-
据国际癌症研究机构(IARC,https://www.iarc.who.int/)提供的数据显示,2020年女性乳腺癌现已成为全球最常见的癌症之一[1]。其中有15%~25%的乳腺肿瘤存在人类表皮生长因子受体2(HER2)过表达。HER2阳性的乳腺癌浸润性强、无病生存期短、预后差,对化疗敏感性差,且易复发[2]。曲妥珠单抗是一株靶向HER2的人源化单克隆抗体。虽然曲妥珠单抗单药对乳腺癌治疗起到了很好的改善的效果, 但其疗效还有所不足,如对HER2过表达的乳腺癌患者初次治疗有效率仅在30%左右[3]。EGCG是绿茶中主要的多酚[4],有抑制肿瘤细胞生长、增殖、转移和血管生成,诱导细胞凋亡和增强抗肿瘤免疫等多种抗肿瘤作用[5-9]。据报道,EGCG在乳腺癌、胃癌、白血病、膀胱癌治疗中均显示有抗肿瘤作用[10-13]。本实验旨在探讨曲妥珠单抗与EGCG对HER2过表达细胞株是否具有协同增殖抑制作用,为HER2高表达乳腺癌的治疗提供新的思路。
-
EGCG(MedChemExpress公司),CCK-8检测试剂盒(美国bimake生物科技有限公司);GAPDH一抗、AKT一抗、p-AKT一抗、MAPK一抗、p-MAPK一抗、EGFR一抗、p-EGFR一抗、HER2一抗、p-HER2一抗、抗兔IgG一抗、抗鼠IgG一抗、HRP抗体二抗(美国Cell Signaling Technology公司),凝胶过滤层析标准品(美国BIO-RAD公司),二抗Goat pAb to Human IgG(英国Abcam公司)。
-
人乳腺癌细胞系BT474、SK-BR-3(购自中国科学院细胞库并保存于本实验室)。
-
AKTA Avant 25蛋白纯化仪、Imager 600超灵敏多功能成像仪(美国Cytiva公司); Agilent 1200 series高效液相色谱仪(美国Agilent公司);Spark多功能酶标仪(瑞士TECAN); Intellicyt® iQue3 高通量流式细胞仪(德国赛多利斯)。
-
用含有曲妥珠单抗重链和轻链表达载体的质粒共转染Expi293F细胞7 d后收集培养上清液,用Protein A亲和层析法进行纯化。SEC-HPLC对抗体的纯度进行检测,并用流式细胞术检测曲妥珠单抗抗体与HER2过表达细胞株SK-BR-3、BT474的结合活性。
-
细胞按3×104个细胞/孔铺于V型底96孔板中,每孔30 μl。曲妥珠单抗按100 nmol/L的起始浓度,3倍比稀释,分成11个浓度梯度,末孔为PBS作为阴性对照,加入铺有细胞的96孔板中,每孔30 μl。曲妥珠单抗与细胞4℃共孵育1~2 h,用含0.1% BSA的PBS洗1遍,加入二抗Goat pAb to Human IgG,1∶200稀释,每孔30 μl,4℃孵育30 min。二抗孵育结束,用含0.1% BSA的PBS洗2遍,每孔加入30 μl 含0.1% BSA的PBS,用 Intellicyt® iQue3 高通量流式细胞仪进行检测。
-
采用含10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基培养SK-BR-3细胞,用含10%胎牛血清的RPMI-1640培养基培养BT474细胞,培养条件为5% CO2,37℃。当细胞密度达到80%~90%时进行传代,每周2~3次。取对数生长期的细胞进行实验。
-
将细胞按1×104个细胞/孔的数量接种于96孔板中,在37℃、5% CO2条件下培养24 h。每孔加入100 μl含设定浓度药物的培养基,培养48 h后,弃去孔内培养基,每孔加入100 μl含10%CCK8试剂的培养基,继续培养1~3 h,用酶标仪在450 nm测定光密度值(A),并计算细胞的增殖抑制率。增殖抑制率=(A对照−A实验)/(A对照−A背景)。联合给药组用CompuSyn软件计算CI值(药物联合指数),通过CI值的数值可以定量判断药物间相互作用的强度以及性质(CI>1为拮抗作用;CI=1为相加作用;CI<1为协同作用)。
-
根据分组将细胞按5×105个细胞/孔的数量接种于6孔板培养24 h。弃去原培养基,加入含设定浓度药物的培养基继续培养24 h。采用细胞裂解液试剂盒提取各组细胞总蛋白,用BCA试剂盒测定蛋白浓度。按每泳道30 μg蛋白样品的上样量进行聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳后,转移至PVDF膜。用5%脱脂奶粉在摇床上室温封闭1 h,加入一抗4 ℃孵育过夜,加入二抗室温孵育1 h。一抗、二抗均按照抗体使用说明书稀释。洗膜后,加ECL发光液,用超灵敏多功能成像仪进行显影,并用ImageJ软件对条带进行灰度值分析。目的蛋白相对表达量=目的蛋白灰度值/内参GAPDH灰度值 。
-
采用 GraphPad prism 8.0软件(Version X,USA)进行统计学分析和作图,用compuSyn软件计算联合指数。两组数据之间比较采用t检验,多组数据之间比较采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
-
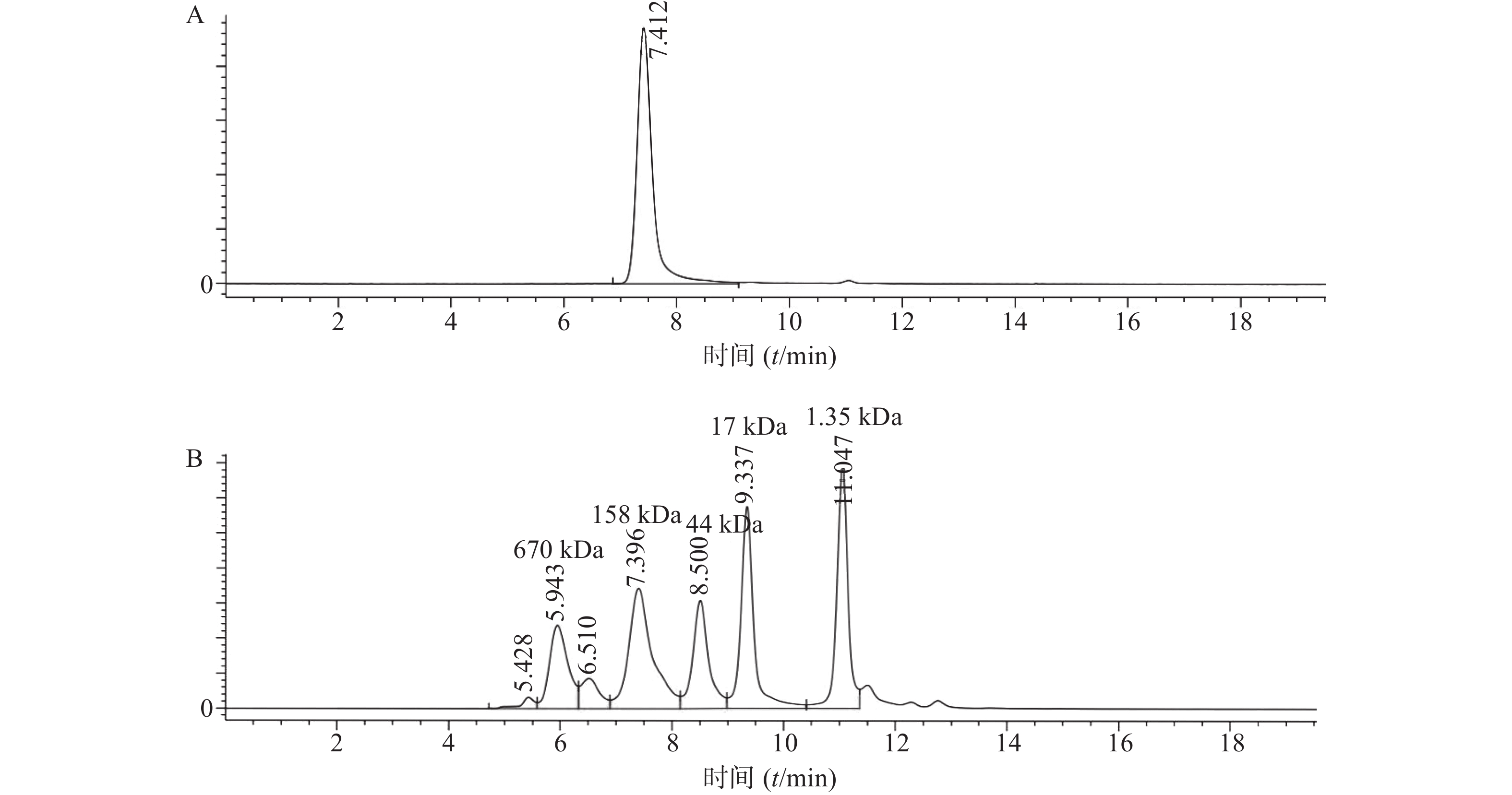
将表达纯化后的曲妥珠单抗用SEC-HPLC进行检测,结果显示曲妥珠单抗的纯度为100%,且分子量大小在150 kDa(1kDa=1×103)左右(图1)。
-
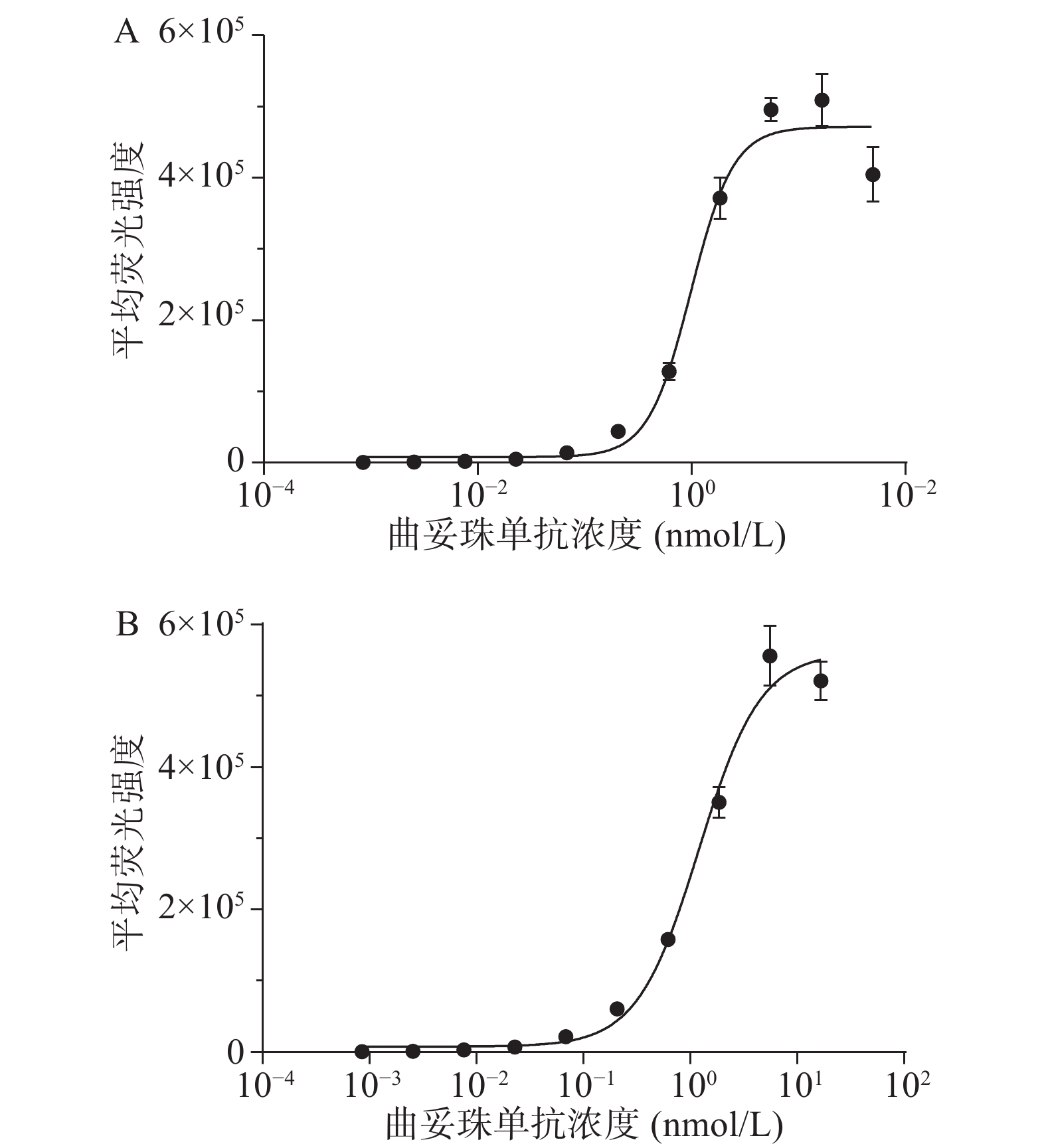
采用流式细胞术测定曲妥珠单抗与HER2过表达乳腺癌细胞株SK-BR-3和BT474的结合活性。结果显示,曲妥珠单抗以浓度依赖性的方式结合SK-BR-3和BT474细胞,其中,曲妥珠单抗与SK-BR-3细胞株结合的EC50值为1.128 nmol/L,与BT474细胞株结合的EC50值为1.203 nmol/L,两者EC50值大约一致(图2)。
-
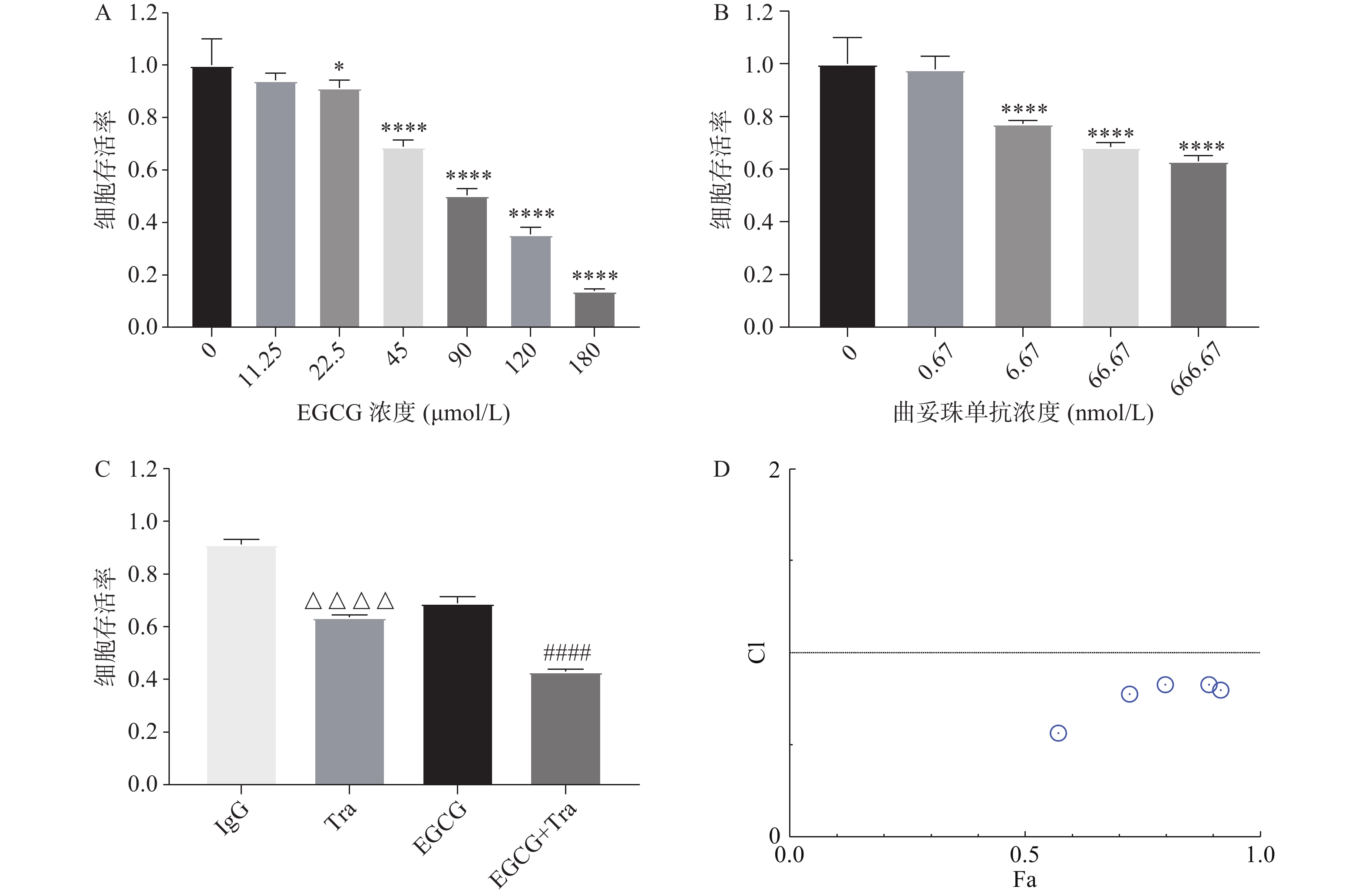
采用CCK8法测定EGCG单药、曲妥珠单抗单药及两者联合对BT474的增殖抑制作用。图3A和图3B结果显示, EGCG和曲妥珠单抗对BT474细胞均显示出浓度依赖性的增殖抑制作用。图3C结果显示EGCG和曲妥珠单抗联合给药组的增殖抑制作用显著强于单药组。图3D结果显示EGCG在一定浓度范围内(45~200 μmol/L)与16.67 nmol/L 曲妥珠单抗联用时显示有协同抗肿瘤作用(CI<1)。
-
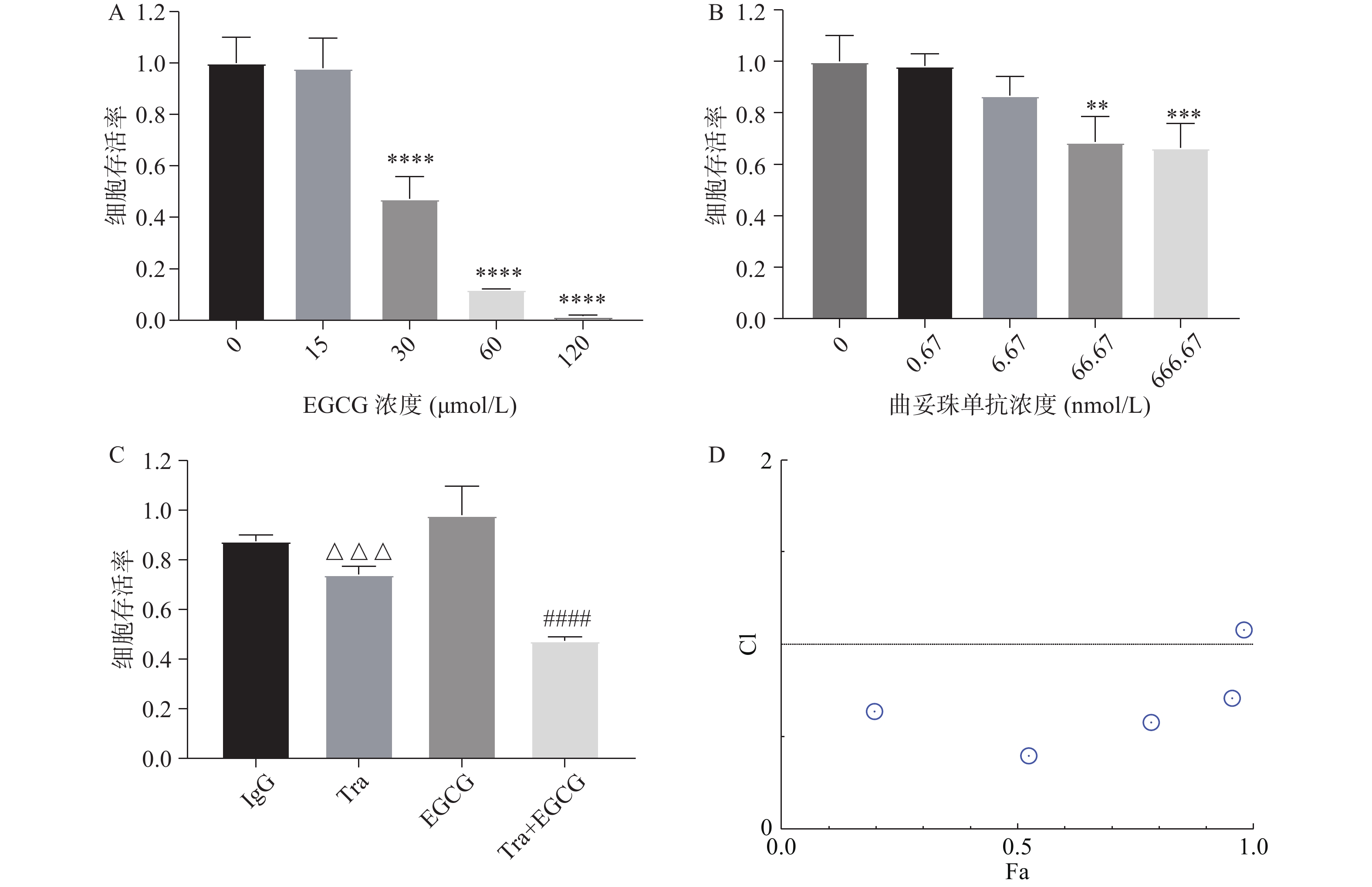
采用CCK8法测定EGCG单药、曲妥珠单抗单药及两者联合对SK-BR-3的增殖抑制作用。图4A和图4B结果显示,EGCG和曲妥珠单抗均对SK-BR-3细胞显示出浓度依赖性的增殖抑制作用。图4C结果显示,EGCG和曲妥珠单抗联合给药组的增殖抑制作用显著强于单药组。图4D结果显示,EGCG在一定浓度范围内(7.5~120 μmol/L)与16.67 nmol/L曲妥珠单抗联用时有协同抗肿瘤作用(CI<1)。
-
图5A-F结果显示,EGCG单药、曲妥珠单抗单药及两者联用组均能显著降低BT474细胞中p-Akt、p-MAPK、p-EGFR的表达。图5G-H结果显示,曲妥珠单抗单药组能显著降低BT474细胞p-HER2的表达,EGCG单药组虽然无显著性差异(P>0.05),但对p-HER2的表达有一定抑制作用。与EGCG和曲妥珠单抗单药组相比,EGCG与曲妥珠单抗联用可进一步显著降低BT474细胞p-Akt、p-MAPK、p-EGFR、p-HER2蛋白的表达。
-
ErbB-2(HER-2/neu)是一种分子量为1.85×105的穿膜受体络氨酸激酶,属于表皮生长因子受体家族[14]。该家族由4个紧密相关的络氨酸激酶(TK)受体组成:HER1(EGFR)、HER2、HER3和HER4。HER2主要是通过与家族中的其他成员形成同源或异源二聚体,激活下游的RAS/MAPK和磷脂酰肌醇-3/激酶(PI3K)/ATK信号通路,进而促进细胞增殖、迁移、血管生成以及抑制细胞的凋亡[15-16]。ERK/MAPK通路是参与细胞增殖控制的主要细胞内信号通路之一。 PI3K/ATK信号通路在控制Her-2/neu过表达细胞的生长和转化表型中起重要作用[17-18]。HER2过表达的癌症表现出较强的转移能力和浸润能力,对化疗敏感性差,且易复发。
曲妥珠单抗是一株靶向HER2的人源化单克隆抗体。1998年,被美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)批准应用于治疗HER2阳性的转移性乳腺癌[19]。曲妥珠单抗可能通过下调HER2受体在细胞膜上的表达,阻断HER2和HER3形成异源二聚体从而抑制下游通路,导致细胞周期阻滞,以及抗体依赖的细胞介导的细胞毒性活性[20]等。虽然曲妥珠单抗单药治疗起到了一定的效果, 但大部分HER2过表达的乳腺癌患者对曲妥珠单抗治疗不产生反应,初次治疗有效率大约在30%, 即使对曲妥珠单抗产生反应的患者也有约50%会在1年内发生耐药。
茶多酚可以抑制多种与细胞增殖和肿瘤进展相关的酶活性。EGCG是茶多酚中的主要成分之一。研究显示,在人A431表皮样癌细胞中,EGCG可能通过阻断EGF与其受体的结合进而抑制EGFR活性[21]。EGCG能抑制结肠癌细胞中EGFR、HER2、HER3的激活,并抑制细胞生长[22]。
为了进一步提高HER2靶向治疗疗效,在本研究中我们探讨了曲妥珠单抗和EGCG在乳腺癌细胞的联合抗肿瘤作用。实验结果发现EGCG与曲妥珠单抗在一定浓度范围内可以协同抑制HER2过表达乳腺癌细胞的生长,提示临床治疗中如果利用EGCG和曲妥珠单抗联合治疗则需重点关注两者各自的剂量。可以先利用乳腺癌荷瘤小鼠模型对不同剂量的EGCG和曲妥珠单抗的联合抗肿瘤作用进行评价,并参考动物体内药效实验的结果进行EGCG和曲妥珠单抗联合用药临床试验的设计,通过临床试验的结果确定临床治疗时最佳的联合用药剂量。
本研究还对EGCG和曲妥珠单抗的联合抗肿瘤作用机制进行了阐明:与EGCG和曲妥珠单抗单药组相比,EGCG与曲妥珠单抗联用可进一步显著降低BT474细胞中p-EGFR、p-HER2和p-Akt、p-MAPK的表达,提示EGCG和曲妥珠单抗联用对HER2过表达乳腺癌细胞的协同增殖抑制活性可能与其显著增强的对Akt和MAPK信号通路的抑制作用有关。本研究为EGCG与曲妥珠单抗的联合应用提供了理论支持,并为HER2过表达乳腺癌的治疗提供新的思路。
The effect and mechanism of epigallocatechol gallate combined with trastuzumab on the proliferation of HER2 overexpressing breast cancer cells
-
摘要:
目的 研究表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG)联合曲妥珠单抗对人表皮生长因子受体2(HER2)过表达乳腺癌细胞增殖的影响及其作用机制。 方法 表达纯化曲妥珠单抗;用CCK-8 细胞增殖检测试剂盒(CCK8)检测不同浓度EGCG、曲妥珠单抗及两药联用对HER2过表达乳腺癌细胞BT474、SK-BR-3的增殖抑制作用;用Western blot法检测EGCG、曲妥珠单抗及两药联用对BT474乳腺癌细胞中HER2,表皮生长因子受体(EGFR),丝裂原激活的蛋白激酶(MAPK)和蛋白激酶B(Akt)及它们的磷酸化蛋白的表达水平的影响。 结果 细胞增殖试验结果显示,EGCG、曲妥珠单抗以及二者联用均能有效抑制BT474和SK-BR-3细胞的增殖,且在一定浓度范围内,EGCG与曲妥珠单抗联用显示出协同增殖抑制作用。Western blot结果显示EGCG、曲妥珠单抗以及二者联合均能抑制BT474细胞中Akt,MAPK,EGFR,HER2的磷酸化蛋白表达,与单药相比,二者联合抑制作用显著增强,其差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 EGCG联合曲妥珠单抗能协同抑制HER2过表达乳腺癌细胞的增殖,其机制可能与Akt、MAPK信号通路有关。 -
关键词:
- 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 /
- 曲妥珠单抗 /
- 人表皮生长因子受体2过表达 /
- 乳腺癌 /
- 协同 /
- 增殖抑制
Abstract:Objective To study the effect and mechanism of epigallocatechol gallate (EGCG) combined with trastuzu-mab on the proliferation of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpressing breast cancer cells. Methods Trastuzumab was expressed and purified. The cell proliferation of HER2 overexpressing breast cancer cells BT474 and SK-BR-3 treated with trastuzumab, EGCG, or trastuzumab plus EGCG was evaluated by CCK8 assay. The effects of EGCG and trastuzumab on the expression of HER2, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), protein kinase B (Akt), and their phosphorylated proteins in BT474 breast cancer cells were detected by Western blot. Results The results of cell proliferation assay indicated that EGCG and trastuzumab, alone or in combination, effectively inhibited the proliferation of BT-474 and SK-BR-3 cells. And within a certain concentration range, EGCG and trastuzumab showed a synergistic proliferation inhibitory effect on HER2 overexpressing breast cancer cells. Consistent with these results, Western blot results showed that trastuzumab and EGCG, alone or in combination significantly reduced the phosphorylation levels of Akt, MAPK, EGFR, and HER2 in BT474 cells. Moreover, the inhibition effect of EGCG plus trastuzumab was significantly more potent than either EGCG or trastuzumab. Conclusion EGCG and trastuzumab could synergistically inhibit the proliferation of HER2 overexpressing breast cancer cells, which may be related to the regulation of Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. -
Key words:
- EGCG /
- trastuzumab /
- HER2 overexpression /
- breast cancer /
- synergy /
- proliferation inhibition
-
心房颤动(房颤)是最常见的心律失常之一。据统计,成年人房颤患病率在2%~4%,并且随着年龄的增长不断提高[1]。非瓣膜性心房颤动(NVAF)社区人群发病率为0.1%~4%、住院人群发病率为2.8%~14%[2],研究显示[3]70%以上的NVAF发生人群为65岁及以上老人,其发生率与年龄增加呈正相关。作为中风的独立危险因素,房颤可使包括中风在内的主要心血管事件风险增加5倍[4],因此,合理的抗凝可以降低老年人群中风及其他心血管事件的风险。
新型口服抗凝药达比加群酯可以直接抑制凝血酶,能够可逆性、竞争性地与凝血酶Ⅱa结合,阻止纤维蛋白原转化为纤维蛋白,从而抑制血小板聚集。达比加群酯口服吸收快,口服后有80%以原形通过肾脏排泄,其余经肝脏代谢,并且经P450酶系代谢的药物不会与其产生相互作用[5]。但是随着达比加群酯在临床上的广泛应用,其引起的出血等不良事件也越来越多,而老年人由于肝肾功能退化,成为了血栓和出血的高危人群[6-7],因此,对于达比加群酯在老年非瓣膜性房颤患者中安全性研究愈加重要。
1. 资料和方法
1.1 研究对象
收集2020年12月至2021年6月上海市第七人民医院门诊和住院的非瓣膜性房颤患者的临床资料,年龄65~80岁,在其他常规对症治疗基础上,选择达比加群酯胶囊抗凝治疗(110mg/片×10片/盒,勃林格殷格翰公司)。用法:110 mg,口服,每天2次(早、晚各1次),治疗6个月。
本方案经医院伦理委员会批准通过,所有入组患者及其家属对治疗方案均知情并签署知情同意书。
1.2 研究方法
纳入标准:①符合欧洲心脏病学会2010年《心房颤动管理指南》中非瓣膜性房颤的诊断标准;②心脏超声检查排除退行性瓣膜病及风湿性心脏病等瓣膜性心脏病;③既往未进行过规范化抗凝治疗,无抗凝禁忌证,血常规及凝血时间均在正常参考值范围内,尿便隐血阴性;④入选前6个月内未发生任何卒中。
排除标准:①急性冠状动脉综合征及冠状动脉介入术后1年、心包炎、心肌炎、甲状腺功能亢进症、严重肺部疾病、肝酶异常及肌酐清除率(Ccr)≤30ml/min者;②对本研究药物过敏或不能随访或中途更换抗凝药者。
1.2.1 实验室指标
入选患者于入院后24h内统一抽取静脉血送检。实验室观察指标:包括活化部分凝血活酶时间(APTT)、血浆凝血酶时间(TT)、纤维蛋白原(FIB)和D-二聚体(D-D);肝功能指标包括谷草转氨酶(AST)、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)、总胆红素(TBIL);肾功能指标包括尿素(UREA)和肾小球滤过率估计值(eGFR);血常规指标包括血红蛋白量(HGB)、红细胞沉降率(ESR)。观察服药1个月后、6个月后与治疗前相比的各项指标变化。
1.2.2 观察指标
根据指南要求在治疗前对所有研究对象进行血栓栓塞及出血风险评估。血栓栓塞风险采用CHA2DS2-VASc评分进行评价[8]:年龄65~74岁计1分,慢性心衰计1分,高血压计1分,年龄≥75岁计2分,糖尿病计1分,卒中/短暂性脑缺血发作计2分,血管病计1分,女性计1分。CHA2DS2-VASc≥2分的患者推荐使用口服抗凝药物(OAC);CHA2DS2-VASc为1分的患者口服OAC或阿司匹林,但更倾向OAC;CHA2DS2-VASc为0分可服用阿司匹林或者不进行抗栓治疗。出血风险评估采用HAS-BLED评分进行评价[9]:有未控制的高血压,即SPB>160mmHg计1分,肾功能异常(长期透析或肾移植或血清肌酐≥200μmol/L)或肝功能异常(慢性肝病或胆红素>2倍同时转氨酶>3倍)计1或2分,卒中计1分,既往出血史或出血体质、贫血等计1分,INR不稳定计1分,老年(即年龄>65岁)计1分,药物(同时应用抗血小板药和非甾体抗炎药)或酗酒计1分。HAS-BLED评分≥3分为出血高危组,启动OAC或阿司匹林治疗后均须密切随访。不良事件统计采用随访的方法,统计时长共计6个月,记录药物相关不良事件的发生率。
1.3 统计分析方法
采用SPSS 21.0软件进行数据分析,正态分布计量资料以(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )表示,组间比较采用单因素方差分析和t检验,以P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。2. 结果
2.1 入选病例基本资料
按照入选标准和排除标准共收集病例80例,男性45例,女性35例,年龄(76.0±0.8)岁,CHA2DS2-VASc评分(4.1±0.2),HAS-BLED评分(2.5±0.1),主要相关症状见表1。
表 1 80例心房颤动患者其他相关症状情况其他相关症状 病例数[n, (%)] 高血压 57(71.25) 糖尿病 22(27.50) 冠状动脉粥样硬化 49(61.25) 心律失常 33(41.25) 脑梗死 5(6.25) 高尿酸血症 1(1.25) 2.2 服药前后凝血指标变化
患者服药后1个月、6个月的APTT和TT分别与服药前比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);且服药6个月与服药1个月比较,差异亦有统计学意义(P<0.05)。FIB和D-D与服药前比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表2。
表 2 服用达比加群酯前后患者凝血指标变化(n=80,$ \bar x \pm s $ )组别 APTT(s) TT(s) FIB(g/L) D-D(mg/L) 服药前 34.37±0.59 19.98±0.45 3.17±0. 08 0.85±0.03 服药1个月 39.99±1.18* 75.30±7.38* 3.48±0.13 0.84±0.03 服药6个月 51.08±1.78*# 90.79±8.36*# 3.34±0.10 0.83±0.02 *P<0.05,与服药前比较;#P<0.05,与服药后1个月比较 2.3 服药前后肝功能指标变化
患者服药后1个月、6个月的ALT、AST、TBIL分别与服药前比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表3。
表 3 服用达比加群酯前后患者肝功能指标变化(n=80,$ \bar x \pm s $ )组别 ALT(U/L) AST(U/L) TBIL(µmol/L) 服药前 20.85±1.22 24.38±0.95 16.31±0.64 服药1个月 22.37±1.83 25.27±1.47 17.58±1.05 服药6个月 25.86±3.23 26.29±1.06 17.96±0.79 2.4 服药前后肾功能指标变化
患者服药后1个月、6个月的UREA、eGFR分别与服药前比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表4。
表 4 服用达比加群酯前后患者肾功能指标变化(n=80,$ \bar x \pm s $ )组别 UREA(mmol/L) eGFR[ml/(min·1.73m2)] 服药前 6.42±0.39 106.3±1.273 服药1个月 7.16±0.51 105.2±2.310 服药6个月 7.51±0.44 104.4±2.687 2.5 服药前后血常规指标变化
患者服药后1个月、6个月的HGB、ESR分别与服药前比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表5。
表 5 服用达比加群酯前后患者血液指标变化(n=80,$ \bar x \pm s $ )组别 HGB(g/L) ESR(mm/h) 服药前 138.20±1.96 17.38±1.36 服药1个月 143.20±3.22 19.90±2.05 服药6个月 146.30±3.76 20.94±2.00 2.6 服药后不良事件发生情况
患者服用达比加群酯后共发生25例不良事件,其中胸闷9例,牙龈出血10例,消化道出血1例,血栓形成3例,脑卒中2例,分别占全部病例的11.25%、12.5%、1.25%、3.75%和2.50%。
3. 讨论
2013年欧洲房颤指南[10]指出APTT谷值高于正常值上限2倍具有较高出血风险;Chin等[11]研究认为TT可作为服用达比加群酯治疗患者的监测指标,并可根据此指标的反馈来调节达比加群酯的剂量。另有研究显示[12],老年患者服用达比加群酯后,APTT和TT较用药前有所增加,达比加群酯剂量、患者肌酐清除率、合用P-gp抑制剂等均可影响APTT;但是不同个体间APTT波动较小,而TT个体间差异大,因此,可将APTT作为监测达比加群酯抗凝疗效的指标,TT作为抗凝疗效监测的补充指标。
纤维蛋白原(FIB)是凝血过程中的主要蛋白质,Lindahl等[13]研究认为FIB的影响因素较多,与达比加群酯的凝血活性并没有太大关系。本研究也显示该指标受达比加群酯的凝血活性影响不大,因此,可不考虑FIB的变化。
服用达比加群酯后1个月、6个月患者的凝血功能指标(APTT、TT)与服药前相比差异有统计学意义,且数值有升高趋势,提示达比加群酯可改变患者凝血功能,对预防和治疗老年非瓣膜性房颤患者血栓形成有效。通过研究发现,患者凝血功能指标在治疗6个月后与治疗1个月后相比,数值有升高的趋势。笔者分析可能原因有两方面:一是与患者用药依从性有关,同年轻人相比,老年人往往合并多种慢性疾病,因此需要同时服用多种药物,此时用药的依从性至关重要。兰博等[14]对老年人心血管用药现状调查发现,老年人使用降脂药的依从性与老年人的年龄及文化程度显著相关,其依从性仅为49. 2% ,原因主要为慢性病用药观念不强及初始治疗时忘记服药,随着时间的延长以及研究者推进,用药依从性逐渐好转,因此出现6个月后凝血功能指标数值升高的趋势;二是与抗凝药物的使用有关,根据实验结果,达比加群酯可改变老年患者APTT和TT水平[15-17]。
服药1个月、6个月后患者肝功能指标(ALT、AST、TBIL、D-D)、肾功能指标(UREA、eGFR)与服药前的差异无统计学意义,提示达比加群酯对肝肾功能无明显的毒性作用;服药1个月、6个月后患者血常规指标(HGB、ESR)在服药前后差异无统计学意义,提示达比加群酯对患者血红蛋白量、红细胞沉降率无显著影响。
患者服药后的不良事件主要表现为胸闷、 牙龈出血、 消化道出血 、血栓形成和脑卒中,并未发生严重出血和威胁生命或器官衰竭的出血。不良事件中较为严重的事件包括3例血栓形成和2例脑卒中发生,分析这5例患者发现,2例血栓形成患者均存在血脂控制不良现象,1例体重较大,考虑血栓形成与血脂控制不良和极端体重相关;2例脑卒中患者年龄分别为75岁和80岁,属高龄患者,考虑高龄患者肾功能减退,从而导致血药浓度增加[18]。近期国内外Meta分析[16-18]也显示达比加群酯出血事件少、使用安全。因此,基于目前的研究数据,可以认为达比加群酯对老年非瓣膜性房颤患者的安全性良好,适于老年患者使用。
-
图 3 EGCG单药组、曲妥珠单抗单药组及两者联用组对BT474细胞增殖的影响
注:A.EGCG对BT474细胞增殖的影响;B.曲妥珠单抗对BT474细胞增殖的影响;C.16.67 nmol/L曲妥珠单抗、16.67 nmol/L IgG 曲妥珠单抗同型对照、45 μmol/L EGCG、16.67 nmol/L曲妥珠单抗与45 μmol/L EGCG联用对BT474细胞增殖的影响;D.16.67 nmol/L曲妥珠单抗联合不同浓度EGCG对BT474细胞增殖的影响,计算联合指数(CI),Fa表示效应值;*P<0.05,****P<0.0001,与空白组比较;△△△△P<0.0001,与IgG组比较;####P<0.0001,与曲妥珠单抗组比较
图 4 EGCG单药组、曲妥珠单抗单药组及两者联用组对SK-BR-3细胞增殖的影响
注:A.EGCG对SK-BR-3细胞增殖的影响;B. 曲妥珠单抗对SK-BR-3细胞增殖的影响;C. 16.67 nmol/L 曲妥珠单抗、16.67 nmol/L IgG 曲妥珠单抗同型对照、15 μmol/L EGCG、16.67 nmol/L曲妥珠单抗与15 μmol/L EGCG联用对SK-BR-3细胞增殖的影响;D. 16.67 nmol/L曲妥珠单抗联合不同浓度EGCG对SK-BR-3细胞增殖的影响,计算联合指数(CI),Fa表示效应值;**P<0.01,***P<0.001,与空白组比较;△△△P<0.001,与IgG组比较;####P<0.0001,与曲妥珠单抗组比较
图 5 EGCG单药组、曲妥珠单抗单药组及两者联用组对BT474细胞中MAPK、Akt、EGFR、HER2及其磷酸化蛋白的表达的影响
注:A. p-Akt、Akt的蛋白表达水平;B. p-Akt、Akt的相对蛋白表达量;C. p-MAPK、MAPK的蛋白表达水平;D. p-MAPK、MAPK的相对蛋白表达量;E. p-EGFR、EGFR的蛋白表达水平;F. p-EGFR、EGFR的相对蛋白表达量;G. p-HER2、HER2的蛋白表达水平;H. p-HER2、HER2的相对蛋白表达量;****P<0.0001,与对照组比较;##P<0.01、###P<0.001、 ####P<0.0001,与曲妥珠单抗组比较
-
[1] FERLAY J, COLOMBET M, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: an overview[J]. Int J Cancer,2021:ijc.33588. [2] LOIBL S, GIANNI L. HER2-positive breast cancer[J]. Lancet,2017,389(10087):2415-2429. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32417-5 [3] VOGEL C L, COBLEIGH M A, TRIPATHY D, et al. Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab as a single agent in first-line treatment of HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol,2002,20(3):719-726. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.20.3.719 [4] LUO H, VONG C T, CHEN H, et al. Naturally occurring anti-cancer compounds: shining from Chinese herbal medicine[J]. Chin Med,2019,14:48. doi: 10.1186/s13020-019-0270-9 [5] NI J, GUO X H, WANG H, et al. Differences in the effects of EGCG on chromosomal stability and cell growth between normal and colon cancer cells[J]. Molecules,2018,23(4):788. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040788 [6] FLORES-PÉREZ A, MARCHAT L A, SÁNCHEZ L L, et al. Differential proteomic analysis reveals that EGCG inhibits HDGF and activates apoptosis to increase the sensitivity of non-small cells lung cancer to chemotherapy[J]. Prot Clin Appl,2016,10(2):172-182. doi: 10.1002/prca.201500008 [7] TUDORAN O, SORITAU O, BALACESCU O, et al. Early transcriptional pattern of angiogenesis induced by EGCG treatment in cervical tumour cells[J]. J Cell Mol Med,2012,16(3):520-530. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01346.x [8] DENG Y T, LIN J K. EGCG inhibits the invasion of highly invasive CL1-5 lung cancer cells through suppressing MMP-2 expression via JNK signaling and induces G2/M arrest[J]. J Agric Food Chem,2011,59(24):13318-13327. doi: 10.1021/jf204149c [9] ZHANG J, LEI Z, HUANG Z, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate(EGCG) suppresses melanoma cell growth and metastasis by targeting TRAF6 activity[J]. Oncotarget,2016,7(48):79557-79571. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12836 [10] MANJEGOWDA M C, DEB G, KUMAR N, et al. Expression profiling of genes modulated by estrogen, EGCG or both in MCF-7 breast cancer cells[J]. Genom Data,2015,5:210-212. doi: 10.1016/j.gdata.2015.05.040 [11] DETTLAFF K, STAWNY M, OGRODOWCZYK M, et al. Formulation and characterization of EGCG for the treatment of superficial bladder cancer[J]. Int J Mol Med,2017,40(2):329-336. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3024 [12] BORUTINSKAITĖ V, VIRKŠAITĖ A, GUDELYTĖ G, et al. Green tea polyphenol EGCG causes anti-cancerous epigenetic modulations in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells[J]. Leuk Lymphoma,2018,59(2):469-478. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1339881 [13] YANG C G, DU W F, YANG D G. Inhibition of green tea polyphenol EGCG((–)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate) on the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by suppressing canonical wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway[J]. Int J Food Sci Nutr,2016,67(7):818-827. doi: 10.1080/09637486.2016.1198892 [14] KLOS K S, ZHOU X, LEE S, et al. Combined trastuzumab and paclitaxel treatment better inhibits ErbB-2-mediated angiogenesis in breast carcinoma through a more effective inhibition of Akt than either treatment alone[J]. Cancer,2003,98(7):1377-1385. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11656 [15] CITRI A, YARDEN Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2006,7(7):505-516. [16] ZHANG H, BEREZOV A, WANG Q, et al. ErbB receptors: from oncogenes to targeted cancer therapies[J]. J Clin Invest,2007,117(8):2051-2058. doi: 10.1172/JCI32278 [17] IGNATOSKI K M, MAEHAMA T, MARKWART S M, et al. ERBB-2 overexpression confers PI 3' kinase-dependent invasion capacity on human mammary epithelial cells[J]. Br J Cancer,2000,82(3):666-674. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.1999.0979 [18] PIANETTI S, ARSURA M, ROMIEU-MOUREZ R, et al. Her-2/neu overexpression induces NF-κB via a PI3-kinase/Akt pathway involving calpain-mediated degradation of IκB-α that can be inhibited by the tumor suppressor PTEN[J]. Oncogene,2001,20(11):1287-1299. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204257 [19] YAKES F M, CHINRATANALAB W, RITTER C A, et al. Herceptin-induced inhibition of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and Akt Is required for antibody-mediated effects on p27, cyclin D1, and antitumor action[J]. Cancer Res,2002,62(14):4132-4141. [20] SPECTOR N L, BLACKWELL K L. Understanding the mechanisms behind trastuzumab therapy for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol,2009,27(34):5838-5847. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.1507 [21] LIANG Y C, LIN-SHIAU S Y, CHEN C F, et al. Suppression of extracellular signals and cell proliferation through EGF receptor binding by (–)-epigallocatechin gallate in human A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells[J]. J Cell Biochem,1997,67(1):55-65. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19971001)67:1<55::AID-JCB6>3.0.CO;2-V [22] SHIMIZU M, DEGUCHI A, JOE A K, et al. EGCG inhibits activation of HER3 and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human colon cancer cells[J]. J Exp Ther Oncol,2005,5(1):69-78. 期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)
-






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载: