-
高海拔地区最大的环境特征是大气压降低,从而使机体从空气中摄取的氧气含量减少。大脑是最耗氧的器官之一,对缺氧异常敏感,这种生理反应使机体处于缺氧环境中可能导致严重的脑损伤,如学习和记忆障碍[1-3]。近年来,治疗或改善低压低氧引起的中枢神经系统(CNS)损伤在高原医学领域引起了越来越多的关注[4-5]。有研究表明,急性暴露在缺氧环境中会加速活性氧(ROS)的积累,并在海马和皮层区域引发氧化应激,而氧化应激是高原学习记忆障碍的主要诱因[6-8],随着进入高海拔地区学习、工作和旅游的人群日益增加,寻找能够改善高原缺氧记忆损伤的药物成为高原缺氧损伤防治研究的重点。
利舒康胶囊为国药准字(Z20025932)药品,其主要成分为红景天、手掌参、甘青青兰、烈香杜鹃四味藏药辅以黄柏、甘草,经提取加工而制成,具有抗缺氧、抗疲劳、增强体力等作用,主要用于防治各种急、慢性高原病。临床实践表明,该药还可用于慢性缺血缺氧症侯群、脑梗死伴眩晕症、血管性痴呆、非痴呆性血管性认知功能障碍等缺血缺氧性相关疾病的治疗,其作用机制可能与抑制脂质过氧化,清除自由基减轻氧化应激有关[9]。本研究利用大型低压氧舱模拟高原海拔7500 m缺氧72 h,从行为学、组织形态学和Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路等方面,探讨利舒康胶囊对高原学习记忆损伤的干预作用,以期进一步阐明其可能的作用机制,为扩大利舒康胶囊的药理作用和临床适用范围提供理论依据。
-
本研究符合《实验动物福利伦理指南》的规定,并取得中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九四〇医院伦理委员会的认可(审批编号:2021KYLL205)。实验动物选取体重质量为18~22 g的SPF级Balb/C雄性小鼠60只,购于兰州大学动物科,饲养于中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九四〇医院动物实验科[合格证号:SCXK(京)2016-0006]。
-
Anti-Keap1抗体、Anti-Nrf2抗体、Anti-HO-1抗体、Anti-Caspase-3抗体、Anti-Bcl-2抗体、Anti-Bax抗体(abcam公司);β-Actin单克隆抗体(中杉金桥公司);RM-200八臂迷宫分析测试系统(成都泰盟科技有限公司);DYC-1703070大型低压氧舱(贵州风雷航空军械有限公司);Tissuelyser-24多样品组织研磨机(上海净信实业发展有限公司);免疫印迹分析仪( BIO-RAD公司)。
-
海马体对空间工作记忆和参考记忆都是至关重要的,Xu等[10]研究发现八臂迷宫以食物作为诱饵,并在食物臂上贴上信号图,使实验动物可以在参考记忆任务中优先进入下一个选择的手臂的轨迹,在工作记忆任务中优先进入先前访问过的手臂的轨迹。Li和Du等[11-12]研究表明,八臂迷宫模型能很好地反映高原缺氧环境下小鼠的空间工作记忆情况和参考记忆情况。本实验将60只Balb/C雄性小鼠(体重18~22 g)进行适应性训练3 d(将小鼠置于迷宫中,八个臂均放入饵料自由进食5 min),适应性训练结束后,称重,将小鼠随机分为正常对照组、缺氧模型组、红景天胶囊组[400 mg/kg],利舒康胶囊低剂量组[400 mg/kg]、中剂量组[600 mg/kg]、高剂量组[800 mg/kg],每组10只,在之后的饲养中给予小鼠少许食物,第4 d开始正式实验,训练时,在1、3、4、7(食臂末端有信号图)食臂中放入饵料,将一只小鼠置于迷宫中央用塑料罩罩住,30 s后打开使其自由进食,训练总时间为5 min,5 min内吃完则系统自动停止,5 min内仍未吃完则实验终止。测试指标为:①工作记忆错误(WME),即在同一个训练中小鼠再次进入已经放置饵料的臂;②参考记忆错误(RME),即小鼠进入没有放置饵料的臂;③小鼠探究总时间(TT),即小鼠吃完所有饵料所花的时间;④错误总次数(TE)。小鼠训练成功的标准为:WME=0;RME≤1。每次训练结束后清理小鼠排泄物,立即用75%酒精擦拭八臂迷宫内部祛除气味干扰。连续训练30 d。
-
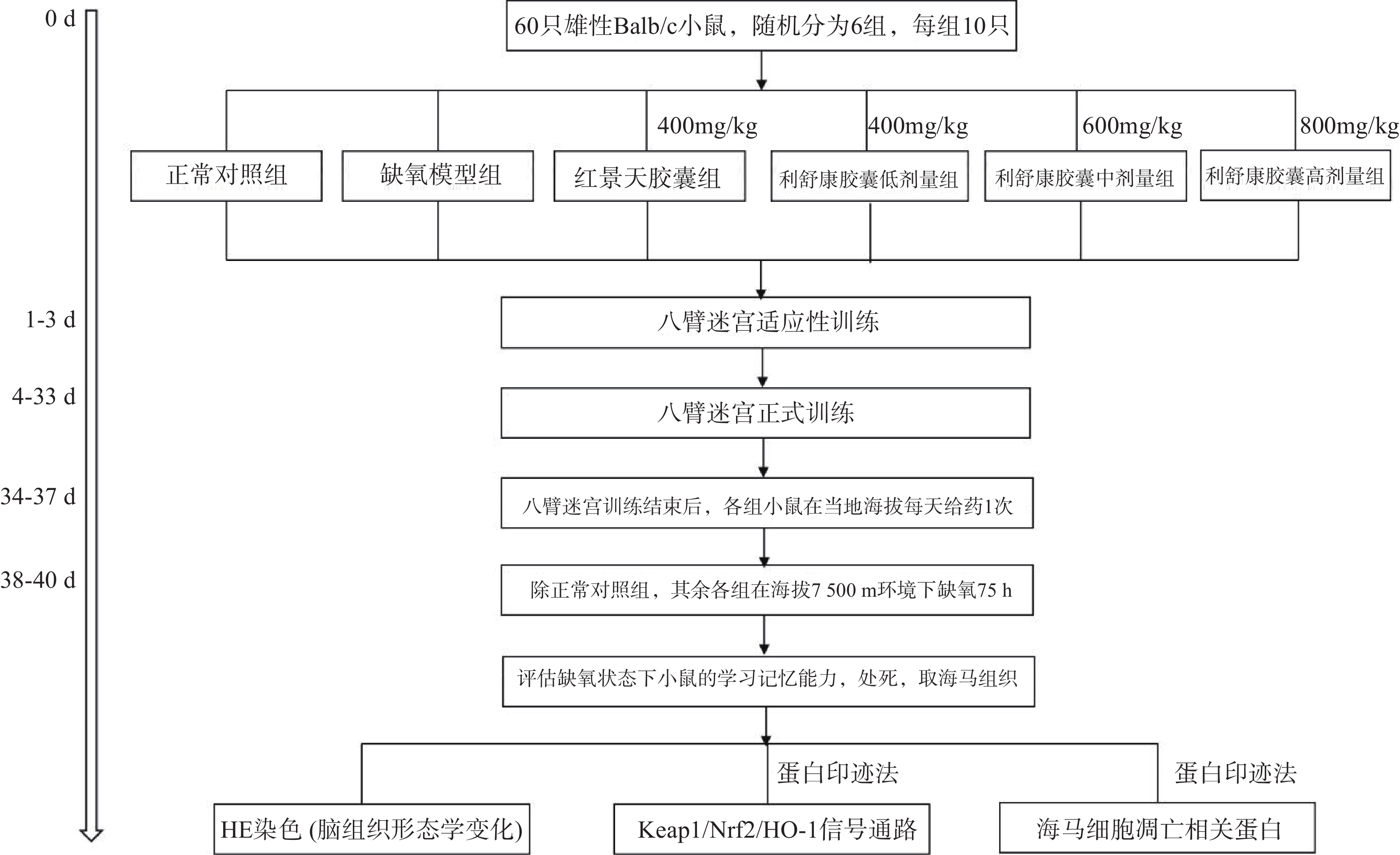
在小鼠训练30 d后,第31 d开始对所有实验小鼠进行灌胃给药,每天一次。正常对照组和缺氧模型组给予等体积的生理盐水,连续给药7 d(舱外给药4 d+舱内给药3 d),期间所有小鼠正常在当地海拔进行八臂迷宫训练。在灌胃给药第4 d后停止八臂迷宫训练,除正常对照组外,将其余各组小鼠放入大型低压低氧动物实验舱内,借助实验舱可以模拟不同海拔高度。小鼠以极快的速度(10 m/s)从当地海拔上升到海拔7500 m高度。之后每天上午实验员进入实验舱内(舱内海拔由7500 m降至3500 m,下降速度为20 m/s),在模拟海拔3 500 m处对小鼠进行灌胃给药,连续3 d。每天给药完毕后,将海拔上升至预定海拔7500 m处,小鼠在舱内自由进食和摄水,正常对照组小鼠同时饲养于动物实验科(当地海拔1500 m)。缺氧结束后将舱内海拔降至3500 m,实验人员进入舱内,检测高原损伤后小鼠的学习记忆能力,评价利舒康胶囊对高原学习记忆损伤的干预作用。实验流程如图1。实验结束后麻醉小鼠,取出海马组织,按照测定要求对其进行处理。
-
各组取2只小鼠,取脑组织,经生理盐水漂洗后放入10%甲醛溶液中浸泡,1周后,将样品送至联勤保障部队第940医院病理科,进行石蜡包埋,组织切片,染色以及光镜观察。
-
将实验小鼠大脑取出,剖出海马体后,用BCA法测定其蛋白浓度,之后加入缓冲液,100 ℃水浴5 min,流水冷却后重复水浴5 min使其充分变性。以β-action为内参,配制10% SDS聚丙烯酰氨凝胶进行电泳、转膜和抗体孵育。次日使用ECL液进行显影,Image J图像分析软件对条带进行分析。其中一抗稀释比例为:β-action(1: 2000)、Keap1(1∶1000)、Nrf2(1∶2 000)、HO-1(1∶2 000)、Caspase-3(1∶2 000)、Bax(1∶1000)、BCL-2(1∶1000)。
-
采用SPSS 13.0统计软件分析结果,符合正态分布的实验数据以
$ \bar x \pm s $ 表示。多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。 -
与正常对照组相比,缺氧模型组小鼠WME、RWE、TE、TT均显著升高(P<0.01);与缺氧模型组相比,利舒康胶囊三个剂量组小鼠四项指标均有不同程度降低,其中利舒康胶囊高剂量组800 mg/(kg·d)具有显著性差异(P<0.05或P<0.01),表明高原低氧缺氧能导致小鼠空间记忆障碍,而利舒康胶囊高剂量组能够增强高原缺氧小鼠的短期记忆和长期记忆能力,改善大鼠认知,有望对高原缺氧导致的学习记忆损伤患者提供预防和治疗。结果见表1和图2。
表 1 利舒康胶囊对高原缺氧小鼠空间记忆的影响(
$ \bar x \pm s $ ,n=10)组别 剂量(mg/kg) WME(次) RME(次) TT(秒) TE(次) 正常对照组 − 0.43±0.35 0.50±0.41 63.47±9.64 1.50±0.17 缺氧模型组 − 3.00±1.58## 2.70±1.52## 119.99±43.00## 3.10±0.48## 红景天胶囊组 400 0.57±0.35** 0.79±0.49* 81.78±28.20 1.83±0.29#** 利舒康胶囊低剂量组 400 2.43±0.89#▲ 1.36±0.56 99.45±25.27## 3.06±0.58##▲▲ 利舒康胶囊中剂量组 600 2.14±1.14#▲ 1.43±1.10 98.75±30.51 3.04±0.52##▲▲ 利舒康胶囊高剂量组 800 1.07±0.61* 0.71±0.49** 69.38±31.69* 1.73±0.37** # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, 与正常对照组比较;* P<0.05, ** P<0.01,与缺氧组比较 ;▲P<0.05, ▲▲P<0.01,与红景天胶囊组比较 -
海马体在学习和记忆中发挥关键作用,尤其容易受到缺氧损伤。在本研究中,小鼠脑组织病理学切片结果显示(见图3),正常对照组小鼠海马神经元密集,细胞核大而圆,神经元呈层状有序分布,各层细胞形态饱满而数量多,细胞排列整齐且致密;缺氧模型组小鼠海马神经元细胞分布受到破坏,细胞形态不规则,部分细胞缺失或有空泡(黑色箭头),出现明显核固缩(蓝色箭头),细胞排列紊乱,CA1区有较多不规则形状的深染细胞(绿色箭头),表明脑组织出现神经元死亡;经过红景天胶囊和利舒康胶囊药物干预后,缺氧模型组脑组织损伤有所改善;神经元细胞排列整齐,核固缩现象减轻(蓝色箭头),深染细胞数量减少(绿色箭头),少有细胞缺失或空泡(黑色箭头),细胞形态较好,排列整齐,且利舒康胶囊高剂量组脑组织形态趋于正常。
-
与正常对照组比较,缺氧模型组小鼠海马组织中Keap1蛋白含量显著升高(P<0.01),Nrf2、HO-1蛋白含量显著降低(P<0.01);与缺氧模型组相比,利舒康胶囊组Keap1蛋白含量降低(P<0.01),Nrf2、HO-1蛋白含量显著升高(P<0.01),其中以利舒康胶囊高剂量组蛋白水平变化最为显著,且效果优于阳性药红景天胶囊组。结果见图4和表2。
表 2 各组小鼠脑组织蛋白表达比较(
$ \bar x \pm s $ ,n=3)分组 剂量
(mg/kg)Keap1 Nrf2 HO-1 Caspase-3 Bax BCL-2 正常对照组 − 0.36±0.08 0.76±0.08 1.03±0.14 0.03±0.01 0.09±0.02 0.79±0.09 缺氧模型组 − 0.91±0.15## 0.45±0.03## 0.31±0.05## 0.95±0.12## 0.99±0.08## 0.31±0.02## 红景天胶囊组 400 0.44±0.03** 0.92±0.15** 0.86±0.03 0.75±0.16## 0.73±0.11##** 0.65±0.02#** 利舒康胶囊低剂量组 400 0.42±0.03** 0.77±0.09** 0.67±0.02## 0.86±0.17## 0.81±0.05##** 0.62±0.02##** 利舒康胶囊中剂量组 600 0.41±0.04** 0.83±0.09** 0.98±0.13 0.64±0.06## 0.79±0.06##** 0.73±0.09** 利舒康胶囊高剂量组 800 0.33±0.02**▲▲ 1.21±0.11##**▲▲ 1.23±0.08**▲▲ 0.46±0.01##**▲▲ 0.52±0.05##**▲ 0.76±0.11** # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, 与正常对照组比较;* P<0.05, ** P<0.01,与缺氧组比较;▲P<0.05, ▲▲P<0.01,与红景天胶囊组比较 -
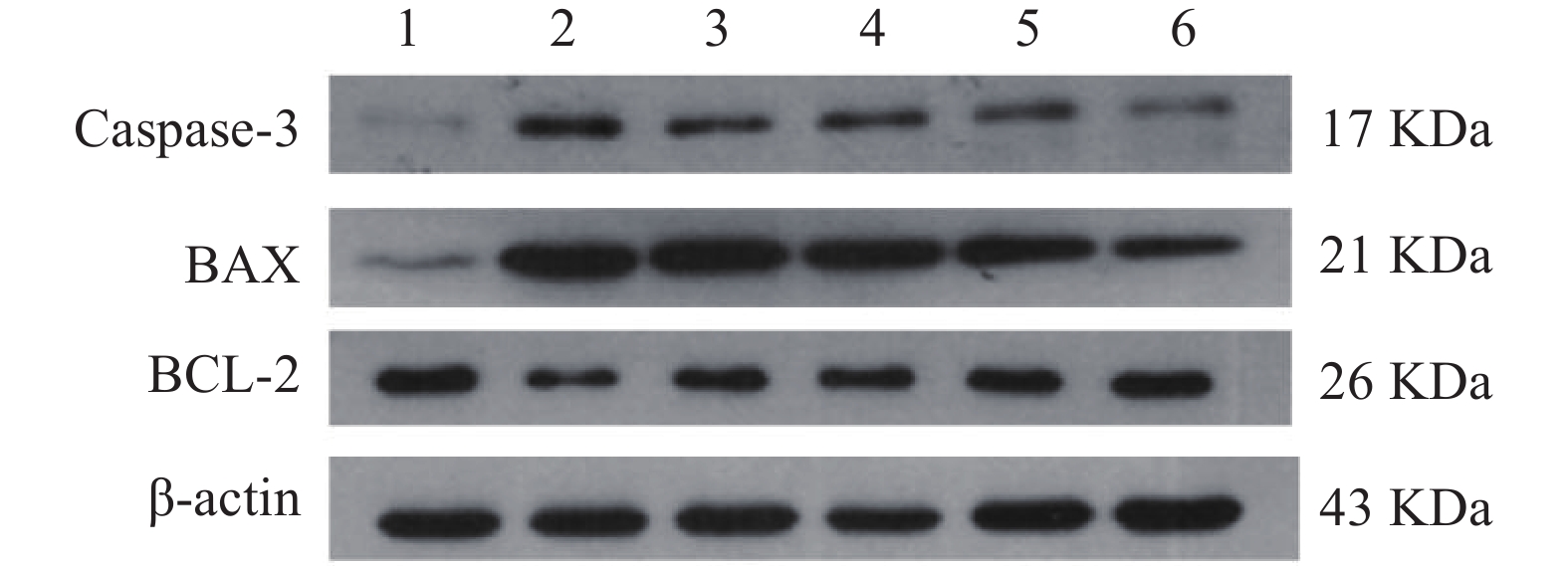
与正常对照组相比,缺氧模型组小鼠海马组织中Caspase-3和Bax的表达显著升高(P<0.01),Bcl-2蛋白表达显著降低(P<0.01);与缺氧模型组相比,利舒康胶囊组Caspase-3和Bax蛋白表达显著降低(P<0.01),BCL-2蛋白表达显著升高(P<0.01),其中利舒康胶囊高剂量组蛋白水平变化尤为显著,且效果优于阳性药红景天胶囊组。结果见图5和表2。
-
缺氧会引起机体组织细胞形态结构、功能和代谢的异常变化[13]。大脑对缺氧刺激异常敏感,短期暴露于高海拔地区的急性低压低氧会导致认知能力下降,尤其是空间学习、短期记忆和工作记忆能力下降。高原脑缺氧可引起中枢神经系统氧化性损伤,大量证据表明,氧化应激和细胞凋亡是神经元变性和死亡的主要诱因,进而造成机体认知功能损伤,且这种损伤为不可逆缺陷[14]。在本研究中,采用八臂迷宫实验方法检测高原缺氧环境下小鼠的空间记忆能力。通过利舒康胶囊高剂量组干预治疗后,WME、RME、TE和TT与缺氧模型组相比显著减少(P<0.05或P<0.01),表明利舒康胶囊能明显提高高原缺氧环境下小鼠的空间记忆能力。海马体是大脑中对缺氧最敏感的区域之一,也是形成空间记忆的关键区域[15]。HE染色结果显示,与正常对照组相比,缺氧模型组小鼠海马神经元细胞形态不规则,部分细胞缺失或有空泡;经利舒康胶囊干预后,细胞形态较好,排列整齐,少有细胞缺失或空泡。提示进行利舒康胶囊药物干预可以修复高原低压低氧造成的海马组织神经元损伤,防止了小鼠因暴露在高海拔环境中而导致的空间记忆障碍。
Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路是机体内保持细胞稳态的防御系统,在预防由氧化应激引起的细胞损伤中起重要作用,Nrf2是一种具有细胞保护和抗氧化活性的诱导蛋白,可被视为氧化应激反应的主调控因子[16-18],HO-1可以催化血红素的分解,从而抑制中性粒细胞、淋巴细胞和巨噬细胞介导的炎性反应。在正常条件下,Keap1形成E3泛素连接酶的一部分,紧密调控Nrf2的活性,这时的Nrf2活性处在相对较低水平。在氧化应激条件下,Nrf2通过与细胞质中含有半胱氨酸残基的阻遏蛋白Keap-1分离而被激活,进而激活其相关的抗氧化酶HO-1表达,达到抵抗氧化应激的作用[19]。本文研究结果显示,与正常对照组相比,缺氧模型组海马细胞中Keap1蛋白表达升高(P<0.01)、Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达下降(P<0.01),表明机体在缺氧环境中,ROS积累导致氧化还原状态失衡。经利舒康胶囊干预后,与缺氧模型组相比,Keap1蛋白表达下降,且具有显著性差异(P<0.01),Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达均显著升高(P<0.01),且利舒康胶囊高剂量组治疗效果最好,本课题组前期对利舒康胶囊对高原脑损伤防治的研究结果显示[20],机体暴露在高原环境下,活性氧(ROS)大量累积导致氧化性损伤,利舒康胶囊能降低脑组织内MDA含量,提高SOD的活力,具有良好的抗氧化应激的作用。因此我们推测,利舒康胶囊可以通过调控Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路,发挥抗氧化作用。
氧化应激和炎症在脑损伤中起关键作用,导致细胞凋亡。细胞凋亡是器官生长、发育和维持正常体内平衡的重要过程,也是脑缺氧后神经元死亡的主要形式[21]。海马锥体神经元的凋亡可导致学习和记忆障碍[22]。Caspase-3作为凋亡激活剂是重要的凋亡调节因子,是缺氧诱导的脑细胞凋亡的重要标志,抗凋亡基因Bcl-2和促凋亡基因Bax可能参与病理性凋亡和坏死细胞死亡途径[23-25]。在本研究中,与正常对照组相比,缺氧模型组Caspase-3蛋白含量和Bax/Bcl-2比值表达显著增加(P<0.01),说明缺氧可引起脑组织细胞凋亡。而利舒康胶囊可通过降低Caspase-3蛋白表达和Bax/Bcl-2比值来逆转这些变化,抑制了氧化应激引起的脑细胞凋亡和炎症引发的脑损伤,且利舒康胶囊高剂量组优于阳性药红景天胶囊组。
综上所述,利舒康胶囊可以改善高原缺氧小鼠脑损伤,提高小鼠在高原缺氧环境下的抗氧化能力,其机制可能是通过调控Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路发挥抗氧化应激作用,减轻缺氧引起的ROS积累;同时通过抗氧化和抗凋亡机制在低压低氧暴露期间为海马神经元提供神经保护作用,从而改善缺氧诱导的小鼠空间记忆损伤。
利益冲突
所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
Study on the effect of Lishukang capsule on learning and memory impairment in mice with high altitude hypoxia based on Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway
-
摘要:
目的 基于Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路探讨利舒康胶囊对高原缺氧小鼠学习记忆障碍的改善作用。 方法 将 60只Balb/C雄性小鼠随机分为正常对照组、缺氧模型组、红景天胶囊组:400 mg/kg、利舒康胶囊低、中、高剂量组:400 mg/kg、600 mg/kg、800 mg/kg,每组10只。各组灌胃给药7 d,第4 d给药结束后,正常对照组饲养于当地海拔(1500 m),其余各组置于低压低氧动物实验舱模拟高原海拔7500 m缺氧3 d,期间每天灌胃给药一次,正常对照组和缺氧模型组给予生理盐水,末次给药后1 h,采用八臂迷宫检测小鼠在模拟高原缺氧状态下空间记忆能力;HE染色观察小鼠脑组织海马区的形态学变化;Western blot 法检测海马组织中Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路蛋白含量变化及凋亡相关蛋白含量变化。 结果 与正常对照组相比,缺氧模型组小鼠空间记忆能力明显损伤(P<0.01);HE染色观察小鼠海马神经元损伤严重;Keap1蛋白含量及凋亡相关蛋白Bax、Caspase-3含量均上升(P<0.01);Nrf2、HO-1及凋亡相关蛋白Bcl-2含量下降(P<0.01)。与缺氧模型组相比,利舒康胶囊高剂量组小鼠在八臂迷宫行为学实验中错误率显著降低(P<0.05,P<0.01);HE染色观察神经元细胞排列整齐,细胞形态较好;Keap1蛋白含量及凋亡相关蛋白Bax、Caspase-3含量均下降(P<0.01);Nrf2、HO-1及凋亡相关蛋白Bcl-2含量上升(P<0.01)。 结论 高原缺氧可以导致小鼠氧化应激损伤、诱导凋亡相关基因的表达,从而加重了小鼠认知功能的障碍;利舒康胶囊能有效改善缺氧引起的小鼠学习记忆障碍,其作用机制可能与调控Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路、降低凋亡有关。 Abstract:Objective Study on the effect of Lishukang capsule on learning and memory impairment in mice with high altitude hypoxia based on Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway. Methods Sixty male Balb/C mice were randomly divided into normal control group, hypoxia model group, Rhodiola capsule group: 400 mg/kg, low, medium and high dose groups of Lishukang capsule: 400 mg/kg, 600 mg/kg, 800 mg/kg, with 10 mice in each group. The normal control group was fed at the local altitude (1500m) after 7 days of intragastric administration in each group, and the rest groups were fed at the low pressure and hypoxia animal experimental cabin to simulate the altitude of 7500 m for hypoxia for 3 days. During this period, the normal control group and the hypoxia model group were given normal saline once a day, and 1 hour after the last administration, the eight arm maze was used to test the spatial memory ability of mice under simulated high altitude hypoxia; HE staining was used to observe the morphological changes of hippocampus in mice; Western blot was used to detect the changes of protein content of Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway and apoptosis related protein in hippocampus of mice. Results Compared with the normal control group, the spatial memory ability of mice in the hypoxia model group was significantly impaired (P<0.01); HE staining showed that hippocampal neurons in mice were seriously injured; the content of brain tissue Keap1 protein and apoptosis related protein Bax and Caspase-3 increased (P<0.01); the content of Nrf2, HO-1 and apoptosis related protein Bcl-2 decreased (P<0.01). Compared with the hypoxia model group, the error rate of mice in the high dose group of Lishukang capsule in the eight arm maze behavior experiment was significantly reduced (P<0.05, P<0.01); HE staining showed that the neurons were arranged orderly and the cell morphology was good; the content of Keap1 protein and apoptosis related protein Bax and Caspase-3 decreased (P<0.01); the content of Nrf2, HO-1 and apoptosis related protein Bcl-2 increased (P<0.01). Conclusion High altitude hypoxia can lead to oxidative stress injury in mice and induce the expression of apoptosis related genes, thus aggravating the cognitive dysfunction of mice; Lishukang capsule can effectively improve the learning and memory impairment in mice caused by hypoxia, and its mechanism may be related to regulating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway and reducing apoptosis. -
高海拔地区最大的环境特征是大气压降低,从而使机体从空气中摄取的氧气含量减少。大脑是最耗氧的器官之一,对缺氧异常敏感,这种生理反应使机体处于缺氧环境中可能导致严重的脑损伤,如学习和记忆障碍[1-3]。近年来,治疗或改善低压低氧引起的中枢神经系统(CNS)损伤在高原医学领域引起了越来越多的关注[4-5]。有研究表明,急性暴露在缺氧环境中会加速活性氧(ROS)的积累,并在海马和皮层区域引发氧化应激,而氧化应激是高原学习记忆障碍的主要诱因[6-8],随着进入高海拔地区学习、工作和旅游的人群日益增加,寻找能够改善高原缺氧记忆损伤的药物成为高原缺氧损伤防治研究的重点。
利舒康胶囊为国药准字(Z20025932)药品,其主要成分为红景天、手掌参、甘青青兰、烈香杜鹃四味藏药辅以黄柏、甘草,经提取加工而制成,具有抗缺氧、抗疲劳、增强体力等作用,主要用于防治各种急、慢性高原病。临床实践表明,该药还可用于慢性缺血缺氧症侯群、脑梗死伴眩晕症、血管性痴呆、非痴呆性血管性认知功能障碍等缺血缺氧性相关疾病的治疗,其作用机制可能与抑制脂质过氧化,清除自由基减轻氧化应激有关[9]。本研究利用大型低压氧舱模拟高原海拔7500 m缺氧72 h,从行为学、组织形态学和Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路等方面,探讨利舒康胶囊对高原学习记忆损伤的干预作用,以期进一步阐明其可能的作用机制,为扩大利舒康胶囊的药理作用和临床适用范围提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验动物
本研究符合《实验动物福利伦理指南》的规定,并取得中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九四〇医院伦理委员会的认可(审批编号:2021KYLL205)。实验动物选取体重质量为18~22 g的SPF级Balb/C雄性小鼠60只,购于兰州大学动物科,饲养于中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九四〇医院动物实验科[合格证号:SCXK(京)2016-0006]。
1.2 主要材料和仪器
Anti-Keap1抗体、Anti-Nrf2抗体、Anti-HO-1抗体、Anti-Caspase-3抗体、Anti-Bcl-2抗体、Anti-Bax抗体(abcam公司);β-Actin单克隆抗体(中杉金桥公司);RM-200八臂迷宫分析测试系统(成都泰盟科技有限公司);DYC-1703070大型低压氧舱(贵州风雷航空军械有限公司);Tissuelyser-24多样品组织研磨机(上海净信实业发展有限公司);免疫印迹分析仪( BIO-RAD公司)。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 八臂迷宫实验检测高原缺氧小鼠的学习记忆能力
海马体对空间工作记忆和参考记忆都是至关重要的,Xu等[10]研究发现八臂迷宫以食物作为诱饵,并在食物臂上贴上信号图,使实验动物可以在参考记忆任务中优先进入下一个选择的手臂的轨迹,在工作记忆任务中优先进入先前访问过的手臂的轨迹。Li和Du等[11-12]研究表明,八臂迷宫模型能很好地反映高原缺氧环境下小鼠的空间工作记忆情况和参考记忆情况。本实验将60只Balb/C雄性小鼠(体重18~22 g)进行适应性训练3 d(将小鼠置于迷宫中,八个臂均放入饵料自由进食5 min),适应性训练结束后,称重,将小鼠随机分为正常对照组、缺氧模型组、红景天胶囊组[400 mg/kg],利舒康胶囊低剂量组[400 mg/kg]、中剂量组[600 mg/kg]、高剂量组[800 mg/kg],每组10只,在之后的饲养中给予小鼠少许食物,第4 d开始正式实验,训练时,在1、3、4、7(食臂末端有信号图)食臂中放入饵料,将一只小鼠置于迷宫中央用塑料罩罩住,30 s后打开使其自由进食,训练总时间为5 min,5 min内吃完则系统自动停止,5 min内仍未吃完则实验终止。测试指标为:①工作记忆错误(WME),即在同一个训练中小鼠再次进入已经放置饵料的臂;②参考记忆错误(RME),即小鼠进入没有放置饵料的臂;③小鼠探究总时间(TT),即小鼠吃完所有饵料所花的时间;④错误总次数(TE)。小鼠训练成功的标准为:WME=0;RME≤1。每次训练结束后清理小鼠排泄物,立即用75%酒精擦拭八臂迷宫内部祛除气味干扰。连续训练30 d。
1.3.2 低压低氧实验
在小鼠训练30 d后,第31 d开始对所有实验小鼠进行灌胃给药,每天一次。正常对照组和缺氧模型组给予等体积的生理盐水,连续给药7 d(舱外给药4 d+舱内给药3 d),期间所有小鼠正常在当地海拔进行八臂迷宫训练。在灌胃给药第4 d后停止八臂迷宫训练,除正常对照组外,将其余各组小鼠放入大型低压低氧动物实验舱内,借助实验舱可以模拟不同海拔高度。小鼠以极快的速度(10 m/s)从当地海拔上升到海拔7500 m高度。之后每天上午实验员进入实验舱内(舱内海拔由7500 m降至3500 m,下降速度为20 m/s),在模拟海拔3 500 m处对小鼠进行灌胃给药,连续3 d。每天给药完毕后,将海拔上升至预定海拔7500 m处,小鼠在舱内自由进食和摄水,正常对照组小鼠同时饲养于动物实验科(当地海拔1500 m)。缺氧结束后将舱内海拔降至3500 m,实验人员进入舱内,检测高原损伤后小鼠的学习记忆能力,评价利舒康胶囊对高原学习记忆损伤的干预作用。实验流程如图1。实验结束后麻醉小鼠,取出海马组织,按照测定要求对其进行处理。
1.3.3 HE染色观察高原缺氧小鼠脑组织形态学变化
各组取2只小鼠,取脑组织,经生理盐水漂洗后放入10%甲醛溶液中浸泡,1周后,将样品送至联勤保障部队第940医院病理科,进行石蜡包埋,组织切片,染色以及光镜观察。
1.3.4 Western blot法检测高原缺氧小鼠海马中Nrf2途径蛋白含量及凋亡相关蛋白含量
将实验小鼠大脑取出,剖出海马体后,用BCA法测定其蛋白浓度,之后加入缓冲液,100 ℃水浴5 min,流水冷却后重复水浴5 min使其充分变性。以β-action为内参,配制10% SDS聚丙烯酰氨凝胶进行电泳、转膜和抗体孵育。次日使用ECL液进行显影,Image J图像分析软件对条带进行分析。其中一抗稀释比例为:β-action(1: 2000)、Keap1(1∶1000)、Nrf2(1∶2 000)、HO-1(1∶2 000)、Caspase-3(1∶2 000)、Bax(1∶1000)、BCL-2(1∶1000)。
1.4 统计学处理
采用SPSS 13.0统计软件分析结果,符合正态分布的实验数据以
$ \bar x \pm s $ 表示。多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。2. 结果
2.1 利舒康胶囊对高原缺氧小鼠学习记忆的干预作用
与正常对照组相比,缺氧模型组小鼠WME、RWE、TE、TT均显著升高(P<0.01);与缺氧模型组相比,利舒康胶囊三个剂量组小鼠四项指标均有不同程度降低,其中利舒康胶囊高剂量组800 mg/(kg·d)具有显著性差异(P<0.05或P<0.01),表明高原低氧缺氧能导致小鼠空间记忆障碍,而利舒康胶囊高剂量组能够增强高原缺氧小鼠的短期记忆和长期记忆能力,改善大鼠认知,有望对高原缺氧导致的学习记忆损伤患者提供预防和治疗。结果见表1和图2。
表 1 利舒康胶囊对高原缺氧小鼠空间记忆的影响($ \bar x \pm s $ ,n=10)组别 剂量(mg/kg) WME(次) RME(次) TT(秒) TE(次) 正常对照组 − 0.43±0.35 0.50±0.41 63.47±9.64 1.50±0.17 缺氧模型组 − 3.00±1.58## 2.70±1.52## 119.99±43.00## 3.10±0.48## 红景天胶囊组 400 0.57±0.35** 0.79±0.49* 81.78±28.20 1.83±0.29#** 利舒康胶囊低剂量组 400 2.43±0.89#▲ 1.36±0.56 99.45±25.27## 3.06±0.58##▲▲ 利舒康胶囊中剂量组 600 2.14±1.14#▲ 1.43±1.10 98.75±30.51 3.04±0.52##▲▲ 利舒康胶囊高剂量组 800 1.07±0.61* 0.71±0.49** 69.38±31.69* 1.73±0.37** # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, 与正常对照组比较;* P<0.05, ** P<0.01,与缺氧组比较 ;▲P<0.05, ▲▲P<0.01,与红景天胶囊组比较 2.2 利舒康胶囊对缺氧小鼠脑组织形态学的影响
海马体在学习和记忆中发挥关键作用,尤其容易受到缺氧损伤。在本研究中,小鼠脑组织病理学切片结果显示(见图3),正常对照组小鼠海马神经元密集,细胞核大而圆,神经元呈层状有序分布,各层细胞形态饱满而数量多,细胞排列整齐且致密;缺氧模型组小鼠海马神经元细胞分布受到破坏,细胞形态不规则,部分细胞缺失或有空泡(黑色箭头),出现明显核固缩(蓝色箭头),细胞排列紊乱,CA1区有较多不规则形状的深染细胞(绿色箭头),表明脑组织出现神经元死亡;经过红景天胶囊和利舒康胶囊药物干预后,缺氧模型组脑组织损伤有所改善;神经元细胞排列整齐,核固缩现象减轻(蓝色箭头),深染细胞数量减少(绿色箭头),少有细胞缺失或空泡(黑色箭头),细胞形态较好,排列整齐,且利舒康胶囊高剂量组脑组织形态趋于正常。
2.3 利舒康胶囊对高原缺氧小鼠海马组织中Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路蛋白水平的影响
与正常对照组比较,缺氧模型组小鼠海马组织中Keap1蛋白含量显著升高(P<0.01),Nrf2、HO-1蛋白含量显著降低(P<0.01);与缺氧模型组相比,利舒康胶囊组Keap1蛋白含量降低(P<0.01),Nrf2、HO-1蛋白含量显著升高(P<0.01),其中以利舒康胶囊高剂量组蛋白水平变化最为显著,且效果优于阳性药红景天胶囊组。结果见图4和表2。
表 2 各组小鼠脑组织蛋白表达比较($ \bar x \pm s $ ,n=3)分组 剂量
(mg/kg)Keap1 Nrf2 HO-1 Caspase-3 Bax BCL-2 正常对照组 − 0.36±0.08 0.76±0.08 1.03±0.14 0.03±0.01 0.09±0.02 0.79±0.09 缺氧模型组 − 0.91±0.15## 0.45±0.03## 0.31±0.05## 0.95±0.12## 0.99±0.08## 0.31±0.02## 红景天胶囊组 400 0.44±0.03** 0.92±0.15** 0.86±0.03 0.75±0.16## 0.73±0.11##** 0.65±0.02#** 利舒康胶囊低剂量组 400 0.42±0.03** 0.77±0.09** 0.67±0.02## 0.86±0.17## 0.81±0.05##** 0.62±0.02##** 利舒康胶囊中剂量组 600 0.41±0.04** 0.83±0.09** 0.98±0.13 0.64±0.06## 0.79±0.06##** 0.73±0.09** 利舒康胶囊高剂量组 800 0.33±0.02**▲▲ 1.21±0.11##**▲▲ 1.23±0.08**▲▲ 0.46±0.01##**▲▲ 0.52±0.05##**▲ 0.76±0.11** # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, 与正常对照组比较;* P<0.05, ** P<0.01,与缺氧组比较;▲P<0.05, ▲▲P<0.01,与红景天胶囊组比较 2.4 利舒康胶囊对缺氧小鼠海马细胞凋亡相关蛋白Caspase-3、Bax和Bcl-2的影响
与正常对照组相比,缺氧模型组小鼠海马组织中Caspase-3和Bax的表达显著升高(P<0.01),Bcl-2蛋白表达显著降低(P<0.01);与缺氧模型组相比,利舒康胶囊组Caspase-3和Bax蛋白表达显著降低(P<0.01),BCL-2蛋白表达显著升高(P<0.01),其中利舒康胶囊高剂量组蛋白水平变化尤为显著,且效果优于阳性药红景天胶囊组。结果见图5和表2。
3. 讨论
缺氧会引起机体组织细胞形态结构、功能和代谢的异常变化[13]。大脑对缺氧刺激异常敏感,短期暴露于高海拔地区的急性低压低氧会导致认知能力下降,尤其是空间学习、短期记忆和工作记忆能力下降。高原脑缺氧可引起中枢神经系统氧化性损伤,大量证据表明,氧化应激和细胞凋亡是神经元变性和死亡的主要诱因,进而造成机体认知功能损伤,且这种损伤为不可逆缺陷[14]。在本研究中,采用八臂迷宫实验方法检测高原缺氧环境下小鼠的空间记忆能力。通过利舒康胶囊高剂量组干预治疗后,WME、RME、TE和TT与缺氧模型组相比显著减少(P<0.05或P<0.01),表明利舒康胶囊能明显提高高原缺氧环境下小鼠的空间记忆能力。海马体是大脑中对缺氧最敏感的区域之一,也是形成空间记忆的关键区域[15]。HE染色结果显示,与正常对照组相比,缺氧模型组小鼠海马神经元细胞形态不规则,部分细胞缺失或有空泡;经利舒康胶囊干预后,细胞形态较好,排列整齐,少有细胞缺失或空泡。提示进行利舒康胶囊药物干预可以修复高原低压低氧造成的海马组织神经元损伤,防止了小鼠因暴露在高海拔环境中而导致的空间记忆障碍。
Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路是机体内保持细胞稳态的防御系统,在预防由氧化应激引起的细胞损伤中起重要作用,Nrf2是一种具有细胞保护和抗氧化活性的诱导蛋白,可被视为氧化应激反应的主调控因子[16-18],HO-1可以催化血红素的分解,从而抑制中性粒细胞、淋巴细胞和巨噬细胞介导的炎性反应。在正常条件下,Keap1形成E3泛素连接酶的一部分,紧密调控Nrf2的活性,这时的Nrf2活性处在相对较低水平。在氧化应激条件下,Nrf2通过与细胞质中含有半胱氨酸残基的阻遏蛋白Keap-1分离而被激活,进而激活其相关的抗氧化酶HO-1表达,达到抵抗氧化应激的作用[19]。本文研究结果显示,与正常对照组相比,缺氧模型组海马细胞中Keap1蛋白表达升高(P<0.01)、Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达下降(P<0.01),表明机体在缺氧环境中,ROS积累导致氧化还原状态失衡。经利舒康胶囊干预后,与缺氧模型组相比,Keap1蛋白表达下降,且具有显著性差异(P<0.01),Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达均显著升高(P<0.01),且利舒康胶囊高剂量组治疗效果最好,本课题组前期对利舒康胶囊对高原脑损伤防治的研究结果显示[20],机体暴露在高原环境下,活性氧(ROS)大量累积导致氧化性损伤,利舒康胶囊能降低脑组织内MDA含量,提高SOD的活力,具有良好的抗氧化应激的作用。因此我们推测,利舒康胶囊可以通过调控Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路,发挥抗氧化作用。
氧化应激和炎症在脑损伤中起关键作用,导致细胞凋亡。细胞凋亡是器官生长、发育和维持正常体内平衡的重要过程,也是脑缺氧后神经元死亡的主要形式[21]。海马锥体神经元的凋亡可导致学习和记忆障碍[22]。Caspase-3作为凋亡激活剂是重要的凋亡调节因子,是缺氧诱导的脑细胞凋亡的重要标志,抗凋亡基因Bcl-2和促凋亡基因Bax可能参与病理性凋亡和坏死细胞死亡途径[23-25]。在本研究中,与正常对照组相比,缺氧模型组Caspase-3蛋白含量和Bax/Bcl-2比值表达显著增加(P<0.01),说明缺氧可引起脑组织细胞凋亡。而利舒康胶囊可通过降低Caspase-3蛋白表达和Bax/Bcl-2比值来逆转这些变化,抑制了氧化应激引起的脑细胞凋亡和炎症引发的脑损伤,且利舒康胶囊高剂量组优于阳性药红景天胶囊组。
综上所述,利舒康胶囊可以改善高原缺氧小鼠脑损伤,提高小鼠在高原缺氧环境下的抗氧化能力,其机制可能是通过调控Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路发挥抗氧化应激作用,减轻缺氧引起的ROS积累;同时通过抗氧化和抗凋亡机制在低压低氧暴露期间为海马神经元提供神经保护作用,从而改善缺氧诱导的小鼠空间记忆损伤。
利益冲突
所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
-
表 1 利舒康胶囊对高原缺氧小鼠空间记忆的影响(
$ \bar x \pm s $ ,n=10)组别 剂量(mg/kg) WME(次) RME(次) TT(秒) TE(次) 正常对照组 − 0.43±0.35 0.50±0.41 63.47±9.64 1.50±0.17 缺氧模型组 − 3.00±1.58## 2.70±1.52## 119.99±43.00## 3.10±0.48## 红景天胶囊组 400 0.57±0.35** 0.79±0.49* 81.78±28.20 1.83±0.29#** 利舒康胶囊低剂量组 400 2.43±0.89#▲ 1.36±0.56 99.45±25.27## 3.06±0.58##▲▲ 利舒康胶囊中剂量组 600 2.14±1.14#▲ 1.43±1.10 98.75±30.51 3.04±0.52##▲▲ 利舒康胶囊高剂量组 800 1.07±0.61* 0.71±0.49** 69.38±31.69* 1.73±0.37** # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, 与正常对照组比较;* P<0.05, ** P<0.01,与缺氧组比较 ;▲P<0.05, ▲▲P<0.01,与红景天胶囊组比较 表 2 各组小鼠脑组织蛋白表达比较(
$ \bar x \pm s $ ,n=3)分组 剂量
(mg/kg)Keap1 Nrf2 HO-1 Caspase-3 Bax BCL-2 正常对照组 − 0.36±0.08 0.76±0.08 1.03±0.14 0.03±0.01 0.09±0.02 0.79±0.09 缺氧模型组 − 0.91±0.15## 0.45±0.03## 0.31±0.05## 0.95±0.12## 0.99±0.08## 0.31±0.02## 红景天胶囊组 400 0.44±0.03** 0.92±0.15** 0.86±0.03 0.75±0.16## 0.73±0.11##** 0.65±0.02#** 利舒康胶囊低剂量组 400 0.42±0.03** 0.77±0.09** 0.67±0.02## 0.86±0.17## 0.81±0.05##** 0.62±0.02##** 利舒康胶囊中剂量组 600 0.41±0.04** 0.83±0.09** 0.98±0.13 0.64±0.06## 0.79±0.06##** 0.73±0.09** 利舒康胶囊高剂量组 800 0.33±0.02**▲▲ 1.21±0.11##**▲▲ 1.23±0.08**▲▲ 0.46±0.01##**▲▲ 0.52±0.05##**▲ 0.76±0.11** # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, 与正常对照组比较;* P<0.05, ** P<0.01,与缺氧组比较;▲P<0.05, ▲▲P<0.01,与红景天胶囊组比较 -
[1] MA J Q, WANG C Y, SUN Y B, et al. Comparative study of oral and intranasal puerarin for prevention of brain injury induced by acute high-altitude hypoxia[J]. Int J Pharm, 2020, 591:120002. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.120002 [2] 赵敏, 陈垚, 李文华. 高原低氧影响学习记忆功能的机制研究进展[J]. 西北国防医学杂志, 2019, 40(9):536-541. doi: 10.16021/j.cnki.1007-8622.2019.09.002 [3] LI Y, WANG Y. Effects of long-term exposure to high altitude hypoxia on cognitive function and its mechanism: a narrative review[J]. Brain Sci, 2022, 12(6):808. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12060808 [4] ZHU M X, XU M K, ZHANG K X, et al. Effect of acute exposure to hypobaric hypoxia on learning and memory in adult Sprague-Dawley rats[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2019, 367:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.03.047 [5] WANG X B, HOU Y, LI Q Y, et al. Rhodiola crenulata attenuates apoptosis and mitochondrial energy metabolism disorder in rats with hypobaric hypoxia-induced brain injury by regulating the HIF-1α/microRNA 210/ISCU1/2(COX10) signaling pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2019, 241:111801. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.03.028 [6] ZHOU F, WANG M D, JU J, et al. Schizandrin A protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress and regulating the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway regulation[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2019, 11(1):199. [7] CHEN C, LI B, CHEN H T, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorated iron accumulation and apoptosis and promoted neuronal regeneration and memory/cognitive functions in the hippocampus induced by exposure to a chronic high-altitude hypoxia environment[J]. Neurochem Res, 2022, 47(8):2254-2262. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03611-2 [8] ZHANG X Y, ZHANG X J, DANG Z C, et al. Cognitive protective mechanism of crocin pretreatment in rat submitted to acute high-altitude hypoxia exposure[J]. BioMed Res Int, 2020, 2020:1-15. [9] 李燕. 利舒康胶囊对慢性缺血缺氧症侯群的疗效探讨[J]. 中西医结合心血管病电子杂志, 2018, 6(22): 102, 104. [10] XU H B, BARACSKAY P, O'NEILL J, et al. Assembly responses of hippocampal CA1 place cells predict learned behavior in goal-directed spatial tasks on the radial eight-arm maze[J]. Neuron, 2019, 101(1): 119-132. e4. [11] LI M X, ZHU Y T, LI J, et al. Effect and mechanism of verbascoside on hypoxic memory injury in plateau[J]. Phytother Res, 2019, 33(10):2692-2701. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6443 [12] DU X, LIU T L, TAO W D, et al. Effect of aqueous extract of Astragalus membranaceus on behavioral cognition of rats living at high altitude[J]. Chung I Tsa Chih Ying Wen Pan, 2022, 42(1):58-64. [13] ZHANG Z A, SUN Y F, YUAN Z Y, et al. Insight into the effects of high-altitude hypoxic exposure on learning and memory[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022:4163188. [14] JING L L, WU N Z, ZHANG J, et al. Protective effect of 5, 6, 7, 8-Tetrahydroxyflavone on high altitude cerebral edema in rats[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2022, 928:175121. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175121 [15] KOESTER-HEGMANN C, BENGOETXEA H, KOSENKOV D, et al. High-altitude cognitive impairment is prevented by enriched environment including exercise via VEGF signaling[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2018, 12:532. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00532 [16] WU C T, DENG J S, HUANG W C, et al. Salvianolic acid C against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by attenuating inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis through inhibition of the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019:9056845. [17] 姚娟, 吴平安, 李芸, 等. Keap1-Nrf2-ARE信号通路及其激活剂的研究进展[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2019, 35(10):1342-1346. [18] HUANG C Y, DENG J S, HUANG W C, et al. Attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by hispolon in mice, through regulating the TLR4/PI3K/akt/mTOR and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways, and suppressing oxidative stress-mediated ER stress-induced apoptosis and autophagy[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(6):1742. doi: 10.3390/nu12061742 [19] LI J C, LU K M, SUN F L, et al. Panaxydol attenuates ferroptosis against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. J Transl Med, 2021, 19(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02745-1 [20] 马慧萍, 张俊, 贾正平, 等. 利舒康胶囊对模拟高原缺氧动物的保护作用研究[J]. 药学实践杂志, 2018, 36(3):255-259. [21] LIU X T, LIN X, ZHANG S Y, et al. Lycopene ameliorates oxidative stress in the aging chicken ovary via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. Aging, 2018, 10(8):2016-2036. doi: 10.18632/aging.101526 [22] MOKHTARI SANGDEHI S R, HAJIZADEH MOGHADDAM A, RANJBAR M. Anti-apoptotic effect of silymarin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles on hippocampal caspase-3 and Bcl-2 expression following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Int J Neurosci, 2022, 132(11):1102-1109. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2020.1860971 [23] ABOUTALEB N, SHAMSAEI N, KHAKSARI M, et al. Pre-ischemic exercise reduces apoptosis in hippocampal CA3 cells after cerebral ischemia by modulation of the Bax/Bcl-2 proteins ratio and prevention of caspase-3 activation[J]. J Physiol Sci, 2015, 65(5):435-443. doi: 10.1007/s12576-015-0382-7 [24] WANG J L, XU X X, JIA W Y, et al. Calcium-/ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) inhibition induces learning and memory impairment and apoptosis[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021:4635054. [25] GUO Z Y, RUAN Z Z, ZHANG D D, et al. Rotenone impairs learning and memory in mice through microglia-mediated blood brain barrier disruption and neuronal apoptosis[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 291(Pt 2): 132982. -





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:


