-
2型糖尿病(T2DM)是一种以高血糖为特征的慢性代谢性疾病,主要是由于胰岛素分泌不足而导致的空腹血糖升高[1]。冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病(CHD,简称冠心病)是一种常见的心血管疾病,主要是由于冠状动脉的粥样性硬化引起的血管阻塞或管腔狭窄,从而导致心肌缺血或缺氧性坏死,进而影响心脏功能[2]。近年来,T2DM的患病人数不断增加。据相关不完全统计,预计到2045年,全球T2DM患病人数将增加至7.83亿,已成为全球关注的重要人类问题之一[3]。目前,我国60岁以上的老年人中T2DM患病率超过20%,其中心血管疾病是最常见的并发症,而CHD则是T2DM患者最常见的致残或致死原因[4, 5]。有研究表明,T2DM患者发生心血管疾病的概率是非T2DM人群的2~4倍,葡萄糖耐受量受损是影响CHD进展的重要因素[6]。由此可见,T2DM与CHD相互影响,相互促进。
中药复方制剂麝香保心丸源于宋代《太平惠民和剂局方》中治疗“寒闭证”的经典名方苏合香丸,由戴瑞鸿教授在1972年改良而来。麝香保心丸已在临床应用40余年,方中麝香通窍温阳、活血化瘀为君药;苏合香辟秽通窍、人参扶正益气为臣药;牛黄开窍醒神、肉桂助阳通脉、蟾酥开窍止痛为佐药;冰片开窍醒神为使药。全方寒温并用、通补兼施、益气强心,主要用于治疗气滞血瘀所致的胸痹,症见心前区疼痛固定不移,心肌缺血所致的心绞痛、心肌梗死等[7-9]。目前临床上将麝香保心丸与基础西药中的降糖药联合应用,表现出比单用降糖药更好的血糖调节效果[10],还可以降低患者血清胆固醇水平[11],显著降低心血管事件发生率[12]。但目前关于麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD共同作用机制的研究相对不足。本研究旨在通过运用网络药理学方法,探索麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的共同作用机制,为今后的研究和应用提供理论依据。
-
运用中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP)、中药成分数据库(TCMID)、中医药百科全书数据库(ETCM)和BATMAN-TCM数据库,以“人工麝香、人参提取物、人工牛黄、苏合香、蟾酥、肉桂、冰片”为关键词,检索麝香保心丸的化学成分。将口服生物利用度(OB)≥20%、类药性(DL)≥0.1,同时文献报道具有确切活性的化合物,以及本课题组前期研究鉴定的入血成分,均视为麝香保心丸的活性化合物。取BATMAN-TCM中score≥48、TCMID中score≥400、ETCM中score≥0.8的靶点,同时将仅有1个成分对应的靶点去除,筛选得到麝香保心丸的潜在作用靶点,然后通过Uniprot数据库规范靶点蛋白的基因名。
-
在DisGeNET数据库和GeneCards数据库中以“type 2 diabetes mellitus”和“coronary heart disease”为关键词筛选出T2DM和CHD的相关靶点,为获得与疾病相关度更高的靶点,将GeneCards数据库中score≤10的靶点去除。
-
绘制麝香保心丸组方中筛选出的化合物靶点、T2DM相关靶点和CHD相关靶点的Venn图,取三者交集,得到麝香保心丸同时治疗T2DM和CHD的潜在作用靶点。
-
运用Cytoscape 3.8.2软件构建麝香保心丸发挥“异病同治”作用的“药物-成分-靶点”网络图,运用“Network Analyzer”功能进行分析,其中节点代表药物、成分、靶点,边代表药物与成分、成分与靶点之间的关系。
-
运用STRING数据库,导入“药物-疾病”交集靶点,物种限制为“人”,构建PPI网络图,然后将STRING数据库得到的数据导入Cytoscape 3.8.2软件进行网络分析,依据度值筛选出核心靶点。
-
运用DAVID在线数据库导入交集靶点进行GO功能富集分析和KEGG通路富集分析,研究麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD可能靶点的潜在关键生物学过程和相关通路。
-
通过TCMSP、TCMID、ETCM和BATMAN-TCM数据库共检索得到2 535个化学成分,以OB≥20%、DL≥0.1,文献报道具有确切活性的化合物,以及本课题组前期研究鉴定的入血成分,并以BATMAN-TCM中取score≥48;TCMID中取score≥400;ETCM中取score≥0.8,同时将仅有1个成分对应的潜在靶点去除为标准,共筛选出七味中药的108个活性成分,对应451个靶点。
-
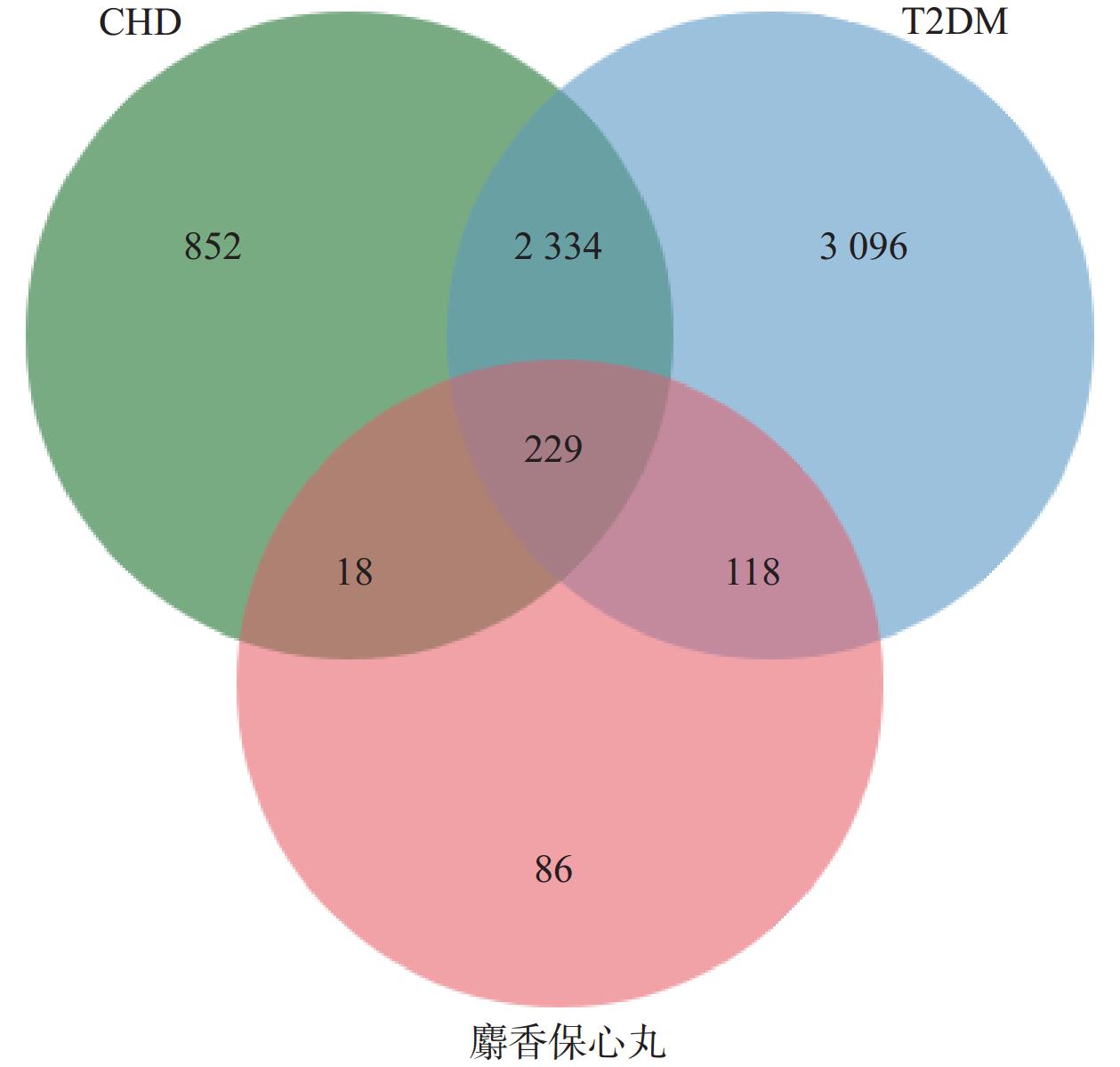
在DisGeNET和GeneCards数据库中共检索筛选得到T2DM相关靶点5 777个,CHD相关靶点3 433个。利用Venn图将麝香保心丸预测筛选出的活性成分潜在靶点与疾病靶点作交集,得到麝香保心丸作用于T2DM和CHD的潜在共同靶点229个(图1)。
-
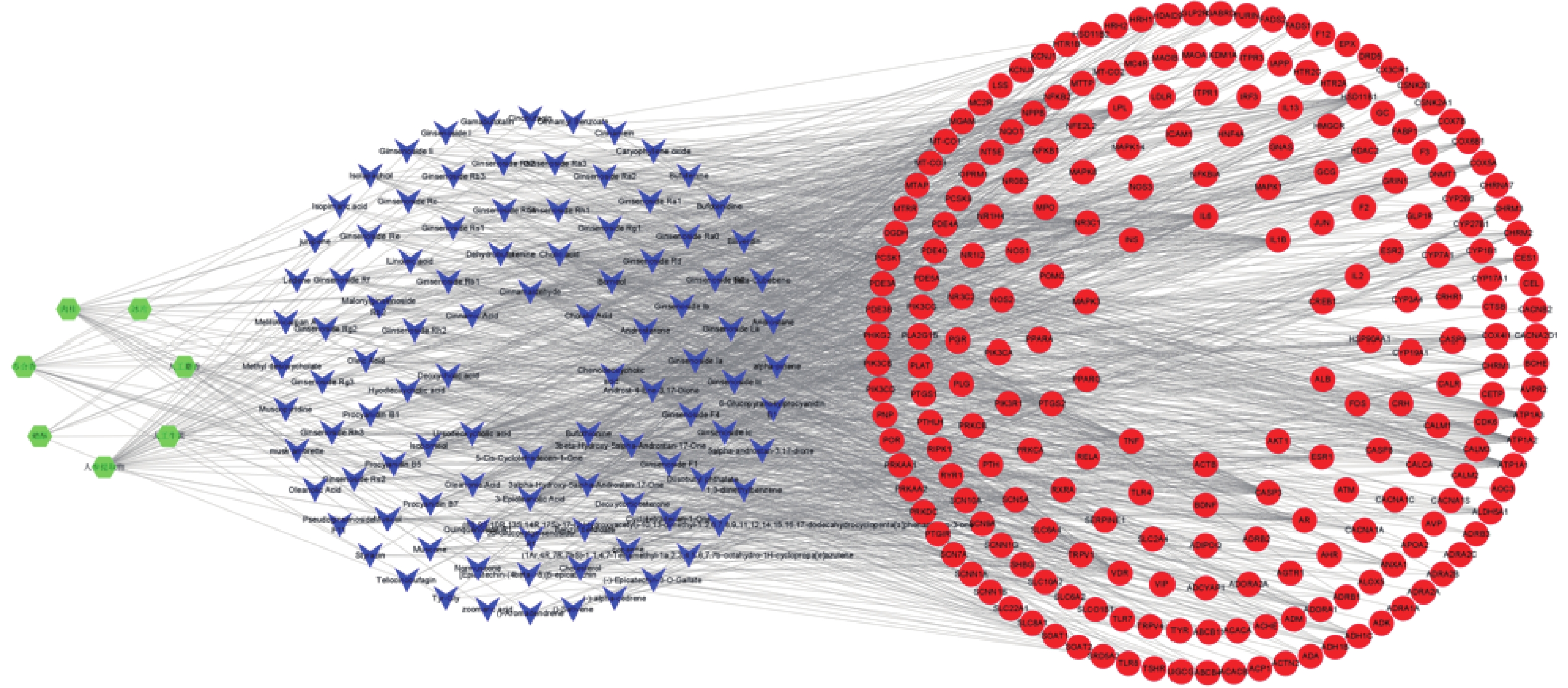
运用Cytoscape 3.8.2软件构建“药物-成分-靶点”网络图,网络中共有337个节点,其中药物7个、活性成分101个、靶点229个。其中绿色代表麝香保心丸组方中的7味中药,蓝色代表活性成分,红色代表作用于疾病的靶点。根据度值大小筛选贡献较大的活性成分,其中鹅去氧胆酸、熊去氧胆酸、肉桂醛、胆汁酸、人参皂苷Rh2、人参皂苷Rb1、肉桂酸等活性成分排名靠前,可能是麝香保心丸发挥治疗T2DM和CHD作用的主要贡献成分(图2)。
-
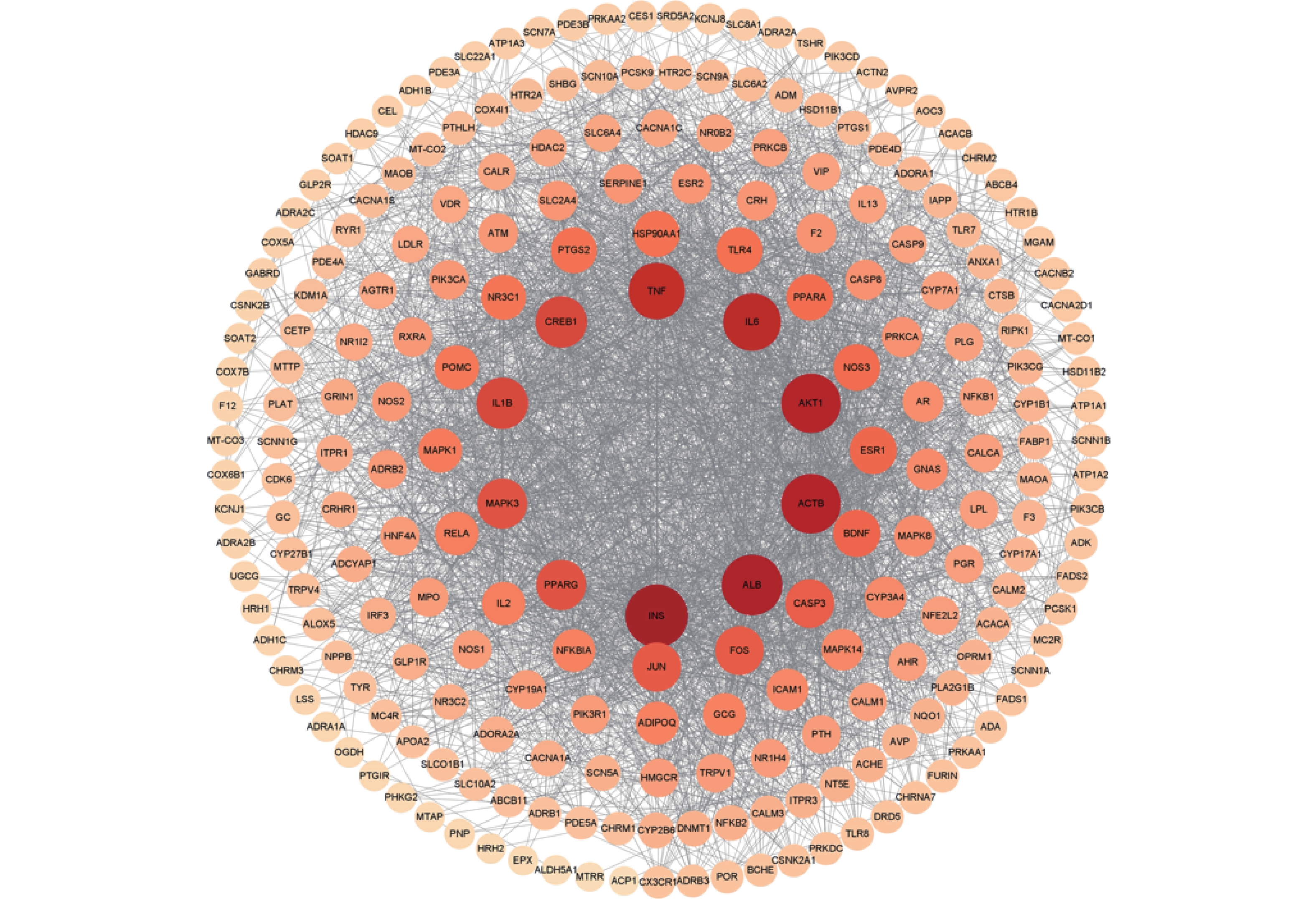
将麝香保心丸229个交集靶点导入STRING数据库中,并利用Cytoscape 3.8.2软件对PPI图进行可视化分析(图3)。根据度值由大到小对节点进行筛选,选取排名前10的潜在核心靶点,分别是胰岛素(INS)、白蛋白(ALB)、蛋白激酶B(Akt1)、白介素-6(IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)、环腺苷酸反应元件结合蛋白1(CREB1)、白细胞介素-1(IL-1β)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶3(MAPK3)、过氧化物酶体增生激活受体γ(PPARG),这些靶点可能是麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD的关键核心靶点。
-
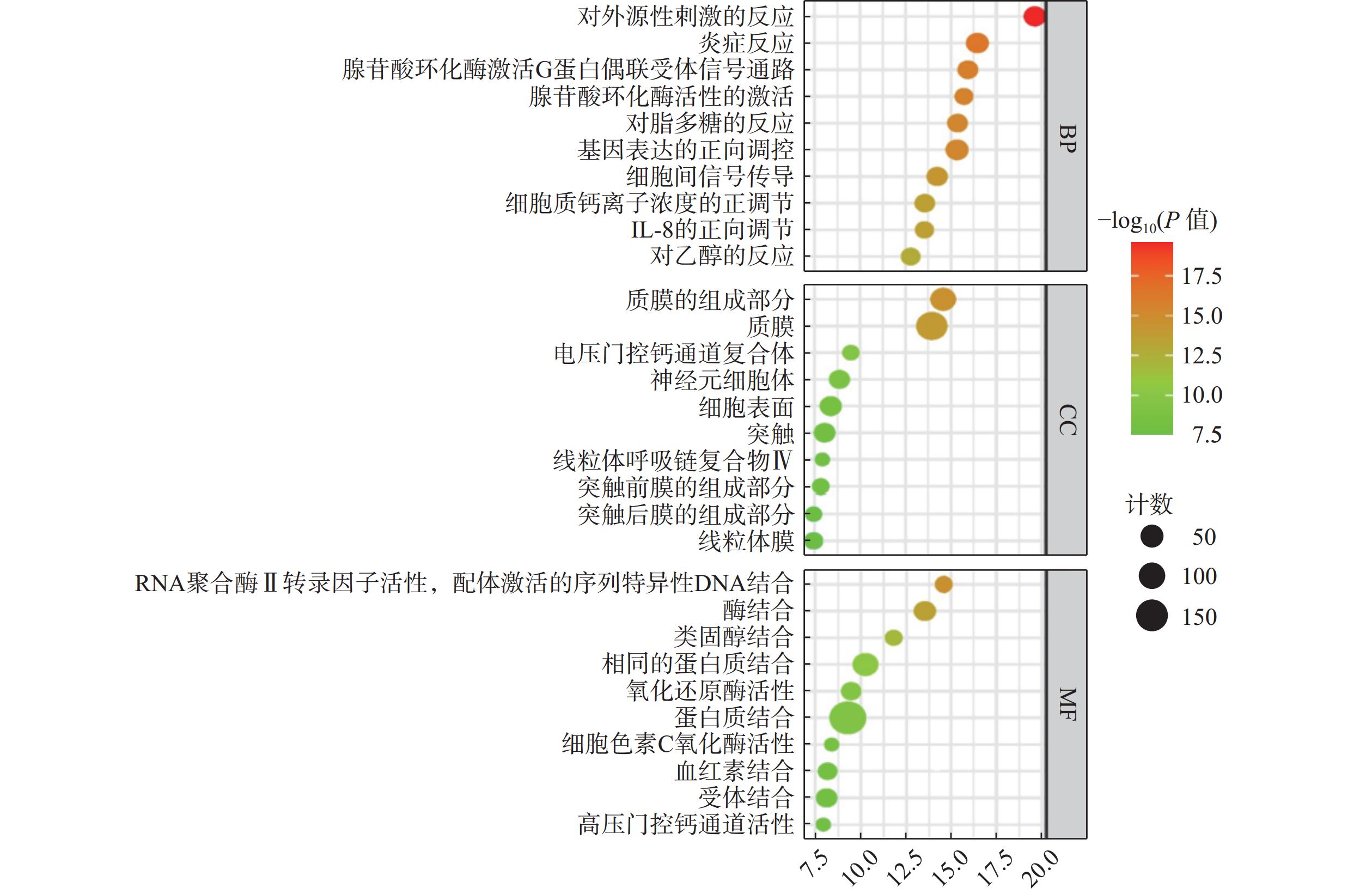
将麝香保心丸229个交集靶点导入DAVID在线数据库进行GO功能富集分析,以P≤0.05为筛选标准,共筛选出生物过程(BP)724条、细胞成分(CC)112条、分子功能(MF)208条,分别选取前10条绘制气泡图(图4)。BP主要涉及对外源性刺激的反应、炎症反应、基因表达的正调控等过程;CC主要涉及质膜、电压门控钙通道复合物、神经元细胞体等过程;MF主要涉及RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录因子活性、配体激活序列特异性DNA结合、类固醇结合、氧化还原酶活性等过程。
-
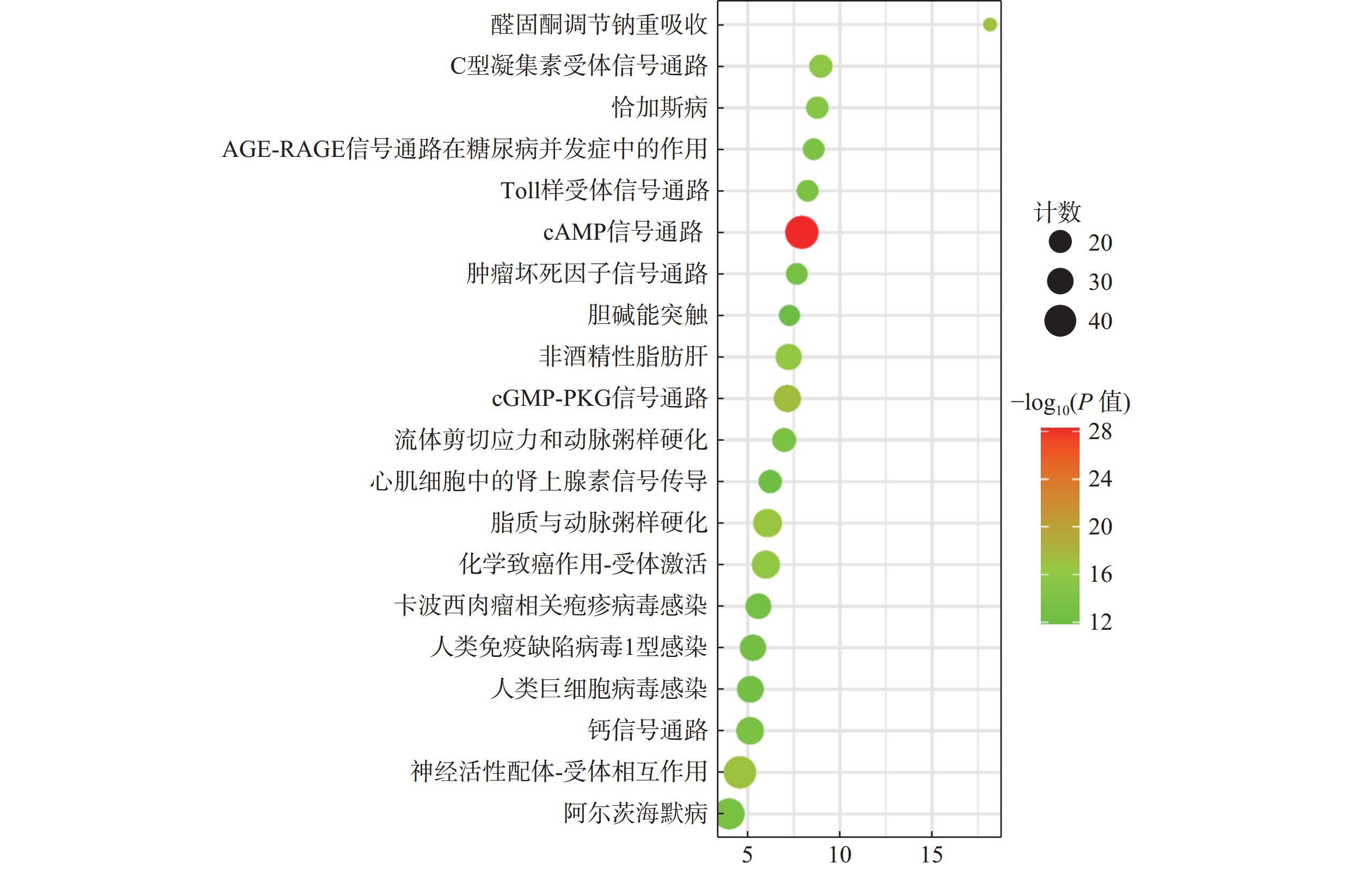
通过KEGG通路富集分析229个交集靶点,以P≤0.05为筛选标准,共得到麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD的188条信号通路,选取排名前20的绘制气泡图(图5)。cAMP信号通路、cGMP-PKG信号通路、糖尿病并发症中的AGE-RAGE信号通路、Toll样受体信号通路、TNF信号通路、钙信号传导通路等可能在麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD中发挥重要作用。
-
中医将以多饮、多食、多尿、身体消瘦为主要特征的T2DM归结为“消渴症”范畴,以气阴两虚和阴虚内热为主要病机[13]。CHD以气虚血瘀为主要病机,虚证多以阳虚、气虚、气阴两虚为主,实证多以气滞血瘀、痰凝寒浊为主[14]。中药复方制剂麝香保心丸作为中医经典名方“苏合香丸”的发展延续,是我国目前最常用的芳香温通类药物,为益气活血剂,临床上广泛应用于治疗心血管疾病[15]。由于T2DM与CHD均有“气阴两虚”表型,故现临床上将麝香保心丸用于治疗T2DM比单用西药进行基础治疗表现出更好的控制血糖、促进心功能恢复、改善糖尿病患者微循环障碍、降低血液粘度等作用[15, 16]。虽然麝香保心丸在治疗T2DM和CHD方面具有良好的临床疗效,但其“异病同治”的作用机制尚不明确。本研究主要运用网络药理学方法,探讨麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的潜在作用机制。
本研究运用网络药理学分析方法共筛选得到麝香保心丸的101个活性成分和“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的共同靶点229个。其中人参总皂苷提取物是麝香保心丸的臣药,文献报道其具有抑制IL-1β等炎性因子的表达[17],调节线粒体能量代谢和糖脂代谢,改善胰岛素抵抗、抑制心肌细胞凋亡[18]的作用,人参皂苷Rg1、Rb1可通过抑制IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α等炎症因子的表达,减轻肝脏损伤和胰岛素抵抗[19] ,缓解心肌损伤[20]。已有研究表明,肉桂提取物可以减少氧化应激,保护胰岛β细胞,增加胰岛素分泌[21],改善血脂异常[22],减轻糖尿病心肌并发症症状。肉桂中的有效成分肉桂醛[23]可通过自噬途径减轻缺氧复氧导致的H9C2心肌细胞的损伤,抑制自噬水平,增强心肌细胞活力。肉桂酸[24]则能通过激活PI3K/Akt/FoxO1信号通路,降低db/db小鼠空腹血糖水平、调节血脂、改善胰岛素抵抗。牛黄中的有效成分熊去氧胆酸可增加肝脏能量消耗、改善线粒体功能和胆汁酸代谢,减少甘油三酯(TG)和FFA,改善糖脂代谢[25]。由此可见,麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD可能是其多个活性成分共同发挥作用的结果。
绘制PPI网络图,根据度值分析得到排名前10的核心靶点,INS、ALB、Akt1、IL-6、TNF、CREB1、IL-1β、MAPK3、PPAGR、ACTB是麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的潜在核心靶点。研究表明,促炎细胞因子和炎症相关核转录因子与胰岛素分泌受损有关,可能会诱导T2DM的发生[26],例如,IL-6被认为可能与胰岛素抵抗和β细胞功能障碍有关[27]。此外,有研究表明,在血管生物学中,IL-6还可能与动脉粥样硬化形成相关的成纤维细胞和内皮细胞分泌有关[28]。因此,抑制IL-6炎症因子的激活能有效改善胰岛素抵抗,缓解动脉粥样硬化。有研究表明,PPARG(即PPARγ)是一种过氧化物酶体增殖受体,是配体激活受体,参与能量稳态调节,其在脂肪组织、脾脏和大肠中的表达最高,主要表现为调节脂肪生成、脂质和葡萄糖代谢以及炎症途径,因此,激活PPARG受体不仅可以改善胰岛素敏感性,还可以调节血管生成[29]。ACTB是一种β-肌动蛋白,是重要的细胞骨架蛋白,可以通过调节内皮NO合酶活性改变NO产生,从而导致内皮功能障碍,这被认为可能是导致CHD的潜在作用机制[30]。同时有研究表明,ACTB是与T2DM风险有关的一种可靠的基因蛋白[31]。由此可见,麝香保心丸通过作用于多个靶点发挥“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的治疗作用。
GO生物功能分析发现,麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的潜在调控生物过程,主要涉及炎症反应、基因表达的正调控、对脂多糖的反应、酶结合、蛋白质结合、受体结合、电压门控钙通道复合物等生物过程。KEGG通路富集分析发现,麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD的通路主要富集在脂质与动脉粥样硬化、糖尿病并发症中的AGE-RAGE信号通路、TNF信号通路、Toll样受体信号通路、cGMP-PKG信号通路等信号通路。晚期糖基化终产物(AGEs)是游离还原性糖和蛋白质、脂质、核酸之间非酶促糖化反应的结果,主要发生于持续高血糖状态的患者体内,属于有害分子,AGEs会与其晚期糖基化终产物受体(RAGE)发生非特异性作用[32],产生氧化应激,导致促炎细胞因子产生和炎症反应,从而干扰细胞内信号,导致胰岛素抵抗[33]。有研究表明,AGE水平升高与动脉壁硬度增加、冠状动脉疾病等心血管风险有关,与T2DM患者冠状动脉粥样硬化的严重程度和心血管事件的发生有关,这主要是因为AGE诱导的血管和心肌蛋白交联会降低血管弹性和心肌灵活性,导致血管壁柔韧性降低,血管和心肌僵硬以及影响细胞内皮功能,最终导致CHD[34]。Toll样受体(TLRs)属于炎症小体,主要有2个亚型:①在其外域中具有多个半胱氨酸簇的TLR(mccTLRs);②在其外域中具有单个半胱氨酸簇的TLR(sccTLRs)[35]。动脉粥样硬化主要是由慢性炎症引起的血管壁结构和功能异常,TLR信号通路的激活参与动脉粥样硬化的炎症过程,其中TLR2和TLR4在动脉硬化过程中上调使CHD进一步加剧[36]。胰岛素抵抗是T2DM的主要症状之一,起因之一是肥胖,脂肪组织分泌各种激素和细胞因子,在代谢应激的作用下,TLR4信号传导的激活会引起免疫细胞释放促炎因子,使脂肪组织中的巨噬细胞聚集极化为M1和M2亚型,导致慢性低度炎症,干扰代谢组织中的胰岛素信号传导,进而发展成T2DM[37]。cAMP是一种单磷酸腺苷,由腺嘌呤、核糖以及磷酸基团组成,是细胞内的第二信使分子。cAMP信号通路主要包括cAMP合成环化酶、降解磷酸二酯酶(PDE)和cAMP效应,主要来源是细胞质膜上的跨膜腺苷酸环化酶(tmACs)和细胞内的可溶性腺苷酸环化酶(sAC),负责激素诱导的肝糖原分解[38],可刺激胰岛素分泌,是胰岛素依赖性cAMP信号通路[39]。蛋白激酶A(PKA)是主要的cAMP效应靶标,cAMP水平升高和PKA激活可调节内皮屏障稳态,促进血管舒张[40]。上述分析结果表明,麝香保心丸发挥治疗T2DM和CHD的作用是方中的多种化学成分作用于多个信号通路的结果,主要涉及氧化应激和炎症反应。
-
“异病同治”治疗思想是中医对《黄帝内经》“同病异治”传统理论的继承与发展,目前临床应用广泛,但相关作用机制尚不明确[41]。本文运用网络药理学方法研究发现,麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的靶点和信号通路主要涉及炎症反应和氧化应激,与目前关于T2DM和CHD的相关作用机制研究相符,证实麝香保心丸通过多成分、多靶点、多通路发挥治疗T2DM和CHD的共同作用。研究结果为麝香保心丸的临床应用及进一步实验验证研究提供了理论依据。
Mechanisms of Shexiang Baoxin Pill in homo-therapy for heteropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease based on network pharmacology
-
摘要:
目的 基于网络药理学方法研究麝香保心丸“异病同治”2型糖尿病(T2DM)和冠心病(CHD)的作用机制。 方法 运用中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP)、中药成分数据库(TCMID)、中医药百科全书数据库(ETCM)和BATMAN-TCM数据库筛选麝香保心丸中七味中药的化学成分和作用靶点,利用DisGeNET和GeneCards数据库获取与CHD和T2DM相关的疾病靶点。运用Cytoscape3.8.2软件构建“药物-成分-靶点”网络图,利用STRING数据库构建蛋白互作(PPI)网络图,利用DAVID在线数据库对麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD的共同作用靶点进行GO生物过程分析和KEGG通路富集分析。 结果 共筛选出麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD的潜在活性成分101个,对应229个靶点。网络分析结果表明,麝香保心丸治疗T2DM和CHD的共同主要成分可能是鹅去氧胆酸、熊去氧胆酸、肉桂醛、胆汁酸、肉桂酸及人参皂苷类成分。通路富集分析结果显示,麝香保心丸“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的作用机制可能与抑制炎症反应和氧化应激有关。 结论 麝香保心丸可通过多成分、多靶点、多途径发挥“异病同治”T2DM和CHD的作用,为麝香保心丸的临床应用及进一步研究提供理论基础。 Abstract:Objective To probe into the mechanism of Shexiang Baoxin Pill in homo-therapy for heteropathy for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and coronary heart disease (CHD) based on network pharmacology. Methods All chemical components and action targets of these seven traditional Chinese medical in Shexiang Baoxin Pill were screened by Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP), Traditional Chinese Medicines Integrated Database (TCMID), The Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine (ETCM) and BATMAN-TCM platform, and the DisGeNET and GeneCards databases were used to obtain CHD and T2DM-related Disease targets. The “drug-component-target” network map was constructed by Cytoscape 3.8.2 software, the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network map was constructed by STRING database, and the GO biological process analysis and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis were performed on the common targets of Shexiang Baoxin Pill for T2DM and CHD using DAVID online database. Results A total of 101 potential active ingredients for the treatment of T2DM and CHD in Shexiang Baoxin Pill were screened out, corresponding to 229 targets. Network analysis results showed that the common main active ingredients in Shexiang Baoxin Pill for treating T2DM and CHD might be chenodeoxycholic acid, ursodeoxycholic acid, cinnamic aldehyde, bile acids, cinnamic acid, and ginsenosides. The results of pathway enrichment analysis showed that the mechanism of action of Shexiang Baoxin Pill in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and coronary heart disease in treating T2DM and CHD might be related to the inhibition of inflammatory response and oxidative stress. Conclusion Shexiang Baoxin Pill could play a role in treating CHD and T2DM through multiple components, multiple targets and multiple pathways, which provided a certain theoretical basis for the clinical application and further research of Shexiang Baoxin Pill. -
山楂为蔷薇科植物山里红Crataegus pinnatifida Bge. var. major N. E. Br. 或山楂 Crataegus pinnati- fida Bge. 的干燥成熟果实,焦山楂为其炒制品[1]。现代药理研究证明,焦山楂抑菌作用强于生山楂,而某些特定菌群与消化功能密切相关[2]。而山楂炒焦后产生新的物质—类黑素,类黑素是在食品热处理过程中形成的。目前,类黑素的抗菌活性已得到证实。大多数类黑素对微生物作用的研究都是在特定的微生物生长培养基中进行的,这些研究表明类黑素可以刺激微生物生长[3],也可以抑制微生物生长[4-5]。肠道菌群与人体健康密切相关,药物和功能食品可能通过调节肠道微生物来改善胃肠功能,帮助消化[6-7]。双歧杆菌和大肠杆菌是典型的有益菌和有害菌,双歧杆菌常被加入酸奶饮品中帮助消化。乙酸是双歧杆菌的主要代谢物质,随着乙酸的增多,pH值降低从而抑制大肠杆菌的生长繁殖。本实验通过研究山楂,焦山楂以及焦山楂炒制过程中产生的类黑素对大肠杆菌、双歧杆菌以及其代谢物乙酸的影响,探究“山楂炒焦长于消食导滞”的作用机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 实验仪器
低温培养箱(美墨尔特有限公司,德国),生物安全柜(赛默飞世尔科技公司,美国),高压灭菌锅(三洋公司,日本),纯水机(密理博公司,美国),厌氧罐(北京陆桥技术股份有限公司,北京);紫外可见分光光度计(上海佑科仪器仪表有限公司,上海);7890B型气相色谱仪(安捷伦科技有限公司,美国);HP-FFAP型毛细管柱(货号:19091F-413,安捷伦科技有限公司,美国);GM900型非接触红外测温仪(深圳聚茂源科技有限公司,深圳)。
1.1.2 实验试剂
MRS固体培养基、PYG液体培养基、厌氧产气袋和厌氧指示剂(北京陆桥技术股份有限公司);蛋白胨、酵母粉(英国OXOID公司);乙酸(98.85%,国药集团化学试剂有限公司,中国);其余试剂均为分析纯。
1.1.3 山楂和实验菌株
净山楂饮片(四川同善堂中药饮片有限责任公司,批号:180501);双歧杆菌(GDMCC1.1258)、大肠杆菌(ATCC25922)(中国科学院微生物研究所)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 焦山楂的炮制
参照2015版《中国药典》一部山楂项下制备焦山楂。取生山楂150 g,中火(380~420)℃炒制10 min,至药材表面呈焦黄或焦褐色,内部颜色加深,并具有焦香气味,取出,常温封存,即得。
1.2.2 生山楂,焦山楂和类黑素浸膏的制备
(1)生山楂和焦山楂浸膏的制备
取生山楂和焦山楂各100 g进行水浸提,料液比为1:15,浸提8 h,浸提2次。生山楂和焦山楂浸提液分别在4 ℃下以3 600 r/min离心10 min,取上层清液各1 000 ml。将500 ml上层清液进行蒸发浓缩至胶状,停止加热,余温使其自然干燥,得生山楂浸膏13.75 g,焦山楂浸膏14.02 g。
(2)焦山楂中类黑素的提取
取焦山楂100 g,按照“1.2.2”项中⑴的方法提取得到1 000 ml上层清液。取500 ml上层清液蒸发浓缩得棕褐色浓缩液50 ml,进行大孔树脂吸附,室温吸附流速1.5 ml/min,60%乙醇作为洗脱剂,洗脱至色谱柱上无棕色为止,收集洗脱液500 ml。洗脱液蒸发浓缩至胶状,停止加热,余温使其自然干燥,得焦山楂类黑素浸膏13.12 g。
(3)类黑素的紫外检测
取类黑素浸膏1 g,蒸馏水溶解定容至100 ml,取10 ml溶液,分别定容至50 ml;因波长420 nm处是类黑素的特征吸收波长,测其特征吸收下的吸光度值,焦山楂类黑素浸膏吸光度值为0.492,说明焦山楂中类黑素提取成功。
1.2.3 山楂炮制品及类黑素对肠道菌群生长繁殖的影响
(1)双歧杆菌测试菌菌液的制备
以接种环自双歧杆菌标准菌种管挑取菌种,划线接种至MRS固体培养基,36 ℃厌氧培养48 h,挑取单菌落接种至PYG液体培养基,36 ℃厌氧培养48 h,以生理盐水调整浓度至1.0麦氏浓度,作为受试菌初始菌液,按10:1浓度加入试验体系。
(2)大肠杆菌测试菌液的制备
以接种环自大肠杆菌标准菌种管挑取菌种,划线接种至LB固体培养基(配方:蛋白胨10 g,酵母粉5 g,氯化钠10 g,琼脂粉15 g,加入1 L蒸馏水,以5 mol/L氢氧化钠调节pH至7.0,121 ℃高压灭菌15 min备用),36 ℃有氧培养24 h,挑取单菌落接种至LB液体培养基(配方:蛋白胨10 g,酵母粉5 g,氯化钠10 g,加入1 L蒸馏水,以5 mol/L氢氧化钠调节pH至7.0,121 ℃高压灭菌15 min备用),36 ℃有氧培养6 h,以生理盐水调整浓度至0.5麦氏浓度,作为受试菌初始菌液,按10:1浓度加入试验体系。
(3)样本药液的处理
准确称取生山楂,焦山楂和类黑素浸膏各10 g,加入100 ml去离子水,超声振荡处理,期间手动震摇数次,直至样本完全溶解,配制10%母液,并经115 ℃高压灭菌处理15 min后4 ℃保存备用。
(4)乙酸含量测定
①样本前处理:将经过微生物培养的溶液1 ml,经过高速离心机4 000 r/min离心,之后再过0.2 µm有机相滤头于进样瓶,样品量大于0.5 ml,或者使用内插管,上机测定。
②标准溶液及标准曲线:称取60.05 g乙酸于100 ml容量瓶,用一级水定容至刻度,摇匀,作为储备标准溶液,浓度为101.33 mmol/L。将标准储备溶液依次稀释1、3、10、20、100、200倍得标准工作溶液。
③色谱条件:洗针液为甲醇,进样量0.5 µl,进样口温度240 ℃;压力6.1219 psi;分流比10:1,流量为1.0 ml;升温程序:初始温度:100 ℃,保持0 min;梯度一:以5 ℃/min升到120 ℃,保持0 min;梯度二:以20 ℃/min升到200 ℃,保持10 min;总运行时间:18 min;检测器(FID)温度:240 ℃;空气流量:300 ml/min;氢气流量:33 ml/min;尾吹氮气流量:20 ml/min;数据采集频率/峰宽:20 Hz/0.01 min。
1.3 统计学方法
使用SPSS 22.0进行独立样本t检验,数据以平均数±标准差(
$\bar x \pm s$ )表示,P<0.05认为存在显著性差异。2. 结果
2.1 乙酸标准曲线的建立
乙酸浓度在0.51~101.33 mmol/L线性关系良好。以乙酸峰面积(Y)为纵坐标,乙酸含量(X)为横坐标,绘制标准曲线,得到线性回归方程为Y=3.670 5X−4.300 8,r=0.999 0,残留标准误差为6.644 2,如图1所示。
2.2 山楂饮片及类黑素对双歧杆菌体外生长的影响
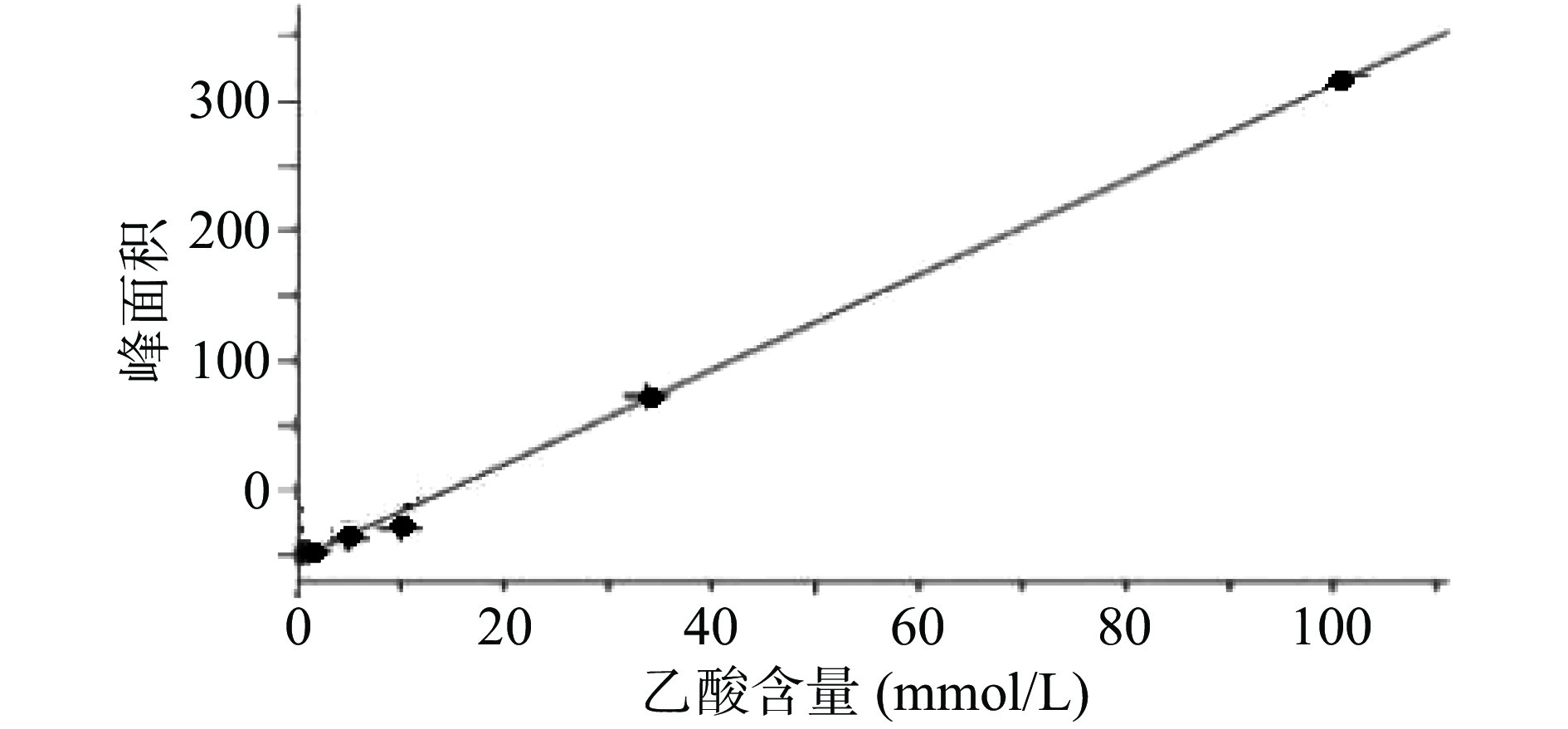
生山楂和焦山楂加速生长期双歧杆菌的生长繁殖,达稳定期后,由于生山楂中多种物质被分解,菌群产生大量代谢废物,于衰亡期加速双歧杆菌的衰亡;由于焦山楂中多种物质被分解,菌群产生大量代谢废物,于衰亡期加速双歧杆菌的衰亡;但因焦山楂中存在类黑素且其他物质较少,衰亡速率慢于生山楂组;类黑素加速生长期双歧杆菌的生长繁殖,但由于无其他物质,其生长速率慢于生山楂组,但在衰亡期中明显改变双歧杆菌生长规律,使生长期延长(生长速率变缓),双歧杆菌衰亡延后,如图2。
2.3 山楂饮片及类黑素对大肠杆菌体外生长的影响
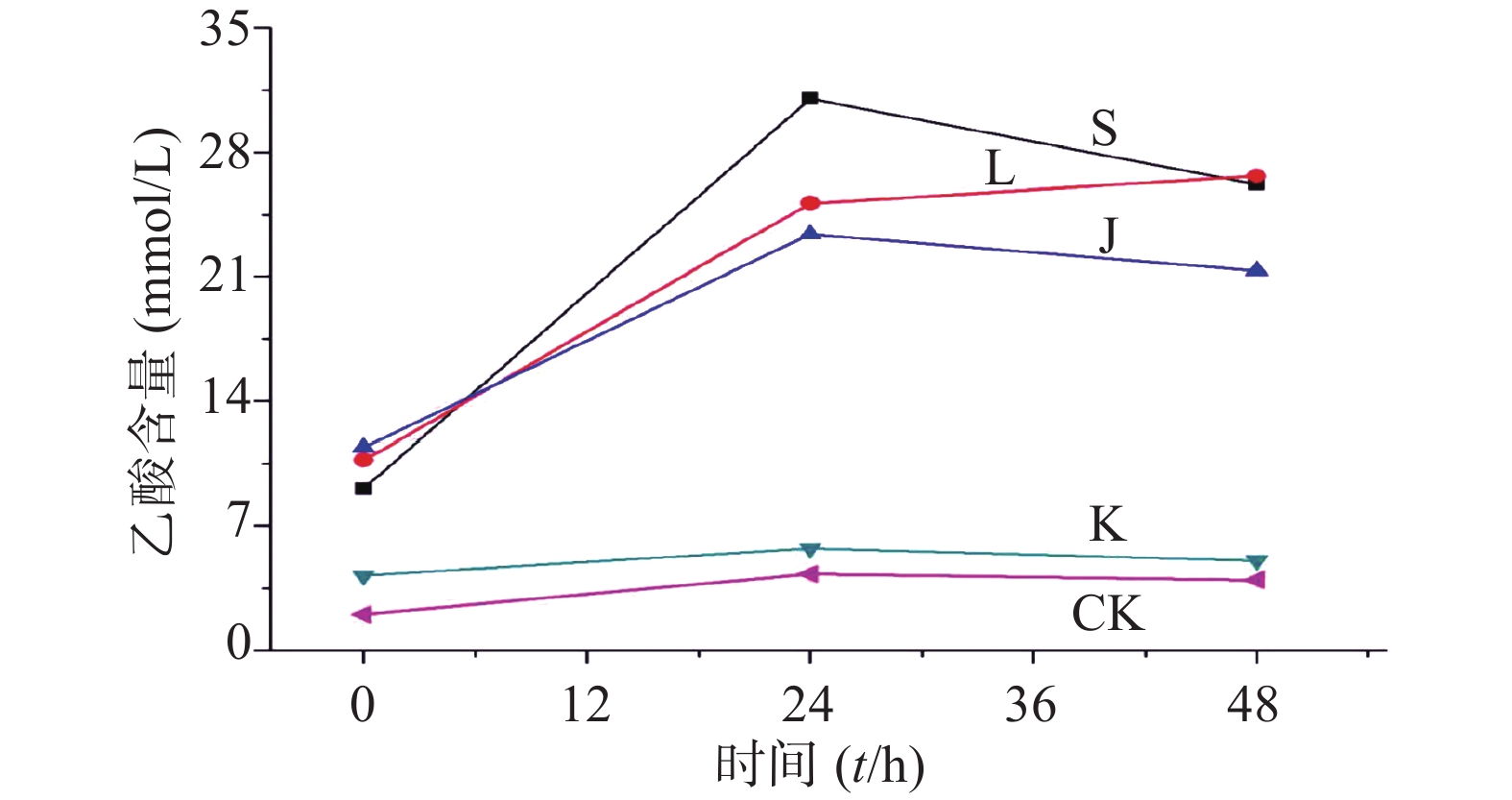
生山楂促进大肠杆菌生长期前期的生长繁殖,但由于代谢废物的逐渐增加,乙酸堆积,使生长速率逐渐变缓;焦山楂促进大肠杆菌生长期前期的生长繁殖,但由于类黑素及代谢废物的影响使生长期变短,稳定期提前;类黑素对大肠杆菌生长期前期无明显影响,但生长期后期明显促进大肠杆菌的生长繁殖,如图3所示。
3. 讨论
3.1 焦山楂炮制工艺研究
《中国药典》一部中对焦山楂炮制方法为:取净山楂,中火条件下炒至药材表面焦褐色,内部焦黄色,并具有焦香气味。因无可控工艺参数,焦山楂炮制过程中易出现饮片表面以及内部颜色不均一,山楂炒制成品质量不稳定等情况。结合课题组前期实验,采用分别100、150、200和250 g净山楂为炮制对象,中火条件为(340~380)℃、(380~420)℃和(420~460)℃,炮制时间为8、10、12和14 min;不同质量同一批号的净山楂在不同的中火条件下炮制不同的时间,采用非接触式红外测温仪检测炒制温度,并以炒锅初温和山楂药材炒制末温辅助控温。实验筛选出150 g净山楂中火条件(380~420)℃下炒制10 min,可得到质量稳定,颜色均一的焦山楂。
3.2 焦山楂类黑素提取工艺研究
类黑素的提取方法主要是水浸提法,Borrelli等[8]在90 ℃条件下,采用1:6料液比,对咖啡中的类黑素进行水提;Langner等[9]在室温条件下采用1:12料液比,水浸提1 h,提取到土豆类黑素粗制品。类黑素成分复杂,提纯困难。目前,主要的纯化方法有大孔树脂、超滤和凝胶层析等方法。何健[10]等发现X-5大孔树脂是曲霉型豆豉类黑素的最佳吸附树脂。秦礼康等[11]利用S-8树脂分离得到豆豉两个类黑素组分。本实验在水浸提法的基础上进行改良,最终获得最优提取工艺。结果显示类黑色素在420 nm处有较强吸收[12]。
3.3 气相色谱条件的筛选
实验采用气相色谱法检测菌群代谢物乙酸的含量。参照文献[13-14],结果显示其色谱条件对于本样品分析效果不佳;在柱温选择中,恒温法对乙酸检测效果不理想,峰形不稳定,因此实验采取梯度升温。经反复试验,最终获得正文中的检测参数,分离效果好,可作为本实验乙酸检测条件。
-
[1] SATIN L S, SOLEIMANPOUR S A, WALKER E M. New aspects of diabetes research and therapeutic development[J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2021, 73(3):1001-1015. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000160 [2] HUANG X Y, CHU Y, REN H, et al. Antioxidation function of EGCG by activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in mice with coronary heart disease[J]. Contrast Med Mol Imaging, 2022, 2022:1-8. [3] SUN H, SAEEDI P, KARURANGA S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2022, 183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119 [4] TIAN X, GAO Y, ZHONG M, et al. The association between serum Sestrin2 and the risk of coronary heart disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. BMC Cardiovas Disord, 2022, 22(1):1-8. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02434-3 [5] CAI X L, SHEN J, YE B Q, et al. Characteristics, treatment patterns, and glycemic control of older type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in China[J]. Chin Med J, 2021, 134(23):2893-2895. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001674 [6] KATSIKI N, BANACH M, MIKHAILIDIS D P. Is type 2 diabetes mellitus a coronary heart disease equivalent or not? Do not just enjoy the debate and forget the patient![J]. Arch Med Sci, 2019, 15(6):1357-1364. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.89449 [7] 钟钰灵. 基于网络药理学的麝香保心丸治疗冠状动脉微循环疾病的机制研究[D]. 桂林: 桂林医学院, 2022. [8] 叶健, 李凌燕, 席鑫, 等. 麝香保心丸基于miR-144-3p/SLC7A11通路减轻心肌细胞铁死亡的机制研究[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2022, 42(11):1335-1340. [9] 李芃琪, 信琪琪, 袁蓉, 等. 麝香保心丸调控冠心病血管新生的研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(14):242-253. [10] 侯志杰. 麝香保心丸治疗冠心病合并2型糖尿病患者55例临床观察[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2014, 27(20):2701-2702. [11] 费震宇, 徐玫, 陈宇明, 等. 麝香保心丸对2型糖尿病患者尿微量白蛋白/肌酐比值的影响[J]. 上海医药, 2020, 41(10):23-25. [12] 李勇萍, 杜从云, 刘桃喜. 麝香保心丸对冠心病伴糖尿病患者发生心血管临床事件的影响分析[J]. 中西医结合心血管病电子杂志, 2018, 6(18): 163, 166. [13] 华姞安, 孟靓, 孟智睿, 等. 中成药治疗2型糖尿病用药规律及作用靶点分析[J]. 世界中医药, 2023, 18(5):692-698,703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2023.05.019 [14] 卢李娜, 郑娴. 从气虚血瘀论治冠心病的研究进展[J]. 实用中医内科杂志, 2023, 37(4):38-41. [15] 中国医师协会中西医结合医师分会心血管病专业委员会, 国家中医心血管病临床医学研究中心. 麝香保心丸治疗冠心病专家共识[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2022, 42(7):782-790. [16] 李桂梅, 谢秀峰. 麝香保心丸配合强化抗血小板治疗对急性心肌梗死合并糖尿病患者疗效研究[J]. 创伤与急危重病医学, 2020, 8(6):426-430. [17] 郭施勉, 楚英杰. 人参皂苷Rg1对冠心病大鼠心肌细胞凋亡的影响及机制研究[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2021, 19(23):4054-4059. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2021.23.008 [18] ZHOU P, XIE W J, HE S B, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 as an anti-diabetic agent and its underlying mechanism analysis[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(3):204. doi: 10.3390/cells8030204 [19] FAN X, ZHANG C, NIU S, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates hepatic insulin resistance induced by high-fat and high-sugar by inhibiting inflammation[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2019, 854:247-255. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.04.027 [20] CHANG X, ZHANG T, ZHANG W, et al. Natural drugs as a treatment strategy for cardiovascular disease through the regulation of oxidative stress[J]. Oxidative Med Cell Longevity, 2020, 2020:5430407. [21] LI W, QIAO J, LIN K, et al. Ethyl-acetate fraction from a cinnamon-cortex extract protects pancreatic β-cells from oxidative stress damage[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14:1111860. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1111860 [22] NAIR A, PREETHA RANI M R, SALIN RAJ P, et al. Cinnamic acid is beneficial to diabetic cardiomyopathy via its cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-dyslipidemia, and antidiabetic properties[J]. J Biochemi Molecular Toxicol, 2022, 36(12):e23215. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23215 [23] 王笑, 张恒, 李媛媛, 等. 肉桂醛预处理对H9C2心肌细胞缺氧复氧损伤后自噬的影响[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2021, 37(3):30-34. [24] 赵丹, 王明慧, 张程斐, 等. 肉桂酸对db/db小鼠肝脏PI3K/AKT/FoxO1信号通路的影响[J]. 世界科学技术(中医药现代化), 2021, 23(10):3613-3620. [25] CHEN Y S, LIU H M, LEE T Y. Ursodeoxycholic acid regulates hepatic energy homeostasis and white adipose tissue macrophages polarization in leptin-deficiency obese mice [J]. Cells, 2019, 8(3):253. [26] LI D D, ZHONG J X, ZHANG Q R, et al. Effects of anti-inflammatory therapies on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14:1125116. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1125116 [27] AKBARI M, HASSAN-ZADEH V. IL-6 signalling pathways and the development of type 2 diabetes[J]. Inflammopharmacol, 2018, 26(3):685-698. doi: 10.1007/s10787-018-0458-0 [28] RIDKER P M, RANE M. Interleukin-6 signaling and anti-interleukin-6 therapeutics in cardiovascular disease[J]. Circ Res, 2021, 128(11):1728-1746. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319077 [29] WAGNER N, WAGNER K D. Pharmacological utility of PPAR modulation for angiogenesis in cardiovascular disease[J]. Int Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3):2345. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032345 [30] JIN J L, ZHU C, WANG J X, et al. The association between ACTB methylation in peripheral blood and coronary heart disease in a case-control study[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9:972566. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.972566 [31] BOUTCHUENG-DJIDJOU M, BELLEAU P, BILODEAU N, et al. A type 2 diabetes disease module with a high collective influence for Cdk2 and PTPLAD1 is localized in endosomes[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(10):e0205180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205180 [32] WAGHELA B N, VAIDYA F U, RANJAN K, et al. AGE-RAGE synergy influences programmed cell death signaling to promote cancer[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2021, 476(2):585-598. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03928-y [33] SHEN C Y, LU C H, WU C H, et al. The development of Maillard reaction, and advanced glycation end product (AGE)-receptor for AGE (RAGE) signaling inhibitors as novel therapeutic strategies for patients with AGE-related diseases[J]. Mol, 2020, 25(23):5591. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235591 [34] KOSMOPOULOS M, DREKOLIAS D, ZAVRAS P D, et al. Impact of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) signaling in coronary artery disease[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Mol Basis Dis, 2019, 1865(3):611-619. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.01.006 [35] BRENNAN J J, GILMORE T D. Evolutionary origins of toll-like receptor signaling[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2018, 35(7):1576-1587. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy050 [36] KOUSHKI K, SHAHBAZ S K, MASHAYEKHI K, et al. Anti-inflammatory action of statins in cardiovascular disease: the role of inflammasome and toll-like receptor pathways[J]. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol, 2021, 60(2):175-199. doi: 10.1007/s12016-020-08791-9 [37] AAMIR K, KHAN H U, SETHI G, et al. Wnt signaling mediates TLR pathway and promote unrestrained adipogenesis and metaflammation: therapeutic targets for obesity and type 2 diabetes[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2020, 152:104602. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104602 [38] ZACCOLO M, ZERIO A, LOBO M J. Subcellular organization of the cAMP signaling pathway[J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2021, 73(1):278-309. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000086 [39] WANG Y N, LIU Q, KANG S G, et al. Dietary bioactive ingredients modulating the cAMP signaling in diabetes treatment[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(9):3038. doi: 10.3390/nu13093038 [40] SADEK M S, CACHORRO E, EL-ARMOUCHE A, et al. Therapeutic implications for PDE2 and cGMP/cAMP mediated crosstalk in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(20):7462. [41] 张晓囡, 孙长鑫, 陈纪烨, 等. 基于“异病同治”理论探讨四妙勇安汤在心血管疾病中的应用[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2023, 21(5):946-949. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2023.05.040 -





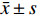
 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载: