∞分别比c.421CA和c.421CC基因型高100%和144%。c.421AA基因型携带者的阿托伐他汀AUC0-∞比c.421CC高72%[1]。携带ABCG2 rs2622604的日本患者的阿托伐他汀口服生物利用度比非携带者增加了55%(95%CI:16%~131%)[20]。亚洲人群的ABCG2 c.421C>A突变率较高,具有变异等位基因的患者使用他汀类药物需减少剂量。
2.3 P-gp
MDR1中的同义单核苷酸多态性C3435T和非同义单核苷酸多态性G2677T/A是药物处置和疗效差异的潜在因素。ABCB1 TTT/TTT基因型携带者的辛伐他汀酸AUC0-12h和阿托伐他汀AUC0-∞分别比CGC-CGC高60%和55%,且TTT/TTT型的阿托伐他汀的半衰期比CGC-CGC型长24%(P<0.05)[21]。ABCB1 rs1128503 (1236C>T)、rs2032582 (2677G>T/A)和rs1045642 (3435C>T)显著影响阿托伐他汀的AUC和阿托伐他汀治疗的降脂效果[22]。
ABCB1 C3435T与阿托伐他汀疗效下降相关。Kajinami等[23]发现 C3435T多态性与降LDL-C作用减弱相关,并且仅在女性中存在变异基因型携带者升HDL-C作用增强的现象。Rodrigues等[24]评估了G2677T/A和C3435T MDR1多态性对阿托伐他汀治疗前后血脂水平的影响,阿托伐他汀疗效与MDR1多态性之间没有显著相关性(P>0.05)。单倍型分析显示,与非T/T基因携带者相比,T/T携带者有较高的基础TC和LDL-C水平,提示MDR1多态性可能对巴西高胆固醇血症患者的基础胆固醇水平有重要影响。DeGorter等[25]报道的一项病例对照研究中,未发现ABCB1 2677T与阿托伐他汀血药浓度之间的关联。由于ABCB1变异的临床研究结果不确定且不一致,目前不建议临床常规使用ABCB1基因分型来预测他汀类药物的毒性。尽管如此,ABCB1在他汀类药物转运中发挥重要作用,未来可能包括ABCB1变异的多基因指导他汀类药物治疗。
3. 药物作用靶点及其基因多态性
3.1 HMGCR
HMGCR是内源性胆固醇合成途径中的限速酶,他汀类药物竞争性抑制HMGCR。外显子13上选择性剪切HMGCR pre-mRNA,产生两个全长(FL)HMGCR和D13 HMGCR[26]。缺少外显子13的选择性剪接HMGCR转录物的表达量与体内TC、LDL-C、APOB和TC的降低呈负相关[27]。Yu等[28]的研究表明,HNRNPA1的过表达降低了HMGCR酶的活性,增强了LDL的摄取并增加APOB。同时,rs1920045是一种与HNRNPA1外显子8选择性剪接相关的SNP,其与他汀类药物降TC作用减弱有关。Leduc等[29]发现HMGCR的选择性剪接可以解释家族性高胆固醇血症患者对他汀类药物应答的22%~55%的差异。携带rs3846662 AA基因型女性在接受他汀治疗后LDL-C的降低百分比显著低于非AA基因型女性(38.4%vs46.2%,P<0.05)。rs3846662多态性和HMGCR mRNA的选择性剪接显著影响女性对他汀治疗的反应。Cuevas等[30]发现在接受阿托伐他汀治疗的智利患者中,HMGCR rs17671591 T等位基因比野生型C等位基因,显示出更明显地降低LDL-C和升高HDL-C效应(LDL降低8%,P=0.021;HDL增加7.7%,P=0.039)[22]。
4. 脂质代谢相关基因多态性
4.1 ApoE
载脂蛋白E (ApoE)是脂质代谢的重要组成部分。ApoE基因的多态性与血脂水平和他汀类药物的降脂反应有关。APOE ε2等位基因的男性携带者LDL-C的降低率比野生型个体高7%~10% (P=0.01)[31]。Cerda等[32]报道APOE ε2等位基因者对高胆固醇血症具有保护作用,并减少致动脉粥样硬化的脂质分布。Deshmukh等[33]发现 APOE rs445925变异与阿托伐他汀治疗后LDL降低相关,而APOE rs4420638变异对阿托伐他汀治疗后LDL下降作用减弱相关。Jenny等[34]报道阿托伐他汀对139名智利受试者的降脂作用与APOE变异相关,E3/4基因型携带者的降胆固醇作用较E3/3基因型差(LDL-C:-18%vs-29%,P<0.001)。E2等位基因携带者的疗效优于E3和E4携带者,E4基因携带者需增加用药剂量才能达到目标调脂作用。
4.2 CYP7A1
CYP7A1为胆固醇7a羟化酶,是催化胆固醇合成胆汁酸排泄途径的限速酶。CYP7A1基因是胆固醇排泄途径中最重要的调控基因,CYP7A1的基因突变可能会影响他汀类药物的反应。rs8192870位于CYP7A1基因第一个内含子,与阿托伐他汀降低LDL有关,阿托伐他汀治疗后,GG/GA基因型携带者LDL水平降低27.89%,AA基因型携带者LDL水平降低35.26%(P=0.021)[35]。
4.3 ABCG5/G8
ABCG5/G8的胆固醇排泄和CYP7A1催化的胆汁酸生物合成是胆固醇排泄到胆汁中的主要途径。ABCG8 D19H变异体与阿托伐他汀治疗后降低LDL-C作用增强相关,而降TC作用没有显著性差异[36]。ABCG8 H19等位基因携带者比野生型D19等位基因携带者降低LDL-C作用更显著。ABCG8 H19和CYP7A1 C-204 等位基因对阿托伐他汀反应以剂量依赖性方式相互作用[37]。这些组合多态性分析比单一多态性分析(CYP7A1为4.2%,ABCG8 D19H为3.0%)更能有效解释降LDL-C差异,临床上应组合多态性分析以指导特定基因型患者合理用药。
4.4 CETP
胆固醇酯转运蛋白CETP虽然不是他汀类药物的药物靶点,但在胆固醇逆向转运过程、脂蛋白的分解代谢、不同脂蛋白类型的转化中发挥重要作用。CETP 629C/A的突变频率为0.412。与CC或CA基因型携带者相比,AA基因型携带者具有较低的CETP水平(P=0.026)和较高的HDL-C水平(P=0.035)。连续服用阿托伐他汀一年后,CC基因型携带者比CA或AA基因型降低LDL-C、降低LP(A)(P=0.005),升高HDL-C(P=0.045)疗效更显著(P<0.001)[38]。
5. 不良反应
他汀类药物是临床上首选的调血脂药物,并不是所有患者对他汀类药物反应良好,多数患者并未达到调脂目标值,还有部分患者出现不良反应(肌毒性、横纹肌溶解、肝转氨酶持续升高等)。
5.1 肌毒性
他汀相关肌肉症状(SAMS)是最常见的药物不良反应,常导致患者用药依从性差或停药。他汀类肌炎的特征是肌肉组织炎症导致肌肉疼痛或无力,并伴有肌酸激酶浓度持续升高。SAMS症状出现在开始他汀类药物治疗的最初6个月内,并在他汀类药物剂量降低或停止后消退,他汀类药物治疗需要密切监测血清肌酸激酶(CK)水平以预防SAMS。临床应用阿托伐他汀的群体中,SAMS的发病率更高。欧洲动脉粥样硬化协会共识小组发布的注册和观察性研究中,SAMS的发生率为7%~29%[39]。他汀诱导的肌毒性在体内外均呈现浓度依赖性,从轻度肌痛到潜在致命的横纹肌溶解或暴发性横纹肌溶解合并肌红蛋白尿最终导致急性肾功能衰竭。使用辛伐他汀的患者发生SAMS频率最高,其次是阿托伐他汀,氟伐他汀SAMS频率最低[40]。
遗传变异和高血药浓度是他汀类药物诱导肌病的关键原因。一项涉及1550名阿托伐他汀使用者的Meta分析表明,SLCO1B1 c.521T>C与阿托伐他汀不良反应之间存在显著相关性。未发现SLCO1B1 c.388A>G多态性与不良反应或疗效之间的关联(P>0.05)[41]。SLCO1B1 rs4149056与辛伐他汀治疗后肌病的发生显著相关,辛伐他汀诱导相关肌病的作用可能比阿托伐他汀更强[42]。与SLCO1B1 521 TT基因型携带者相比,TC或CC基因型阿托伐他汀的不良反应发生率高2.3倍[43]。Liu等[44]发现携带至少一个SLCO1B1 521C等位基因的患者发生肌毒性的风险更高。在接受瑞舒伐他汀治疗的个体中,SLCO1B1 521C突变等位基因突变与肌肉毒性风险显著相关。然而,521C突变等位基因与阿托伐他汀和辛伐他汀诱导肌毒性风险之间无显著相关性。SLCO1B1 c.521 T>C突变能降低OATP1B1的转运功能,使他汀类药物血药浓度升高,携带突变基因型的患者应降低药物剂量以减少不良反应。
CYP3A 基因型与阿托伐他汀诱导的肌肉损伤严重程度增加有关。在具有CYP3A5*3变异等位基因的个体中,肌酸激酶水平高于野生型个体(P=0.01)[45]。CYP3A基因型与阿托伐他汀诱导肌肉损伤的严重程度增加有关。服用阿托伐他汀的CYP3A5*3/*3基因型患者出现肌痛的可能性更大且更严重[45]。因此,携带CYP3A5*3变异等位基因的个体应减少药物剂量以减轻肌肉损伤程度。发生他汀类相关横纹肌溶解不良反应约60%与药物相互作用有关[46]。临床上使用CYP3A4酶的抑制剂或诱导剂会影响阿托伐他汀的血药浓度,导致发生不良反应的风险增加。
5.2 肝毒性
他汀类药物的另一种常见不良反应是肝毒性。肝毒性的发生率以血中转氨酶浓度升高为特征,远低于SAMS。ABCB1 rs2032582可预测日本人群患阿托伐他汀诱导的肝损伤(AILI)的风险。ABCB1中的一个SNP位点(rs2032582:2677G>T/A)与AILI显著相关(P=0.00068,OR=2.59,95%CI为1.49~4.50),提示G等位基因可能是AILI的危险因素。利用稳定表达ABCB1 rs2032582编码的ABCB1蛋白的Flp-In-293细胞,研究阿托伐他汀的细胞毒性,明确ABCB1 rs2032582 G等位基因在体内和体外是一个重要的AILI危险因素[47]。ABCB1 rs2032582可能是导致AILI的危险因素,携带该突变基因的个体应减少用药剂量。
6. 结语
阿托伐他汀的有关药物代谢酶、转运体、药物作用靶点以及脂质代谢相关基因多态性对阿托伐他汀药动学及药效学的影响,国内外已有很多研究,但仍不完善且许多研究结论不一致,可能是选取人群种族和样本数量的差异造成。目前缺乏多基因相互作用对他汀类药物治疗的影响研究,未来还需参考更多基因多态性以指导临床他汀类药物个体化合理用药。
-
[1] 胡治勇, 崔龙, 董晓颖, 等. 糖尿病患者骨质疏松评估、危险因素及相关机制的研究进展[J]. 重庆医学, 2020, 49(4):660-664. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2020.04.033 [2] ALAM, JAFARIRM, DEHPOURAR. Diabetes mellitus and osteoporosis correlation: challenges and hopes[J]. Curr Diabetes Rev,2020,16(9):984-1001. doi: 10.2174/1573399816666200324152517 [3] 吕茵, 周围, 何文娜, 等. 2型糖尿病合并骨质疏松影响因素研究[J]. 新医学, 2020, 51(1):33-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9802.2020.01.007 [4] 黄燕霞, 梅思. 糖尿病性骨质疏松的研究进展[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2020, 40(1):182-187. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2020.01.031 [5] 倪利华. 糖尿病性骨质疏松症的研究进展[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2020, 40(7):1897-1901. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2020.07.043 [6] PASCHOU S Α, DEDE A D, ANAGNOSTIS P G, et al. Type 2 diabetes and osteoporosis: a guide to optimal management[J]. J ClinEndocrinolMetab,2017,102(10):3621-3634. [7] 李弘磊, 杨涛, 范红旗. 2型糖尿病合并骨质疏松的相关因素分析[J]. 中国医药, 2015, 10(5):644-648. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4777.2015.05.012 [8] POIANA C. Osteoporosis and fracture risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. ActaEndo (Buc),2019,15(2):231-236. doi: 10.4183/aeb.2019.231 [9] 易云平, 张思伟, 潘虹. 老年2型糖尿病骨质疏松相关因素分析[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2017, 23(1):59-61,111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2017.01.013 [10] ARDAWI M S M, AKHBAR D H, ALSHAIKH A, et al. Increased serum sclerostin and decreased serum IGF-1 are associated with vertebral fractures among postmenopausal women with type-2 diabetes[J]. Bone,2013,56(2):355-362. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.06.029 [11] 韩栋, 王奔, 卢晓栋, 等. 中老年2型糖尿病患者发生骨质疏松的影响因素[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制, 2020, 28(2):149-151. doi: 10.16386/j.cjpccd.issn.1004-6194.2020.02.016 [12] XU H, WANG Z D, LI X R, et al. Osteoporosis and osteopenia among patients with type 2 diabetes aged ≥50: role of sex and clinical characteristics[J]. J Clin Densitom,2020,23(1):29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jocd.2019.04.004 [13] 郑倩莲, 徐家林. 唑来膦酸注射液在糖尿病骨质疏松患者中的实施意义[J]. 糖尿病新世界, 2020, 23(16):78-80. doi: 10.16658/j.cnki.1672-4062.2020.16.078 [14] SCHWARTZ A V. Efficacy of osteoporosis therapies in diabetic patients[J]. Calcif Tissue Int,2017,100(2):165-173. doi: 10.1007/s00223-016-0177-8 [15] SEALAND R, RAZAVI C, ADLER R A. Diabetes mellitus and osteoporosis[J]. CurrDiabetes Rep,2013,13(3):411-418. [16] 赵蕾, 王立, 鲁梅花, 等. 唑来膦酸与阿仑膦酸钠治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的效果和安全性比较[J]. 中国综合临床, 2017, 33(12):1134-1137. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1008-6315.2017.12.019 [17] KURRA S, FINK D A, SIRIS E S. Osteoporosis-associated fracture and diabetes[J]. EndocrinolMetabClinN Am,2014,43(1):233-243. [18] 马远征, 王以朋, 刘强, 等. 中国老年骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2018)[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2018, 24(12):1541-1567. [19] 孙军平, 徐向阳, 吕刚. 糖尿病性骨质疏松症的治疗进展[J]. 医学综述, 2017, 23(13):2634-2638. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2017.13.030 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李从艺,曹旺杰,苏韫,龚红霞,刘永琦,和建政,郭家旺,张鑫珏. 基于PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP信号通路探讨四味黄芪散对高原低氧致脑损伤大鼠的保护作用及机制. 中药新药与临床药理. 2024(11): 1661-1668 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 4097
- HTML全文浏览量: 1518
- PDF下载量: 41
- 被引次数: 2




 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
